Can Men Have Breast Lumps
Yes. Men can develop a condition called gynecomastia. The male breast becomes enlarged and sometimes tender. A breast lump may also form underneath the nipple. Gynecomastia often occurs in both breasts. This condition can be related to a hormonal imbalance or a side effect of medication, although additional workup may be considered to determine a cause. Most often, a cause is never determined; it is called idiopathic.
Men can also develop breast cancer, so if you feel a lump in your breast, see your healthcare provider for an evaluation.
Symptoms Of Soft Tissue Tumor
1. Systemic manifestation: both benign tumor patients and early malignant tumor patients rarely have obvious systemic symptoms. Late malignant tumor patients, such as bone sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma or metastatic carcinoma, can have cachexia symtoms, such as anaemia, emaciation, loss of appetite, weight loss, fever, etc.
2. Local manifestation: pain of bones, joints, soft tissue, osseous or soft tissue mass, dysfunction, these are common local manifestations of malignant bone tumors.
Pain: pain is the most common symptom of tumors of rapid growth. At the beginning, the pain is light and intermittent, and gradually develops into a violent persistent pain. This is mainly due to tension or pressure imposed by bone tumor to sensitive periosteum or endosteum. But the pain does not necessarily explain the tumor is malignant, because some benign tumors, such as osteoid osteoma may cause pain due to reactive bone growth and pain. If pain suddenly and violently attacks, this may easily cause pathological fracture.
Mass: benign tumors often present hard and non-tender lumps. Malignant tumors of rapid growth often present as a diffuse swelling, tenderness, skin fever, superficial venous engorgement.
Dysfunction and compression: if tumor is close to joint, activities will be restricted; pain would increase when the joint moves. For tumors occurred in spinals, no matter benign or malignant, spinal cord compression would be caused and further lead to paralysis.
Common Invasive Breast Cancers
Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer. These tumors have developed in the milk ducts and invaded nearby breast tissue.
Invasive lobular carcinoma tumors have developed in the lobules and have invaded nearby breast tissue.
Once the tumor has spread outside the lobules or milk ducts, it can begin to spread to other nearby tissues, lymph nodes, and organs.
Also Check: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
Things That Can Cause A Lump In Your Breasts
According to the American Cancer Society, 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer in their lifetime. However, if you feel a lump, it is important to know what factors may be causing this change in the texture of your breast tissue – as cancer may not always be the culprit. Here are seven reasons why a lump may develop in the breast, and what to do if you suspect you may be experiencing one of these issues.
Fat Necrosis And Lipoma
If fatty tissue in the breast becomes damaged or broken down, fat necrosis may occur. Noncancerous lumps can form in the breast. They may be painful. There may be a nipple discharge and a dimpling of the skin over the lump.
A lipoma is soft, noncancerous lump that is generally movable and painless. It is a benign, fatty tumor.
Read Also: Where To Find Breast Cancer Lumps
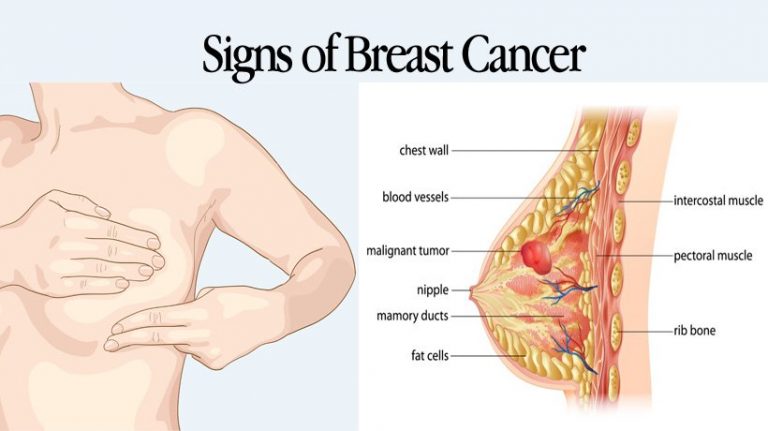
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can usually be treated successfully if it is diagnosed before the cancer has spread. The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump or mass in the breast. A painless, hard mass with irregular edges is more likely to be a breast cancer tumor, but they can also be painful, soft, and/or round.
Other potential breast cancer signs include:
- Swelling of all or part of a breast.
- Change in the size, shape, temperature, or appearance of a breast.
- Skin dimpling or pitting.
- Red, dry, flaking, peeling, scaling, crusting, or thickened nipple or breast skin.
- Nipple discharge.
- Swollen lymph nodes .
These symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than breast cancer. It is important to get any new breast mass, lump, or breast change checked by an experienced medical professional.
How To Look For Changes
Standing in front of a mirror, a person should look at the overall appearance of the breasts and nipples. Here are some questions to think about while doing so:
- Are they similar in size, shape, and height?
- Is one a different color than the other?
- Are there any visible skin lesions, marks, color changes, or moles?
- Are there any signs of swelling, lumpiness, pitting, or contour changes?
- Are the nipples facing outward or inward?
A person should run through this checklist twice: once with their arms at their sides and once with their arms above their head.
Breasts are rarely identical, but noticing changes can help detect a problem early. Having an idea of the usual size, shape, appearance, and feel of the breasts can help a person be aware of any changes.
Don’t Miss: Does Red Wine Cause Breast Cancer
What Are Breast Cysts
Breast cysts are fluid-filled round or oval lumps in the breast. There may be one or more, and they can vary in size, number, and symptoms.;
About 25% of all breast masses turn out to be cysts. Most breast cysts are benign and having them does not increase the risk of developing breast cancer.;
A physical examination alone cannot definitively distinguish between a benign breast cyst and breast cancer. Only a medical examination with tests such as ultrasound can determine whether a lump is a breast cyst or breast cancer.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider About A Breast Lump
Breast tissue is naturally lumpy. If the lumpiness feels like the rest of your breast, or like your other breast, you probably dont need to worry. Call your healthcare provider if you notice:
- An unusual lump or mass in your breast or under your arm that feels harder than the rest of the breast or is different on one side as compared to the other.
- Other breast changes including nipple inversion , dimpled skin, or bloody/clear nipple discharge.
- Redness, pain or focal tenderness in your breast.
- Nipple changes such as excoriation or scaling.
Breast lumps have many causes. Most of the time, theyre not cancer. If you feel a breast lump or any other change in your breast, talk to your healthcare provider. They can figure out the cause of the lump and if you need treatment. Dont put off taking care of your breast health. If the lump is cancer, treatment is most successful if started early.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/14/2021.
References
Don’t Miss: Do People Survive Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Biopsies For Breast Cancer
During a biopsy, a doctor extracts a sample of tissue from the suspected tumor site. These are sent to a laboratory for analysis by a pathologist to determine whether the cells in the sample are cancerous. They may also look for certain hormone receptors that can affect prognosis and treatment. There are different kinds of breast biopsies, and the type of biopsy a patient receives is determined by several factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the number of tumors, and the type of breast cancer suspected.
During a fine needle aspiration biopsy, a doctor uses a thin, hollow needle attached to a syringe to remove fluid and small pieces of tissue from the tumor. If the tumor is near the surface of the skin, the doctor may aim the needle by feel. If the tumor is deeper inside the breast, the doctor may use a mammogram, MRI, or ultrasound to guide the needle.
A core needle biopsy is usually the preferred type of biopsy for diagnosing breast cancer. During this type of biopsy, a doctor uses a hollow needle to remove a small cylinder of tissue from the tumor. Core needle biopsies are usually done with local anesthesia, where a numbing agent is injected into the skin and other tissues over the biopsy site, although some procedures may require general anesthesia . As with a fine needle aspiration, the doctor may guide the needle by feel or with an imaging scan.
Immunotherapy For Breast Cancer
Immunotherapy uses medicines to stimulate the bodyâs own immune system to combat cancer. It is a good option for some patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Immunotherapy is often combined with chemotherapy to treat advanced cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
The main type of immunotherapy drugs used for breast cancer are immune checkpoint inhibitors, which target checkpoint proteins on immune cells that need to be turned on or off to trigger an immune response. Breast cancer cells sometimes use these checkpoint proteins to avoid being attacked by the immune system, so checkpoint inhibitor drugs can help to restore the appropriate immune response against cancer cells.
Atezolizumab is a PD-1 inhibitor approved by the FDA for PD-L1-positive locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer that cannot be removed with surgery and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.
Pembrolizumab is a PD-L1 inhibitor approved by the FDA to treat PD-L1-positive metastatic breast cancer or cancer that cannot be treated with surgery. In addition, it is approved in combination with a few different chemotherapy drugs to treat metastatic or locally recurrent triple-negative breast cancer that cannot be treated with surgery.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
What Do Benign Breast Lumps Look And Feel Like
The majority of lumps found in the breasts are not cancerous. If you find a lump, the best thing you can do is go to your doctor for guidance. As one MyBCTeam member shared, My doctor was wonderful in teaching me about discerning how a lump might feel as opposed to a cyst, scar tissue, or a fold in the implant. Have a talk with your doctor.
The following are other breast conditions that can cause noncancerous lumps:
- Fibroadenomas
- Sclerosing adenosis
Treatment For Cysts And Tumors Depends On Several Factors

Location, cause, and whether its cancerous all help determine next steps.
Most cysts dont require treatment. They typically dont cause any symptoms and may go away on their own. But this can depend on where the cyst is located. If a cyst hurts or you dont like the way it looks, some options are removing it or draining its fluid.
You can usually let a benign tumor be, unless it is pressing on a vital organ and is interrupting its functionthen it may need to be removed. Cancerous tumors generally require treatment with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these and other therapies.
You May Like: Does Breast Pain Indicate Cancer
What Will Happen At My Appointment
The doctor will ask questions about your health history. Theyll perform a breast exam to feel for lumps or other changes in the breast tissue and under your arms.
If theres fluid coming out of your nipple, the doctor may order blood tests to check hormone levels and collect a sample to check for abnormal cells.
They may also do a mammogram or;ultrasound;to see if the lump is solid or filled with fluid.
Your doctor may order a test called a biopsy. Theyll take a tiny sample of the lump with a needle or small cut and send it to a lab.
Causes Of Soft Tissue Tumor
Currently, causes of soft tissue tumor have not been defined yet, but it is well-known that soft tissue tumor is related to the following factors: 1. Gene theory: gene mutations of normal cells can cause cancer. Tumor cells constantly proliferate and inherit the biological characteristics, such as hereditary multiple exostosis. 2. Chronic stimulation theory: chemical chronic stimulation, physical factors. 3 Virus theory has found that blood serum of patients with osteosarcoma contain specific antibodies of osteosarcoma. 4. canceration.
Don’t Miss: How To Screen For Breast Cancer
Surgery For Breast Cancer
Surgery is a primary treatment for breast cancer that has not spread beyond the breast or lymph nodes. The most common surgeries to treat breast cancer are lumpectomies and mastectomies. For women with invasive breast cancer, surgical evaluation of the lymph nodes is performed with a procedure called sentinel node biopsy.
During a lumpectomy, the surgeon removes the tumor and a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue. This type of surgery is usually best for removing smaller tumors in patients with early-stage cancer. Some patients with larger tumors may undergo chemotherapy or hormonal therapy before surgery to shrink the tumor to make it possible to remove the cancer completely with a lumpectomy procedure.
During a mastectomy, the surgeon removes the entire breast, including all of the breast tissue. Some women may also receive a double mastectomy, in which both breasts are removed. Skin-sparing mastectomies and nipple-sparing mastectomies are becoming common operations for breast cancer to improve the appearance of the breast. Some women with a high risk of developing breast cancer choose to have preventive mastectomies.
Breast Sarcomas Staging And Treatment
Staging and treatment of breast sarcomas differ from other types of breast cancer.; Lymph node status is not as important in staging breast sarcomas as in other kinds of breast cancer. When sarcomas spread, they typically do not travel through the lymphatic system. Even in the case of large breast sarcomas, the lymph nodes are usually negative for cancer, and axillary node dissection is usually not required.Local therapy is aimed at preventing the cancer from coming back in the breast, and will include surgery such as wide excision, in which the tumor and extra tissue are removed, or mastectomy, in which the whole breast is removed.;; Radiation therapy may also be given.Systemic therapy is used to prevent the cancer from coming back or from spreading to another part of the body. Systemic therapy for a sarcoma may be recommended if the tumor is very large or is known to have spread outside of the breast, and includes chemotherapy.; Because sarcoma tumor cells are not ductal breast cells, they do not typically have hormone or HER2 receptors, so endocrine and HER2- targeted therapies are generally not used. Your oncology team will recommend a treatment plan based on what is known about breast sarcomas in general and tailored specifically to your disease.
Request an Appointment
Don’t Miss: Does Stress Cause Breast Cancer
You Should Have Any Lump Or Bump Checked Out
Most cysts and most lumps, statistically speaking, are benign, Chu said. They just need the appropriate follow-up. Its important to have these cysts or tumors evaluated by a specialist, like those at Fox Chase.
See your doctor sooner, rather than later, if you have a mass that grows quickly, changes color, looks red or swollen, or if it bleeds, is painful, or interferes with your daily activities.
Its possible that the nature of a mass can be determined with a scan. Ultrasounds and CT scans are often used for this purpose. If the lump is filled with fluid, a needle may be used to aspirate some of the liquid for testing. Sometimes, part of a lump must be biopsied or the entire mass must be surgically removed for diagnosis. A pathologist will examine the cells and determine what type they are and if they are benign, malignant, or even precancerous.
Common Causes Of Benign Breast Lumps
Most benign breast lumps and conditions are directly related to your menstrual cycle, to fluctuations in your hormones, and to the fluid buildup that comes with your monthly period. Other benign breast lumps and conditions may be related to plugged milk ducts, infections, or even breast injuries. The risk for benign breast conditions increases for women who have never had children and those who have a history of irregular menstrual cycles or a family history of breast cancer.
Here are some of the most common benign breast conditions.
Fibrocystic changes;These changes cause a general lumpiness that can be described as ropy or granular, and affect at least half of all women. Symptoms of fibrocystic change include tender, fibrous, rubbery tissue; a thickening of tissue; or a round, fluid-filled cyst. These changes, which are related to hormonal fluctuation, may increase as you approach middle age and disappear with menopause. Sometimes doctors recommend limiting salt and caffeine consumption to ease fluid buildup. Birth control pills may also ease symptoms.
Mastitis;An infection of the milk duct, mastitis can create a lumpy, red, and warm breast, accompanied by fever. It occurs most commonly in women who are breastfeeding, but can occur in non-breastfeeding women as well. Treatment involves warm compresses and antibiotics. Because these symptoms are similar to inflammatory breast cancer, if they occur in a non-breastfeeding woman a doctor may want to do a biopsy.
Read Also: What Does It Feel Like To Have Breast Cancer
Different Kinds Of Breast Lumps
There are different types of breast lumps. The following descriptions and illustraitons provides some details. If you have any questions, follow-up with your doctor.;
Benign
BENIGNAlthough any lump formed by body cells may be referred to technically as a tumor. Not all tumors are malignant . Most breast lumps 80% of those biopsied are benign . Following are examples of the most common benign breast conditions which produce lumps.
Fibrocystic changes:;This is not a disease, but rather a benign condition affecting 50 to 60 percent of all women. Fibrous breast tissue, mammary glands, and ducts;overreact to the normal hormones produced during ovulation, resulting in the development of fibrous lumps and/or
numerous, small multiple cysts, . Fibrocystic changes are an exaggerated response of;breast tissue to changes of ovarian hormones.
Fibrocystic changes are the most common non-cancerous breast condition.;They are most;common in women between the ages of 20 and 50. They are unusual after menopause;unless a woman is taking hormones.;;
The size and tenderness of Fibrocystic lumps usually increase before menstruation, decreasing after the period ends. This condition, also known as cystic mastitis, generally disappears after menopause. Medical opinion is still divided over whether Fibrocystic disease increases the risk of breast cancer.
MALIGNANT TUMORS
| Give us a call |