What Is Cancer Staging
Staging is a way of describing how extensive the breast cancer is, including the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to lymph nodes, whether it has spread to distant parts of the body, and what its biomarkers are.
Staging can be done either before or after a patient undergoes surgery. Staging done before surgery is called the clinical stage, and staging done after surgery is called the pathologic stage. Doctors use diagnostic tests to find out the cancer’s stage, so staging may not be complete until all of the tests are finished. Knowing the stage helps the doctor recommend the best kind of treatment and can help predict a patient’s prognosis, which is the chance of recovery. There are different stage descriptions for different types of cancer.
This page provides detailed information about the system used to find the stage of breast cancer and the stage groups for breast cancer, such as stage IIA or stage IV.
Enlarged Axillary Lymph Nodes
Enlarged axillary lymph nodes can be a symptom of a serious medical condition, including breast cancer. If you, or a loved one, notice swelling and/or feel a solid mass in the armpit area please contact a medical professional.
The Lymphatic System
The human circulatory system includes the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems, two networks that play complementary roles. As you may recall from a high school biology class, the cardiovascular system consists of arteries and veins. Arteries transfer blood, enriched with oxygen and fuel, to cells. Veins return blood, carrying carbon dioxide, back to the lungs.
The lymphatic system is a nearly parallel structure and plays a critical role in the bodys immune system. The lymphatic system moves lymph between tissue and the bloodstream via lymph ducts, lymph nodes, lymph vessels and organs. It also includes adenoids, the spleen, the thymus and tonsils.
- Lymph: a clear-to-white fluid made up of white blood cells that attack bacteria found in the bloodstream. Lymph can also be found in the intestines , where they hold proteins and fats.
- Lymph Nodes : are found throughout the human body and are linked together through lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes screen and/or remove foreign substances .
If the lymph nodes detect an unrecognizable substance they will create an antibody, which flows in blood circulation to target and destroy the foreign material in cells throughout the body.
Enlarged Axillary Lymph Nodes
Description Of The Condition
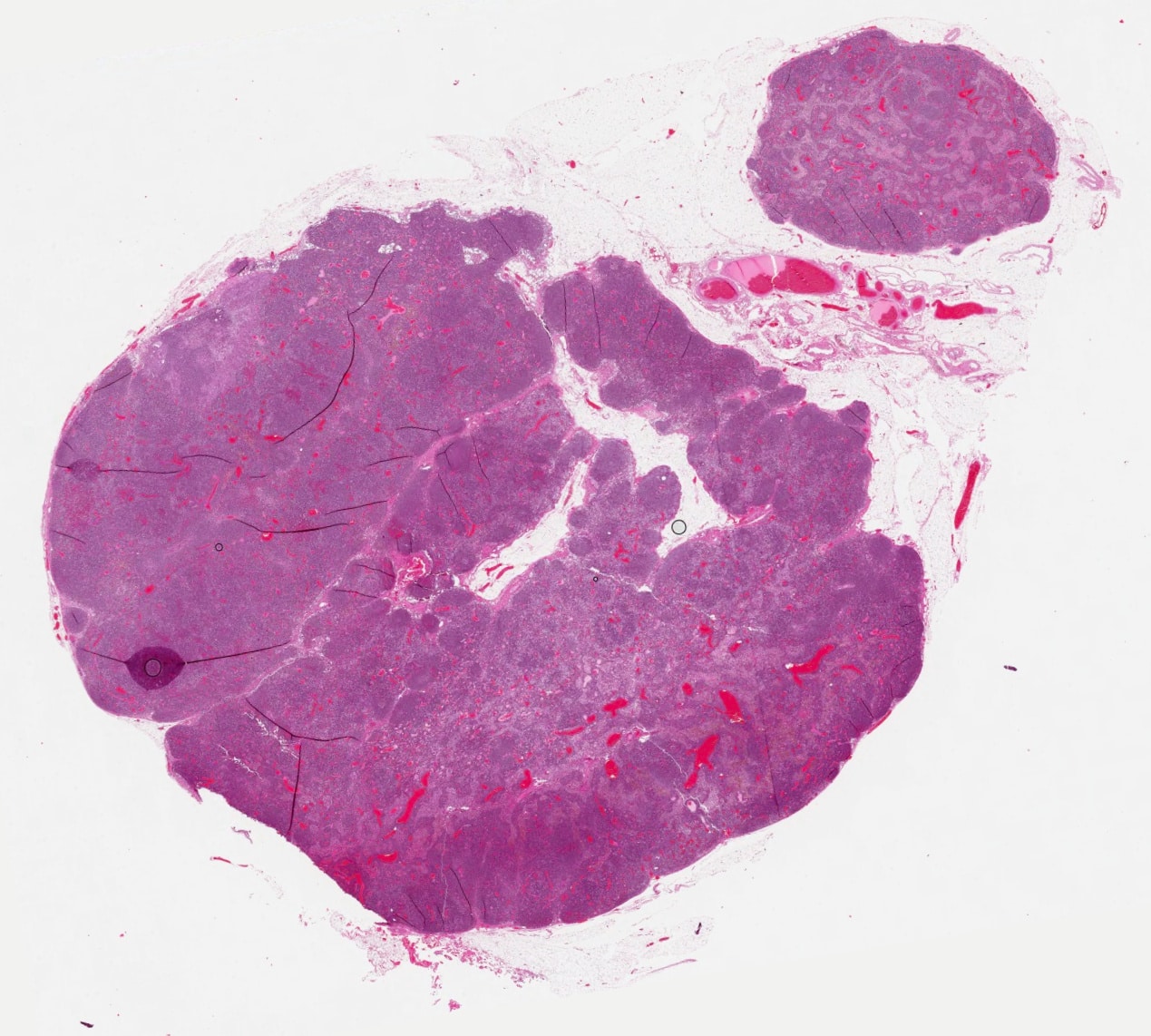
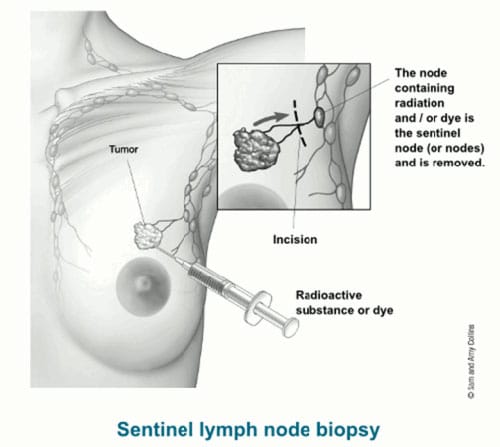
Breast cancer is the most frequent cancer affecting women worldwide . For example, in the UK more than 45,000 people are diagnosed with breast cancer each year and the majority of these patients undergo surgical treatment . Patients with early-stage invasive breast cancer undergo breast surgery, which could be lumpectomy or mastectomy. These patients also have one or two lymph nodes removed from the axilla during this surgery to check if the cancer has spread to the nodes a procedure called sentinel node biopsy . In around a quarter of patients, the cancer has spread to the nodes. Current practice is that these patients with cancer in the nodes undergo axillary treatment, which is either surgical removal of the remaining axillary nodes or axillary radiotherapy.
You May Like: Breast Cancer And Lymph Nodes
Deep Learning Radiomics Model
The enrolled patients were randomly divided into the training cohort and independent test cohort with the ratio of 4:1 and the training cohort were then used to optimize the model parameters. We also randomly chose 25% of training images to form a validation cohort to guide the choice of hyper parameters. The whole pipeline of our model was shown in Fig. . Resnet was adopted as the base model which pre-trained on Imagenet,. In particular, the last 1000 nodes FC layer was replaced with our specifically designed three FC layers with Xavier initialized weights. The detailed architecture of the network is shown in Supplementary Table .
Fig. 6: The overall pipeline of the model.
The parallel pre-trained ResNet model encodes the input images to features which be combined with clinical parameters. Then the combined features be classified by an SVM model.
Risks Associated With Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
Risks associated with axillary lymph node dissection include:
- Severed nerves during surgery, which results in the loss of feeling on the back of the arm or armpit
- Discomfort in the back of the arm
- Limited range of motion in the arm
- Vein inflammation in the arms as they pass through the armpit
- Damage to the shoulder blade if the nerves in the shoulder blade are cut during the procedure
- Infection in the surgical area
Recommended Reading: How To Help Breast Cancer Awareness
Prediction Of Aln Status Among N0 N+ And N+
This model was extended to be compatible with three groups of tasks to predict ALN status. As described above, the clinical endpoints were categorized into three parts: N0, N+, and N+. The number of lesions of the three categories is 337 , 150 ), and 97 ), respectively. The DLR model was built on breast conventional US and SWE images and was classified by axillary US findings, clinicopathologic data. The overall accuracy of differentiating the three groups was 0.805 and the confusion matrix was shown in Fig. . The model performed well in differentiating the N0 group while showed poorer results in the other two groups.
Fig. 4: The confusion matrix of predicting metastasis among disease-free axilla , low metastatic burden of axillary disease ) and heavy metastatic burden of axillary disease ).
Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
Cancer can appear in the lymph nodes in 2 ways: it can either start there or it can spread there from somewhere else.
Cancer that starts in the lymph nodes is called lymphoma. You can read more about lymphoma in Hodgkin Lymphomaand Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
More often, cancer starts somewhere else and then spreads to lymph nodes. That is the focus of this section.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat During Breast Cancer Treatment
You May Like: Can Anyone Get Breast Cancer
What Size Lymph Node Should Be Biopsied
Nodes are generally considered to be normal if they are up to 1 cm in diameter however, some authors suggest that epitrochlear nodes larger than 0.5 cm or inguinal nodes larger than 1.5 cm should be considered abnormal. 7,8 Little information exists to suggest that a specific diagnosis can be based on node size.
Types Of Lymph Node Surgery
Even if the nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged, they will still need to be checked for cancer. This can be done in two different ways. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is the most common way and only a few lymph nodes are removed. But in some cases, an axillary lymph node dissection , which removes more lymph nodes, might be needed.
Lymph node surgery is often done as part of the main surgery to remove the breast cancer, but sometimes it might be done as a separate operation.
Recommended Reading: Surgery To Remove Breast Cancer
How Long Could You Have Lymphoma Without Knowing
Low-Grade Lymphoma These grow so slowly that patients can live for many years mostly without symptoms, although some may experience pain from an enlarged lymph gland. After five to 10 years, low-grade disorders begin to progress rapidly to become aggressive or high-grade and produce more severe symptoms.
Breast Cancer Staging And Lymph Nodes
After an initial cancer diagnosis, youll need to know if it has spread beyond the primary tumor. If you have enlarged lymph nodes, your doctor may be able to perform a needle biopsy. Otherwise, the lymph nodes can be checked when you have breast surgery.
Your doctor will assign a clinical stage based on:
- a physical exam
- a biopsy of the tumor
After surgery, youll have more detailed information from the breast tissue and lymph nodes. This information helps provide the pathological stage.
Lymph node involvement is a key factor in staging breast cancer. In the TNM staging system:
- T is for tumor size
- N represents lymph node involvement
- M is for metastasis
Heres a closer look at what to know about cancer cells and lymph node involvement.
Read Also: How Many Different Kinds Of Breast Cancer Are There
Scar Tissue In The Armpit
Some women develop scar tissue in the armpit after lymph node removal. The connective tissues in the armpit get inflamed, which forms one or more tight bands. This usually happens within the first few weeks or months after the operation.
The scar tissue is called cording or banding or axillary web syndrome. It can feel something like a guitar string. It can extend down the arm past the elbow, possibly as far as the wrist or thumb.
Cording is harmless but can be painful and can limit your arm movement. Massaging the area regularly can help. Tell your breast care nurse if you develop cording. They can refer you to a physiotherapist. They can show you how to massage the area and teach you stretching exercises. It usually gets better within a few months. Taking anti inflammatory painkillers may also help. Speak to your nurse or doctor about taking these.
-
Early Breast Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines 2019F Cardoso and others
-
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, September 2013
-
A systematic review of axillary web syndrome WM Yeung and othersJournal of Cancer Survivorship, 2015. Volume 9, Issue 4, Pages 576 – 598
Measures Of Treatment Effect
We will carry out statistical analysis using Review Manager 5.1 . We will use fixed-effect meta-analysis for combining data in the absence of heterogeneity. For those outcomes where there are moderate or high levels of heterogeneity, where clinically meaningful, we will use random-effects analysis and these results will be presented as average treatment effects.
For dichotomous data, we will present results as summary risk ratio with 95% confidence intervals. For continuous data, we will use the mean difference if outcomes were measured in the same way between trials. We will use the standardized mean difference to combine trials that measured the same outcome, but using different methods. If there is evidence in the trials of abnormally distributed data, we will report this.
Also Check: Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment Drugs
Treatment For Cam And Prognosis
There were 2 patients who refused any treatment after CAM. Of the remaining cases, 52 patients received chemotherapy, 8 patients received anti-HER2 therapy, 6 patients received contralateral axillary radiotherapy, and 16 patients received endocrine therapy. A total of 20 patients underwent contralateral axillary lymph node dissection or low-middle level ALND, and 3 patients underwent surgical castration. Detailed information on the pathological results of lymph nodes at different levels was queried in 12 patients . Contralateral mastectomy was performed in 5 patients, and no tumor was found in the gland.
Table 3 Metastatic status of contralateral axillary lymph nodes.
The prognosis of isolated CAM patients was better than that of patients with other distant metastases in terms of CAM-OS and PFS with significant differences and OS without significant differences .
Figure 2 Survival curves of CAM patients with or without other distant metastases. CAM-OS of CAM patients with or without other distant metastases. PFS of CAM patients with or without other distant metastases. OS of CAM patients with or without other distant metastases.
For the isolated CAM patients, 22 patients developed tumor progression after CAM treatment with a mean PFS of 34.4 months, and 18 patients survived during the follow-up. The five-year survival rate of isolated CAM patients was 67.4%, and the five-year disease-free survival rate was 52.9%.
Physical Exams And Pathology Exams
Sometimes, positive lymph nodes can be felt during a physical exam or seen on breast imaging. However, a pathologists exam of the lymph nodes removed during a biopsy or surgery is needed to determine lymph node status.
During a physical exam, your health care provider will feel under your arm to check if the lymph nodes are enlarged. If the lymph nodes feel enlarged, its likely the breast cancer has spread there. However, the cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes even if they dont feel enlarged.
The pathologist will check the lymph nodes under a microscope. Some women with negative lymph nodes based on a physical exam have nodes with cancer found during the pathology exam . And some women with enlarged nodes during a physical exam have cancer-free nodes .
Also Check: Male Breast Cancer Risk Factors
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
11 January 2021
Soo -Yeon Kim, Yunhee Choi, Jung Min Chang
15 February 2022
Peng Xue, Jiaxu Wang, Youlin Qiao
19 April 2021
Xuejun Qian, Jing Pei, K. Kirk Shung
29 June 2020
Qiyuan Hu, Heather M. Whitney & Maryellen L. Giger
19 February 2019
Xiaoyu Cui, Nian Wang, Ruimei Chai
volume 11, Article number: 1236
An to this article was published on 12 July 2021
This article has been
Surgery To Remove Lymph Nodes
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If it does spread, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. These lymph nodes drain the lymphatic fluid from the breast and arm.
It is important to know if there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit and how many. This helps the doctors work out the stage of your cancer and plan the best treatment for you.
You May Like: Staging Of Breast Cancer Tnm
Indications Of Level Iii Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
The NCCN Guidelines for clinical practice in breast cancer indicate that in the absence of gross disease in level II nodes, lymph node dissection should include tissue inferior to the axillary vein from the latissimus dorsi muscle laterally to the medial border of the pectoralis minor muscle .2 Only in cases with gross diseases in level I/II, level III dissection to the thoracic inlet should be performed.
Early clinical studies of the extent of lymph node metastasis in positive lymph node breast cancer patients found that 2058% of patients with axillary lymph node metastasis were restricted to level I 2029% and 1632% of patients with lymph node metastasis were confined to levels I+II and levels I+III, respectively. About 20% of patients were diagnosed with pathological level III metastasis.23,24 The level metastasis rate was highest in Khafagys study.25 Of 59 positive axillary lymph node patients, 31 had level III axillary lymph node metastasis. In a study by Tao et al, of 87 positive axillary lymph nodes patients, 18 had level III axillary lymph node metastasis.26 Yildirim reported a level III axillary lymph node metastasis rate of 1531%.21 In a study of T0-2 axillary lymph node-positive breast cancer patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, 0.9% of patients had level III axillary lymph node invasion.27
Data Collection And Analysis
Selection of studies
Two authors will independently scan the title, abstract and keywords of every record identified by the search. We will assess the full articles if the information given suggests that the study may conform to our criteria. We will resolve differences in assessment by discussion and, in cases of disagreement, we will consult another review author.
Data extraction and management
Two authors will perform data extraction independently using a standard form, and we will resolve disagreements by discussion. We will enter data on outcome measures into Review Manager 5.1 software for analysis. Where possible, we will extract data on tumor and patient characteristics, size of nodal metastasis, surgery performed and adjuvant treatments.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors will independently assess the quality and risk of bias of the eligible studies using the Cochrane Collaborations risk of bias tool . Any disagreements will be resolved by discussion or by involving a third assessor.
Sequence generation
We will describe for each included study, the methods used to generate the allocation sequence. The methods will be assessed as:
low risk of bias ,
high risk of bias or,
unclear risk of bias.
Allocation concealment
We will assess whether intervention allocation could have been foreseen in advance of, or during recruitment, or changed after recruitment:
low risk of bias
high risk of bias or,
unclear risk of bias.
Blinding
Read Also: Vitamin D And Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Checking The Lymph Nodes Before Surgery
Before your surgery you have an ultrasound scan to check the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. This is to see if they contain cancer cells.
You usually have a biopsy of any lymph nodes that look abnormal. The biopsy is sent to the laboratory to check for cancer cells.
If this shows that the cancer has spread to the nodes in the armpit, you will have surgery to remove all or most of them. You have this at the same time as your breast surgery. This is called an axillary lymph node dissection or clearance.
If the lymph nodes look normal during the ultrasound scan, you dont have a biopsy. But you will have a sentinel lymph node biopsy at the same time as your breast surgery. You have this to check if cancer cells have spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
Understanding Your Cancer And Treatment
Not all breast cancers are alike. Someone elses experience with their treatment may be completely different from yours. Understanding your type and stage can help make sense of your doctors recommendations. This may help you feel better about your treatment choices.
A big part of cancer treatment is the relationship between you and your oncology team. Here are some things youll want to know about early on so youre well informed about your specific type of breast cancer:
Also Check: Why Are Dense Breasts More Prone To Cancer
A Perspective Of The Future: Radiomics And Radiogenomics Era
Radiomics, a new and rapidly evolving field of research, converts medical images into quantifiable data such as phenotypic characteristics of the entire tumor . To date, radiomics research in breast imaging has mainly focused on dynamic contrastenhanced magnetic resonance imaging and the assessment of the primary tumor for the differentiation of molecular breast cancer subtypes, correlation with recurrences scores, or correlation with individual gene signatures . Recently, radiomics and radiogenomics analyses have also focused on nodal assessment with encouraging results. In a recently published study in 2018, Dong et al. reported the potential of radiomics analysis extrapolated from T2weighted fat suppression and DWI for the preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph nodes . The authors found AUCs from 0.770 to 0.863 for both the T2wFS model and DWI models and concluded that full utilization of breast cancerspecific textural features extracted from anatomical and functional MR images improves the performance of radiomics in predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis, providing a noninvasive approach in clinical practice.
Abbreviations: LN, lymph node ROI, region of interest.
The presented results demonstrate that the fields of radiomics and radiogenomics need further development but that they have already shown to open new frontiers for the assessment of lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer.