What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Is Called Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Or Carcinoma With Ductal And Lobular Features
Breast carcinomas are often divided into 2 main types: invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma, based on how they look under the microscope. In some cases, the tumor can have features of both and is called a mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma. Another term for invasive ductal carcinoma is invasive mammary carcinoma of no special type, because it is the most common type of breast carcinoma.
Both invasive ductal carcinomas and invasive lobular carcinomas arise from the cells lining the ducts and lobules in the breast. In general, invasive lobular and invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast arent treated differently.
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
Understanding The 5 Stages Of Breast Cancer And Prognosis
Considering that there are more than 3.1 million breast cancer survivors as reported by the American Cancer Society, most people are personally affected by breast cancer either directly or through association. Understanding the stages of breast cancer and prognosis for each stage can be extremely confusing. Thankfully, there is a wealth of information available for those who are dealing with a breast cancer diagnosis and for their families. The following can help you interpret these facts and better understand the stages of breast cancer and prognosis for each.
You May Like: What Is The Highest Stage Of Breast Cancer
Why Is Staging Important
During your initial diagnosis, you and your cancer team will work together to develop a treatment plan. Staging allows you to answer the following questions:
- How does this cancer typically progress?
- Which treatments may work?
Some of the staging may be even more in-depth, but in general, its designed to prepare a more tailored approach to your disease. Your care team will be able to explain any new terms and what they mean for you.
Expert cancer care
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
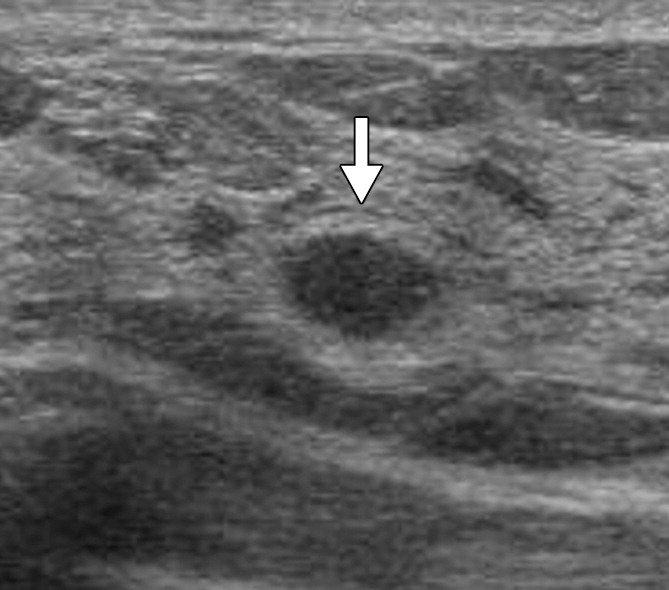
Your healthcare provider will perform a breast examination and ask about your family history, medical history and any existing symptoms. Your healthcare provider will also recommend tests to check for breast abnormalities. These tests may include:
- Mammogram. These special X-ray images can detect changes or abnormal growths in your breast. A mammogram is commonly used in breast cancer prevention.
- Ultrasonography. This test uses sound waves to take pictures of the tissues inside of your breast. Its used to help diagnose breast lumps or abnormalities.
- Positron emission tomography scanning: A PET scan uses special dyes to highlight suspicious areas. During this test, your healthcare provider injects a special dye into your veins and takes images with the scanner.
- Magnetic resonance imaging : This test uses magnets and radio waves to produce clear, detailed images of the structures inside of your breast.
If your healthcare provider sees anything suspicious on the imaging tests, they may take a biopsy of your breast tissue. Theyll send the sample to a pathology lab for analysis.
Read Also: What Is Considered Early Stage Breast Cancer
Is Inoperable Breast Cancer Still Treatable
Although stage 3C breast cancer is defined as either operable or inoperable, an inoperable diagnosis doesnt necessarily mean that it cant be treated.
The term inoperable may mean that all the cancer in the breast and surrounding tissue cant be removed through simple surgery. When breast cancer is removed, a rim of healthy tissue around the tumor, called a margin, is also removed.
For breast cancer to be successfully removed, there needs to be healthy tissue in all margins of the breast, from your clavicle down to a few inches below the breast mound.
It is possible for inoperable breast cancer to become operable following a treatment to shrink the cancer.
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, including:
Can cancer form in other parts of the breast?
When we say breast cancer, we usually mean cancers that form in milk ducts or lobules. Cancers can also form in other parts of your breast, but these types of cancer are less common. These can include:
- Angiosarcoma. This rare type of cancer begins in the cells that make up the lining of blood or lymph vessels.
- Phyllodes tumors. Starting in the connective tissue, phyllodes tumors are rare. Theyre usually benign , but they can be malignant in some cases.
You May Like: How Do You Diagnose Inflammatory Breast Cancer
T1a Tnbc Had Worse Prognosis Than T1a And T1b Her2+/hor Cancer
Both univariate and multivariate analyses proved worse BCSS and OS of T1a TNBC tumors than T1a HER2+/HoR tumors , whereas T1b TNBC patients revealed no survival difference compared with T1b HER2+/HoR tumors in terms of BCSS or OS . For T1c tumor, T1c TNBC had poorer survival than T1c HER2+/HoR .
Figure 2Table 3
Since T1a TNBC had worse prognosis than T1a HER2+/HoR and showed a trend with poorer survival than T1b TNBC, it raised the concern that whether T1a TNBC had the worst prognosis among small tumors of TNBC and HER2-rich subtypes. To prove this hypothesis, further comparison was performed between T1a TNBC and T1b HER2+/HoR. BCSS of T1a TNBC was significantly worse than that of T1b HER2+/HoR in both univariate and multivariate analyses. Multivariate analyses for OS also drew the similar conclusion that T1a TNBC associated with increasing mortality . Both BCSS and OS data supported the notion that T1a TNBC without chemotherapy has the worst prognosis among all the small tumor of TNBC and HER2-rich subtypes.
Figure 3Table 4vs.
What This Means For You
If youâve been diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer, your doctor may recommend treatments after surgery to reduce your risk of recurrence.
If you were diagnosed with hormone receptor-positive, early-stage breast cancer, itâs likely that your doctor will recommend you take some type of hormonal therapy medicine â either tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor depending on your menopausal status â for five to 10 years after surgery.
Chemotherapy after surgery is usually completed in three to six months. If youâre also receiving a targeted therapy, such as Herceptin , with chemotherapy, you may continue to receive the targeted therapy for up to a year after completing chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy after surgery can be completed in one to seven weeks.
So, hormonal therapy after surgery takes the longest to complete. Hormonal therapy medicines also can cause troubling side effects, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and joint pain. Less common but more severe side effects include heart problems and blood clots.
Research has shown that about 25% of women who are prescribed hormonal therapy to reduce the risk of recurrence after surgery either donât start taking the medicine or stop taking it early, in many cases because of side effects.
Learn more about Staying on Track With Treatment. You can read about why itâs so important to stick to your treatment plan, as well as ways to manage side effects after radiation, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy.
Recommended Reading: Does Beer Cause Breast Cancer
What Are Cancer Survival Statistics
A key part of making a prognosis is looking at survival rates. These are numbers researchers collect over many years in people with the same type of cancer. These numbers are based on large groups of people. For breast cancer, there are two main measurements:
Breast cancer survivalrates reflect the percentage of women who are alive 5 years or longer after their diagnosis. This means the numbers are based on women who were found to have breast cancer at least 5 years ago. Advances in diagnosing and treating cancer have led to steadily improving survival rates, so the outlook for women diagnosed today is likely better.
Relative survival rates donât take into account the cause of death. Theyâre a measure of the percentage of people with cancer who have lived for a certain time after diagnosis, compared with people who did not have cancer.
Survival Rates And Mortality Rates
Survival depends on mortality. You start with 100 percent of the people in the group.
100 percent mortality rate = survival rate
Say, the mortality rate in the group of people is 5 percent. Survival would be 95 percent .
Similarly, the number of people in a group who survive depends on the number of people who die. Say, 500 people are in the group and 1 person dies. This means 499 people survived .
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Causes Of Breast Cancer
How Is Prognosis Estimated
Prognosis is estimated by looking at what has happened over many years to large groups of people diagnosed with a similar cancer. However, everyones situation is different so no one can say for certain what will happen to you. Also, treatments and survival rates are constantly improving, which affects the accuracy of estimates for people being treated today.
Prognosis is described in different ways. It may be put into words or numbers. Its often expressed as a five- or ten-year survival rate. This is an estimate of how many people are likely to be alive five or ten years following their diagnosis.
A 90% five-year survival rate means that 90 out of 100 people diagnosed with breast cancer are likely to be alive five years after their diagnosis. It doesnt mean these people will only live for five years it just states how many people are likely to be alive at that point.
Cancer Research UK has general statistics on five- and ten-year breast cancer survival rates on their website. Remember, these statistics are based on large groups of patients and cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
How Your Prognosis Might Affect You
It can be difficult to take in and make sense of information about your prognosis. Having a good prognosis may reassure you, although you may still worry. If your prognosis is less good, you may feel anxious about the future. However you feel, theres no evidence that peoples attitude to having cancer alters their prognosis.
No tests can tell you with complete certainty what will happen to you. Sometimes people with a poor prognosis live for a long time. Equally, breast cancer can come back in people with a seemingly excellent prognosis.
Its normal to want to make plans for the future and the uncertainty about a diagnosis of breast cancer can be hard to live with. Most people find that it gets easier over time but sometimes you may need more support. This can come in all sorts of ways: from your friends or family, your breast care nurse, specialist or GP. You can also be referred to a counsellor who is trained to help people explore their feelings following a diagnosis of, and treatment for, breast cancer.
Whatever challenges or concerns youre facing, Breast Cancer Now is here to support you. Whether you want to speak to our nurses, join our online Forum or connect with volunteers who have faced what youre facing now, we can help you feel more in control.
For more information, visit our support for you section.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer Without Surgery
What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Report Also Mentions Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Intraductal Carcinoma Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Or In
These are terms for certain atypical or pre-cancer changes that can sometimes be seen on biopsy that arent as serious as invasive cancer. If they are found in a needle biopsy that also shows invasive cancer, they are typically not important. They may, however, need to be removed completely as a part of treatment. If they are seen on an excisional biopsy at or near a margin , more tissue may need to be removed .
What If My Report Mentions Her2/neu Or Her2
Some breast cancers have too much of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu . The HER2/neu gene instructs the cells to make this protein. Tumors with increased levels of HER2/neu are referred to as HER2-positive.
The cells in HER2-positive breast cancers have too many copies of the HER2/neu gene, resulting in greater than normal amounts of the HER2 protein. These cancers tend to grow and spread more quickly than other breast cancers.
All newly diagnosed breast cancers should be tested for HER2, because women with HER2-positive cancers are much more likely to benefit from treatment with drugs that target the HER2 protein, such as trastuzumab , lapatinib , pertuzumab , and T-DM1 .
Testing of the biopsy or surgery sample is usually done in 1 of 2 ways:
- Immunohistochemistry : In this test, special antibodies that will stick to the HER2 protein are applied to the sample, which cause cells to change color if many copies are present. This color change can be seen under a microscope. The test results are reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+.
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization : This test uses fluorescent pieces of DNA that specifically stick to copies of the HER2/neu gene in cells, which can then be counted under a special microscope.
Many breast cancer specialists think that the FISH test is more accurate than IHC. However, it is more expensive and takes longer to get the results. Often the IHC test is used first:
Also Check: How To Feel If You Have Breast Cancer
Compliance With Ethical Standards
The research work complied with the current laws of China and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Peking Union Medical College Hospital . The data released by the SEER database do not require patient informed consent because cancer is a reportable disease in every state of the United States and the procedures are in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rectal Cancer Survival In The Uk Compared To Europe
Five-year relative survival for rectal cancer in men in England is below the average for Europe . Wales is also below the European average but Scotland and Northern Ireland are similar to the European average. Across the European countries for which data is available, five-year relative survival in men ranges from 37% to 78% .
Five-year relative survival for rectal cancer in women in England is below the average for Europe . Wales , Scotland and Northern Ireland are similar to the European average. Across the European countries for which data is available, five-year relative survival in women ranges from 36% to 67% .
Rectal Cancer , Age-Standardised Five-Year Relative Survival, Adults , European Countries, 2000-2007
You May Like: How Can Guys Get Breast Cancer
Reproductive Factors And Steroid Hormones
Late age at first pregnancy, nulliparity, early onset of menses, and late age of menopause have all been consistently associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Prolonged exposure to elevated levels of sex hormones has long been postulated as a risk factor for developing breast cancer, explaining the association between breast cancer and reproductive behaviors.
Clinical trials of secondary prevention in women with breast cancer have demonstrated the protective effect of selective estrogen receptor modulators and aromatase inhibitors on recurrence and the development of contralateral breast cancers. Use of SERMs in women at increased risk for breast cancer has prevented invasive ER-positive cancers. These data support estradiol and its receptor as a primary target for risk reduction but do not establish that circulating hormone levels predict increase risk.
A number of epidemiologic and pooled studies support an elevated risk of breast cancer among women with high estradiol levels. The Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group reported a relative risk of 2.58 among women in the top quintile of estradiol levels.
A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer of 58 international studies that included 143,887 postmenopausal women with invasive breast cancer and 424,972 without breast cancer concluded the following about menopausal HRT and breast cancer :
What Is The Prognosis
Your prognosis will depend on many factors, including the grade and stage of your cancer, as well as your long-term care plans. Follow-up appointments and tests can help your doctor detect a recurrence of cancer or any other complications.
Like other cancers, ILC is staged on a 0 to 4 scale. Staging has to do with the size of the tumors, lymph node involvement, and whether tumors have spread to other areas of the body. Higher numbers represent more advanced stages.
Research shows that ILC often has a good prognosis because the cancer cells are generally low grade, and they respond well to hormone treatment.
This responsiveness to treatment is favorable to your prognosis. Most of these types of cancers are hormone receptor-positive, usually estrogen positive. This means the cancer cells must have the hormone to grow. So medication that blocks the effects of estrogen can help prevent a return of disease and improve your prognosis.
But ILC tumors can often spread aggressively. People diagnosed with ILC are on average 3 years older at diagnosis compared with those with IDC. ILC is also most often diagnosed at a more advanced stage.
Several studies demonstrate that the overall long-term outcome for people diagnosed with ILC may be similar to those diagnosed with other types of invasive breast cancer. Some subgroups of people with ILC have worse outcomes than IDC, primarily related to the type of tumor they have and its treatment.
Also Check: When Is Radiation Therapy Used For Breast Cancer