Benign Breast Lumps And Future Cancer Risk
According to a 2019 study in the International Journal of Cancer, women with benign breast disease have an increased risk of developing breast cancer in the future. In addition, women with BBD, a family history of breast cancer, and genetic mutations have an even greater risk of developing breast cancer.
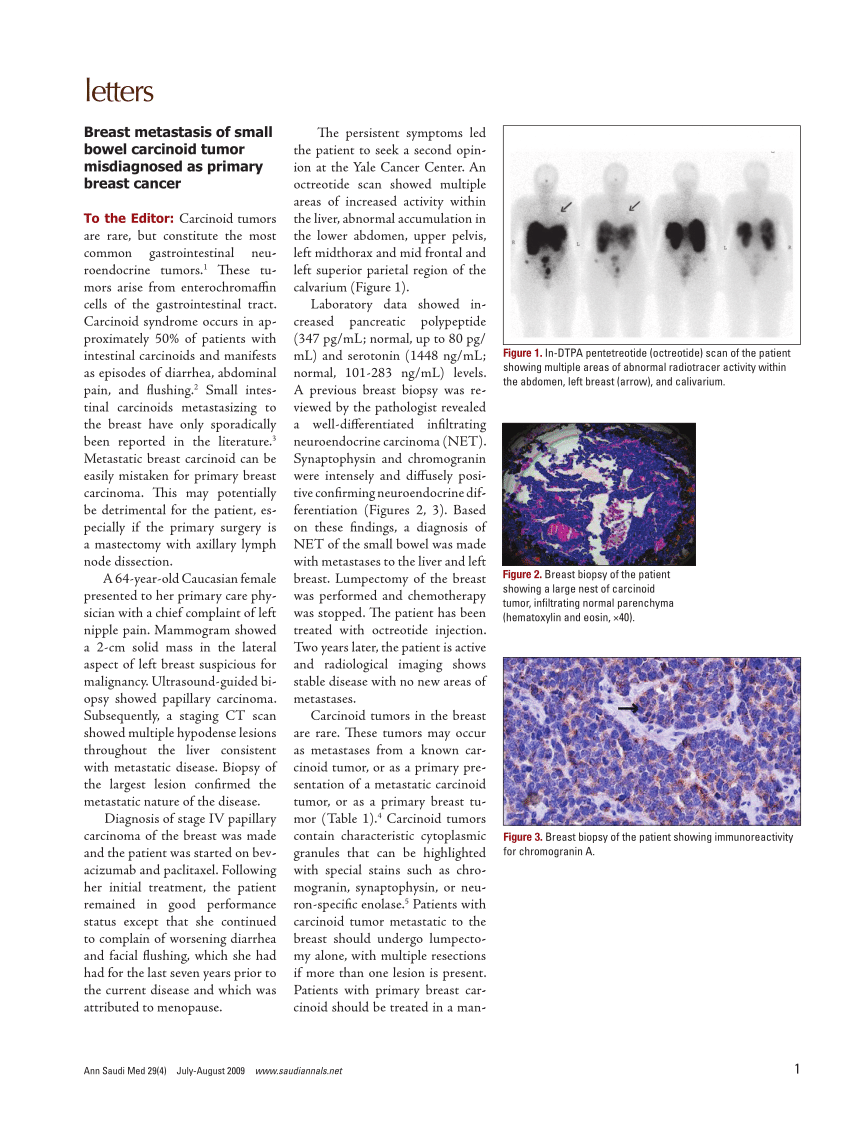
What Causes Breast Cysts
Breasts are made up of lobules and ducts . The milk glands are surrounded by fibrous support tissue and fat, known as breast tissue. This tissue gives breasts their size and shape. Sometimes, the milk glands can fill up with fluid these are breast cysts.
Cysts may appear naturally as the breast alters with age, due to normal changes in the oestrogen hormone levels. During the menstrual cycle oestrogen causes fluid to be produced. Although you can develop breast cysts at any age, theyre most common in women over 35.
After the menopause , as oestrogen levels fall, cysts usually stop forming. Women who have hormone replacement therapy may still get cysts.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Breast Cysts
If youve been diagnosed with a breast cyst, consider asking your provider:
- What type of breast cyst is it ?
- Does it need to be aspirated or removed?
- Do I need more frequent mammograms?
- Should I continue on hormone replacement therapy?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Breast cysts are common, especially among women in their forties. The good news is that these cysts are almost always harmless. Though cysts are common, always have your healthcare provider check out any new lumps or bumps you find.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/24/2020.
References
You May Like: What Age Group Does Breast Cancer Affect
Questions You Can Ask Your Doctor
Ask your doctor to take a closer look at any new or unusual breast changes that concern you. However, being specific about your particular concern can be helpful. For example, clearly stating which part of the breast is affected and how long you have noticed the change.
Some questions you might like to have ready if you see your doctor about your breast change:
- What can you feel in my breast?
- Which tests do I need to check a breast lump?
- When will I get the results?
- What were the results of my tests?
- Will I need a biopsy ?
- If more tests/treatment is needed, will you refer me to a breast specialist?
- What do I do if the cyst comes back after it has been drained ?
- Do you have anything I can take away with me to read more about this? What websites do you recommend?
Words: Francesca Brook
What Causes Fat Necrosis
Fat necrosis can be caused by any type of trauma to the breast including:
- Breast surgery including lumpectomy, breast reduction, reconstruction or enlargement
- Radiotherapy to the breast
- Lipomodelling: when fat taken from another part of the body is injected into the breast, for example to improve the appearance of dents following surgery
- Damage or injury caused by an accident such as a seat belt injury or fall
Fat necrosis can be found at any time after breast surgery or an injury.
Sometimes it develops without any trauma and many women with fat necrosis do not remember a specific injury.
You May Like: Breast Cancer Rash On Breast Pictures
Can Fat Necrosis Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Having fat necrosis does not increase your risk of developing breast cancer.
Some people worry the fat necrosis might turn into breast cancer, but theres no evidence that this can happen.
However, its still important to be breast aware and go back to your GP if you notice any changes in your breasts, regardless of how soon these occur after your diagnosis of fat necrosis.
If you have any questions about fat necrosis or would just like to talk it through with a nurse, you can call our free Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the growth of breast tissue cells that cannot be controlled. These cells form a lump that grows underneath the breast tissue. When cancerous cells attack healthy cells in these lumps, cancer is the result. Although both women and men can develop cancer, it is more prominent in women over the age of 40.
There are signs indicating that breast cancer is present, although not all women will experience these symptoms. Possible signs of the cancer include:
- Change in the size or shape of the breast
- Clear fluid or blood discharge from the nipples
- Breast redness/ irritation
Self-examinations help diagnose lumps and the other symptoms listed above. Conducting regular self-examinations is important. These examinations allow early detection of cancer.
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death in women. Each year, more than 235,000 people are diagnosed with the disease. This is 1 in every eight women. Of those women, nearly 40,000 will lose their lives battling the condition.
Chemotherapy, radiation, lifestyle and diet changes are all treatments available for cancer however, prevention and early detection of the disease are best.
Don’t Miss: Is It Possible To Get Breast Cancer At 18
How Common Are Cysts
Breast cysts are very common. Studies have reported cysts in up to 50% of women who attend breast clinics. Cysts can develop in women of any age. They are most common in the 3050 year age group. They usually disappear after menopause, but in some women they can last throughout life. Cysts are more common in post-menopausal women who take hormone replacement therapy than in post-menopausal women who do not. All of these factors support the theory that breast cysts are hormonally responsive, although it is not clear why some women form cysts and others do not.
How To Do A Breast Self
Performing a breast self-exam will help familiarize you with whats normal for your breasts. This can make it easier to notice any changes that may occur later on. If you menstruate, the best time for a self-exam is a few days after your period has ended.
Follow these steps when doing a self-exam:
- Stand unclothed in front of a mirror. Keep your shoulders straight with your arms at your sides. Look for changes in the size, shape, or color of your breasts. Also look for swelling and nipple changes, including discharge.
- Repeat with your arms raised.
- Next, lie down and lift your right arm over your head.
- Continue to examine your entire breast, from your collarbone to the top part of your abdomen, and from the center of your chest to your armpit. Try to follow a pattern so you cover your entire breast. Before you finish, gently squeeze your nipple to check for any discharge.
- Finally, stand or sit up, lift your right arm over your head and massage your breast in a similar manner to the steps above. Doing this in a shower when your skin is wet may make it easier to feel your breasts.
- Once youre done with one breast, switch sides and repeat. Try to do a self-exam once a month, around the same time each month.
Important
If you notice anything unusual, call your doctor. A breast exam doesnt take the place of routine medical care and breast cancer screening.
See your doctor if you feel an unexplained lump in your breast or notice other changes, like:
Recommended Reading: What Percentage Of People Survive Breast Cancer
Breast Cyst Treatment Options
No treatment is needed for simple cysts that cause no symptoms, after the diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound.
If ultrasound indicates that the cyst contains a solid component , a biopsy may be needed to exclude the possibility of cancer. However, some doctors may recommend that the cyst be monitored closely by ultrasound, particularly if the solid components are small.
If the cyst is large or causing discomfort, fine-needle aspiration can be used to remove fluid from the cyst to ease symptoms.
Cysts that are drained can come back or new cysts can form in nearby tissue. It is possible to drain the cyst again.
Occasionally, surgery can be recommended to remove cysts, although this is uncommon. Surgery is usually only reserved for cysts that continue to come back and cause symptoms, or cysts that show worrisome features in imaging or pathology tests.
Ductal Or Lobular Hyperplasia
Atypical lobular hyperplasia and atypical ductal hyperplasia are considered precancerous conditions. Atypical describes cells that look abnormal under a microscope, and hyperplasia means there is an overgrowth of cells. Breast tumors that have these characteristics are more likely to turn into cancer therefore, close monitoring or surgical excision is required to treat these conditions.
Read Also: Do Vegetarians Get Breast Cancer
Beginning The Treatment Journey
Everything changed as soon as we got to Phoenix and walked in the hospital door. The way they spoke to me and the way their attitude was toward meeverything was exactly the opposite of at home. I saw the surgical oncologist first. He gave me an overview of everything that was going to happen and turned me over to oncology because tumors over five centimeters required chemotherapy before surgery.
The oncologist didn’t think I had another day to waste before starting chemohe thought I probably had cancer for at least nine months by then. He told me that I would be in for a rough year but that there would be a light at the end of the tunnel, which is what I wanted to hear.
Initially, back home, they had diagnosed me with stage IV breast cancer because they thought cancer had spread to my liver. But when I got to Mayo Clinic, after they looked at all the imaging, they thought within 90% certainty that it was not cancer on my liver and downgraded me to stage IIIB. But we were still waiting to find out whether the cancer was a type known as HER2-positive.
According to MedlinePlus, a resource of the National Library of Medicine, HER2-positive breast cancers mean that there are high levels of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein . Too much HER2 tends to cause cells to divide, grow, and spread faster.
I did my six treatments my last one was on my son’s fifth birthday. My nurses remembered and brought him a cake and everything, which was very sweet.
Do Cysts Lead To Cancer
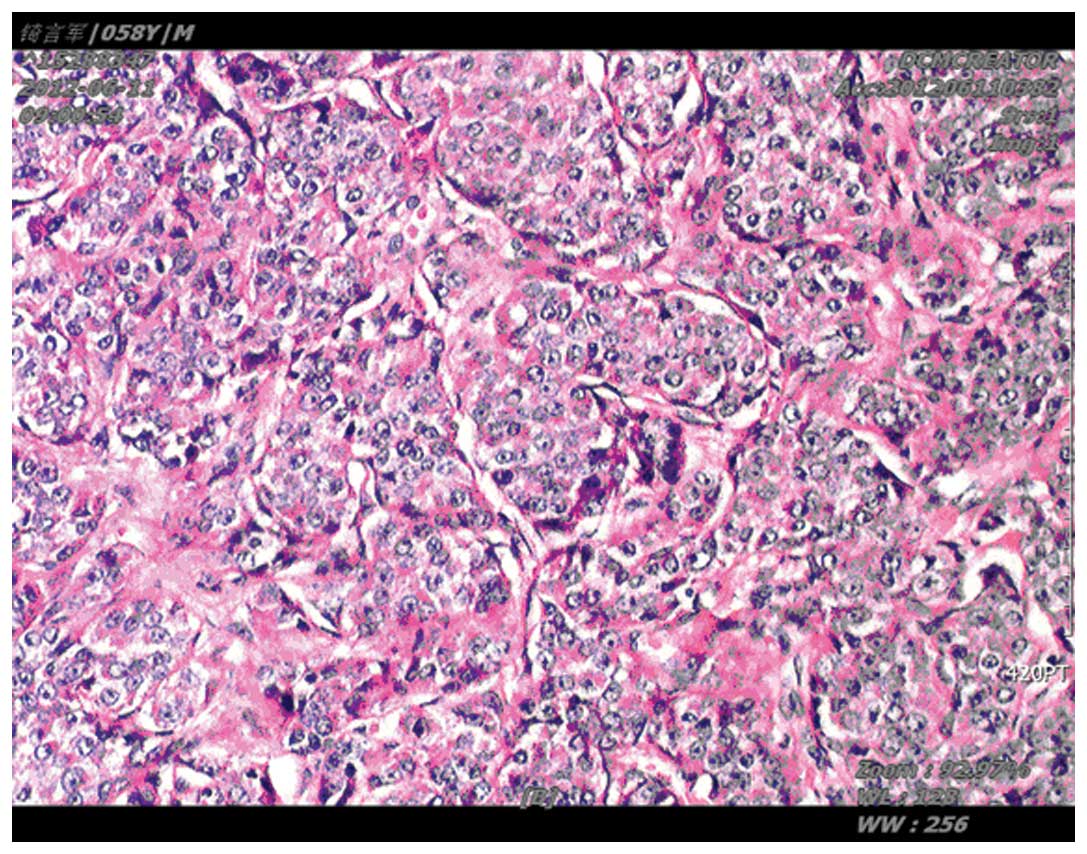
Nearly all simple cysts are just that simple. They are almost never associated with a higher risk of cancer. The only possible exception in which a cyst might indicate a slightly elevated risk for cancer is when other risk factors for cancer, such as a strong family history, are already present, or when further examination of imaging studies reveals some debris inside or along the edge or margin of it.
You May Like: Nipple Retraction Breast Cancer Staging
How Are Fibroadenomas Diagnosed And Treated
Your healthcare provider may diagnose this type of lump simply by feeling it. But, he or she will want to confirm the diagnosis with a mammogram or ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration. Sometimes, in very young women, the fibroadenoma is not removed. However, since sometimes these tumors enlarge with pregnancy and breastfeeding, your provider may suggest having it surgically removed.
While most fibroadenomas do not lead to cancer, there is a type of fibroadenoma that has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, particularly in women with a family history of the disease.
What Is A Cyst
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops in the breast tissue. They most often happen in women between the ages of 35 and 50 and are common in those nearing menopause. The cysts often enlarge and become sore just before your period. They may seem to appear overnight. Cysts are rarely cancerous and may be caused by blocked breast glands.
Cysts can feel either soft or hard. When close to the surface of the breast, cysts can feel like a large blister, smooth on the outside, but fluid-filled on the inside. When they are deep in breast tissue, cysts will feel like hard lumps because they are covered with tissue.
Don’t Miss: What Puts You At Higher Risk For Breast Cancer
What Does A Breast Cyst Feel Like
Breast cysts may be found in one or both breasts. If you have a breast cyst, you may feel:
- A smooth, easily movable lump under the skin
- Breast pain or tenderness in the area of the breast lump
If you notice any new or unusual breast change, please speak with your doctor without delay. Most breast changes are not caused by cancer, however some lumps may not be cysts and will require further investigation.
The Breast Cancer Misdiagnosis Problem
According to the Center for Disease Control, breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death among women. And by some estimates, up to 80,000 people die each year in part to breast cancer misdiagnosis.
Problems of an Accurate Diagnosis
According to an examination of breast cancer cases by The New York Times, accurately diagnosing the earlier stages of breast cancer is difficult. The tests are vulnerable to outright error and case-by-case disputes over whether cell clusters are cancerous or not.
The most common misdiagnoses include cysts and infections. There is also a lot of disagreement over a certain kind of cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ . Differing opinions as to the definition of DCIS has led to differing approaches to treating it. Some experts say its non-invasive. Others say it is. Depending on the age of the patient, some physicians incorrectly rule out breast cancer altogether.
Experts can agree on one thing a delayed diagnosis of cancer can have devastating consequences. The longer cancers are left unchecked, the greater the chance they will become unmanageable.
Testing for Breast Cancer
Needle biopsies are commonly used to determine whether cell clusters are cancerous or benign. But they can produce mixed results. A reported 17 percent of DCIS cases can be misdiagnosed through this testing method.
Abetting Misdiagnoses
Don’t Miss: How To Check Myself For Breast Cancer
When To See Your Doctor
If you notice any new or unusual changes in your breasts, please speak to your doctor without delay. This includes breast changes such as a new lump, a lump that grows or persists, or changes on the skin of the breast.
Most breast changes are not caused by cancer. However, it is important to speak with your doctor so that the breast change can be checked. Even if you have been diagnosed with breast cysts before, it is important that every new breast lump be checked as some lumps may not be cysts and will require further follow up.
How Are Breast Cysts Treated
In most cases, you dont need treatment. Simple breast cysts dont cause any harm and sometimes even go away on their own.
If the cyst is uncomfortable, your healthcare provider can drain the fluid from it with a needle biopsy. However, the fluid could come back. If it returns and continues to be painful, you may need surgery to remove it.
For complicated or complex breast cysts, you may need more frequent checkups to keep tabs on any changes.
Read Also: What To Wear For Radiation Breast Cancer
Detecting Breast Cancer Earlier
Breast cancer cant usually be prevented, but you can take three important steps to help detect it earlier. The free resource, 3 Steps to Early Detection, can increase your chance of finding breast cancer before it spreads.
Tell us where we can send you your copy.
Materials on this page provided by: Johns Hopkins Medicine
Medically Reviewed on April 15, 2020
Doctor’s Notes On Breast Cancer Vs Cyst Differences And Similarities
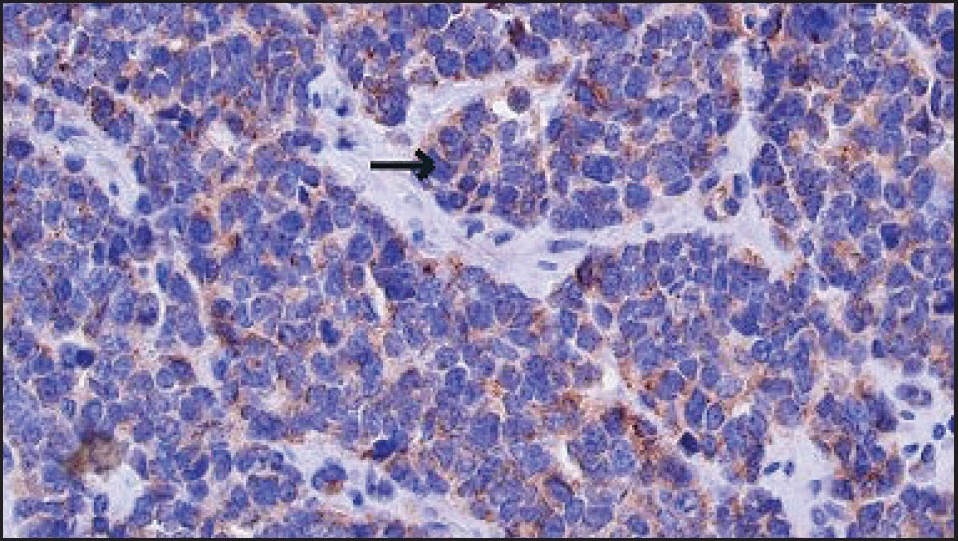
Breast cancer is the abnormal growth, development, and spread of breast tissue. A cyst is a thin-walled hollow cavity usually containing a fluid. Most breast cysts are not cancerous and do not contain cancer cells, although a few may . Some cysts may self-resolve, but breast cancer does not. Early breast cancer and small cysts may have no symptoms, but as breast cancer advances, lumps, breast discharge, nipple inversion, and breast skin changes may occur. If a cyst produces signs or symptoms, it may cause redness, swelling, or tenderness at the site. A doctor should investigate all breast cysts carefully to rule out breast cancer.
The root cause of breast cancer development is unknown, but it occurs in women mainly and may be related to hormonal changes, alcohol consumption, diet, and other factors. The same is true for the cause of breast cyst development although some evidence suggests that excess estrogen may contribute to their development.
What Are the Treatments of Breast Cancer vs. Cysts?
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the treatment for a cyst is dependent on if it is causing problems and/or if there is an underlying problem. The majority of cysts are benign and do not need treatment. However, if they are causing symptoms, the following treatments may be used:
- Aspirating a cyst with a needle or catheter
- Surgically removing the cyst
- Medical treatment is limited to treating underlying causes
Read Also: Does Chemo Really Work For Breast Cancer
What Are Breast Cysts
- Breast cysts are fluid filled sacs inside the breast, usually round or oval shaped and feel a little like a grape but can sometimes feel firm. Occasionally, they can cause pain and discomfort.
- They are usually not cancerous and are not indicative of an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
- Breast cysts are most common in women aged between 35 and 50 years but can present in women of any age.
- It is not known what causes breast cysts, but they may develop as a result of hormonal changes in the menstrual cycle.
- Some evidence suggests excess estrogen can stimulate breast tissue causing cysts to form.