Age At First Childbirth
A first pregnancy is linked to an increased short-term risk of breast cancer, but a decreased long-term risk of breast cancer. The impact of these risks depends on a womans age at the time of her first pregnancy .
Women who give birth to their first child at age 35 or younger tend to have a decreased risk of breast cancer .
Breast cancer risk is increased for about 10 years after a first birth . After that, women who give birth tend to have a lower risk of breast cancer than women who never give birth .
Women who give birth to their first child at later ages have a higher risk of breast cancer than women who have their first child at younger ages .
Women who are over 35 when they give birth to their first child have a small increased risk of breast cancer compared to those who never give birth . For these women, the increased risk related to a first pregnancy is never fully offset by the long-term decreased risk related to childbirth .
Who Should Get Screened
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force suggest that females aged 5074 years who are at average risk of developing breast cancer should go for screening every 2 years.
Those aged 4049 years, particularly those with a higher risk of breast cancer, should speak to their doctor about the risks and benefits of undergoing regular screening.
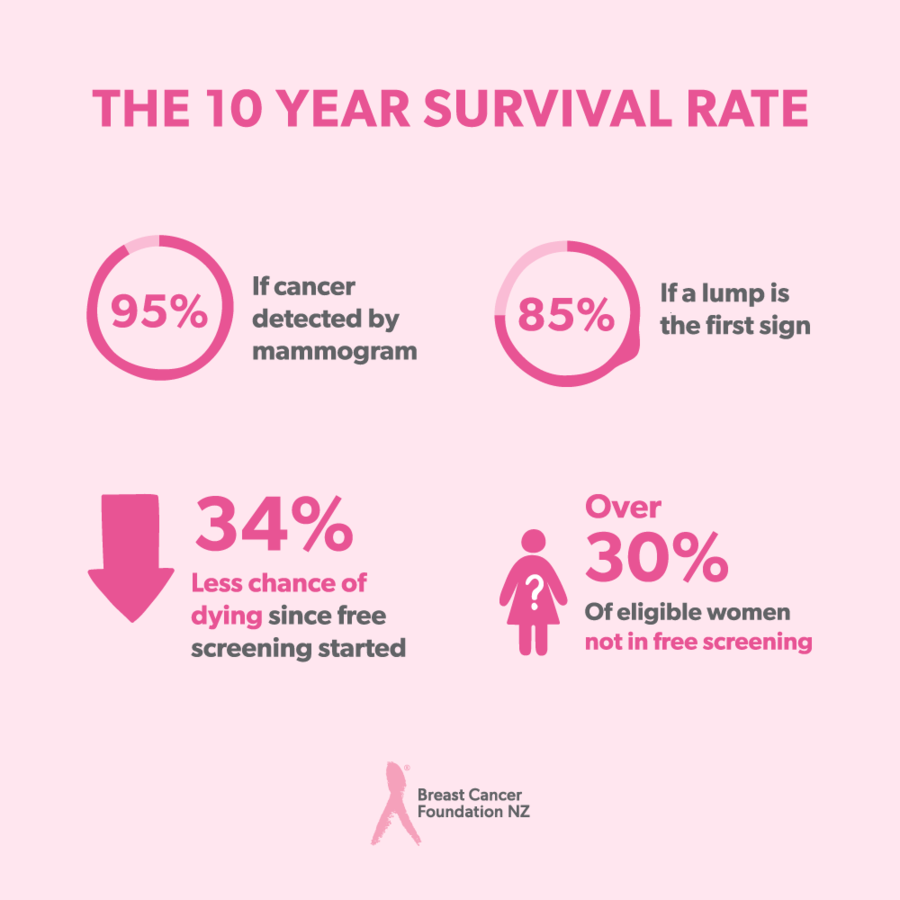
Doctors tend to use a mammogram to screen people for breast cancer. A mammogram is a breast X-ray that can help detect breast cancer early on, before it starts to produce symptoms.
Other exams available for people at a higher risk of breast cancer include:
There are both risks and benefits associated with regularly screening for breast cancer. Many people conclude that the benefits outweigh the risks, but getting screened is a personal decision.
The risks of screening for breast cancer include:
- False positives: A false positive occurs when a test result falsely suggests that a person has cancer. False positives can prompt additional tests, which may cause anxiety and can be expensive and time consuming.
- Overtreatment: Some cancers are benign and do not go on to cause symptoms or other problems. Treating these types of cancers is called overtreatment, and it can lead to unnecessary side effects, expense, and anxiety.
- False negatives: A false negative occurs when a test result misses the presence of a cancer. False negatives can delay diagnosis and treatment.
What Are The Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
CDCs Dr. Lisa Richardson explains the link between drinking alcoholic beverages and breast cancer risk in this video.
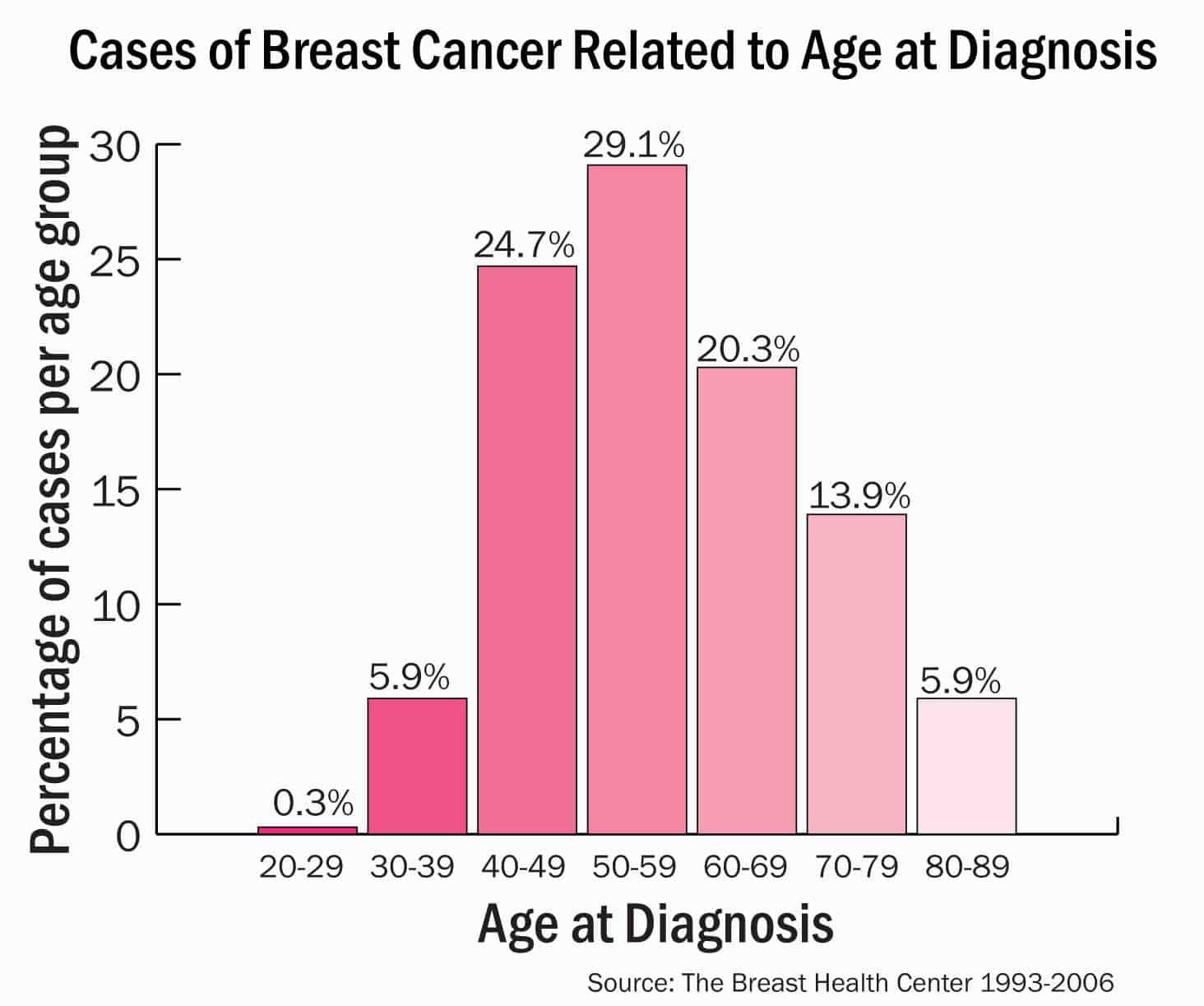
Studies have shown that your risk for breast cancer is due to a combination of factors. The main factors that influence your risk include being a woman and getting older. Most breast cancers are found in women who are 50 years old or older.
Some women will get breast cancer even without any other risk factors that they know of. Having a risk factor does not mean you will get the disease, and not all risk factors have the same effect. Most women have some risk factors, but most women do not get breast cancer. If you have breast cancer risk factors, talk with your doctor about ways you can lower your risk and about screening for breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: How You Know You Have Breast Cancer
What Is The Risk Of Breast Cancer In Women In Their 30s
A womans risk of breast cancer throughout her 30s is just 1 in 227, or about 0.4 percent. By age 40 to 50, the risk is roughly 1 in 68, or about 1.5 percent. From age 60 to 70, the chance increases to 1 in 28, or 3.6 percent. Out of all types of cancer, though, breast cancer is the most common among U.S. women.
Individualized Breast Cancer Treatment For Older Adults
Tran says her groups approach to dealing with breast cancer in patients of any age is highly individualized. We recommend both the treatments and the order in which the patient will receive them, which is very important. For instance, radiation is not common before surgery, since it makes wound healing more difficult.
Recommended Reading: What Is Lobular Breast Cancer
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyBCTeam is the social network for people with breast cancer and their loved ones. On MyBCTeam, more than 53,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with breast cancer.
Are you worried about your risk of developing breast cancer? Share your experiences in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on MyBCTeam.
What Is The Average American Womans Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer During Her Lifetime
Based on current incidence rates, 12.9% of women born in the United States today will develop breast cancer at some time during their lives . This estimate, from the most recent SEER Cancer Statistics Review , is based on breast cancer statistics for the years 2015 through 2017.
This estimate means that, if the current incidence rate stays the same, a woman born today has about a 1 in 8 chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer at some time during her life. On the other hand, the chance that she will never have breast cancer is 87.1%, or about 7 in 8.
For men born in the United States today, the lifetime risk of breast cancer is 0.13%, based on breast cancer statistics for the years 2015 through 2017. This means that a man born today has about a 1 in 800 chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer at some time during his life.
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Lumps Be Visible
Risk Factors You Can Change
Being physically active can help lower your risk of getting breast cancer.
- Not being physically active. Women who are not physically active have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Being overweight or having obesity after menopause. Older women who are overweight or have obesity have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than those at a normal weight.
- Taking hormones. Some forms of hormone replacement therapy taken during menopause can raise risk for breast cancer when taken for more than five years. Certain oral contraceptives also have been found to raise breast cancer risk.
- Reproductive history. Having the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
- Drinking alcohol. Studies show that a womans risk for breast cancer increases with the more alcohol she drinks.
Research suggests that other factors such as smoking, being exposed to chemicals that can cause cancer, and changes in other hormones due to night shift working also may increase breast cancer risk.
Why Does Age Matter
During pregnancy, breast cells grow rapidly. If theres any genetic damage in the breast cells before pregnancy, its copied as the cells grow. This increased genetic damage in the cells can lead to breast cancer.
The chance of having such genetic damage goes up with age. This may help explain why women who have their first child at a later age have a higher risk of breast cancer than women who have their first child at a younger age.
Also Check: What Are The Two Types Of Breast Cancer
How Many People Survive Breast Cancer
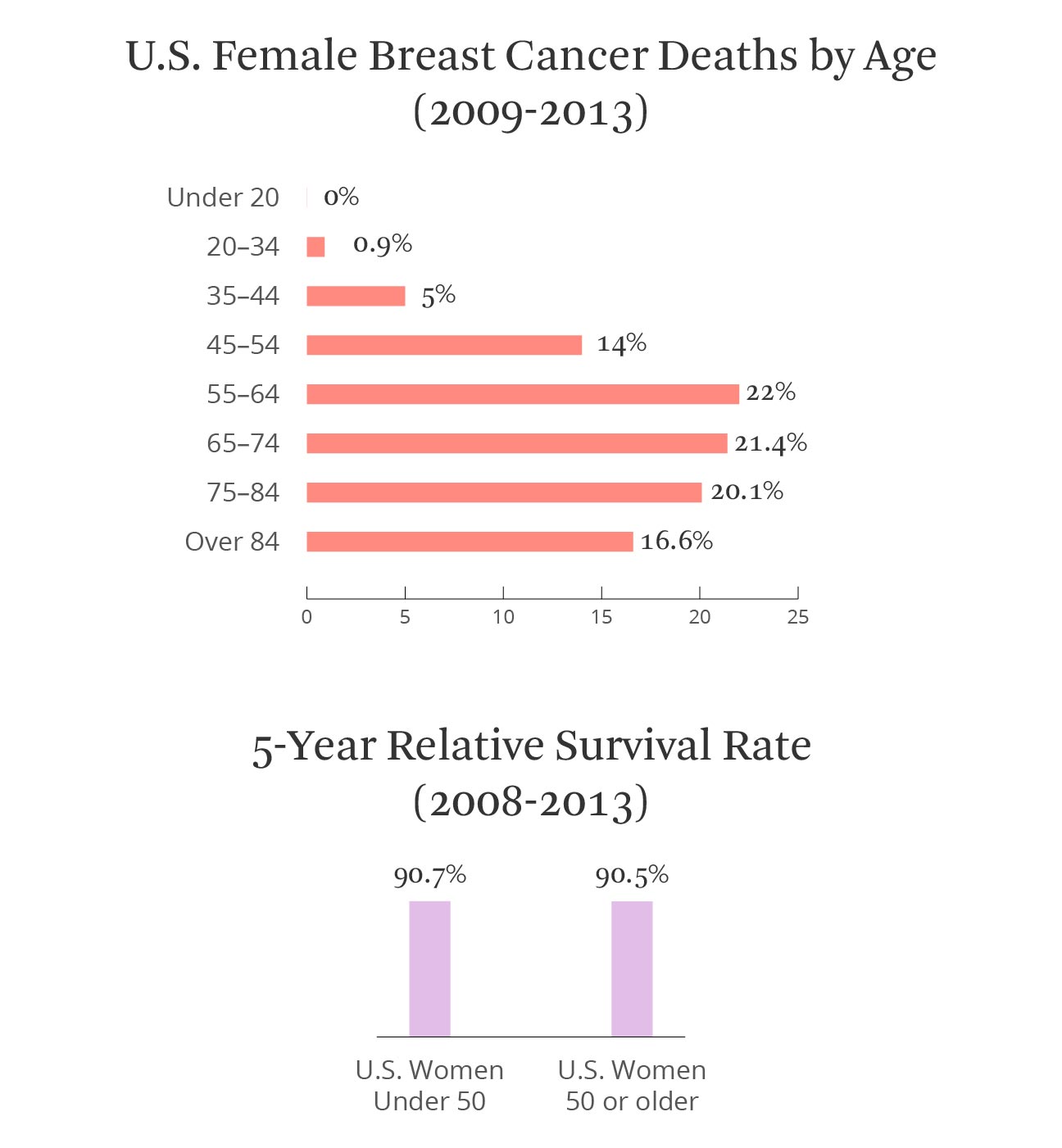
- Almost nine in ten of women survive breast cancer for five years or more.
- Breast cancer survival is improving and has doubled in the past 40 years in the UK due to a combination of improvements in treatment and care, earlier detection through screening and a focus on targets, including faster diagnosis.
- An estimated 600,000 people are alive in the UK after a diagnosis of breast cancer. This is predicted to rise to 1.2 million in 2030.
For many the overwhelming emotional and physical effects of the disease can be long-lasting.
Every year around 11,500women and 85 men die from breast cancer in the UK thats nearly 1,000 deaths each month, 31 each day or one every 45 minutes.
Breast cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the UK.
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death in women under 50 in the UK.
How Old Is Too Old To Get Breast Cancer
Females over 50 years of age are more likely to receive a breast cancer diagnosis. A persons risk of developing breast cancer increases as they get older. As people age, abnormal changes in their cells are more likely to occur. Breast cancer is most common in females over the age of 50 years. Trusted Source.
Don’t Miss: Which Breast Implants Cause Cancer
Understanding Your Risk Of Breast Cancer
Several breast cancer risk assessment tools have been developed to help people estimate their chance of developing breast cancer. The best studied is the Gail model, which is available on the National Cancer Institutes website at www.cancer.gov/bcrisktool. After you enter some personal and family information, including your race/ethnicity, the tool provides you with a 5-year and lifetime estimate of the risk of developing invasive breast cancer. Because it only asks for information about breast cancer in first-degree family members and does not include their ages at diagnosis, the tool works best at estimating risk in people without a strong inherited breast cancer risk. In addition, it cannot be used by patients who have a personal history of breast cancer to determine their risk of developing a new breast cancer. For people with a personal history of breast cancer or a strong family history of breast cancer, other ways of determining their risk of breast cancer may work better. People with a strong family history of breast cancer risk should consider talking to a genetic counselor.
It is important to talk with your doctor about how to estimate your personal risk of breast cancer and to discuss risk-reducing or prevention options .
What Is Different About Breast Cancer In Younger Women
- Diagnosing breast cancer in younger women is more difficult because their breast tissue is generally denser than the breast tissue in older women, and routine screening is not recommended.
- Breast cancer in younger women may be more aggressive and less likely to respond to treatment.
- Women who are diagnosed with breast cancer at a younger age are more likely to have genetic mutations predisposing them to breast and other cancers.
- Younger women who have breast cancer may ignore the warning signssuch as a breast lump or unusual dischargebecause they believe they are too young to get breast cancer. This can lead to a delay in diagnosis and poorer outcomes.
- Some healthcare providers may also dismiss breast lumps or other symptoms in young women or adopt a “wait and see” approach.
- Breast cancer poses additional challenges for younger women as it can involve issues concerning sexuality, fertility, and pregnancy after breast cancer treatment.
Recommended Reading: Is Her2 Negative Breast Cancer Aggressive
Absolute Risk By Attained Age Parity Age At Births And Time Since Births
Figure 5AF shows the predicted incidence of breast cancer according to attained age in subgroups defined by parity, age at birth and time since birth. Each figure shows the risk pattern for women of parity 03, with the same ages at births. Thus, these curves illustrate the effect of having an additional child at different ages. The prediction is based on a model with age at births in 5-year categories. When a single birth occurs within a specific age-category, the contribution to risk starts at the midpoint in the age interval. Otherwise, the first birth starts contributing at the lowest age and the subsequent births at 2-year intervals.
Predicted incidence rate of breast cancer for women of parity 03 by attained age, with additional contribution from each subsequent child according to time since the most recent birth, in specific combinations of ages at first, second and third birth , respectively. represent combinations with an early first birth, , a first birth at an intermediate age, and a late first birth. Results are adjusted for age and birth-cohort.
Short-term effects in terms of absolute risk
Long-term effects in terms of absolute risk
Atypical Hyperplasia Or Atypia
Either atypical hyperplasia or atypia indicates the growth of abnormal cells in the breast. The diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia can be made from a core biopsy or excisional biopsy, and has been correlated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
The diagnosis of atypia can be made from nipple aspiration, ductal lavage, or fine needle aspiration , and also indicates an increased breast cancer risk. Although these cells are not yet cancerous, they do raise a woman’s risk of eventually developing breast cancer. While biopsies and FNAs are usually reserved for when there is a current indication that a woman might have breast cancer, nipple aspiration and ductal lavage are methods that may help assess a woman’s future risk of breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Does Nipple Pinching Cause Breast Cancer
What Percentage Of Breast Cancer Is Inherited
Roughly 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are linked to inherited gene mutations. The most well-known are breast cancer gene 1 and breast cancer gene 2 . If you have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, your doctor may suggest testing your blood for these specific mutations. Breast cancer in your 20s and 30s has been
Age At First Period First Childbirth And Menopause
The longer a persons breast cells are exposed to the hormone estrogen, the higher their breast cancer risk. The role of the hormone progesterone is less clear. The ovaries start producing these hormones during puberty. This means that women who go through puberty before the age of 12 have an increased chance of developing breast cancer. Likewise, the ovaries stop making estrogen and progesterone at menopause. Women who go through menopause after the age of 55 are at higher risk of breast cancer.
There is a complicated link between breast cancer and pregnancy. A womans risk of developing breast cancer increases in the short term after giving birth she is more likely to be diagnosed within 10 years of having her first child. However, after this time period, women who have had children have a lower risk of breast cancer than women who have never given birth.
Additionally, the younger a woman is when she has her first child, the more her breast cancer risk drops. A woman who has her first child after she turns 35 is 40 percent more likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer than a woman who has her first child before she turns 20.
Also Check: Can You Get Breast Cancer From Getting Punched
Personal History Of Breast Disease
Females who have previously had breast cancer are at risk of developing a second breast cancer, either in the other breast or in a different part of the same breast. This is not the same as the first cancer returning.
Having a personal history of certain noncancerous breast conditions can also increase a persons risk of breast cancer. This can include conditions such as atypical hyperplasia, lobular carcinoma in situ, and ductal carcinoma in situ.
People with a history of breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer should ask their doctors about .
Why Is Weight A Factor
Women who are overweight or obese have higher levels of estrogen in their bodies. Even though the ovaries stop making estrogen after menopause, the hormone is still stored and produced in fat tissue. Estrogen causes certain types of breast cancer to grow and spread. Work with your doctor to develop a weight loss plan that fits your life, if necessary.
Don’t Miss: What Is Oncotype Dx Test For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer: Risk Factors And Prevention
Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will find out more about the factors that increase the chance of developing breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
A risk factor is anything that increases a persons chance of developing cancer. Although risk factors often influence the development of cancer, most do not directly cause cancer. Some people with several risk factors never develop cancer, while others with no known risk factors do. Knowing your risk factors and talking about them with your doctor may help you make more informed lifestyle and health care choices.
Most breast cancers are sporadic, meaning they develop from damage to a persons genes that occurs by chance after they are born. There is no risk of the person passing this gene on to their children, as the underlying cause of sporadic breast cancer is a combination of internal, or hormonal, exposures lifestyle factors environmental factors and normal physiology, such as DNA replication.
Inherited breast cancers are less common, making up 5% to 10% of cancers. Inherited breast cancer occurs when gene changes, called mutations or alterations, are passed down within a family from parent to child. Many of those mutations are in tumor suppressor genes, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2. These genes normally keep cells from growing out of control and turning into cancer. But when these cells have a mutation, it can cause them to grow out of control.
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer is when breast cancer spreads from the breast to other parts of the body, becoming incurable. Breast cancer most commonly spreads to the bones, brain, lungs or liver.
While it cannot be cured, there are treatments that can help control certain forms of the disease for some time and relieve symptoms to help people live well for as long as possible.
There are an estimated 35,000 people living with secondary breast cancer in the UK. In around 5% of women, breast cancer has already spread by the time it is diagnosed.
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Treatments For Breast Cancer