In Breast Swollen Lymph Nodes
Asked by: Asa Pfeffer
Lymph nodes can enlarge when there is inflammation or infection. When this occurs, they may feel painful or tender this doesn’t always mean that there is something wrong, however, your health care provider may recommend a mammogram or an ultrasound to rule out a more serious condition.
Survival And Mortality Rates
Survival depends on mortality. You start with 100 percent of the people in the group.
100 percent mortality rate = survival rate
Say, the mortality rate in the group of people is 5 percent. Survival would be 95 percent .
Similarly, the number of people in a group who survive depends on the number of people who die. Say, 500 people are in the group and 1 person dies. This means 499 people survived .
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Surgery To Remove Lymph Nodes
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If it does spread, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. These lymph nodes drain the lymphatic fluid from the breast and arm.
It is important to know if there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit and how many. This helps the doctors work out the stage of your cancer and plan the best treatment for you.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Also Check: How To Prevent Breast Cancer
Lymphangiogenesis And Lymphatic Metastasis
While the promoting effect of angiogenesis and vascularization of the tumor in the progression of the disease is well documented, there is little information with regard to lymphangiogenesis and its function in metastasis. Certain studies have indicated that the tumors are devoid of lymphatic vessels, while others have suggested that tumors invade and destroy lymphatic vessels . Furthermore, other studies have indicated that tumor cells may induce lymphangiogenesis, some form of lymphatic sprouting, or hyperplasia in close proximity to the periphery of the tumors . Therefore, the pertinent question is whether lymphangiogenesis is necessary for lymphatic metastasis. Although it is possible for lymphatic metastasis to occur via preexisting vessels that were incorporated into the tumors, there is evidence to suggest that increased lymphatic vessel density due to lymphangiogenesis significantly improves metastasis .
What Do Cancer Stages And Grades Mean

The stage of a cancer describes the size of a tumour and how far it has spread from where it originated. The grade describes the appearance of the cancerous cells.
If you’re diagnosed with cancer, you may have more tests to help determine how far it has progressed. Staging and grading the cancer will allow the doctors to determine its size, whether it has spread and the best treatment options.
Don’t Miss: How Is Chemotherapy Administered For Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
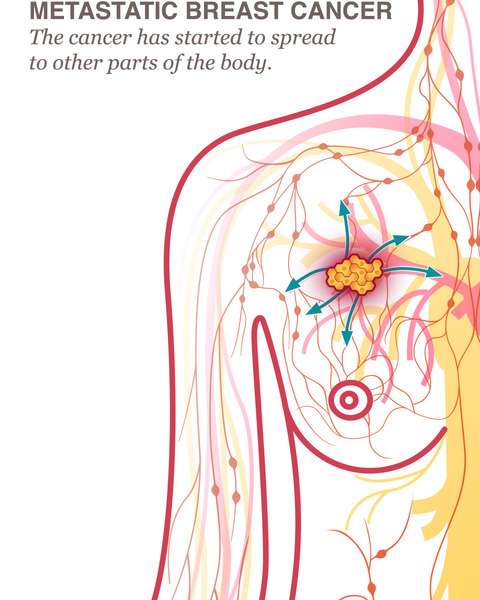
Secondary breast cancer means that a cancer that began in the breast has spread to another part of the body. Secondary cancer can also be called advanced or metastatic cancer.
It might not mean that you have secondary breast cancer if you have the symptoms described below. They can be caused by other conditions.
How Is Cancer In Lymph Nodes Found
Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when theres infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the bodys surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer.
The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy. Doctors may remove lymph nodes or take samples of one or more nodes using needles. The tissue thats removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist to find out if there are cancer cells in it. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, they may remove one or more of the nearby lymph nodes as well. Removal of one lymph node is considered a biopsy, but when many lymph nodes are removed, its called lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, theres a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo,immunotherapy, targeted therapy or radiation, might be needed after surgery.
Also Check: Where Can Breast Cancer Lumps Appear
Most Common Places It Spreads
It’s still breast cancer, even if it’s in another organ. For example, if breast cancer spreads to your lungs, that doesn’t mean you have lung cancer. Although it can spread to any part of your body, there are certain places it’s most likely to go to, including the lymph nodes, bones, liver, lungs, and brain.
3
When To Contact A Doctor
If a person notices any signs of cancer having spread to their lymph nodes, they should speak with a doctor immediately.
Additionally, if a person with cancer notices any unusual new symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The sooner a person receives treatment for cancer that has spread, the better their chances of survival.
Don’t Miss: Will I Survive Breast Cancer
The Role Of Lymph Nodes In Breast Cancer
One of the first places breast cancer can spread outside of the breast is in the nearby lymph nodes. When tests show that the breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, its called lymph node involvement.
Lymph node involvement can change how your oncologist plans to treat the breast cancer. Once breast cancer cells have entered the lymph nodes, the clear lymph fluid that travels throughout the body to help fight infections and clear your body of toxins now also contains breast cancer cells. Treatment options after lymph node involvement must also travel throughout the body to kill breast cancer cells that may be in the lymph fluid.
If All The Cancer Was Removed With Surgery Why Do I Need Any Additional Treatment
It has long been recognized that breast cancer is not always cured by locoregional treatment alone.
The goal of treating early breast cancer is to remove the cancer and keep it from coming back . Most people diagnosed with breast cancer will never have a breast cancer recurrence. However, everyone who has had breast cancer is at potential risk of recurrence, and that is why in most cases, there is a recommendation for treatment in addition to surgery, which is known as adjuvant therapy. The risk of recurrence can never be entirely eliminated, but the aim of adjuvant therapy is to reduce recurrence risk to the absolute minimum.
Don’t Miss: What Is Mitotic Rate In Breast Cancer
Where Does Breast Cancer Spread To
Breast cancer cells seem to prefer to settle into:-
- long bones in the arms and legs
- ribs
- skull
With an osteolytic metastasis, the cancer kind of eats away at the bone, creating holes.
With an osteoblastic bone metastasis, the bone mineral density actually increases, but this can cause the bones to fracture more easily. This requires a little more explanation. Breast cancer metastases tend to be lytic when they are untreated, and then they become densely sclerotic as they respond to treatment.
Even if no treatment is given yet, an osteoblastic metastasis from breast cancer generally indicates that the persons own body is trying to fight cancer with some success.
A CT scan may also be used to check for metastasis to the lungs or liver. A CT scan is essentially an X-ray linked to a computer. The breast cancer doctor injects a contrast dye agent into the bloodstream and this makes any cancer cells in the liver and chest easier to see.
Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, its not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
You May Like: Can Hickies On Your Breast Cause Cancer
Diagnosing Symptoms Related To Lymph Nodes
When touching an affected area, swollen lymph nodes may feel soft and round, like lumps the size of a pea, peanut or grape. If theyre painful when touched, that may be a sign of inflammation. Since lymph nodes appear in parallelas, for instance, on both sides of the neckyou can feel lymph glands on both sides to see whether they are a normal size on one side and enlarged on the other, which may be a sign of infection.
In determining a diagnosis, its important for doctors to look at other symptoms or factors. Swollen lymph nodes near the ear may indicate an ear infection, for instance. Swollen glands in the neck area near the collarbone, combined with a sore throat and cough, may be a sign of an upper respiratory infection. When multiple regions of lymph nodes are swollen, it may indicate a body-wide disease that needs immediate attention.
Besides reviewing your medical history, doctors may use some of the following methods to diagnose the cause of swollen lymph nodes:
- Physical examination, feeling with fingers the nodes in the affected area to check their size and whether they feel hard, tender or warm
- Lab tests, including blood tests to check for suspected underlying conditions
Breast Cancer Progression Tends To Be Consistent And Predictable
There are many ways that breast cancer can develop but most of the time it starts in the breast ducts.
While cancer is still confined to the breast ducts, specialists refer to it as ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS. The good news is that if breast screening detects cancer at this in-situ stage, the chance of survival is close to 100%.
As cancer moves into the breast duct wall and finally begins to affect the surrounding breast tissue, specialists call it infiltrative or invasive breast cancer.
If treatment does not occur, breast cancer will usually spread to other areas of the body . Very often the first area that cancer usually spreads to is the lymph nodes in the underarm area .
Once cancer enters the lymphatic system, it can and usually does spread to other areas of the body. Sometimes this is called distant metastasis.
Not all breast cancers spread first to the axillary lymph nodes and then to the rest of the body. If the breast tumor occurs near the nipple, cancer may spread first to the internal mammary nodes beneath the sternum. And in some cases, the breast cancer can spread via the bloodstream without involving the lymphatic system.
Also Check: How To Tell If Cancer Has Metastasized
You May Like: How Do You Test For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Treatment Options For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Treatment for metastatic breast cancer often is based on systemic therapies, which use drugs rather than surgery or radiation. Metastases treatments are designed to shrink tumors and slow their growth, help ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment may change, such as when one therapy stops working, or the side effects become too uncomfortable. Rather than having only one treatment, most patients undergo several treatments combined to help fight the cancer.
The four broad categories of drug-based treatments are:
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass or sheet of cells called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. When breast cancer is limited to the breast and/or nearby lymph node regions, it is called early stage or locally advanced. Read about these stages in a different guide on Cancer.Net. When breast cancer spreads to an area farther from where it started to another part of the body, doctors say that the cancer has metastasized. They call the area of spread a metastasis, or use the plural of metastases if the cancer has spread to more than 1 area. The disease is called metastatic breast cancer. Another name for metastatic breast cancer is “stage IV breast cancer if it has already spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the original cancer.
Doctors may also call metastatic breast cancer advanced breast cancer. However, this term should not be confused with locally advanced breast cancer, which is breast cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Read Also: What Causes Triple Negative Breast Cancer
How Long After Breast Cancer Treatment Do Recurrences Occur
The risk of recurrence for all breast cancers was highest in the first five years from the initial cancer diagnosis at 10.4%. This was highest between the first and second years after the initial diagnosis. During the first five years after the initial diagnosis, patients with oestrogen receptor positive breast cancer had lower rates of recurrence compared with those with ER negative disease. However, beyond five years, patients with ER positive disease had higher rates of recurrence.
The late recurrence or relapse of breast cancer refers to cancers that come back after five years, but may not return for 10 years, 20 years, or even more. For people who have estrogen receptor-positive tumours, the cancer is actually more likely to recur after five years than in the first five years.
In contrast to the common belief that surviving for five years after cancer treatment is equivalent to a cure, with hormone-sensitive breast tumours there is a steady rate of recurrence risk for at least 20 years after the original diagnosis, even with very small node-negative tumours.
An awareness of the risk of late recurrence is important for a number of reasons. People are often shocked to learn that their breast cancer has come back after say, 15 years, and loved ones who dont understand this risk are often less likely to be supportive as you cope with the fear of recurrence.
Bone Metastases
- Spine
- Pelvis
- The long bones of the arms and legs
Symptoms and Detection
Treatment
Liver Metastases
Prognosis And Survival For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type, stage and characteristics of your cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
Doctors use different prognostic and predictive factors for newly diagnosed and recurrent breast cancers.
Read Also: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 15
Can A Surgeon Tell If A Lymph Node Is Cancerous
Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer. The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy.
Getting The Results During Surgery
In some hospitals, the surgeon gets the results of the sentinel lymph node biopsy during the operation. This is called an intra operative assessment. They can remove the rest of the nodes if necessary. You then avoid having a second operation.
Your surgeon will explain this to you before your operation, so you know what to expect.
Also Check: How To Tell If Breast Cancer Has Metastasized
Stage Iv Breast Cancers May Be Recurrences Following Initial Treatment
Up to 5% of initial breast cancer diagnoses are of the most advanced or metastatic stage. However, this number has significantly reduced with the implementation of widespread breast cancer screening programs.
Metastatic breast cancer can appear to be a rapid deterioration of a disease that has been present for some time undetected.
But metastatic breast cancer can also be the result of a recurrence of breast cancer after successful initial treatment. Sometimes the terms local and regional recurrence indicate a return of breast cancer to the original tumor site or elsewhere in the breast or contralateral breast.
If the cancer returns in other areas of the body it is a distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
For more detail on Stage IV survival rates, recurrence rates and treatment please see our new post HERE.
Lymph Nodes And What They Do
Lymph vessels send lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes are located in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen , and groin. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas.
Read Also: When Breast Cancer Spreads To The Brain