The Wide Window Of Relapse In Breast Cancer
In contrast with other solid tumours in which metastatic recurrence can occur within a few weeks or a few years following diagnosis, breast cancer is characterised by a wide window of relapse, spanning months to decades after surgery. The basis of this peculiar pattern of recurrence is still elusive, but is likely to be linked to the aforementioned molecular differences underlying each subgroup, with basal-like and HER2-enriched patients experiencing early relapses , as opposed to patients with luminal cancers characterised by a more favourable prognosis.,, Nonetheless, patients with luminal B tumours tend to have shorter survival times than luminal A patients. In addition to the contribution of the molecular subtype of the primary tumour, the risk and timing of recurrence is also influenced by other tumour-related factors that constitute the pillars of the TNM classification system: tumour size and spread , regional lymph node involvement and the presence of distant metastasis . Based on the premise that the chance of survival is intimately linked to the anatomic extent of the disease, the TNM staging system stratifies cancer patients at diagnosis into four stageswith patients with Stage I disease having a much better prognosis as opposed to patients with Stage IV diseasethus representing the gold standard tool for prognostication.
Where Does Breast Cancer Spread To
Breast cancer cells seem to prefer to settle into:-
- long bones in the arms and legs
With an osteolytic metastasis, the cancer kind of eats away at the bone, creating holes.
With an osteoblastic bone metastasis, the bone mineral density actually increases, but this can cause the bones to fracture more easily. This requires a little more explanation. Breast cancer metastases tend to be lytic when they are untreated, and then they become densely sclerotic as they respond to treatment.
Even if no treatment is given yet, an osteoblastic metastasis from breast cancer generally indicates that the persons own body is trying to fight cancer with some success.
A CT scan may also be used to check for metastasis to the lungs or liver. A CT scan is essentially an X-ray linked to a computer. The breast cancer doctor injects a contrast dye agent into the bloodstream and this makes any cancer cells in the liver and chest easier to see.
Diagnosing Metastatic Breast Cancer
Getting a clear picture of where breast cancer has spread is essential for creating a personalized treatment plan. Your care team will likely use a combination of the following tests and tools to diagnose both localized and advanced breast cancer:
Ultrasound exam: With this imaging technique, sound waves create a picture of internal areas of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging : This procedure produces detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves.
Blood chemistry studies: A blood sample is taken to measure the amounts of certain substances that are released by your organs and tissues. A higher or lower amount of a particular substance may be a sign of disease.
Biopsy: A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues so a pathologist may view them through a microscope. Your original breast cancer diagnosis was likely confirmed with a biopsy.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Read Also: How To Prevent Metastatic Breast Cancer
Changing Views On Breast Cancer Metastasis
The axillary lymph nodes run from the breast tissue into the armpit. Early theories of breast-cancer metastasis held that cancer cells that had broken free from the main tumor would first travel through these lymph nodes on their way to other organs. That led doctors to believe that removing the axillary lymph nodes could reduce the risk of both cancer recurrence and metastases.
However, more-recent research has suggested that breast cancer may metastasize to other areas of the body through several different routes, explained Dr. Giuliano.
Also, modern treatment for early-stage breast cancer typically includes radiation therapywhich targets some of the same lymph nodesalong with breast-conserving surgery, Dr. Giuliano added.
Most patients additionally receive some sort of systemic treatment, such as hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and, more recently, targeted therapy, all of which can kill cancer cells throughout the body.
How Does Spreading Happen
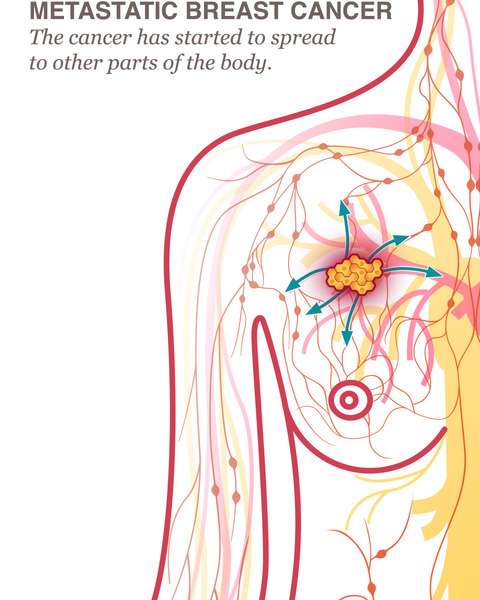
There are several ways cancer can spread in the body.
- Direct invasion happens when the tumor has spread to a nearby organ in the body. The cancer cells take root and begin to grow in this new area.
- Lymphangitic spread occurs when cancer travels through the lymphatic system. Breast cancer often involves the nearby lymph nodes, so the cancer can enter the lymph circulatory system and take hold in different parts of the body.
- Hematogenous spread moves in much the same way as lymphangitic spread but through the blood vessels. The cancer cells travel through the body and take root in remote areas and organs.
When cancer starts in the breast tissue, it may often spread to the lymph nodes before affecting other parts of the body. Breast cancer most commonly spreads to the:
The type of test you end up having will depend on your medical history and symptoms. For example, if you or your doctor suspects the cancer may have spread to your abdomen, you may have an ultrasound.
CT and MRI scans can help your doctor visualize various parts of the body all at once. A PET scan can be helpful if your doctor thinks the cancer may have spread but isnt sure where.
All of these tests are relatively noninvasive, and they shouldnt require a hospital stay. You may be given special instructions before your test.
If you have a CT scan, for instance, you may need to drink an oral contrast agent to help outline different features inside your body.
Don’t Miss: Does Breast Cancer Ever Hurt
The Extrinsic Effect Of Targeted Therapy
Fig. 4: The effects of cell-extrinsic and cell-intrinsic determinants in dictating breast cancer outcomes.
Part I The journey of a breast cancer patient from the development of undetectable disease and its clinical discovery , through its surgical removal and adjuvant ET , to metastatic relapse and death . The presence of tumour lesions across the body is indicated by starsthe smaller referring to the clinically undetectable ones , the bigger ones to the clinically detectable ones . Part II The development of an HR+ breast tumour lesion in the breast , comprising a mixture of ER+/PR+ and ER/PR cells . DTC escape from the primary site can occur early and/or late during tumorigenesis , although the HR phenotype of DTCs at these stages is often unclear. Bones, lungs and liver are represented as common secondary sites for breast cancer metastases, albeit the sequential patterns of DTC spread among these organs are still elusive . Targeted treatment for HR+ breast cancer patients relies on adjuvant ET. Several mechanisms of ET resistance cytostasis, ESR1 mutations and HR function regulationcontribute to DTC outgrowth. DTC disseminated tumour cell, ER oestrogen receptor, ET endocrine therapy, HR hormone receptor, PR progesterone receptor. Figure created with BioRender.com.
Newly Diagnosed Or Worried About A Symptom
In the days or weeks after a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer, you may feel distressed and find it hard to think clearly.
You can read our information for people newly diagnosed with secondary breast cancer, including where to find support.
If you havent been diagnosed but are worried about a symptom, find out more about the signs and symptoms of secondary breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Does Breast Cancer Work
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer In The Lung
Secondary breast cancer in the lung happens when breast cancer cells spread to the lung. It can also be known as lung metastases or secondaries in the lung.
Secondary breast cancer in the lung is not the same as cancer that started in the lung.
Usually secondary breast cancer occurs months or years after primary breast cancer. But sometimes its found at the same time as the primary breast cancer, or before the primary breast cancer has been diagnosed. In this situation, the breast cancer has already spread to the other parts of the body such as the lung. This is referred to as de novo metastatic breast cancer, meaning the breast cancer is metastatic from the start.
Support For Living With Secondary Breast Cancer In The Lung
Everyones experience of being diagnosed with secondary breast cancer is different, and people cope in their own way.
For many people, uncertainty can be the hardest part of living with secondary breast cancer.
You may find it helpful to talk to someone else whos had a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer.
- Chat to other people living with secondary breast cancer on our online Forum
- Meet other women with a secondary diagnosis and get information and support at a Living with Secondary Breast Cancer meet-up
- Live Chat is a weekly private chat room where you can talk about whatevers on your mind
You can also call Breast Cancer Nows Helpline free on 0808 800 6000.
Don’t Miss: What Does An Ultrasound Show For Breast Cancer
The Tnm Staging System
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M.
The T category describes the original tumor:
-
HER2 status: are the cancer cells making too much of the HER2 protein?
- Advertisement
Oncotype DX score, if the cancer is estrogen-receptor-positive, HER2-negative, and there is no cancer in the lymph nodes
Adding information about tumor grade, hormone-receptor status, HER2 status, and possibly Oncotype DX test results has made determining the stage of a breast cancer more complex, but also more accurate.
In general, according to experts, the new staging system classifies triple-negative breast cancer at a higher stage and classifies most hormone receptor-positive breast cancer at a lower stage.
You also may see or hear certain words used to describe the stage of the breast cancer:
-
Distant: The cancer is found in other parts of the body as well.
The updated AJCC breast cancer staging guidelines have made determining the stage of a cancer a more complicated but accurate process. So, the characteristics of each stage below are somewhat generalized.
How Does Distant Recurrence Occur
Many patients find it hard to understand how they can be apparently cancer free one day and be diagnosed with recurrent cancer the next. If surgery got all of the cancer out and chemotherapy and radiation were supposed to have mopped up the rest, how can recurrence even happen?
In most cases, even the smallest breast cancer detected has been growing for some time before it was caught. During this period of growth, the cancer cells multiplied and divided over and over again, and some cancer cells may splinter off from the main tumour and escaped into the surrounding blood and lymphatic vessels. Cells that spread to lymph nodes can certainly be trapped in those lymph nodes and removed at the time of surgery, but cells can also go into the circulatory system. Even early-stage cancers that originally had no lymph node involvement can recur and develop metastatic disease.
While its less common, cancer cells can bypass lymphatics and lymph nodes and travel via surrounding blood vessels. Cancer cells can continue to circulate and go anywhere the blood vessels will take them, or they can home in on other organs in the body, where they take up residence and continue to grow and divide in that one particular spot.
If and when cancer comes back, the cancer cells that escaped the breast are to blame. Obviously if your recurrence is ten years after your diagnosis, we assume that the cells have been dormant all that time and missed the treatments aimed at dividing cells.
Don’t Miss: What Does Early Signs Of Breast Cancer Look Like
Limited Arm And Shoulder Movement
You might also have limited movement in your arm and shoulder after surgery. This is more common after ALND than SLNB. Your doctor may advise exercises to help keep you from having long-lasting problems .
Some women notice a rope-like structure that begins under the arm and can extend down toward the elbow. This is sometimes called axillary web syndrome or lymphatic cording. It is more common after ALND than SLNB. Symptoms may not appear for weeks or even months after surgery. It can cause pain and limit movement of the arm and shoulder. This often goes away without treatment, although some women may find physical therapy helpful.
A Little Bit About The Internal Mammary Lymph Nodes

The internal mammary nodes are located behind the ribs. Ribs are made of bone, but in the front, they turn into cartilage just before they join the sternum.
So, each rib attaches to the sternum with cartilage and each of these cartilage bars is around 5 cm long. Thus, it can be very difficult to remove an internal mammary node. There is an internal mammary artery and vein along with the lymph ducts and other veins.
If you need to remove an internal mammary node, the cartilage in front needs to be cut out. Cartilage, unfortunately, does not grow back or heal and this will leave a gap which makes the rib essentially useless.
So, it is a judgement call by the surgeon as to whether or not one should attempt a surgical approach to remove internal mammary nodes with positive metastasis. This is because surgical removal is just too damaging to the function of the chest and ribs.
However, electron beam radiotherapy is an effective treatment for internal mammary nodes. The electrons penetrate to about the correct depth to reach the internal mammary nodes.
Treatment of Stage IIIa Breast Cancer
The treatment for women with stage IIIa breast cancers tends to be a modified radical mastectomy and locoregional radiotherapy.
Often, chemotherapy is given as adjuvant therapy, but in some cases , pre-operative chemotherapy is also recommended. Breast conservation is generally not a good option with stage IIIa breast cancers.
Also Check: Can I Get Breast Cancer At 19
Is Tumour Dormancy The Sole Explanation For Recurrence
In pondering the mechanisms of metastatic relapse among breast cancer patients, one obvious question is whether early recurrence is simply the consequence of direct metastatic outgrowth, whereas late relapses reflect a period of tumour dormancy. To address this query, it is imperative to consider how long it takes for a single cancer cell to grow into a clinically detectable metastasis. Pioneering measurements of breast tumour volume doubling time carried out by radiographic analysis on more than 800 women concluded that it takes ~12 years on average for a single cell with a 10-µm diameter to reach a clinically detectable mass of 1cm,, and that metastases can have a TVDT up to twofold higher than their matched primary tumours. However, these initial analyses focused on a small number of samples, without taking into account the vast heterogeneity among breast tumours or the effect that adjuvant therapies might have on their growth rate, as the subjects in this study were untreated.
Fig. 3: The puzzling timing of metastatic relapse in breast cancer patients.
Investigations For Stages Of Breast Cancer
The following procedures may be necessary to check for metastasis:-
So, after a breast cancer diagnosis, while in general, the outlook is favorable , it should really be considered a chronic condition.
But the progression is not going to be the same for everyone, even for patients with similar stages of breast cancer presentation. It is SO important to remember that each case is individual. Indeed breast cancer has been known to return even 20 years after a mastectomy, whilst in others, the progression and systemic development of the disease may be rapid.
Are you considering having NO treatment?
Anxiety, fear, panic, anger and sadness are all common emotions following a breast cancer diagnosis. If you are in the middle of a combination of these feelings, today is not a good day to make important decisions.
Here is my quick imagine a way this all gets better line of reasoning, to help you. Firstly, treatments are so effective nowadays and very well organized. Cancer research and treatments are improving all the time and the people who treat breast cancer are experienced experts.
Give the team some trust and time to explain things properly and accept the treatments. Do one step at a time, one day at a time, and you will be amazed at the results.
Add onto that the following self-help methods:-
Don’t Miss: How Long Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Investigations Are Necessary For Staging Breast Cancer
Breast cancer staging almost always involves a bone scan, as breast cancer is highly prone to metastasize to the bones.
During this test, medics inject a small amount of a radioactive substance into the bloodstream, where it eventually collects in the bones. A radiation scanner is then able to detect accumulations of tracer substance in the bones.
If breast cancer spreads beyond the breast, 25% of the time it goes into bones first.
What Is A Breast Cancer Recurrence
Breast cancer recurrence means that the cancer was diagnosed when limited to the breast and/or armpit lymph nodes, then treated, and at some time later has come back.
This can occur in several ways:
- Local and/or regional recurrence: the breast cancer that was previously treated returns within the breast, chest wall or regional lymph nodes.
- New primary breast cancer: an unrelated new breast cancer occurs in one or the other breast. This actually isnt a local recurrence at allits a new cancer in the breast . This typically occurs many years after the original cancer and in an entirely different area of the breast. Its pathology is often different lobular instead of ductal, for example. Though they are often counted as recurrences in the statistics for breast conservation, they should be treated as completely new cancers, much as with new cancers in the opposite breast.
- Distant or systemic recurrence or metastasis is much more serious than local recurrence and is synonymous with stage 4 disease. For breast cancer patients, the most common areas of spread are the bone, liver, lungs and brain
Breast cancer recurrence occurs if:
- Cells from the original breast cancer diagnosis break away and hide nearby in the breast or spread elsewhere in the body
- Treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and/or hormone therapy have not gotten rid of all these cancer cells from the body.
Read Also: Can You Die From Breast Cancer Surgery