Metastatic Breast Cancer Up
We performed gene expression analysis on publicly available microarray data of lymph node samples from breast cancer patients. Human lymph nodes that contained metastasized breast cancer cells demonstrated an up-regulation of major ECM proteins, such as collagen, fibronectin and several types of integrins as shown in .
Figure 4
Gene expression changes in genes driving the interaction between the ECM and ECM receptors in human lymph nodes containing metastatic breast cancer cells.
Microarray gene expression data were obtained from human lymph nodes affected by infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma cells as compared to unaffected lymph nodes. Total RNA was isolated and prepared for hybridization to human Affymetrix Gene Chip arrays . The heat map and corresponding statistical analysis was generated using the Gene-e matrix visualization and analysis platform . FDR < 0.05 was considered significant.
Western Blot And Luciferase Reporter Assay
Protein samples were harvested by using 2% SDS in PBS with protease inhibitor cocktail and NaF , NaVO4 . SDS gel electrophoresis, immunoblot and a LI-COR Odyssey Infrared Imaging System were employed for detecting the target protein as previously described . The Image Studio Lite software was used for quantification.
The Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed as previously described . Briefly, MDA-MB-231cells or MCF10A cells were seeded into a 24-well plate at the density of 0.1×106/well. 24 h later the cells will reach 80% confluence. Then 0.5 g p3TP-lux and 0.025 g renilla plasmids were transfected into the cells using Fugene HD Transfection Reagent. The cells were starved before 5 ng/ml TGF- was added. The relative luciferase activity was defined as firefly luciferase activity normalized by renilla luciferase activity. The final results were normalized by the relative luciferase activity of the control vector pGL4.10.
Dont Take Your Meds As Prescribed
You may shrug off pain medication because you heard its addictive or it makes you constipated, nauseous, or woozy. But skimping on your medicine isnt smart.
Pain can sometimes interfere with your sleep, appetite, and ability to get around, Whiteson says. And that can make it harder for your body to heal. Ultimately, the goal is to get off medication, but not before youre ready.
You May Like: What Does Stage 3 Breast Cancer Mean
Stiffer Collagen Matrices Inhibit Collective Invasion
Fig. 4: Collagen network stiffening reduces collective invasion but promotes single cell dissemination.
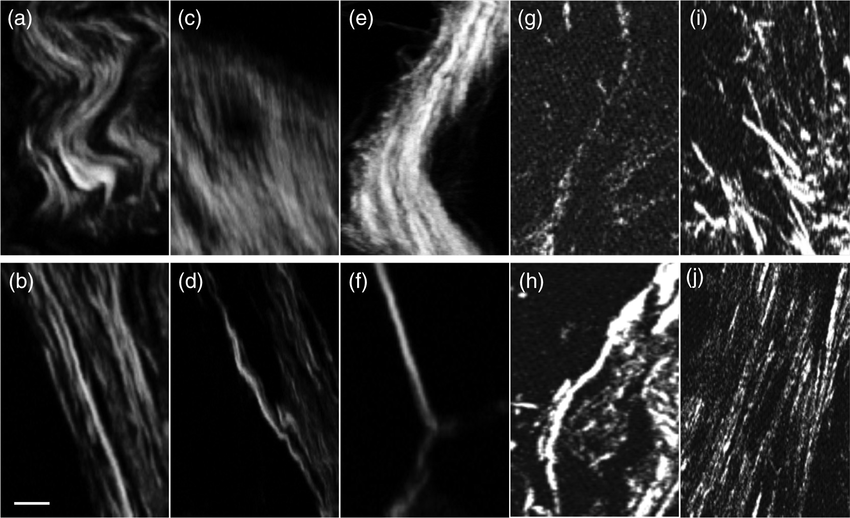
A IDC or ILC MDO cells were seeded in collagen matrices polymerized at 37°C or pre-polymerized at 26°C, and network stiffening was induced using AGE crosslinkers . Scale bar denotes 100µm. B, C Quantification of the invading strands of the IDC PyMT MDO . B Quantification of the length of invading strands of the IDC PyMT MDO . C Quantification of length of invasion of the ILC MDO as defined by major axis of ellipse. Invasive lengths in B and C were normalized to the 37°C control condition . Invasive strand length was normalized to the 37°C control conditions . D Confocal images were obtained from IDC MDO model in Collagen matrices, polymerized at 37°C or pre-polymerized at 26°C and stiffened using AGE crosslinkers. Organoids were stained for F-actin and Collagen . E Collagen alignment in was quantified in the region 050µm from the invasive leader cells after 3 days. Collagen was considered aligned at a 0.2 cut-off . Statistical significance was assessed by the MannWhitney test. Error bars show standard error of the mean. ***p< 0.005. All experiments are biological replicates and were replicated at least three times.
Collagen Xiii Expression Is Increased During Breast Cancer Development

To determine whether collagen XIII expression is induced during breast cancer development, we analyzed collagen XIII protein levels in a panel of non-malignant and malignant mammary epithelial cells. Triple negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, BT549, and T42 expressed higher levels of collagen XIII protein than luminal type breast cancer cell lines and non-malignant mammary epithelial cell lines . By analyzing TCGA and Finak datasets , we found that collagen XIII mRNA levels were significantly increased in human breast cancer tissue compared to normal mammary gland tissue . Collagen XIII expression in ER negative breast cancer was much higher than the expression in ER positive breast cancer . Consistence with cancer cell line data, we also found that triple negative breast cancer tissue had higher level of collagen XIII expression compared with other subtypes .
Fig. 1
Also Check: How Long Can You Live Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Cell Lines And Culture Conditions
MDA-MB-231 were maintained in DMEM/F12 with 10% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep. BT549 cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 with 10% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep. MCF-10A cells were kind gifts from Michael W. Kilgore, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY. MCF10A cells were cultured as previously described . Hs-578 T cells were kept as previously described . S1 and T42 cells are kind gifts from Dr. Mina J Bissell, and they were cultured as previously described . All the cells were tested for mycoplasma contamination every two months.
Could Dietary Supplements Boost Breast Cancer Risk
Some antioxidant supplements may offset the anticancer effects of chemotherapy.
Certain dietary supplements may increase breast cancer recurrence risk and hasten death, according to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. Multivitamins, however, appear to be safe.
While the link between supplement intake and breast cancer risk remains tenuous, some previous research has found that certain supplements may reduce the effectiveness of chemotherapy treatments. Antioxidants in particular break down the cancer-killing free radicals that chemotherapy produces, according to the American Institute for Cancer Research .
The studys researchers recruited 1,134 people receiving chemotherapy for breast cancer who had a high risk of recurrence and followed them for 15 years or until they died of the disease. The participants completed a questionnaire about their supplement intake twice: once upon enrollment in the study and again six months after the conclusion of treatment. In total, 18% reported taking an antioxidant during treatment and 44% reported taking at least one multivitamin during treatment.
Lead study author Christine B. Ambrosone, PhD, the chair of the Department of Cancer Prevention and Control at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, offered a possible explanation for these results. When you just pluck out specific vitamins and minerals from foods, you are losing all the effects that are probably there when using these nutrients from food, she said.
Also Check: Treatment For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
How To Take Collagen Supplements Safely
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended dosing on your collagen supplement.
Oral collagen doses ranging from 2.5 grams to 10 grams per day for up to 24 weeks were found to be generally safe with no adverse effects according to a January 2019 review in the Journal of Drugs and Dermatology.
If you’re considering adding a collagen supplement to your routine, the safest choice is to check with your doctor first. This is especially true if you have any current medical conditions, take medications or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Can Too Much Collagen Be Harmful?
Because there’s no Tolerable Upper Intake Level for collagen established by the Institute of Medicine, it’s impossible to say how much collagen you could take before experiencing harmful effects.
Most research has found no adverse effects when taking between 2.5 to 10 grams of collagen daily.
Is It Safe To Take Collagen Supplements
The answer is yes. The collagen in collagen products is safe for use in the body. However, it is important to note that collagen is not a good source of vitamin D. , and the collagen that is in your skin is also not good for you. It is best to avoid collagen-containing products if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Recommended Reading: What Stage 3 Cancer Means
Vitamins And Minerals In Supplements
Your doctor may recommend certain vitamins and supplements to help you stay healthy after treatment.
Calcium.Chemotherapy can weaken your bones. A calcium supplement with vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium, may protect your bones from changes due to treatment.
Multivitamin. A regular multivitamin may help you get essential vitamins and minerals to improve your overall health.
Probiotics. Probiotics help boost immunity, says Tara Scott, MD, a womens health specialist in Akron, OH. This may help you stay healthy after your treatment. Probiotics have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help protect against cancer. But there isnt enough research yet to know for sure.
Vitamin D. Experts say theres a link between low levels of vitamin D and breast cancer. Theres no evidence a vitamin D supplement will lower your risk of recurrence, but your doctor may recommend it for your overall health.
Continued
Integrin Signaling Is A Key Mediator Of Chemoresistance In Tnbcs
To elucidate the underlying mechanisms of chemoresistance in TNBCs, we modelled the clinical acquired resistance by using xenografts of the well-established TNBC cell line, MDA-MB-231,. Tumor-bearing mice were continuously treated with either vehicle or doxorubicin, and the fast-growing vehicle-treated mice were sacrificed, and tumors were denoted as vehicle. When tumors from the doxorubicin-treated group exhibited initial response to therapy and shrunk, tumors from some of the mice were collected and denoted as sensitive. The rest of the mice were kept under doxorubicin treatment until their tumors exhibited re-growth at rates comparable to vehicle-treated tumors, and those tumors were classified as resistant . The average growth curves and the Waterfall plot showing tumor volume fold change over time for vehicle-treated, doxorubicin-sensitive and -resistant tumors are depicted in Fig. , respectively.
Fig. 1: Integrin signaling is a key mediator of chemoresistance in TNBCs.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer With Positive Lymph Nodes
What Are The Side Effects Of Taking Collagen
The side effect of collagen is that it can cause skin problems. It can also cause a condition called hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigeonemia is a skin condition that can be caused by too much collagen in the skin. , which is the most common type of hyperprolactinemia. This condition is caused when the bodys natural production of the hormone prolactin is too low. The body cant produce enough prolaxin to keep the blood vessels in your skin open. When this happens, the collagen can build up and cause the condition. If you have hyperplasia, you may also have a problem with your blood vessel walls. In addition, collagen may cause your hair to grow too fast. You may have to have your scalp trimmed to remove excess hair.
Estrogens And Breast Health
The hormone that is fundamental to the female of the species is actually a family of three: estradiol, the most active form of estrogen estrone, the inactive storage form of estrogen and estriol, the weaker of the estrogens.
Estrogen has been labeled the angel of life, because it makes cells grow, developing the uterus, breasts, periods, pregnancy and the egg within the ovaryand the angel of death, because in excess it becomes toxic to the body. As they say, too much of a good thing can be dangerous, and too much of an estrogen that causes cells to multiply out of control is a recipe for breast cancer. Determining symptoms of estrogen dominance is a smart move since an imbalance of high estrogen to low progesterone that goes undetected for too long is not a risk worth taking.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Get A Nose Job
Collagen Side Effects Can Be Intense So Why Do People Take It
Collagen is a protein our body produces up until a certain point that creates firm, supple, and tight skin, and it almost seems as though using it would be the equivalent of finding the fountain of youth.
This new staple ingredient seems almost too good to be true. So, we spoke with nutritionists and medical professionals about the health implications of taking or applying collagen to our bodies.
Read on as we go over the potential collagen side effects that can happen the next time you try it. However, some side effects can be harmful to your body, so be sure to consult your doctor before adding any sort of supplements to your day-to-day life.
RELATED: 20 Best Collagen Peptides To Nourish Your Skin And Body
It Can Cause Allergic Reactions
“The riskiest side effects of any treatment are usually allergic reactions,” warns Dr. Malloy.
“Collagen supplements or skin products can produce an allergic reaction, which could, in rare cases, be life-threatening. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include itching or tingling in the mouth or area of skin where collagen is applied, swelling of tongue or skin, wheezing, abdominal pain, nausea, and/or vomiting. If you experience any of these symptoms you should stop taking/using collagen immediately and seek medical attention.”
Read Also: Carcinoma Left Breast
Hollings Researcher Receives Award To Study Collagen Regulation In Breast Cancer Health Disparities
An MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researcher received a $3 million grant from the National Cancer Institute to study how patterns of collagens can serve as biomarkers of breast cancer risk and potentially reveal clues to what might be driving health disparities.
Peggi Angel, Ph.D., is applying innovative proteomic profiling techniques to decipher the biological foundations of lethal breast cancers that impact African American women more than any other race or ethnicity. Alarmingly, African American women are more than twice as likely as white women of European descent to be diagnosed with an aggressive form of breast cancer characterized by triple negative tumor subtypes that are more likely to metastasize, seeding tumor growth in other areas of their bodies and complicating the treatments they receive.
Angel believes that collagen, one of the most abundant types of protein classes in the human body, might play a significant role in driving these disparities in breast cancer severity. Problems with collagen processing are a primary feature of triple negative breast cancer tumors, and these issues appear to be particularly exacerbated in breast tissues of African American women as compared to Caucasians.
Hydroxyproline modification of collagen is critical to tissue stability. The collagen matrix that forms the structural basis of skin, bones and other organs is a highly dynamic environment that is constantly being reorganized and renewed, she explained.
Regular Articletumorigenesis And Neoplastic Progressiontype Iii Collagen Directs Stromal Organization And Limits Metastasis In A Murine Model Of Breast Cancer
- Previous article in issue
-
Supported by National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases grant , the Mari Lowe Center for Comparative Oncology at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, a Jack Miller-Ebrahimi Foundation gift , and NIH grants , , and , and .
-
Disclosures: None declared.
Recommended Reading: Lymph Node Metastasis Breast Cancer
Physiological And Physicochemical Properties Of Collagen
Collagen is a type of right-handed helix glycoprotein that contains three homologous or nonhomologous left-handed helix chains. These chain amino acid sequences are characterized by glycineXY repeats with or without interruptions, with X and Y most likely being proline or hydroxyproline, and the hydroxyproline content of collagen contributes to its thermal stability .
Collagen is released into the extracellular matrix to form a fibril supramolecular assembly that may start in Golgi-to-membrane carriers after procollagen excision or be localized at the plasma membrane of fibroblasts. The stability of collagen assembly is influenced by intramolecular and intermolecular linkages, particularly covalent linkages, chiefly including lysyl oxidase crosslinks , glycosylation crosslinks , and transglutaminase crosslinks , which vary across collagen types.
Different collagens in the ECM are finally degraded by various matrix metalloproteinases belonging to the zinc-dependent endopeptidase family, by proline oxidase, or by sheddases that release the soluble ectodomain of membrane collagens .
Scaffold Molding And Cell Seeding
Eight hundred microgram of collagen/well of a Costar 96 plate was used to mold scaffolds. Collagen samples were lyophilized after collagen deposition on the plates. Samples were frozen at 20°C and then lyophilization was achieved using a Scanvac Coolsafe 55-9 freeze drier . After, scaffold were crosslinked using 1-ethyl- carbodiimide hydrochloride in 80% ethanol at 1% w/v for 90 min. Cross-linked scaffolds were rinsed in deionized water three times and left in 1% glycine overnight, at room temperature, to quench the reaction. Finally, constructs were lyophilized again to get all the residual liquid out and preserve their cylindrical shape.
Read Also: Cancer Stages 3
The Relationship Among Exosomes Micrornas And Collagen In Cancer
Recent studies have highlighted the relationship among exosomes, microRNAs and collagen in cancer .
Exosomes are membrane-enclosed structures that facilitate communication between cancer cells and the ECM to influence cancer cell survival, growth, and metastasis and the immune system . Cancer-derived exosomes induce the formation of CAFs in the collagen matrix to promote EMT and increase the secretion of MMP-14 to regulate collagen . In addition, collagen enhances exosome secretion . Collagen and exosomes form a mutually beneficial feedback loop to promote cancer progression.
The Collagen And Cancer Connection
One of today’s hottest trends in the health and wellness industry is collagen. Many people, especially women are on board to add this promising supplement to their daily routine. Adding it to their coffees, smoothies and even baking with it has become the popular thing to do nowadays. Collagen, also known as the fountain of youth, for its anti-aging and therapeutic benefits has very quickly gained much attention lately especially among those in the health movement. Collagen is the major insoluble fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix and in connective tissue. In fact, it is the single most abundant protein in the animal kingdom. It provides structural support in tissues and it can affect the development and biochemical functions of cells.
The industry circulates many “Collagen Benefits” claims which include, skin health, gut health, joint pain relief, bone loss prevention, muscle growth, stimulates hair and nail growth, weight loss, etc. These claims create a buzz that many swear by while others believe it to be just another trend. There are at least 16 types of collagen, but 8090 percent of the collagen in the body consists of types I, II, and III. Consuming collagen may have a variety of health benefits but is it safe for cancer patients?
Recommended Reading: Stage 1 Breast Cancer Survival Rate