Things Doctors Wish You Knew About Metastatic Breast Cancer
For starters, dont read about survival rates on the internet.
Breast and cancer are never two words you want to hear together, but discovering you have metastatic, or stage IV, breast cancer can make a bad situation feel impossibly worse. A lot of this fear stems from some common misunderstanding about what metastatic breast cancer is, how it spreads, what the prognosis is, and available treatments.
The word metastatic simply means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the original location of the tumor. The cancer originates in the breast, but the cells can travel to any other part of your body, leading to tumors in your lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones, brain, or other places. Nearly 30 percent of women who are diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer will ultimately develop metastatic disease, according to The National Breast Cancer Foundation.
Each year about 255,000 people are diagnosed with stage IV breast cancer. While the majority are women, men can get the disease too. Approximately 41,000 people die of breast cancer each year and metastatic breast cancer is responsible in the majority of the cases, according to NBCF. The five-year survival rate is about 25 percent for women and 20 percent for men.
1. Metastatic breast cancer is not a death sentence
2. Metastatic breast cancer isnt necessarily like other metastatic cancers
3. Metastatic breast cancer cant turn into another cancer
4. A lot of factors go into cancer survival rates
Which Type Of Breast Cancer Is Most Likely To Recur
Among patients who were recurrence-free when they stopped endocrine therapy after five years, the highest risk of recurrence was for those with originally large tumors and cancer that had spread to four or more lymph nodes. These women had a 40 percent risk of a distant cancer recurrence over the next 15 years.
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Advanced breast cancer refers to cancer that has spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body. This process of spreading from the original location to a new location is known as metastasis.
The most common places of breast cancer spread include the bones, liver, lung, and brain. However, breast cancer may also spread to other organs.
The majority of women who are diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer have been diagnosed with an earlier stage of breast cancer before. In this instance, the original cancer in the breast is called the primary cancer. However, for some women, a diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer may be their first diagnosis of cancer .
Don’t Miss: Does Breast Cancer Show Up In Blood Tests
It’s Ok To Scream Cry And Feel Fear Or Sorrow
This will pass. You are not going to die tomorrow, next week or next month. Life will get better, I promise.
In the meantime, a tip: To get you over that hump, ask for whatever chemical help you need. If you’re in pain, get it controlled. Having trouble sleeping? Ask for sleeping pills. Depressed? Get meds.
It’s not necessarily for forever, and there’s no reason to be stoic about anything. pajim
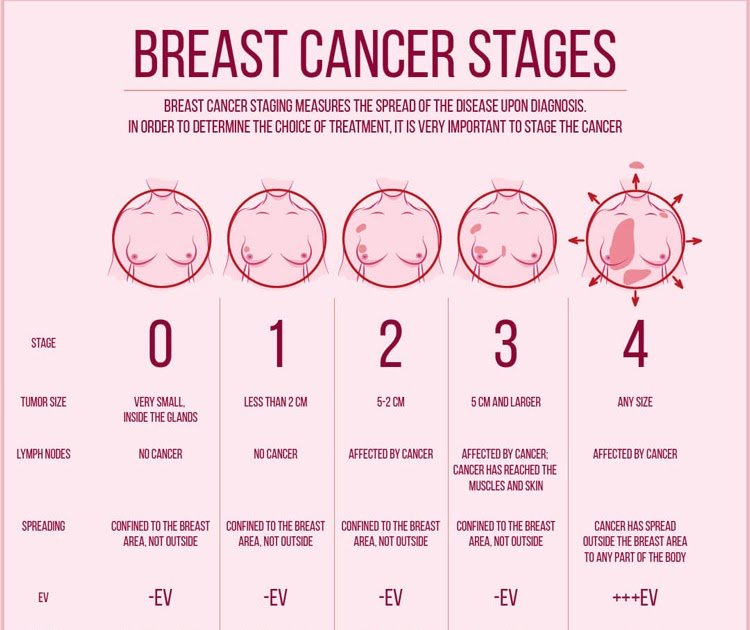
Diagnosis Of Stage 4 Breast Cancer

If you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you may have further tests to determine the extent that the cancer has spread throughout the body. This is called staging. It helps you and your doctors decide on the best treatment options for you.
In addition the numbered staging system, the TNM staging system is also commonly used for breast cancer staging.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Breast Cancer Has Metastasized
Diagnoses Are Way Up In Recent Years
“We’ve seen a huge increase in the number of DCIS cases diagnosed in the last 20 years,” Julia White, MD, director of breast radiation oncology at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, tells Health.
In the 1990s, only about 15,000 to 18,000 DCIS cases were diagnosed per year, she says now, that number has grown to more than 60,000, according to the American Cancer Society. “That’s because so many women are now getting mammograms, and the technology is so good, that we pick up very small lesions,” says Dr. White.
The good news? Women are getting treated earlier than ever, which means there are fewer chances for DCIS to break out of the milk duct and become invasive. The bad news? There’s no way to tell which lesions will become invasive, so some experts say there’s a real danger of overdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment.
How Long Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
The cycle for chemotherapy can vary from once a week to once every three weeks. Each treatment session is followed by a period of recovery. Typically, if you have early-stage breast cancer, you’ll undergo chemotherapy treatments for three to six months, but your doctor will adjust the timing to your circumstances.
Don’t Miss: What Was Your First Breast Cancer Symptom
Prognosis Following The Use Of Complementary And Alternative Medicine In Women Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
This analysis, by Saquib et al, was a secondary analysis of the Womens Healthy Eating and Living study. It looked at 2562 breast cancer survivors and surveyed for rejection of systemic treatment and use of CAM following surgical resection. All women had to be aged 18-70 and had operable Stage I-IIIa breast cancer. In this group, 177 women were identified who declined systemic treatment. 80% of this group used CAM. Compared to women that took chemotherapy, women that declined systemic treatment had a 90% greater risk of an additional breast cancer event, and the risk of death increased by 70%. CAM use had no effect on this finding. In addition, the lack of effect was consistent between high supplement users and low supplement users. The authors concluded that women that decline systemic treatment are at greater risk for subsequent recurrence and death due to breast cancer. The use of CAM had no measurable effect on the recurrence of breast cancer or on the risk of subsequent death.
Tumour Dormancy And Reawakening
Tumour dormancy is generally defined as a prolonged state of asymptomatic micrometastatic disease. In cancer of the breast or prostate, cancer cells can remain dormant for years and even decades before recurring as metastatic disease. During this latent period, patients are considered to be disease-free due to the lack of any symptoms of illness and because they have no detectable neoplasms by clinical imaging. Often described as one of the most wicked cancer cell misbehaviours, tumour dormancy shares many features in common with chronic diseases. Yet, its nature appears to be reversible, as myriad mechanisms have been shown to induce a switch to reawaken indolent DTCs . Furthermore, tumour dormancy is not exclusively a phenomenon of end-stage tumorigenesis, as it can apply to the presence of occult neoplasms until clinical diagnosis , and/or to MRD left behind after treatment . Attention, however, must be paid to the molecular underpinnings of these two scenarios as mechanistic differences between primary and metastatic dormancy might exist.
Don’t Miss: Is Stage Two Breast Cancer Curable
Breast Cancer Is A Heterogeneous Disease
Based on the presence or absence of the oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor , and the expression and amplification of the human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 , breast cancer can be divided into three clinical subtypes: hormone-receptor -positive , HER2-positive and triple-negative ., In the United States, 71% of breast cancers are HR+, 17% are HER2+ and 12% are TN. Following the discovery of five intrinsic molecular subgroups of the disease based on a 50-gene expression classifier luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, basal-like and normal-likeit became apparent that a large degree of unappreciated molecular heterogeneity exists across and within each subtype of breast cancer. While TN and HER2+ patients often present with basal-like and HER2-enriched cancers, respectively, HR+ women are usually diagnosed with luminal A or luminal B tumours. However, despite sharing some common traits, luminal A cancers are generally ER+, PR high and Ki67 low, resulting in low-grade, slow-proliferating neoplasms, whereas luminal B tumours are typically ER+, PR variable and Ki67 variable, translating into more aggressive cancers with a higher proliferative rate.
When Is Radiation Usually Used To Treat Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, radiation therapy may be used after a breast-conserving surgery, or lumpectomy, to mitigate the risk of cancer cells recurring in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, an oncologist may determine that radiation is necessary if the tumor was larger than 5 cm, if there was lymph node involvement, or if cancer was found outside of surgical margins.
You May Like: Does Red Wine Cause Breast Cancer
Additional Tools For Diagnosing Advanced Breast Cancer
The additional tools below are often used specifically for diagnosing advanced cancer:
Sentinel lymph node biopsy: This procedure removes sentinel lymph node cells during surgery for examination. When breast cancer spreads, it often heads first to the lymph nodes.
Chest X-ray: This detailed image of the chest may help doctors see whether cancer has spread to the bones.
Computed tomography scan: Also known as a CAT scan, this procedure takes detailed pictures of internal areas of the body using a computer linked to an X-ray machine. A dye may be used to help the organs show up more clearly in the images.
Bone scan: This procedure looks for bone metastasis, or cancer cells that have spread to the bone. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood, then detected with a scanner.
Positron emission tomography scan: A PET scan is a detailed imaging tool that uses a radioactive drug, known as a tracer, to search for cancer cells within your body.
Why Cancer Cells Tend To Spread To The Parts Of The Body They Do
Where a cancer starts is linked to where it will spread. Most cancer cells that break free from the primary tumor are carried in the blood or lymph system until they get trapped in the next downstream organ or set of lymph nodes. This explains why breast cancer often spreads to underarm lymph nodes, but rarely to lymph nodes in the belly. Likewise, there are many cancers that commonly spread to the lungs. This is because the heart pumps blood from the rest of the body through the lungs blood vessels before sending it elsewhere.
Recommended Reading: Can Cancer Spread To The Breast
Recognize Your Feelings And Concerns
Talking about fears and concerns is important, even when treatment is working well. Tell your health care team about emotional symptoms. People may live for years with metastatic cancer. Your doctor can help you have the best quality of life possible during this time. Hospitals and medical centers have many resources for you and your family.
How Does Cancer Spread Or Metastasize
The spread of cancer usually happens through one or more of the following steps:
- Cancer cells invade nearby healthy cells. When the healthy cell is taken over, it too can replicate more abnormal cells.
- Cancer cells penetrate into the circulatory or lymph system. Cancer cells travel through the walls of nearby lymph vessels or blood vessels.
- Migration through circulation. Cancer cells are carried by the lymph system and the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
- Cancer cells lodge in capillaries. Cancer cells stop moving as they are lodged in capillaries at a distant location and divide and migrate into the surrounding tissue.
- New small tumors grow. Cancer cells form small tumors at the new location
Don’t Miss: How Do Women Get Breast Cancer
Can You Live 20 Years With Breast Cancer
Long Haul for Breast Cancer Survivors: Disease Can Return After 20 Years. New research shows that long-term endocrine therapy can reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in the long term. But side effects keep some women from taking it. The researchers conducted a meta-analysis of 88 trials involving 62,923 women.
Keep Reaching Out To Friends And Loved Ones
even if they seem to be retreating from you. I found that the more I felt them retreating, the less I would reach out, thinking they just don’t want to deal with this. After some experience, I realize a lot of people just don’t know how to help or communicate. You will need your friends and family even if it is just to go shopping with you or to a movie. Don’t get caught in the cycle of retreating as they do or you will be very lonely. artistatheart
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Treatment For Advanced Breast Cancer
Treatment of metastatic breast cancer aims to control the growth and spread of the cancer, to relieve symptoms, reduce pain, and improve or maintain quality of life.
The treatment recommended by doctors will depend on which treatments are likely to control the breast cancer and what side effects the person can cope with. Treatment options may involve:
Why Does My Provider Need To Test The Metastatic Tumor
Your care team will test the metastases to figure out the biology of the tumor, which can help guide your treatment plan. Providers may test tumors for:
- Hormone receptor status: If the cancer is hormone receptor-positive, hormonal therapy may be your first treatment.
- HER2 status: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 is a protein that is overexpressed on some breast cancer cells. HER2-positive cancer responds to specific HER2-targeted therapies.
- PIK3CA gene mutation: If a tumor is hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative, your provider may test for this gene mutation. Specific targeted therapies can be used to treat tumors with this mutation.
- PD-L1 status: Tumors that are hormone receptive-negative and HER2-negative may be tested for PD-L1 status. If the PD-L1 test is positive, you may be recommended to receive a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Screened For Breast Cancer
Meeting The Challenges Of Metastatic Cancer
To understand your situation, you may want to get a second opinion. Many people find that it helps to get an opinion from another oncologist, and many doctors encourage it.
Your doctor can help you cope with cancer symptoms and treatment side effects. For example, if you have pain, your treatment might include surgery to remove a tumor in a painful area. Your doctor might also prescribe pain medication or anti-nausea medication.
What Is Cutaneousmetastasis

Cutaneous metastasis refers to the growth of cancer cells in the skin originating from internal cancer. In most cases, cutaneous metastasis develops after the initial diagnosis of the primary internal malignancy and late in the course of the disease. In very rare cases, skin metastasis may occur at the same time or before the primary cancer has been discovered and may be the prompt for the further thorough investigation.
Cutaneous metastasis may also occur from skin cancer, usually melanoma. The original or primary melanoma produces metastases or secondary growths in surrounding or distant skin sites and other tissues such as the lungs or brain.
Cutaneous metastases
You May Like: Do All Breast Cancer Patients Lose Their Hair
What Is Hospice Care
Hospice care is a type of palliative care, and like palliative care it is more of a philosophy than a place. Many people receive hospice care in their own home, though hospice facilities may be available as well. A typical hospice team includes a physician who specializes in end of life care, hospice nurses, social workers, and chaplains. Its care that seeks to maintain the comfort and dignity of a person and his or her family for as long as he or she lives, while no longer attempting to cure or slow the progress of a serious or terminal disease.
What Are The Chances Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
In women who have breast-conserving treatment, the chance of recurrence is about 3-15% in 10 years, depending on tumor characteristics and margins. Distant recurrence in those who had mastectomy is most influenced by axillary lymph node involvement. When axillary lymph nodes are not cancerous, the recurrence rate is 6% in 5 years. When axillary lymph nodes are cancerous, the recurrence rate is 23% in 5 years with mastectomy but no radiation.
Don’t Miss: Does Breast Hurt With Cancer
Where Breast Cancer Tends To Go
Breast cancer most often spreads to these organs:
Bones. Breast cancer travels to the bones through the bloodstream. The ribs, spine, pelvis, and long bones of the arms and legs are the most common bones that breast cancer reaches. Bone pain and tenderness are signs the cancer is in your bones. Breast cancer cells can also get into bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are made.
Liver. Cancer cells can get into the liver through the bloodstream because the liver filters the blood.
Lungs. The lungs are another common site for metastatic breast cancer to spread because your blood flows through them to pick up oxygen.
Brain. Any type of breast cancer can spread to the brain, but HER2-positive and triple-negative cancers are most likely to reach this organ. Signs of cancer in the brain include headaches, seizures, vision changes, and dizziness.
Rejecting Cancer Treatment: What Are The Consequences
There have been several studies of people who have refused scientific treatments for cancer. The results have not been good.
These do not cure cancer
One of the points Ive tried to emphasize through my contributions to Science-Based Medicine is that every treatment decision requires an evaluation of risks and benefits. No treatment is without some sort of risk. And a decision to decline treatment has its own risks. One of the challenges that I confront regularly as a pharmacist is helping patients understand a medications expected long-term benefits against the risks and side effects of treatment. This dialogue is most challenging with symptomless conditions like high blood pressure, where patients face the prospect of immediate side effects against the potential for long-term benefit. Ones willingness to accept side effects is influenced, in part, by and understanding of, and belief in, the overall goals of therapy. Side effects from blood-pressure medications can be unpleasant. But weighed against the reduced risk of catastrophic events like strokes, drug therapy may be more acceptable. Willingness to accept these tradeoffs varies dramatically by disease, and are strongly influenced by patient-specific factors. In general, the more serious the illness, the greater the willingness to accept the risks of treatment.
Read Also: Will I Need Chemo For Breast Cancer