Living With Breast Cancer
Being diagnosed with breast cancer can affect daily life in many ways, depending on what stage it’s at and the treatment you will have.
How people cope with the diagnosis and treatment varies from person to person. There are several forms of support available, if you need it.
Forms of support may include:
- family and friends, who can be a powerful support system
- communicating with other people in the same situation
- finding out as much as possible about your condition
- not trying to do too much or overexerting yourself
- making time for yourself
Find out more about living with breast cancer.
How Common Is Breast Cancer In Canada
Breast cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in women. Each year, more than 22,000 women develop breast cancer in Canada and more than 5,000 women die of the disease. Based on current rates, one in nine women in Canada is expected to develop breast cancer during her lifetime.
The risk of getting breast cancer goes up as women get older. The risk of developing breast cancer in the next 10 years is as follows:
- 13 out of 1,000 women in their 40s
- 23 out of 1,000 women in their 50s
- 29 out of 1,000 women in their 60s
- 31 out of 1,000 women in their 70s
Since 1999, the rate of new cases of breast cancer has stabilized, and death rates have steadily declined.
What Happens After A Sentinel Node Biopsy
If the lymph nodes do not contain cancer cells, you wont need to have any more nodes taken out.
If cancer cells are in the sentinel nodes, you have another operation to remove most or all of the lymph nodes under your arm. This is an axillary lymph node dissection or clearance. You generally have it about 2 weeks after you get the results.
Some people have radiotherapy to the armpit to destroy any remaining cancer cells instead of surgery.
Recommended Reading: How Likely Am I To Get Breast Cancer
You May Like: Breast Cancer Stage 1 Survival Rate
Cancers Of The Female Genital Tract
Cervical cancer tends to occur in midlife. Most often it is found in women younger than 50. It rarely occurs in women younger than 20. Most cervical cancers can be found early, or even prevented, with screening tests. Vaccines against HPV, the virus linked to most cervical cancers, can also help prevent it. The most common symptom of cervical cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Overall, ovarian cancer is much more common in older women than in women younger than 40. But some less common types of ovarian cancers, known as germ cell tumors, are more common in teens and young women than in older women. Early ovarian cancer usually does not cause symptoms, but some women might feel full quickly when eating or they might have abnormal bloating, belly pain, or urinary symptoms. Women who have any of these symptoms lasting more than a few weeks should see their doctor.
For more information, see Cervical Cancer and Ovarian Cancer.
How Old Do You Have To Be To Get Breast Cancer

A woman has a 12% absolute risk for developing breast cancer in her lifetime, but a womans personal cancer risk changes throughout her life. Breast cancer risk increases with age the two biggest factors for developing breast cancer are getting older and being a woman. Breast cancer doesnt just affect older women, however.
Recommended Reading: Lymph Nodes Cancer Stage 3
In Your 30s You Should Be Aware Of How Pregnancy Changes Your Breast Tissue
“With pregnancy and breastfeeding there are a number of changes in the breast,” Dr. Hunt points out, which is a change that might affect women in their 20s and 30s who are having children. “It’s important to understand these changes and work with your OB-GYN to sort through all of them.”
What to look for? Lumps might occur with the normal breast enlargement during pregnancy, but “we do have to be a little bit more concerned … and have it evaluated with ultrasound right away,” Dr. Hunt says. “That’s because the hormones of pregnancy may influence or increase the growth of breast cancer.”
And while mastitis during breastfeeding can cause normal redness and tenderness that can usually be addressed, “if the breast stays red, swollen and engorged, that can be the presentation of inflammatory breast cancer, which is a particularly aggressive form of cancer that we tend to see more in younger women.”
“That is not to say that every time someone has a red, swollen breast that it is inflammatory breast cancer,” she adds, “but if it does not respond appropriately to interventions, then you need to get it evaluated.”
In Your 50s You Should Optimize Your Health
Continue to build on your healthy habits . “In your 50s, you want to be sure that you’re doing everything in your body to keep cancerous changes from happening,” says Dr. Richardson. That includes:
- Consuming cruciferous vegetables. These contain sulforaphane, which are protective against breast cancer changes
- Avoiding processed foods and sugars. These can trigger insulin receptors which can drive the creation of cancers.
- Getting good sleep! Melatonin, which is created during sleep, is a cancer fighter.
- Avoiding stress.
Read Also: Stage 4 Triple Positive Breast Cancer
Premature Menopause And Loss Of Fertility
Premature menopause and loss of fertility are significant considerations in young women undergoing treatment for breast cancer. The risk of menopause with chemotherapy is dependent on age and the intensity of chemotherapy. The likelihood of menopause following chemotherapy increases with increasing age. A woman who has chemotherapy at age 30 years is unlikely to become menopausal with treatment at age 35 the risk is around 18%, and at age 40 years the risk is around 40%.
If future childbearing is planned, the option of using assisted reproduction techniques before chemotherapy and hormone therapy should be considered. Generally, this is more successful if the woman has a partner so that embryos can be frozen for future use following one or more cycles of in-vitro fertilisation.
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, which develop in different parts of the breast.
Breast cancer is often divided into either:
- non-invasive breast cancer found in the ducts of the breast which has not spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. Non-invasive breast cancer is usually found during a mammogram and rarely shows as a breast lump.
- invasive breast cancer where the cancer cells have spread through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
- invasive lobular breast cancer
- inflammatory breast cancer
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the blood or the axillary lymph nodes. These are small lymphatic glands that filter bacteria and cells from the mammary gland.
If this happens, it’s known as secondary, or metastatic, breast cancer.
You May Like: How Curable Is Breast Cancer
How Does Your Age Affect Treatment
Your doctor will help you choose the most effective breast cancer treatment based on the type, stage, and grade of your tumor. Treatments are generally the same for women of all ages, but a few exceptions exist.
Drugs called aromatase inhibitors arent recommended for women who havent yet gone through menopause. These drugs treat estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by blocking the enzyme aromatase. Aromatase converts the hormone androgen into estrogen. Without estrogen, the tumor cant grow. Women who havent gone through menopause still produce estrogen in their ovaries. This means that aromatase inhibitors will only work if you also take medicine to stop your ovaries from making estrogen.
If medically feasible, you may opt for a more conservative surgery, such as a lumpectomy. This removes the tumor but keeps the breast intact. Chemotherapy, radiation, or both are usually necessary after a lumpectomy. If you need to have a mastectomy, which removes the whole breast, you can ask your surgeon to preserve your nipple. If you plan to have plastic surgery afterward to reconstruct your breast, this can enable your plastic surgeon to create a more natural looking breast.
Risk Factors You Can Change
- Not being physically active. Women who are not physically active have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Being overweight or obese after menopause. Older women who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than those at a normal weight.
- Taking hormones. Some forms of hormone replacement therapy taken during menopause can raise risk for breast cancer when taken for more than five years. Certain oral contraceptives also have been found to raise breast cancer risk.
- Reproductive history. Having the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
- Drinking alcohol. Studies show that a womans risk for breast cancer increases with the more alcohol she drinks.
Research suggests that other factors such as smoking, being exposed to chemicals that can cause cancer, and changes in other hormones due to night shift working also may increase breast cancer risk.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Stage 3 And 4 Cancer
What’s The Best Way For Younger Women To Screen For Breast Cancer
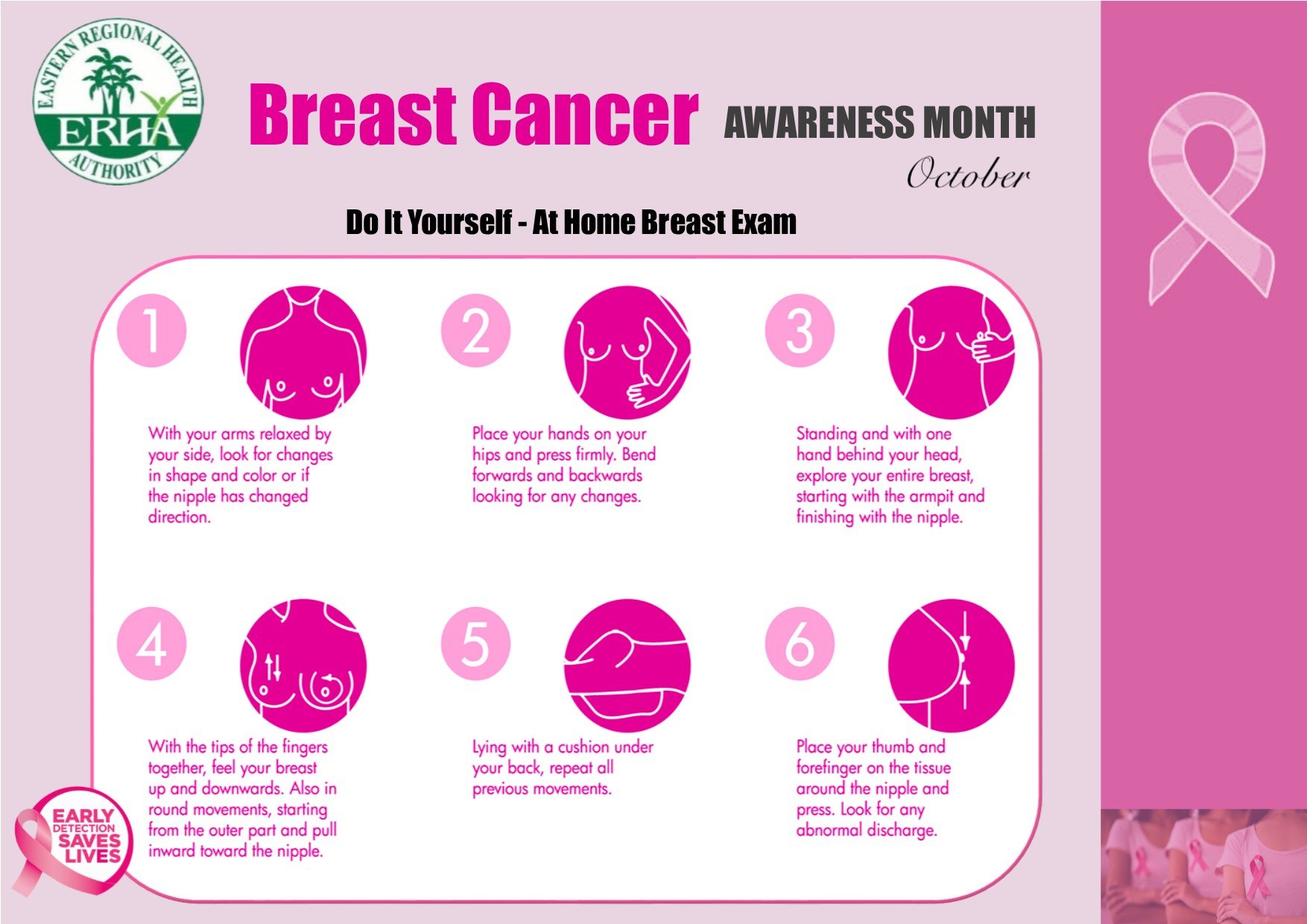
The American Cancer Society recommends that all women know how their breasts look and feel and report any changes to their doctor. The ACS states that research has not shown a clear benefit of performing regular breast self-exams. Talk with your doctor about the pros and cons of breast self-exam.
Regular breast exams done at least every 3 years by your doctor are recommended for women beginning at age 20. Expert groups donât all agree when women should start getting mammograms and you should discuss with your doctor whatâs right for you. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening every 2 years from ages 50 through 74 and also that the decision to start yearly screening mammograms before age 50 should be an individual one..
Talk to your doctor about when you should begin to have mammograms. For younger women, digital mammography may be an alternate to a standard mammogram. Digital mammography is better able to see abnormalities in dense breast tissue.
Are Women Under 40 At Risk For Breast Cancer
Younger women generally do not consider themselves to be at risk for breast cancer. However, breast cancer can strike at any age: 5% of breast cancer cases occur in women under 40 years of age. All women should be aware of their personal risk factors for breast cancer.
There are several factors that put a woman at higher risk for developing breast cancer, including:
- A personal history of breast cancer or a high risk lesion found by biopsy
- A family history of breast cancer, particularly at an early age
- A family history that is concerning for a genetic syndrome that may put them at a higher risk for breast cancer
- History of radiation therapy to the chest
- A known genetic mutation conferring a high risk for the development of breast cancer
- Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
Also Check: Breast Cancer Prognosis Stage 3
Brain And Spinal Cord Tumors
There are many types of brain and spinal cord tumors, and the treatment and outlook for each is different. In children, most brain tumors start in the lower parts of the brain, such as the cerebellum or brain stem . Adults are more likely to develop tumors in upper parts of the brain. Spinal cord tumors are less common than brain tumors in all age groups.
Brain tumors can cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, blurred or double vision, dizziness, seizures, trouble walking or handling objects, and other symptoms.
Soft Tissue And Bone Cancers
Sarcomas are cancers that start in connective tissues such as muscles, bones, or fat cells. There are 2 main types of sarcoma:
- Soft tissue sarcomas
- Bone sarcomas
Sarcomas can develop at any age, but some types occur most often in older teens and young adults.
Soft tissue sarcomas: These cancers can start in any part of the body, but they often develop in the arms or legs. Rhabdomyosarcoma, a cancer that starts in cells that normally develop into skeletal muscles, is most common in children younger than 10, but it can also develop in teens and young adults. Most other types of soft tissue sarcomas become more common as people age. Symptoms depend on where the sarcoma starts, and can include lumps , swelling, or bowel problems.
For more information, see Soft Tissue Sarcoma and Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Bone sarcomas: The 2 most common types of bone cancer,osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma, are most common in teens, but they can also develop in young adults. They often cause bone pain that gets worse at night or with activity. They can also cause swelling in the area around the bone.
Osteosarcoma usually starts near the ends of the leg or arm bones. The most common places for Ewing sarcoma to start are the pelvic bones, the bones of the chest wall , or in the middle of the leg bones.
For more information, see Osteosarcoma and Ewing Family of Tumors.
You May Like: Stage Three Breast Cancer Prognosis
In Your 20 And 30s You Should Adopt Healthy Habits Early
Taking care of your overall health is important to prevention of breast cancer. Dr. Richardson gives the following advice to help lower your risk factors:
- Lay down the foundation of exercising regularly.
- Keep your BMI down and a healthy body weight.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Keep red meat and dairy consumption to a minimum and try to maximize a plant-based diet.
- Dr. Richardson suggests “one cup of soy a day and ground flax seed it’s one of the only food sources of lignans, which are incredibly protective of the breast tissue. They act like plant-based estrogen and calm the breast tissue down and really soothe it. Also, nice, high vitamin D levels.”
What Causes Breast Cancer In Your 20s And 30s
Breast cancer happens when cells in the breast begin to grow and multiply abnormally. Changes in DNA can cause normal breast cells to become abnormal.
The exact reason why normal cells turn into cancerous cells is unclear, but researchers know that hormones, environmental factors, and genetics each play a role.
Roughly 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are linked to inherited gene mutations. The most well known are breast cancer gene 1 and breast cancer gene 2 .
If you have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, your doctor may suggest testing your blood for these specific mutations.
In some cases, breast cancer in your 20s and 30s has been found to differ biologically from the cancers found in older women.
For example, younger women are more likely to receive a diagnosis of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers than older women.
more likely in adolescent and young women than in older women who have a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer means that the cancer has advanced to stage 4. It has moved beyond the breast tissue into other areas of the body, such as the bones or the brain.
Survival rates are lower for cancer that has metastasized to other parts of the body.
According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for women with breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body is 28 percent for all ages.
However, some signs and symptoms of breast cancer may
- changes in the skin
Read Also: Estrogen Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer During Pregnancy
Very few pregnant women are diagnosed with breast cancer. But because more women are choosing to have children later in life, and because the risk of breast cancer increases as women age, there may be more cases in the future. Today about 1 out of 3,000 pregnant women is diagnosed with breast cancer.
Breast cancer presenting during pregnancy may be more difficult to diagnose than breast cancer in the young non pregnant woman due to the hormonal effects of pregnancy on breast tissue. Young women who present with breast cancer during pregnancy tend to have larger, more advanced cancer at diagnosis.
Treatment options for breast cancer that presents during pregnancy depend on the gestational stage at diagnosis. While many women will assume that the pregnancy must be terminated, this is not necessarily the case as breast cancer can be treated successfully during pregnancy. Surgery may be performed at any gestation. It is a commonly held misconception that general anaesthesia significantly increases the risk of spontaneous abortion. While there may be a very small increase in risk to the foetus, this is not of clinical significance. The surgical options of breast conserving surgery and mastectomy are the same as for any breast cancer, with the same considerations of tumour size and location, breast size, likely cosmetic outcome, and patient preference.
How Many People Survive Breast Cancer
- Almost nine in ten of women survive breast cancer for five years or more.
- Breast cancer survival is improving and has doubled in the past 40 years in the UK due to a combination of improvements in treatment and care, earlier detection through screening and a focus on targets, including faster diagnosis.
- An estimated 600,000 people are alive in the UK after a diagnosis of breast cancer. This is predicted to rise to 1.2 million in 2030.
For many the overwhelming emotional and physical effects of the disease can be long-lasting.
Every year around 11,500women and 85 men die from breast cancer in the UK thats nearly 1,000 deaths each month, 31 each day or one every 45 minutes.
Breast cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the UK.
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death in women under 50 in the UK.
Don’t Miss: Grade 3 Breast Cancer Prognosis