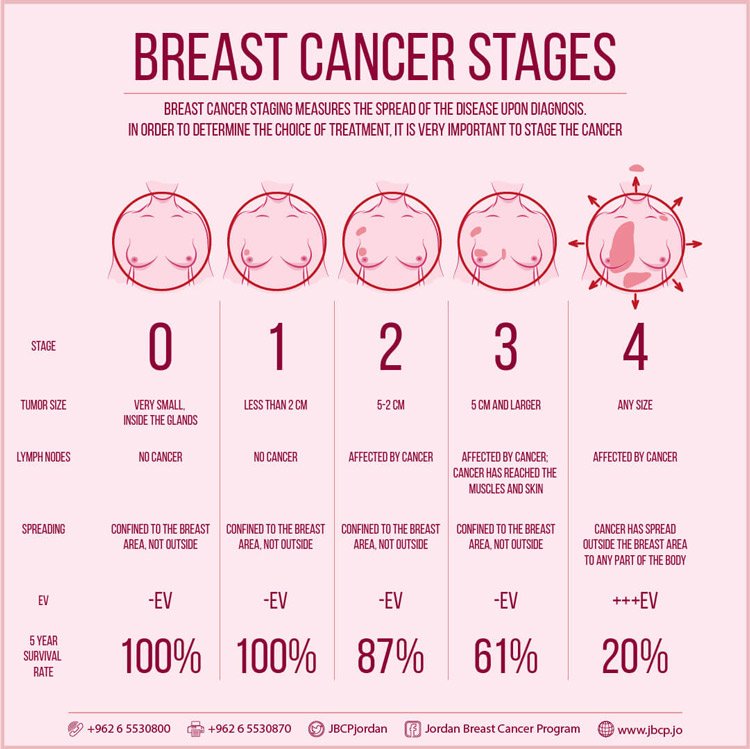
Survival Rates Of Stage 1 And Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to data from the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed, the better the outcome. The survival rates of people diagnosed with breast cancer have also improved over time due to earlier detection and improvements in treatment. Most people with early stage breast cancer can be treated successfully.
You may wish to discuss your prognosis and treatment options with your doctors. However, it is not possible to predict the exact course of your cancer and how long you will live. The length of survival can vary from person to person. Factors that influence this include:
- Response to treatment
- The type of breast cancer that you have
- The rate of tumour growth
- Other factors such as your age, medical history and overall health.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer .
- The type of breast cancer.
- Estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Human epidermal growth factor type 2 receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Whether the tumor tissue is triple negative .
- How fast the tumor is growing.
- How likely the tumor is to recur .
- A womans age, general health, and menopausal status .
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Read Also: How Can You Tell You Have Breast Cancer
When To Consider Joining A Clinical Trial
If youre newly diagnosed with early or locally advanced breast cancer, consider joining a clinical trial before starting treatment. For most people, treatment doesnt usually start right after diagnosis. So, theres time to look for a clinical trial that youre eligible for and fits your needs.
Once youve begun standard treatment for early or locally advanced breast cancer, it can be hard to join a clinical trial.
You May Like: Stage One Breast Cancer Metastasis
Don’t Miss: What To Expect During Radiation For Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 1 Cancer
Stage 1 cancer typically means the cancer is small and localized to one area, and that it has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Even if the cancer spreads or improves, it will still be referred to by the stage at which it was diagnosed. Cancers at the same stage are often treated similarly. For example, treatment for stage 1 cancer generally includes surgery.
Stage 1 cancer is determined in the five most common cancers in the following ways:
Timeline After Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Receiving a breast cancer diagnosis can create many feelings and emotions. Since some breast cancer diagnoses come with a bleak outlook, its common to want to start a treatment plan as soon as possible.
This article is designed to give you a comprehensive understanding of which factors play a role in your prognosis and what you should expect in the coming days, weeks and months following your diagnosis.
You May Like: What Is Stage 3 Cancer Mean
Don’t Miss: Can Airport Scanners Detect Breast Cancer
Statistics Dont Account For Late Recurrences
When comparing triple-negative breast cancer to positive tumors, its important to keep in mind late recurrences. Most statistics are presented as five-year survival rate, and in this setting, triple-negative breast cancer can look more ominous. But looking at longer periods of time, say 20 years following diagnosis, this may be different.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 4 Life Expectancy
Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Require Chemotherapy
In addition to surgery and radiation therapy, stage 1 breast cancer treatment may require chemotherapy, powerful drugs that attack all fast-growing cells in the body. In the past, almost all patients had chemotherapy. Today, the doctor may perform gene tests to help determine whether chemotherapy is likely to benefit you, or if its not necessary because your cancer isnt likely to recur after surgery and other treatment.
Chemotherapy may or may not be used along with other drugs such as hormone therapy, targeted therapy and/or immunotherapy. Your care team will determine which options may be most appropriate by examining your cancers specific characteristics. Patients typically take these drugs after surgery to kill the primary cancer.
You May Like: How Do They Do Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
Key Points To Remember
- Chemotherapy is sometimes used after surgery for early-stage breast cancer to help lower the chances that your breast cancer will come back.
- Some types of cancer have a very small chance of coming back. Women who have those types of cancer may not need chemo. There are gene tests that may show whether having chemo will help you reduce your chances that the cancer will return.
- Your age, type of cancer, tumor size, and hormone receptor status have an effect on how well chemo will work to keep your cancer from coming back.
- Different medicines used for chemo have different side effects. Your doctor can give you other medicines to help you deal with side effects like nausea and vomiting. Some women are bothered a lot by the side effects, but some aren’t.
- The drugs used for chemo can be very expensive. Insurance policies don’t always cover the whole cost. If you have no insurance, your doctor may be able to help you find drug companies or organizations that will help you pay for this treatment.
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow out of control in one or both breasts. These cells can invade nearby tissues and form a mass, called a malignant tumor. The cancer cells can spread to the lymph nodes and other parts of the body.
When is chemotherapy used to treat early-stage breast cancer?
The type of added treatment you have depends on the stage and classification of your breast cancer:
What are the risks of chemotherapy?
Can Receiving Less Chemotherapy Result Ultimately In Better Outcomes
Chemotherapy can shrink cancer and slow its growth, which is why it has been used to treat breast cancer in conjunction with surgery for so many years. But the side effects can be difficult.
In the short term, these side effects can include such problems as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss, which can sometimes last far beyond treatment. We know that, after a course of chemotherapy, a number of women, up to several years out, don’t regain their full vitality, Dr. Winer says.
But even more concerning are the long-term effects, which can include rare, but difficult, complications such as heart problems, neuropathy, and leukemia, which can ultimatelyand indirectlyaffect outcomes.
These potentially debilitating side effects are why personalizing chemotherapy treatment has become so important. If a patient can do just as well with fewer medical treatments, it’s almost always a better thing, says Dr. Winer. Less chemotherapy can mean fewer side effects, less anxiety, improved quality of life, and possibly even a longer life, he adds.
Also, when side effects are truly debilitating, treatment delivery may be impaired, Dr. Lustberg says. If we can enhance how patients are feeling during treatment, they may actually tolerate treatment better, stay on it longer, not need dose reductions or modifications, and have better disease outcomes. It’s all interrelated.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Worst Stage Of Breast Cancer
Will I Need Surgery And What Kind Should I Have
This is an important question but the answer may be less than definitive. It will vary from patient to patient and you may have more than one choice.
According to the American Cancer Society, most women with breast cancer have some type of surgery. But some breast cancers cant initially be surgically removed. In other cases, whether to operate and the type of surgery may depend on the cancers stage, the tumors size and location, the size of your breast and your personal preference.
In women whose breast cancers are operable, the choices are breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy. Mastectomy is the removal of most or all breast tissue and possibly nearby lymph nodes. Within each of those two broad categories are further options. Talk with your oncologist and breast surgeon. If you have any doubts, you may choose to seek a second opinion.
The Development Of Ts
Among the total of 1035 WSIs, 55,078 tiles were cropped from the ROIs. The E-S classifier was used to identify the stroma inside the ROIs. To check the stroma tiles prepared for the following experiments were in the correct classification, a well-trained human observer carefully reviewed all tiles with regions predicted as epithelium or stroma by CNN I . Meanwhile, IHC sections of CK5/6 and P63 were used as the reference standard if necessary. Tiles containing misclassified stroma, blank regions, and necrosis were removed. Finally, 10,344 tiles were excluded and the rest 44,734 were remained.
To develop a stroma-based biomarker for predicting pCR, Inception-V4 was selected as the base DL architecture. Weighted cross-entropy and stochastic gradient descent were used in optimization. Moreover, we used the fast ensemble DL strategy to further boost the optimization of the prediction part of CNN II,,. After scoring all tiles, an averaged value from all the tiles of each WSI was calculated as the TS-score, which reflected the probability of obtaining pCR for an individual patient .
Recommended Reading: Dog Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Treatment Option Overview For Locally Advanced Or Inflammatory Breast Cancer
On the basis of the available evidence, multimodality therapy delivered with curative intent is the standard of carefor patients with locally advanced or inflammatory breast cancer.
The standard treatment options for locally advanced or inflammatory breast cancer may include the following:
- Fungating/painful breast or chest wall lesions.
- After surgery for decompression ofintracranial or spinal cord metastases.
- After fixation of pathologicfractures.
Recommended Reading: Can I Survive Breast Cancer
Do I Need Genetic Counseling And Testing
Your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor. Thats someone who talks to you about any history of cancer in your family to find out if you have a higher risk for getting breast cancer. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage have a higher risk of inherited genetic changes that may cause breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer. The counselor may recommend that you get a genetic test.
If you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer, your doctor may talk about ways to manage your risk. You may also have a higher risk of getting other cancers such as ovarian cancer, and your family may have a higher risk. Thats something you would talk with the genetic counselor about.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Read Also: Triple Negative Breast Cancer Immunotherapy
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Breast Cancer Treatment . Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Chemotherapy For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Advances in treatment are making it possible for women with metastatic breast cancer to live for many years. New drug therapies can not only slow down or stop a tumors growth but also keep symptoms at bay.
Which treatment your doctor recommends will vary based on your medical history, age, and breast cancer type, among other factors. Combinations of drugs are commonly prescribed for women with early-stage disease. Most women with advanced breast cancer generally receive only one drug at a time.
Chemotherapy drugs that MSK doctors commonly prescribe for advanced breast cancer include:
Women with advanced disease can also benefit from genomic testing. This is also called tumor sequencing or molecular profiling. It is offered to all MSK patients with metastatic breast cancer. Genomic testing involves looking at the cancer cells to see if there are any genetic mutations that could be linked to the specific type of breast cancer you have.
Our experts use a highly sophisticated testing approach developed by MSK researchers called MSK-IMPACT. The information gained from MSK-IMPACT can help us personalize your care. We can rule out drug therapies that may not work for you or sometimes recommend cutting-edge clinical trials designed to target the specific mutations in your tumor.
You May Like: Mammogram Pictures Of Breast Cancer
Training And Employment Of The E
For the training data, two annotation strategies for tumor epithelium were used by a well-trained pathological observer to better train the model while using less manual efforts, which were as follows: 105 WSIs were roughly annotated to produce noisy sample one , detail descriptions as follows: annotate the tumor cells inside the black rectangle regions in yellow, ensuing that all tumor cells were included in the annotations and allowing some false annotations 20 WSIs were precisely but partially annotated to produce noisy sample two , detail descriptions as follows: annotate the tumor cells inside the black rectangle regions in yellow, ensuring all the annotated areas were exactly the tumor epithelium and no need to annotate all the tumor cells .
NS_1 contains 992 pairs of images and corresponding noisy labels and NS_2 contains 142 pairs of images and corresponding noisy labels. We also prepared a knowledge base which contains a list of semantic descriptions for tumor segmentation task in pre-treatment HE-stained biopsied images . The prepared NS_1, NS_2 and KB were employed to train an image semantic segmentation model for the task of identifying the tumor stroma. Images were cropped into 256×256 pixels at 10×magnification .
Treating Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large or growing into nearby tissues , or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes. These cancers are treated slightly different from other stage III breast cancers. You can find more details in Treatment of Inflammatory Breast Cancer.
There are two main approaches to treating stage III breast cancer:
Read Also: United Breast Cancer Foundation Reviews
How Long Does Chemotherapy Take For Breast Cancer
Typically, you receive chemotherapy in cycles. You may receive chemo every week or every two, three or even four weeks. Cycles are usually two to three treatments long. Each cycle includes a rest period to allow your body to recover. For example, you may have the same treatment every Monday for three weeks. Then you have an extra week to recover before repeating the cycle. Many people have multiple treatment cycles in a row. Treatment may last three to six months.
Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs that may be given intravenously or by mouth. The drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells in most parts of the body. Sometimes, if cancer spreads to the spinal fluid, which surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord, chemo may be given directly into in this area .
On this page
Also Check: How Do They Check For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low . Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells.Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.
Metabolic markers
How Soon After A Breast Cancer Diagnosis Should You Have Surgery

Breast cancer surgery is often the first course of treatment. In some cases, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy first to help shrink larger cancer cells.
Surgery should come within a few weeks of diagnosis. Research shows the sooner you receive surgery, the better the overall prognosis. For example, a study showed women ages 15 to 39 who had surgery within two weeks had a 84 percent five-year survival rate compared to a 78 percent five-year survival rate for women who waited six weeks or more until surgery. Overall, the optional time for surgery after diagnosis is less than 90 days.
Lumpectomy, mastectomy and lymph node removal are three common surgical procedures to treat breast cancer. A lumpectomy is a breast-conserving procedure in which only a part of the breast that contains cancer cells is removed. A mastectomy removes the entire breast. Some women also undergo a double mastectomy to remove both breasts.
Read Also: Can People Die From Breast Cancer