Pathologic Complete Response As A Surrogate Endpoint In Breast Cancer
touchREVIEWS in Oncology & Haematology
Abstract:
Overview
The metastatic setting has traditionally been the initial venue for the development of new drugs in breast cancer. Neoadjuvant trials, however, which commonly utilize the post-operative surrogate endpoint of pathologic complete response , offer a more efficient and potentially beneficial framework for drug development. This review discusses the basis for using pCR as a surrogate endpoint in breast cancer, compares the validity of pCR amongst different receptor subtypes of breast cancer, examines the relationship between pCR and event-free survival, and evaluates whether or not pCR meets the criteria of a valid and useful surrogate endpoint.
Keywords
Breast cancer, chemotherapy, neoadjuvant, pathologic complete response
Article:
Pathologic complete response and risk of breast cancer recurrence
Differences in pathologic complete response rates among receptor subtypes of breast cancer
Association between pathologic complete response and survival
Using pathologic complete response to compare neoadjuvant regimens
Association between pathologic complete response and survival among trials of targeted therapies
Using pathologic complete response versus residual disease status to guide future therapy
Does pathologic complete response meet the criteria of a good surrogate endpoint?
Article Information:
Disclosure
Compliance With Ethics
Review Process
2021-03-29
Future Directions In Neoadjuvant Trials
As previously discussed, neoadjuvant trials represent an optimal research setting. For example, these trials can help to individualize therapy with the identification of tumoral or circulating markers predictive of response to identify pathways to overcome therapeutic resistance. A new trial modality, the so-called postneoadjuvant trial, may be used to assess the efficacy of a new therapy compared to standard treatment for patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy . Challenges in the neoadjuvant setting include an inaccurate assessment of early response to therapy and the lack of noninvasive means of predicting pCR to therapy in order to identify the best candidates for randomization early in the treatment course.
Identifying Independent Predictors Of Pathological Complete Response Using Multivariate Logistic Regression
Among the entire cohort, triple-negative breast cancer and HER2-amplified patients were more likely to obtain pCR than luminal A and luminal B patients . Among the 60 patients who achieved pCR, 19 were TNBC patients , 18 were HER2-amplified patients , 12 were luminal A patients , and 11 were luminal B patients .
In the training cohort of initial-baseline patients, the subtype, posterior acoustic pattern, and elasticity score were identified as independent predictors of pCR by multivariate logistic regression . Among 47 patients who achieved pCR in the training cohort, 27 patients had enhancement , 15 patients had no change , and five patients had shadowing . The elasticity score was commonly high in pCR patients .
Table 2 Multivariate logistic analysis of pCR in initial-baseline and two-cycle response patients based on the training cohort.
Recommended Reading: What Percentage Of Women Survive Breast Cancer
Vitamin D And Survival By Tumor Subtypes
Regarding OS, we found no statistical difference in the 5-year survival rate for patients with HER2+ and HR+/HER2- tumors, depending on their VD level at diagnosis . Regarding the TNBC subgroup, 5-year-OS was 59% in the VD deficient group versus 70% in the VD sufficient group. This trend was not statistically significant .
Fig. 3
a OS depending on the Vitamin D level in the HER2+ tumor subtype. b OS depending on Vitamin D level in the HR+/HER2- tumors subtypes. c OS depending on the Vitamin D level in the TN tumor subtypes
We analyzed PFS depending on VD level and tumor subtypes. The 5-year-PFS was of 92 and 79% in the VD deficient and the VD sufficient group respectively for patients with HER2+ tumors . Regarding the HR+/HER2- cohort, 5-year-PFS rates were 78 and 89% respectively, this difference was approached statistical significance , Fig. ). Finally, a non-statistically significant trend was observed in the TNBC subgroup .
Fig. 4
Pathologic Complete Response After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy And Impact On Breast Cancer Recurrence And Survival: A Comprehensive Meta
Corresponding Author:
##L. Trippa and A. Bardia contributed equally as co-senior authors of this article.
Prior presentation: This work was previously presented at Advances in Breast Cancer Research, San Francisco, CA, October 2011 American Association of Cancer Research , New Orleans, LA, April 2016 and San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, December 2018.
Corresponding Author:
Clin Cancer Res 2020 26:283848
Clin Cancer Res
Laura M. Spring, Geoffrey Fell, Andrea Arfe, Chandni Sharma, Rachel Greenup, Kerry L. Reynolds, Barbara L. Smith, Brian Alexander, Beverly Moy, Steven J. Isakoff, Giovanni Parmigiani, Lorenzo Trippa, Aditya Bardia Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Survival: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 15 June 2020 26 : 28382848.
Read Also: Does Hormone Replacement Therapy Cause Breast Cancer
Tnm Staging System And Neoadjuvant Therapy
The main method of pathologic staging for breast cancer is the TNM system which stands for .
When TNM is used after neoadjuvant therapy, youll see a y before the T and N measures on your pathology report. Otherwise, the categories are the same as those for tumors not treated with neoadjuvant therapy.
yT = Tumor stage after neoadjuvant therapy
yN = Lymph node status after neoadjuvant therapy
Metastatic status is determined before treatment begins.
M0 = No metastases
M1 = Metastases
Neoadjuvant therapy is only used to treat non-metastatic breast cancer. So, if you get neoadjuvant therapy, you should see M0 on your pathology report.
Comparison With Published Studies
Our results differ from a recent analysis of patients with IBC in the SEER database, which reported the best survival outcome for HR+/HER2+ . Approximately 20% of patients in the SEER analysis had HR+/HER2+ tumors compared with 36% in our study. This may be explained by different inclusion criteria and disease definition in the latter study. For example, we only included non-metastatic patients and also were able to more comprehensively identify IBC patients based on both clinical and pathologic characteristics. Additionally, patients with unknown biologic subtype were excluded in the SEER analysis. Nonetheless, this study reported poor survival for patients with TN-IBC, which is consistent with our report and other studies in the literature .
Approximately 16% of patients in our sample were black. This compares with 17% of IBC patients in the United States Cancer Statistics database who were black . However, only 11% of IBC patients in SEER were black. The latter study also reported that 15% of TN-IBC patients were black compared with 25% in our study. Our percentages of black patients within the three other subtypes of IBC , HR+/HER2+ , and HR/HER2+ ) also were higher than the SEER study , HR+/HER2+ , and HR/HER2+ ). This concurs with other studies in literature suggesting that incidence rates of IBC are higher for black patients than their white counterparts .
You May Like: What Is Radiation Treatment For Breast Cancer
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
The literature search was performed by two independent reviewers by use of a predesigned search strategy. Duplicate studies were manually removed. Each reviewer then reviewed the titles, abstracts and/or full texts of the retrieved manuscripts to ensure that all inclusion criteria was met before extracting the following data:
-
first author name
-
number of patients who successfully achieved a pCR and those with residual disease
-
survival outcomes for EFS, RFS, or OS at yearly intervals after treatment and
-
neoadjuvant treatment characteristics.
Data specific to patient outcomes and survival , 95 per cent confidence intervals and P values) were directly extracted from tables and study text. HR and associated standard errors were calculated from KaplanMeier curves where relevant. Risk of bias and methodology quality assessment was performed in concordance with the NewcastleOttawa scale. In case of discrepancies in opinion between the reviewers, a third reviewer was asked to arbitrate.
Survival And Pcr Depending On The Profile Subgroup
We evaluated the 5-year-OS of our cohort depending on the NAC response and their tumor subtypes. No significant difference in terms of OS was seen in the HER2+ and HR+/HER2- subgroup. Nevertheless, in the TNBC subgroup, the 5-year-OS was statistically significant . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy response appeared as a strong and independent prognostic factor of survival in the TNBC subgroup .
Fig. 6
a OS depending on the pathological response in the different tumors subtypes. b PFS depending on pathological response in the different tumor subtypes
Regarding PFS, 5-year-PFS rate was 77% versus 90% in the non pCR and pCR group respectively in the HER2+ subgroup . In the HR+/HER2- cohort, 5-year-PFS rate was of 81% versus 100% in the non pCR and pCR group respectively . Finally, in the TNBC subtype, 5-years-PFS rate for women not achieving a pCR was 46% while it was 87% for those achieving pCR . Pathological complete response appears as a strong and independent prognostic factor of survival, especially in the TNBC subgroup.
Read Also: What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Construction Of The 33
A reduced E2F4 target gene signature of 34 genes was determined by identifying all E2F4 target genes whose own expression correlated highly with E2F4 scores in the TCGA BRCA dataset. Since all breast cancer datasets used in this study were obtained from one-channel array platforms, we used the Wang data , which contains the expression profiles for 286 lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer patients, to define the formula for calculating E2F4 scores. First, we retrieved the log expression values of 28 genes from the dataset and normalized them into relative expression values by subtracting the average expression values of 5 control genes . Second, we performed principle component analysis on the normalized expression data for these 28 genes to obtain the first principle component . Since these genes are all highly correlated with E2F4 score across samples, PC1 explains a large fraction of their variation and is highly correlated with E2F4 score. Third, based on the PCA result, we calculated E2F4 using the following equation:
EFeenen
Evaluation Of Pathological Complete Response As Surrogate Endpoint In Neoadjuvant Randomised Clinical Trials Of Early Stage Breast Cancer: Systematic Review And Meta
You May Like: Where Can Breast Cancer Spread
Higher Pathological Complete Response Rate Of Less Than 10 Total Axillary Lymph Nodes After Axillary Lymph Node Dissection Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy In Breast Cancer
- 1Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea
- 2Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, South Korea
- 3Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea
- 4Department of Oncology/Hematology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea
- 5Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea
Background: The American Joint Committee on Cancer guideline recommends the evaluation of 10 axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer to assess the N stage. However, the total ALN count in ALN dissection often decreases after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. The authors compared clinicopathological factors and oncological outcomes between < 10 vs. 10 ALNs after ALND following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Methods: Data of 159 patients with breast cancer, treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and ALND, were reviewed, and the cases were classified into two groups . The treatment response was determined based on the RECIST 1.1 criteria, and histopathological regression of the tumor was assessed based on the Miller-Payne grading scales.
How Well Did The Tumor Respond To Neoadjuvant Therapy
After surgery, a pathologist studies the breast tissue removed. The pathologists findings are used to determine how well the breast cancer responded to neoadjuvant therapy. This information may be included on your pathology report.
The breast cancers response to neoadjuvant treatment gives useful information about prognosis .
Recommended Reading: What Causes Her2 Positive Breast Cancer
Clinical Outcomes Among Major Breast Cancer Subtypes
We evaluated the association between pCR and clinical outcomes by three major clinical subtypes of breast cancer . The association of pCR with better EFS was statistically significant in patients with TNBC , HER2+ BC , and trended towards significance for HR+ BC as outlined in eFigures 4AâC. Similarly, the association of pCR with significantly improved survival was seen in TN BC and HER2+ BC as outlined in eFigures 5AâB. A significant relationship between pCR and improved survival was also noted in HR+ BC as outlined in eFigure 5C, but wide probability intervals were observed.
A-D. Relationship between pCR and EFS overall and among the major breast cancer subtypes
Kaplan-Meier curves depicting the relationship between pathologic complete response and event free survival overall , in triple negative breast cancer , HER2-positive breast cancer , and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer , based on hazard ratio data from the studies. The blue line represents the pCR group and the orange line represents the residual disease group. The shaded regions represent the 95% pointwise probability interval for their respective color.
Evaluation Of Treatment Response And Pathological Results
Treatment response was determined based on the RECIST 1.1 criteria . The clinical complete response was defined when there was no evidence of tumor in physical examination with radiological complete response. Clinical partial response was defined when the largest tumor diameter was reduced by more than 30% in radiological images. Clinical stable disease was defined when the largest tumor diameter increased < 20%. However, when the largest tumor diameter showed an increase of the largest tumor diameter of 20% or more, it was regarded as a clinically progressive disease.
For each case, all the available hematoxylin and eosin-stained specimens, including frozen-diagnosed and subsequent frozen-permanent samples, were retrospectively reviewed by two pathologists with 10 and 18 years of experience in breast pathology, respectively, in a blinded manner without information about the clinicopathological data or outcomes. The histopathological reviews were conducted independently. Cases with a discrepancy were repeatedly reviewed until a consensus was reached.
You May Like: Is Metastatic Breast Cancer Terminal
Nomogram Construction Using The Training Cohort
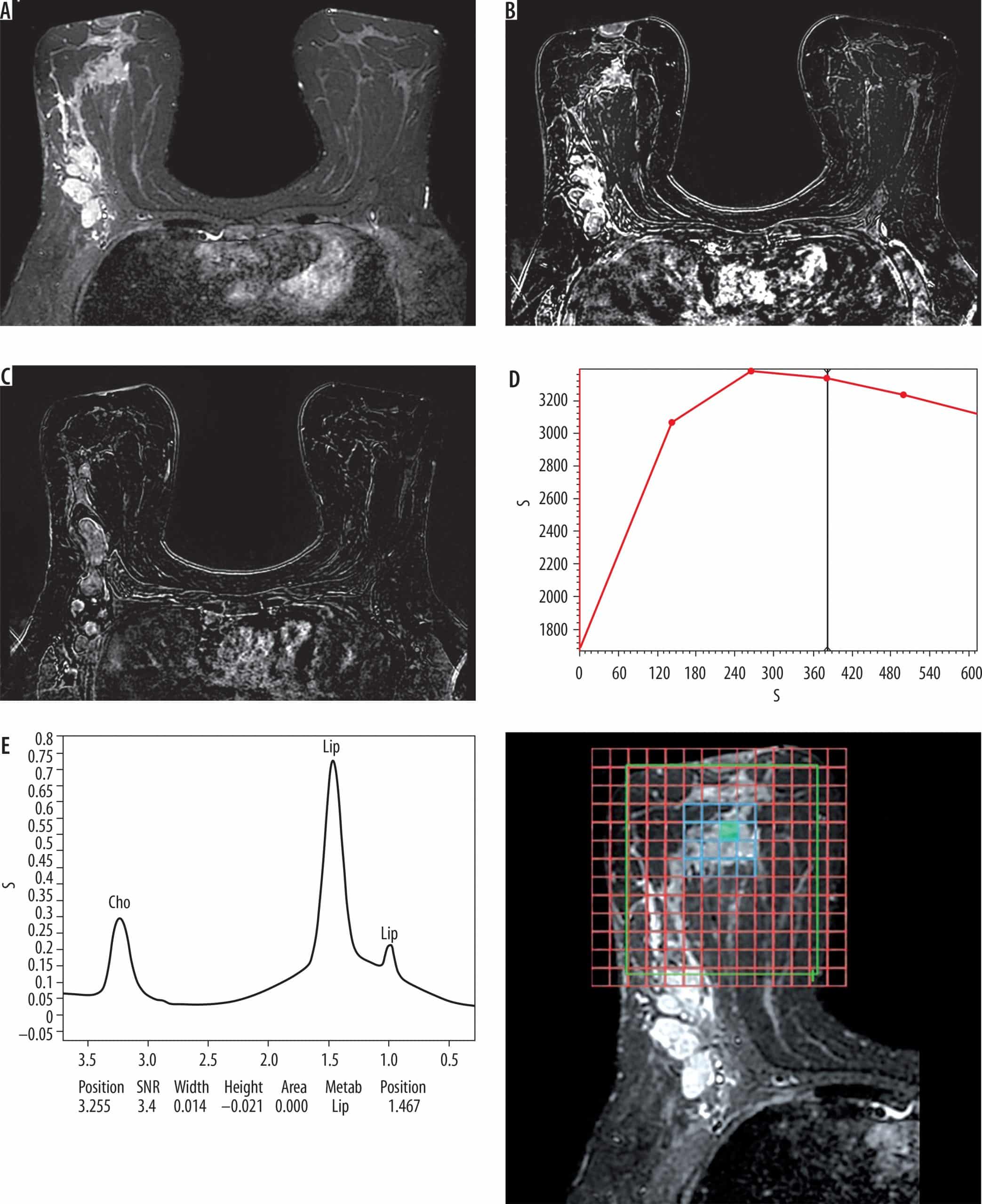
The nomogram was constructed based on significant factors from the multivariate logistic regression analysis using the training cohort to predict pCR . In the nomogram, the estimated probability of pCR could be achieved by summing the scores of each variable and locating them on the total score scale. For instance, one patient with a two-cycle response had a size shrinkage of 40 mm , elasticity score reduction , and posterior acoustic change to shadowing of 124 points, which could be converted to a probability of pCR greater than 99.0%, which indicated a perfect model .
Figure 3 An initial-baseline nomogram was constructed from three informative features . To calculate the probability of patients achieving pCR after NAC, points for each parameter were assigned by corresponding values from the âpointsâ axis, and the sum of the points was plotted on the âtotal pointsâ axis. The probability of achieving pCR after NAC was the value at a vertical line from the corresponding total points . pCR, pathological complete response NAC, neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Figure 4 A two-cycle response nomogram including early response to chemotherapy was constructed from three informative features . When the total points reach 100, the probability of achieving pCR reached 99%, which mean that the prediction efficiency was satisfactory . pCR, pathological complete response.
Data Management And Statistics
Patients data were reviewed in the hospitals digital documentation system . Data were collected using Microsoft Excel 2010® . Further statistics were performed with SPSS 24.0 . Quantitative parameters are given as median and range. Qualitative parameters are presented as frequencies. Binary logistic regression was performed to determine the influence of multiple factors on pCR. Possible influencing factors were age, study participation, tumor biology, genetic mutation , recurrent cancer, discontinuation of chemotherapy , days between diagnosis and begin of chemotherapy as well as days between end of chemotherapy and operation. All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from every individual participant included in the study.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Root Cause Of Breast Cancer
Association Between Pathologic Complete Response After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy And Breast Cancer Outcomes
A large comprehensive patient-level meta-analysis showed that achieving pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy correlates with significantly improved event-free survival and overall survival in patients with localized breast cancer. These findings were particularly robust in triple-negative breast cancer and HER2-positive breast cancer. Event-free and overall survival were similar regardless of whether patients received additional adjuvant chemotherapy. The findings suggest that adjuvant chemotherapy can be abbreviated or even omitted in some patients if they achieve pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Similar outcomes with or without adjuvant chemotherapy in patients who attain pathologic complete response on neoadjuvant chemotherapy support the clinical utility of escalation and de-escalation strategies in the adjuvant setting base on neoadjuvant response. Laura M. Spring, MDTweet this quote
Breast cancer trials have traditionally added additional systemic therapies to reduce recurrence risk, but this adds to toxicity and may represent overtreatment for some patients. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy offers several additional advantages over adjuvant therapy, including rapid assessment of response using surrogate markers like pathologic complete response, she told listeners.
Objectives and Implications
Methods and Findings