How Can You Tell If You Have Dense Breasts
You wont be able to judge a breasts level of density based on its feel or appearance. The only way to measure it for sure is to get a mammogram, according to the National Institute of Health.
The quantification of breast density is something that is determined by the breast radiologist, Dr. Newman told Katie. Women very commonly will have fibrocystic densities that you can feel on clinical breast examination, but that is different from breast density. Every woman has some degree of lumpy bumpiness in the breast, and thats simply a sequela of all the hormonal cycles that our breast sees over a lifetime with some areas of the breast being more glandular, others being fattier.
In some states, doctors are now required to tell patients whether they have dense breasts. Many states also require that insurance cover additional tests, outside of a traditional mammogram, for women with dense breasts. This map shows the regulations
Formulate A Screening Plan With Your Doctor
Many states, including California, Virginia, and New York, require radiologists to tell you if your breasts are extremely dense.
While having dense breasts doesnt necessarily mean you will develop breast cancer, knowing you have dense breasts is a step toward health awareness. Ask your doctor to suggest a screening plan if you have dense breasts or other risk factors for breast cancer.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends a mammogram every 2 years for those between 50 and 70 years old. Early screening or other diagnostic tests may be recommended from ages 40 to 49 depending on personal risk factors.
What Is Dense Breast Tissue
Breast density is a measure of how much fibrous and glandular tissue there is in your breast, as compared to fat tissue. It isnt related to breast size or firmness.
Breasts are made up of lobules, ducts, and fatty and fibrous connective tissue.
- Lobules are the small glands that produce milk, while ducts are the tiny tubes that carry the milk from the lobules to the nipple. Together, the lobules and ducts are referred to as glandular tissue.
- Fibrous tissue and fat give breasts their size and shape and hold the other structures in place.
Fibrous and glandular tissue are harder to see through on a mammogram, so your breast tissue may be called dense if you have a lot of these tissues .
Having dense breast tissue is common. Some women have more dense breast tissue than others. For most women, breasts become less dense with age. But in some women, theres little change.
Also Check: What Is The History Of Breast Cancer
Dense Breasts And Cancer: Tips To Empower You And Improve Your Breast Health
Topics
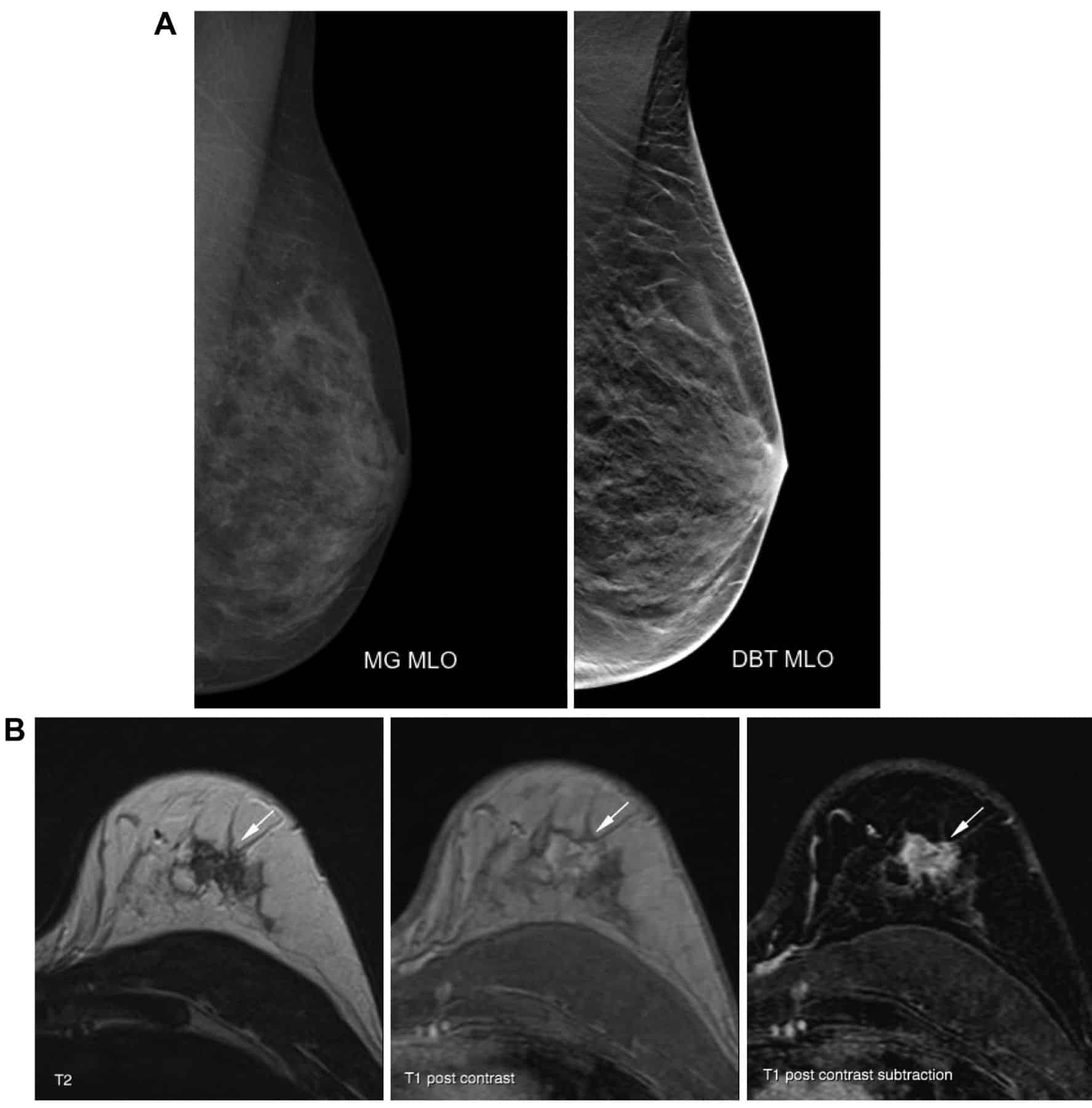
Standard mammograms are an optimal screening tool to find breast cancer in most patients. When breast radiologists review the mammogram results, they can see the ratio of dense to non-dense breast tissue and assign a category of breast density. If the category is dense breasts, then its important for the patient to learn more about the condition, as it poses an increased risk for breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Signs And Symptoms Everyone Should Watch Out For
Hall said it’s important for women to be aware of breast cancer signs and symptoms other than lumps. Changes like new asymmetries, skin dimpling, or nipple inversion are all good reasons to get checked out even if you recently had a normal mammogram, she said.
Skin irritation, nipple discharge, and breast pain can also be symptoms of cancer, Insider previously reported. Women have also told Insider how they first thought
She also said women like her, who have no family history of breast cancer, are still at risk especially as they age. 85% of breast cancer diagnoses occur in women with no family history.
Don’t Miss: Can You Live 10 Years With Metastatic Breast Cancer
How Often Should You Get Screened For Breast Cancer If You Have Dense Breasts
Screening guidelines for breast cancer do not differ depending on breast density, Dr. Dahut said. If you have average risk of developing breast cancer meaning you are not at heightened risk because of family history, genetics or other factors you should get a mammogram each year starting at age 40, Dr. Friedewald said.
If you have dense breasts, you will likely still get screened on that cadence, she said, but you might also get additional imaging, like a breast ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. Consult with your doctor about the best screening plan for you. Online tools, like the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium Risk Calculator, can also help assess your risk.
Ms. Courics announcement is a helpful reminder of just how essential it is for everyone to be mindful of their cancer risk and to screen for it according to medical guidelines, experts said. Breast and cervical cancer screening declined sharply during the pandemic.
Women are so often put in a position of caring for other people, especially in the pandemic, Dr. Comen said. Its so important that women have the space and time and support to take care of themselves.
What Should I Do If I Have Dense Breast Tissue
If your mammogram report says that you have dense breast tissue, talk with your health care provider about what this means for you. Be sure that your doctor or nurse knows if theres anything in your medical history that increases your risk for breast cancer. To learn more about breast cancer risk factors, see Breast Cancer Risk and Prevention.
Any woman whos already in a high-risk group should have an MRI along with her yearly mammogram. To learn more about if youre in a higher-risk group for breast cancer, see American Cancer Society Recommendations for the Early Detection of Breast Cancer.
Read Also: Should I Have Chemo For Breast Cancer
Understanding Your Breast Cancer Risk
The risk of developing breast cancer varies greatly from person to person, so its important to discuss your specific risk level with your doctor. That being said, there are some important risk factors to keep in mind.
In a previous interview with SurvivorNet, Dr. Elizabeth Comen, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, laid out several risk factors for breast cancer including:
What Affects Breast Density
High breast density is common. In the U.S., 40-50 percent of women ages 40-74 have dense breasts .
Breast density varies greatly by age and weight. Dense breasts are more common in both young women and lean women :
- About 50-60 percent of women ages 40-44 have dense breasts, compared to 20-30 percent of women ages 70-74.
- About 50-60 percent of women with a healthy weight have dense breasts, compared to 20-30 percent of obese women.
Medications that contain hormones can also affect breast density. For example :
- Women who take menopausal hormone therapy tend to have denser breasts than they would if they didnt take MHT. As women age, their breasts may become less dense and more fatty. Taking MHT slows this process. MHT is also called postmenopausal hormone use and hormone replacement therapy .
- Women who take the drug tamoxifen tend to have lower breast density than they would if they didnt take tamoxifen.
Also Check: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 24
What Does Almost Entirely Fatty Mean On A Mammogram
A: Almost entirely fatty indicates that the breasts are almost entirely composed of fat. About 1 in 10 women has this result. B: Scattered areas of fibroglandular density indicates there are some scattered areas of density, but the majority of the breast tissue is nondense. About 4 in 10 women have this result.
What Does It Mean When You Feel A Lump In Your Breast
Overview. If you feel a lump in your breast, it may be fat necrosis. Fat necrosis is a lump of dead or damaged breast tissue that sometimes appears after breast surgery, radiation, or another trauma. Fat necrosis is harmless and doesnt increase your cancer risk. It usually isnt painful, but it can cause anxiety.
Read Also: Does Putting Your Phone In Your Bra Cause Breast Cancer
Recommendations On How To Inform Women
Physicians who counsel women about their respective choices regarding breast cancer screening in general, and screening in women with extremely dense breasts in particular, must have expertise in the principles of screening in general, and in screening by imaging in particular.
Such expertise is usually not routinely available in primary healthcare providers.
Accordingly, EUSOBI urges radiologists to assume this important task and directly engage in informing women about the pros and cons of screening. Educating other healthcare providers might be another way to ensure that women receive correct and objective information. The following passages may serve as a guide for womens education
How Can You Reduce Breast Density
- Breast feed for at least six months.
- Increase healthy fats: olive oil and flax seed oil, for example. Use these oils raw, as these have a low burn point.
- Eliminate red meat or greatly reduce it.
- Limit alcohol to one drink a week.
- Sugar has no redeeming value, so cut it out. It feeds cancer cells.
- Eliminate caffeine. Coffee turns into estrogen within 45 minutes.
- Increase fiber intake through flax, chia seeds and psyllium. The more fiber you eat, the more estrogen is removed from the body
- Move toward a plant-based diet. Breasts love all things greenespecially the cruciferous family of vegetables.
- Restrict carbohydrates as they turn into sugar.
- Drink organic green tea.
- Try breast massage with specific oils for breast health.
As you can see, breast density is a very common condition, and there is an environmentally safe solution for both screening and alleviation.
Be proactive when it comes to your breast health, especially if you have dense breasts. Heres to happy healthy breasts!
Warmest regards,
Also Check: Can You Get Breast Cancer From Squeezing Your Nipples
How Do Dense Breasts Increase Breast Cancer Risk
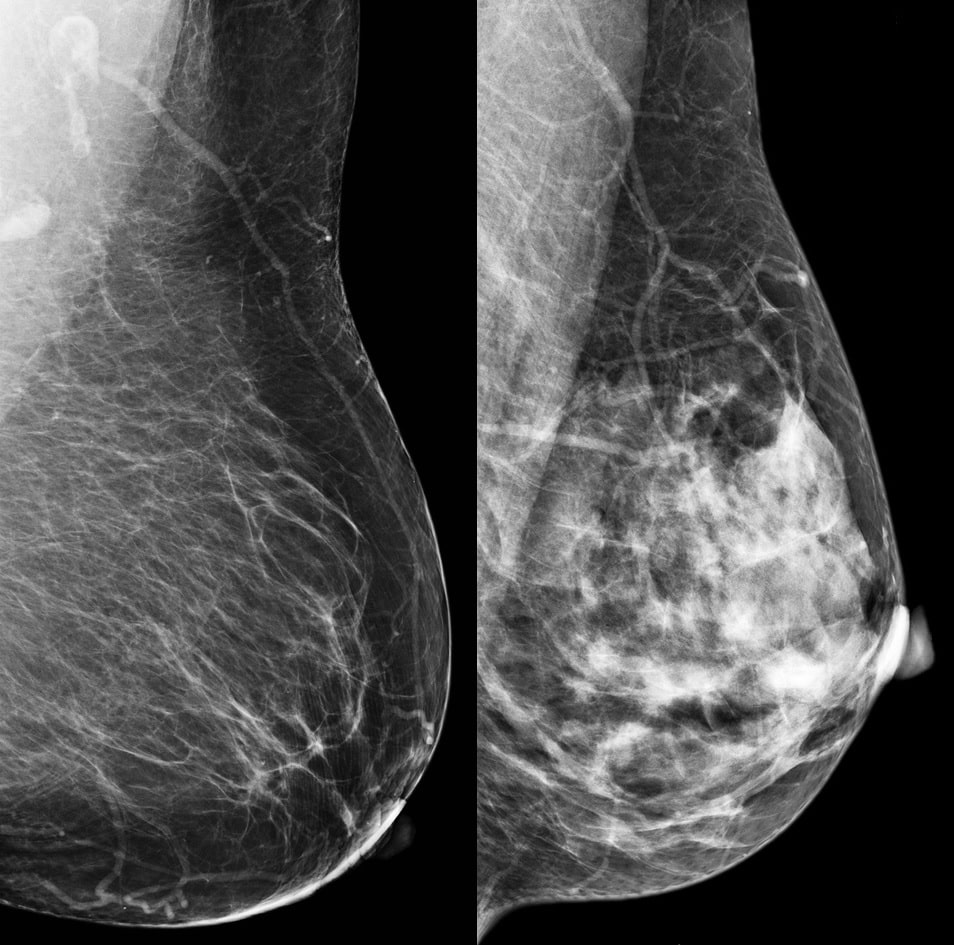
Having dense breasts inherently increases the risk for breast cancer by two to four times. In a mammogram, which is a black-and-white X-ray of the breast, non-dense breast tissue appears black and transparent. Dense breast tissue appears as a white area. Breast masses and cancerous tumors are also white, making them sometimes difficult to spot. Since dense tissue can mask potential cancer, a mammogram might not be enough for cancer detection and supplementary tests may be necessary.
Why Is There A Lump On My Mammogram
Fat necrosis forms into a lump or pseudo-mass due to fat cells that have either died or been damaged. A mammogram will easily detect this mass. The only concern is that sometimes the shape and features of a fat necrosis pseudo-mass can be very similar to certain kinds of breast cancer. Fat necrosis tends to have an irregular or rounded outline.
Don’t Miss: Survivability Rate Of Breast Cancer
How Do Dense Breasts Affect Mammogram Readings
Dense tissue shows up as white on X-rays think of how bones stand out in those images.
When I as a breast imaging radiologist describe a patient as having dense breasts, what I mean is that her mammogram looks white to me, Smetherman said. Cancers will also look white, so looking for something white on a background of white is more difficult to identify.
Fatty tissue, on the other hand, looks gray on a mammogram, so a tumor stands out.
What Is Breast Density
Breast density reflects the amount of fibrous and glandular tissue in a womans breasts compared with the amount of fatty tissue in the breasts, as seen on a mammogram.
On a mammography report, breast density is assigned to one of the following four categories
- The breasts are almost entirely fatty .
- A few areas of dense tissue are scattered through the breasts .
- The breasts are evenly dense throughout .
- The breasts are extremely dense .
Women in the first two categories are said to have low-density, non-dense, or fatty breasts. Women in the second two categories are said to have high-density or dense breasts. About half of women who are 40 years old or older have dense breasts.
Don’t Miss: How Rare Is Male Breast Cancer
How Do Doctors Determine If You Have Dense Breast Tissue
Breast tissue is composed of milk glands, milk ducts and supportive tissue and fatty tissue . Radiologists use mammogram images to grade breast tissue based on the proportion of dense to nondense tissue. According to the BI-RADS reporting system, the levels are A: almost entirely fatty, B: scattered areas of fibroglandular density, C: heterogeneously dense, and D: extremely dense.
Learning About Breast Cancer Screening
Screening for breast cancer is typically done via mammogram, which looks for lumps in the breast tissue and signs of cancer. The American Cancer Society says women should begin yearly mammogram screening for breast cancer at age 45 if they are at average risk for breast cancer. The ACS also says those aged 40-44 have the option to start screening with a mammogram every year, and women age 55 and older can switch to a mammogram every other year, or they can choose to continue yearly mammograms.
For screening purposes, a woman is considered to be at average risk if she doesnt have a personal history of breast cancer, a strong family history of breast cancer, a genetic mutation known to increase risk of breast cancer such as a BRCA gene mutation or a medical history including chest radiation therapy before the age of 30. Beyond genetics, family history and experience with radiation therapy, experiencing menstruation at an early age or having dense breasts can also put you into a high-risk category. If you are at a higher risk for developing breast cancer, you should begin screening earlier.
In a previous interview with SurvivorNet, Dr. Connie Lehman, chief of the Breast Imaging Division at Massachusetts General Hospital, said people who hadnt reached menopause yet should prioritize getting a mammogram every year.
Also Check: Does Alcohol Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer
What Are Dense Breasts And How Common Are They
Having dense breasts is a risk factor for breast cancer. In many states, radiologists must tell you if your screening mammogram shows you have dense breasts.
Breasts are made of both fibrous and glandular tissue, and fat. Breast density describes the amount of fibrous and glandular tissue compared with the amount of fat. There are different levels of dense breasts. Some are more common than others.
- About 1 out of every 10 women have very dense breasts.
- Around 4 out of every 10 women have heterogeneous density. That means their breasts are mostly dense, with some areas of fat.
- Another 4 out of every 10 women have scattered density. That means some areas are dense, but most are not.
- About 1 out of every 10 women have breasts that are mostly fat. They have no fibrous and glandular tissue, or very little.
Sandra Brennan, Director of Radiology at MSK Westchester provides more information below about breast density. She shares steps people with dense breasts can take to find cancer early.
Extra Screening With Ultrasound
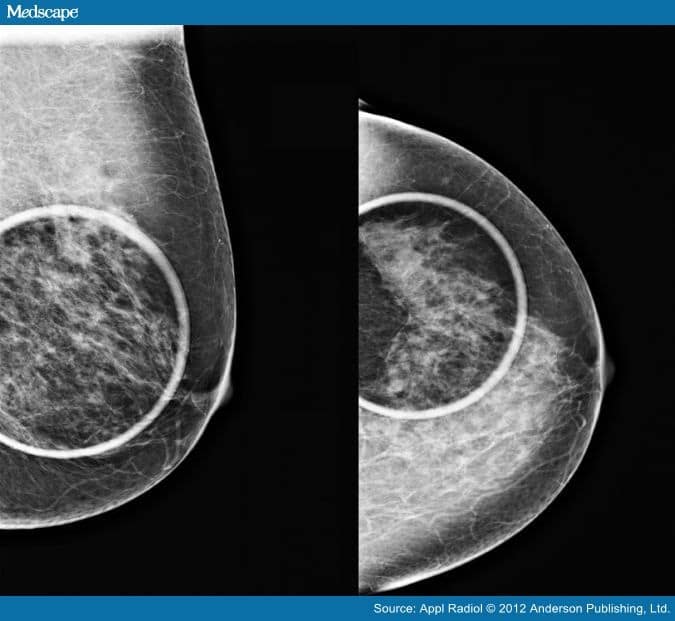
Any woman who has dense breasts may want to consider supplemental screening, usually with breast ultrasound.
Studies show that screening with ultrasound, in addition to mammography, improves detection of breast cancers in women with dense breasts.
A breast ultrasound is performed by an ultrasound technologist with a handheld probe. The technologist applies lubricating gel to the breast and moves the probe across the breast. The breasts are not compressed as they are during a mammogram, although the probe is applied with a little pressure.
One downside of additional screening tests is that women will get more false positives, Friedlander warns. Particularly for a woman who comes for her first ultrasound, we may find lots of new things, but most are not cancer, she says. Women who have ultrasound screening are more likely to need a biopsy and short-term follow-up for something that ultimately is benign.
Friedlander says that for some women with dense breasts, sticking to mammography and forgoing additional imaging is a reasonable option.
Theres no one-size-fits-all plan anymore. And frankly, mammography is the only test that’s proven to have a survival benefit, she says. In an ideal world, every patient would have a discussion with her physician and make these decisions together.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Awareness Pins Free
Here’s What To Do If You Have A Higher
While getting a mammogram is a good way to detect the possibility of breast cancer, it can also detect something else: dense breast tissue. In fact, dense breast tissue is a finding exclusive to a mammogram, wherein certain parts of the breast appear light gray or white, making it harder to detect any present abnormalities, according to the Susan G Komen breast cancer research organization.
Additionally, the American Cancer Society notes that women with dense breast tissue have a higher risk of breast cancer than those with less dense breast tissue, although why that may be is unclear. What else should you know about dense breast tissue, and how do you properly screen for breast cancer if you have it? Read on to learn more.
Screening For Women With Dense Breasts
Dense breast tissue can make abnormal findings hard to see on a mammogram. Screening tools for women with dense breasts are under study.
There are no special recommendations or screening guidelines for women with dense breasts. However, your health care provider may suggest other types of breast imaging in addition to regular mammograms.
Learn more about breast cancer screening.
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Cause Headaches