Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections on Cancer.Net:
- ASCO AnswersFact Sheet: Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to metastatic breast cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
- ASCO AnswersGuide:Get this free 52-page booklet that helps you better understand breast cancer. The booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
- Cancer.Net Patient Education Video: View a short video led by an ASCO expert in metastatic breast cancer that provides basic information and areas of research.
Effect Of Hormonal Changes On Breasts
As women develop from pre-puberty through puberty, pregnancy and to menopause, the breasts will be affected by a variety of fluctuations in hormones.
During puberty, hormones produced by the ovaries cause growth and development of the breast. After puberty, the hormones oestrogen and progesterone will change throughout a womans monthly menstrual cycle. This may cause women to have swollen or tender breasts at different times of the month.
During pregnancy the body will produce additional oestrogen and progesterone, which trigger further growth and development of the breast to prepare mothers for breastfeeding.
Around the time of menopause , the ovaries stop producing female hormones including oestrogen. Without oestrogen, the breast tissue decreases in size. After menopause , monthly menstrual periods stop.
What Is A Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenomas are solid, smooth, firm, noncancerous lumps that are most commonly found in women in their 20s and 30s. They are the most common benign lumps in women and can occur at any age. They are increasingly being seen in postmenopausal women who are taking hormone therapy.
The painless lump feels rubbery and moves around freely. You may find one yourself. Fibroadenomas vary in size and can grow anywhere in the breast tissue.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
What Do Breast Lumps Feel Like
How breast lumps feel depends on their cause, location, and growth. They can vary from painful, hard, and immobile to soft, painless, and easily moveable.
Lumps are most likely to be cancerous if they do not cause pain and are hard, unevenly shaped, and immobile.
Other breast lumps can feel different:
- Fibroadenoma lumps tend to be painless, easily movable, smooth, and rounded. They may disappear on their own.
- Breast cysts are smooth but firm.
- Breast abscesses and mastitis usually cause painful, swollen lumps, and there may also be a fever and flushing around the affected skin.
Read Also: Harrington Breast Cancer Center Amarillo Tx
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Men can get breast cancer too, but they account for less than 1% of all breast cancer cases. Among women, breast cancer is the most second most common cancer diagnosed, after skin cancer, and the second leading cause of cancer deaths, after lung cancer.
On average, 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer in their lifetimes. About two-thirds of women with breast cancer are 55 or older. Most of the rest are between 35 and 54.
Fortunately, breast cancer is very treatable if you spot it early. Localized cancer can usually be treated before it spreads.
Once the cancer begins to spread, treatment becomes more complicated. It can often control the disease for years.
Don’t Miss: Baking Soda And Honey Cancer Cure
Does Breast Cancer Lump Change With Menstrual Cycle
They way breasts look or feel can change over the course of a menstrual cycle in response to fluctuating hormones. Finding a lump, feeling pain, or noticing other breast or chest changes can cause worry, but these symptoms are common and are most often benign .
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, which develop in different parts of the breast.
Breast cancer is often divided into either:
- non-invasive breast cancer found in the ducts of the breast which has not spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. Non-invasive breast cancer is usually found during a mammogram and rarely shows as a breast lump.
- invasive breast cancer where the cancer cells have spread through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
- invasive lobular breast cancer
- inflammatory breast cancer
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the blood or the axillary lymph nodes. These are small lymphatic glands that filter bacteria and cells from the mammary gland.
If this happens, it’s known as secondary, or metastatic, breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
What Does Shoulder Blade Pain Feel Like When Its Related To Breast Cancer
The type of pain you feel usually depends on whats causing it. Some people have shoulder pain due to nerve damage from radiation therapy or a lumpectomy, mastectomy, or lymph node removal.
If you have neuropathic pain, you may feel a shooting or burning sensation. Some people describe the discomfort as an intense tingling or itching feeling.
You might also experience sharp pain when you try to move your arms up or down. This pain can be accompanied by swelling, stiffness, or numbness.
If your pain is caused by cancer that has spread , it might feel like a deep, dull ache in your joints or bones. Pain near your right shoulder blade could mean that your liver is involved.
You may also feel depressed or anxious, and your sleep may be disrupted as a result of your pain. Not getting enough sleep may make your pain feel even worse.
Your shoulder is a complex, interconnected group of bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels. These structures work together to align your posture and help you move your arms.
Your scapula serves several important functions:
- It cups the ball-shaped end of the humerus bone in your upper arm.
- It serves as an attachment plate for several muscles and ligaments.
- It moves in several directions as you use your arms, providing stability and flexibility.
Other treatments damage the nerves around your shoulder blade, causing long-lasting pain in your shoulders, arms, hands, and feet.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- Based on the stage of the cancer, how long do you think Ill live?
- Do you know if my cancer has any of these proteins: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, or the HER2 protein?
- What does it mean if my cancer has any of these proteins?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat breast cancer.
Surgery and radiation are used to treat cancer in a specific part of the body . They do not affect the rest of the body.
Chemotherapy, hormone treatment, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy drugs go through the whole body. They can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body.
Doctors often use more than one treatment for breast cancer. The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The cancer’s stage and grade
- If the cancer has specific proteins, like the HER2 protein or hormone receptors
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Also Check: Estrogen And Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer Prognosis
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
Treatment for breast cancer usually depends on the type of cancer and whether the cancer has spread outside of the breast to other parts of the body.
Here are some common treatments:
- lumpectomy , which removes the cancerous tumor from the breast. A woman usually has this surgery when the cancer is found early and when the lump is small and in only one part of the breast.
- mastectomy , which removes the whole breast. This surgery is done when cancer cells have spread through the breast or into other parts of the body. It’s a good way to remove all or most of the cancer, and can help prevent the cancer from spreading or coming back. Sometimes, a woman who has a mastectomy may choose to have an operation to reconstruct the breast, so her shape will be more like it was before.
- radiation therapy and chemotherapy, which are often used after lumpectomy or mastectomy to make sure that all the cancer cells are destroyed and do not grow back. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill the cancerous cells. Chemotherapy , or chemo, is special medicine that travels throughout the entire body and kills cancer cells.
Page 3
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass or sheet of cells called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread.When breast cancer is limited to the breast and/or nearby lymph node regions, it is called early stage or locally advanced. Read about these stages in a different guide on Cancer.Net. When breast cancer spreads to an area farther from where it started to another part of the body, doctors say that the cancer has metastasized. They call the area of spread a metastasis, or use the plural of metastases if the cancer has spread to more than 1 area. The disease is called metastatic breast cancer. Another name for metastatic breast cancer is “stage IV breast cancer if it has already spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the original cancer.
Doctors may also call metastatic breast cancer advanced breast cancer. However, this term should not be confused with locally advanced breast cancer, which is breast cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: Low Grade Breast Cancer Prognosis
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown. Part of the reason is that estimates based on doubling time assume that the rate stays constant at all times as the tumor grows.
If this were true, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor. A doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be found on exam. In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Most studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days. This means it’s possible that breast cancers diagnosed now began at least 5 years earlier, but again, this assumes the growth rate is constant. It is not.
Is It Normal To Have Little Lumps In Your Breasts

That’s understandable. But breast lumps are common, and most often they’re noncancerous , particularly in younger women. Still, it’s important to have any breast lump evaluated by a doctor, especially if it’s new, feels different from your other breast or feels different from what you’ve felt before.
Read Also: How Fast Do Breast Cancer Tumors Grow
Receptors For Secondary Breast Cancer
Breast cancer cells may have receptors . Hormones, or a protein called HER2, can attach to the receptors and encourage the cells to grow. A doctor called a pathologist tests cancer cells taken during a biopsy or surgery for these receptors. Your doctor uses the results of these tests to help plan your treatment.
If you have had primary breast cancer before, the receptors may not be the same as when you were first diagnosed. This may mean different treatments are useful. Your doctor may be able to diagnose a secondary cancer from your scan results. But they may still recommend a biopsy to find out more about the cancer cell receptors.Cancer that does not have receptors for either hormones or HER2 is called triple negative breast cancer.
Also Check: Stage 3b Breast Cancer Prognosis
How Can You Test For Breast Cancer At Home
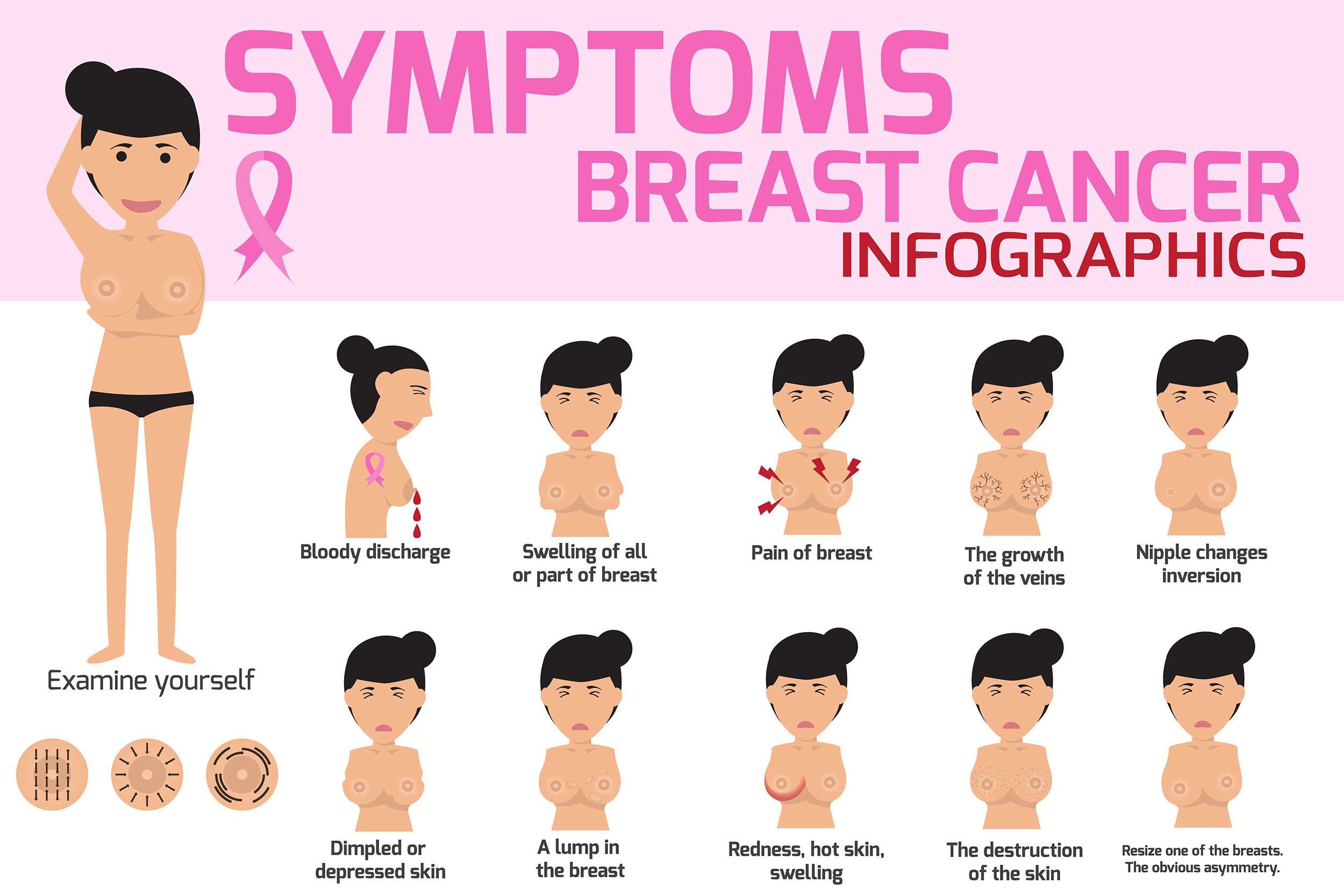
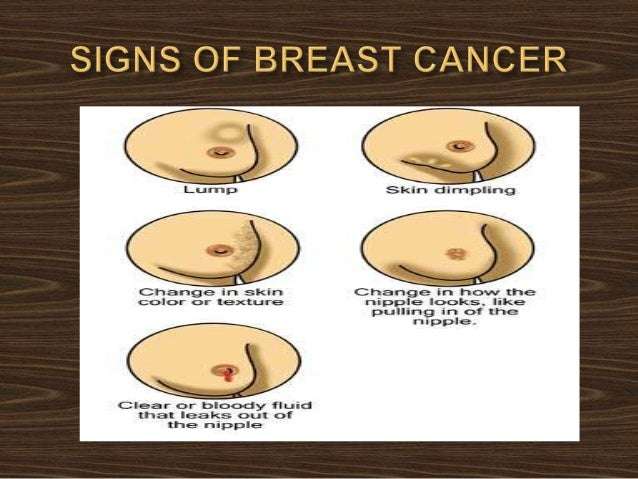
Self breast exams are simple here’s what to do: Stand up straight, hands on hips, and look at your breasts in the mirror. Carefully check for unusual swelling, puckering, dimpling, redness or bulges in and around your breasts. Also look for any changes in the nipples, including discharge or nipple inversion.
Recommended Reading: Hormone Therapy Metastatic Breast Cancer
How Do You Know If You Have A Breast Condition
If you have an underlying breast condition, you might notice changes in how your breasts normally feel, such as: A round, smooth and firm breast lump. A large, solid-feeling lump that moves easily under your skin. A hard, irregular-shaped breast lump. Skin redness or dimpling like an orange. Changes in breast size or shape.
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
One main reason for why people ask about how fast breast cancer grows, or its doubling time, is when they consider how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth rate also is important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Growth Rate
I Found A Breast Lump On Self
I was watching videos on Youtube and came across a video by a breast cancer survivor. In that video, she showed how to conduct a self-breast examination. Curiously, I followed the instructions, and I was surprised to find a lump! For a second, I thought it could just be my imagination, but it was still there the next day. However, I had no pain, discharge, or any other abnormal symptoms.
I had been using the Your Doctors Online application for more than a month at that point, so I logged in and got connected with Dr. Honaker. He calmed me down and took a detailed personal and family history. After I had described what the lump felt like in detail, he told me the likely cause was a fibroadenoma, a noncancerous breast lump. Because I didnt have any symptoms, the lump didnt require treatment.
After the consultation, I finally managed to book an appointment with my GP as well. She further confirmed that it was a fibroadenoma. Your Doctors Online never fails to impress me with their quick and thorough diagnosis. Calla.
What Percentage Of Breast Papillomas Are Cancerous
Most intraductal papillomas are non-cancerous, however 17-20% have been shown to be cancerous upon complete removal of the growth. In addition, about 20% of intraductal papillomas contain abnormal cells. Because there is even a small risk of cancer, papillomas should be surgically removed and biopsied.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Stage 3
What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, rounded structures of about 1 mm to 25 mm that are found throughout the body.
The lymph nodes form part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is an important part of the immune system that protects the body from disease and infection. It contains a network of thin tubes called lymph vessels that are found throughout the body. These lymph vessels transport a clear fluid called lymph between the lymph nodes. The lymph nodes filter the lymph to trap or remove substances harmful to the body, such as bacteria or cancer cells. This helps to protect the body from disease or infection. The lymph then passes back to the blood.
The closest lymph nodes to the breast are those in the armpit, which are known as axillary nodes. The axillary nodes drain lymph from nearby tissues, including the breast. There are also lymph nodes under the breastbone and in the neck . The number of lymph nodes varies between different people. There are usually about 15-30 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Because the lymph vessels carry lymph away from the breast, in the case of breast cancer, cancer cells can enter the lymph vessels and begin to grow in the lymph nodes. The axillary nodes are often the first place of cancer spread outside the breast. Usually, surgery is used to remove one or more of the axillary nodes to help check for cancer spread. Cancer found in the lymph nodes affects the staging and treatment of breast cancer.
How Does Cancer Start In The Breast
To understand how cancer can originate, it can be helpful to understand how regular cells and tissues function and develop.
Healthy cells are the basic building blocks of all tissues and organs in the body. The body is constantly making new cells to replace worn out tissue or to heal injuries. Normal cells are programmed to grow and divide in an orderly and controlled manner, so that each new cell replaces ones that are lost.
Sometimes cells become abnormal and keep growing. As they grow, they can form a mass or lump called a tumour. However, not all tumours are cancer. Some tumours are benign , which means they tend to grow slowly and usually do not invade surrounding tissue or other parts of the body. Tumours that are malignant have the potential to invade and spread to other parts of the body.
Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to grow abnormally. These cells have the potential to grow out of control and invade the surrounding tissue. When this occurs, this is called invasive breast cancer. If the cancer cells continue to grow, they may spread beyond the breast to other parts of body, which could become life-threatening.
There are different types of breast conditions which are named after the areas of the breast where they start:
Non-invasive breast conditions
Invasive breast cancers
Also Check: What Causes Hormonal Breast Cancer