Breast Cancer Risk Estimates And Risk Factors Included In The Gail Model
summarizes Gail model risk estimates and demographics of the study participants. The average age for the 99 subjects studied was 51.5 years . Of the 99 subjects, 45 were postmenopausal, 28 were premenopausal, 18 were perimenopausal, and 8 had unclear menopausal status at the time of trial entry. Breast cancer risk was greater than the eligibility criterion of the BCPT of 1.67% risk of developing breast cancer over the next 5 years as calculated by the Gail model: the average 5-year risk of our study population was 4.1% . Because calculation of the Gail model lifetime risk calculation is conditional upon current age, it is possible for a woman to have less than population lifetime risk , while still having an elevated 5-year risk. Consequently, for our study population, the average calculated lifetime breast cancer risk according to the Gail model was 23.5% .
Table 1.
Strengths And Limitations Of The Study
The strengths of this study include the use of a large representative cohort of regularly screened Spanish women, the high participation rate, and the relatively long follow-up period with negligible losses to follow-up, virtually complete case ascertainment, and information on tumor receptor status.
Calibration Of The Gail Model
Twenty-four studies incorporating 29 records were included to evaluate the calibration of the Gail model . The pooled E/O ratio was 1.16 with a high level of heterogeneity between studies . Sensitivity analysis showed that the combined E/O ratio and 95% CI were not significantly altered before and after the omission of each dataset . Cumulative analysis showed that by continually increasing the publication year and the sample size, the 95% CI became narrower and the pooled E/O ratio was closer to 1.0, which indicates that the precision of the pooled E/O ratio was gradually improved . Publication bias was detected by funnel plot . According to the trim-and-fill method, the adjusted pooled E/O ratio was 1.25 after trimming .
Table 1 Characteristics of the included studies for estimating the calibration of the Gail model
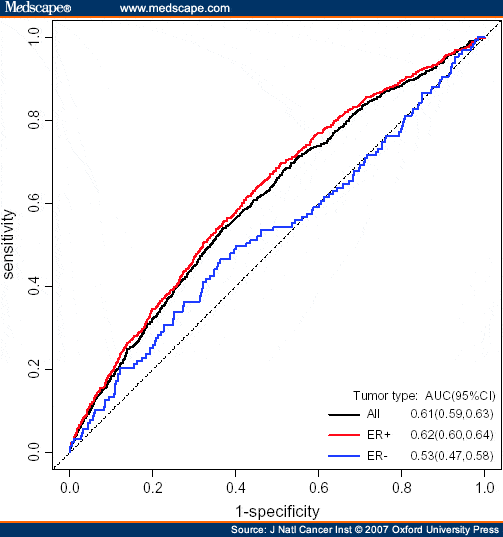
When stratified by geographic region, the pooled sensitivity, specificity and DOR in American and European women were 0.26 , 0.84 and 1.79 , respectively and Deeks funnel plot showed no publication bias . With respect to Asian women, the pooled sensitivity, specificity and DOR were 0.63 , 0.91 and 17.56 , respectively . However, publication bias persisted .
Also Check: Where Is Breast Cancer Most Likely To Spread
Developing A Core Risk Factors Set For Assessment Of Breast Cancer Risk In Iranian Females: A Qualitative Delphi Consensus
2022
Abstract
Background: There have been several methods designed to assess the risk of breast cancer. But according to studies conducted in Iran, the risk to Iranian women could not be accurately calculated with current tools. The aim of this study was to obtain consensus regarding potential breast cancer risk factors in Iran. Methods: A long list of risk factors identified from an integrative review of literature and specialist interviews were used to design a questionnaire survey. In round 2 specialists were asked to rate the importance of each risk factor. Items considered very important after round 2 were carried out to the primary draft of core risk factors set and less important items were excluded. In round 3, respondents were asked to reprioritize moderate important risk factors. The items considered very important in round 3 must be included in core risk factors set.Results: In first round 11 specialists were interviewed and a total of 119 items were obtained of the first rou…
Literature Selection For The Systematic Review And Meta
For the calibration of the Gail model, 435 studies were found in the electronic databases and 10 were manually retrieved. After careful examination, 419 publications were excluded: 62 were duplicated records, 235 were not related, 70 were reviews and 52 were conference abstracts. In addition, two studies were excluded as they focused on the same population but with smaller sample size than other studies . In the end, 24 studies with 29 datasets were included.
After excluding the duplicated records, 356 studies were retrieved for estimating the discrimination of the Gail model. Of these, 311 were excluded in the preliminary screening and 19 were further eliminated by full-text reading. Moreover, seven studies were also excluded as they focused on the same population but with a shorter study period or smaller sample size than other included studies . In total, 26 studies incorporating 29 datasets were included in this meta-analysis.
For the diagnostic accuracy of the Gail model, 455 publications were retrieved at the beginning. After preliminary screening and the full-text reading, 13 studies were finally included .
Fig. 1
Flowchart of study selection in the meta-analyses for estimating the calibration, discrimination and diagnostic accuracy of the Gail model. AUC area under the curve, CI confidence interval, CNKI China National Knowledge Infrastructure
Don’t Miss: What Is Negative Breast Cancer
Menstrual And Obstetric History
Factors that increase the number of menstrual cycles also increase the risk of breast cancer, probably due to increased endogenous estrogen exposure. Such factors include the following:
- Menarche when younger than 13 years
- First full pregnancy when older than 30 years
- Not breastfeeding
- Menopause when older than 50 years
Conversely, late menarche, anovulation, and early menopause are protective, owing to their effect on lowering endogenous estrogen levels or shortening the duration of estrogenic exposure.
Other factors affecting the risk of breast cancer include the following:
- Tobacco exposure
- Diethylstilbestrol exposure in utero
- Alcohol consumption
- Exposure to dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene , a metabolite of the insecticide dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
- Socioeconomic class
- Hair product use
Neoplastic And Benign Risk Factors
Neoplastic conditions that increase the risk of breast cancer include the following:
- Previous breast cancer
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
- Lobular carcinoma in situ
Benign breast conditions that slightly increase the risk of breast cancer include the following :
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Microglandular adenosis
Interestingly, a personal history of cervical cancer is associated with a lower incidence of developing breast cancer.
Also Check: What Is The Average Age To Get Breast Cancer
Family History And Genetic Factors
A family history of breast cancer in a first-degree relative is the most widely recognized breast cancer risk factor, but only 5-10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a known genetic predisposition. Women with a family history of breast cancer in a mother or sister have a 1.5-3 fold increase in the risk of developing breast cancer.
Family history of breast cancer is a heterogeneous risk factor that depends on the number of family members affected and the age at diagnosis, as well as the number of unaffected women in the pedigree. Even in the absence of a known genetic risk factor, the presence of a family history may suggest the presence of an unknown genetic risk, or a shared environmental risk.
A family history of ovarian cancer in a first-degree relative, especially if the disease occurred at an early age , has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer risk.
The family history characteristics that suggest increased risk of cancer are summarized as follows :
- One or more relatives with breast or ovarian cancer
- Breast cancer occurring in an affected relative younger than 50 years
- Male relatives with breast cancer
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
- Ataxia-telangiectasia heterozygotes
- Ashkenazi Jewish descent (2 times greater risk independent of BRCA positivity
- Malignant melanoma
Other rare genetic disorders, such as Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma , are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
How Are The Models Used
1. To identify women who may benefit from risk-reducing medications
The Gail model is used to determine risk for purposes of advising on use of medications to reduce risk. In the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P1 study, women at increased risk for breast cancer were defined as follows: 1) age 35 to 59 years with at least a 1.66% five-year risk for developing breast cancer by the Gail model or 2) personal history of lobular carcinoma in situ or 3) age over 60 years. 13,388 such women were randomized to receive tamoxifen or placebo daily for five years. Tamoxifen reduced the risk of invasive breast cancer by 49% and reduced the risk of noninvasive cancer by 50%.
The reduced risk of breast cancer was only seen for estrogen-receptor expressing tumors. There was a 2.5-fold increase in risk of endometrial cancer in women taking tamoxifen and a decrease in hip and spine fracture risk. Blood clots causing stroke and deep vein thrombosis are increased in women taking tamoxifen .
2. To identify women who may carry a pathogenic mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2
Some models will also calculate the probability of a BRCA1/2 mutation however, most testing guidelines are now criterion based as opposed to probability based. In practical terms, clinical decision-making around genetic testing is rarely based on a priori probabilities.
3. To identify women who meet criteria for high-risk screening MRI
References Cited
You May Like: Where Can I Get Free Breast Cancer Screening
Other Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tools
Some tools, such as the Claus model, use family history to estimate breast cancer risk. Such tools can be used for women who have one or more relatives with breast cancer, or one or more relatives with ovarian cancer.
Other tools, such as IBIS and BOADICEA, use family history and other factors to estimate breast cancer risk.
The BWHS Breast Cancer Risk Calculator tool is based on data from Black women in the U.S. The tool uses a womans personal and family health history as well as her reproductive history to estimate her breast cancer risk.
Epidemiology Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in women, comprising 30% of all womens cancer diagnoses in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates that 281,550 new cases of breast cancer will be diagnosed in women in 2021 . After lung cancer, breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in women, accounting for 15% of cancer-related deaths.
The incidence of breast cancer has consistently outpaced the incidence of all other cancers in women in the US. In 2014-2018, the incidence rate of female breast cancer in the US was 129.1 per 100,000 population. Of note, the incidence of invasive breast cancers decreased between 1999 and 2004, which coincides with and is possibly attributable to better adherence to recommended screening mammography for the general population of women, as well as decreasing use of menopausal hormone replacement therapy .
Worldwide, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women. Although the United States and Western Europe have a five-fold higher number of new cases of breast cancer compared with Africa and Asia, since 1990, the death rate of breast cancer has declined by 24% in the United States . This may be due to increased use of screening mammography and of adjuvant chemotherapy.
Read Also: How Common Is Breast Cancer In Women
The Application Of Gail Model To Predict The Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer Among Jordanian Women
Hikmat Abdel-Razeq
Abstract
1. Introduction
Breast cancer has been the most common cancer affecting women in Jordan . While its incidence appears to be decreasing or leveling off in certain western countries , incidence continues to rise in Jordan. A total of 1187 cases were reported in 2014 compared with only 445 in 1996 . Compared with the West, and despite the recent establishment of early breast cancer detection programs, breast cancer is still diagnosed with more advanced stages where cure rates are low and cost of treatment is high. In addition, breast cancer affects the younger age group the median age of affected Jordanian women is only 51 years, compared with 60 years in western societies . The national early detection program was recently established in Jordan, but with the current logistics and infrastructure, mass screening for breast cancer is not doable.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
Women aged 18 years or older with histologically confirmed diagnosis of breast cancer were included. All women underwent a comprehensive breast cancer risk assessment in which information on known risk factors for breast cancer were collected. It includes demographics family history of breast, ovarian, or any other cancer reproductive history history of benign breast disease , estrogen exposure .
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
Managing Breast Cancer Risk
If Gail Model analysis shows youre at high risk, specialists may recommend additional screening or preventive treatment. Screenings and treatments include:
- Frequent breast exams: A physical breast exam twice each year.
- Annual mammogram: Mammogram once each year, regardless of age.
- Breast MRI: A test using radio waves and a strong magnet to create a detailed image of the breasts.
- Chemoprevention: Taking certain medicines, such as chemotherapy drugs, to help prevent breast cancer.
- Mastectomy: Surgery to remove the breasts to lower breast cancer risk.
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Cancer Of The Breast
Gail Model For Breast Cancer: Why Choose Aurora Baycare Medical Center
We use a sophisticated tool known as the Gail Model to assess breast cancer risk. Our program offers:
- Recognized experts: Our board-certified and fellowship-trained surgeons, oncologists and radiologists are highly trained in determining breast cancer risk.
- Leading-edge diagnostic tools: We use the latest breast imaging techniques for rapid and accurate diagnosis.
- National distinction: The National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers has accredited our program. This accreditation means you can count on us for care that meets or exceeds national standards.
Performance Of The Gail Model After Excluding Studies Published In Chinese
When excluding studies retrieved in the WANFANG, VIP and CNKI databases, no effect was found on the calibration of Gail model 1. The E/O ratios of the Caucasian-American Gail model and the Asian-American Gail model for Asian women were reported as 2.46 and 1.82 , respectively .
The pooled AUC for Gail model 1 was 0.55 . After excluding studies published in Chinese, only one study validated discrimination of Asian-American Gail model 2 and Caucasian-American Gail model 2 for Asian females and the AUCs were shown as 0.54 and 0.55 , respectively .
For the diagnostic accuracy of the Gail model, after excluding studies conducted in China, the pooled sensitivity, specificity and the DOR of the Gail model were 0.24 , 0.85 and 1.79 , respectively. When stratified by different versions of the Gail model, the sensitivity, specificity and the DOR of the Caucasian-American Gail model were 0.25 , 0.85 and 1.89 , respectively. Only one study remained to evaluate the performance of Gail model 1, and the sensitivity and specificity were reported as 0.15 and 0.86 , respectively .
You May Like: Male Breast Cancer Stage 4
Other Risk Assessment Tools
Other risk assessment tools are more appropriate for women who have a history of certain medical conditions. Below is a list of alternative resources for women with a medical history of:
Breast Cancer or Lobular Carcinoma in Situ or Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
- Women with a history of breast cancer have risks of recurrence that depend on the type of breast cancer, its stage at diagnosis, and treatment. A cancer doctor can provide guidance on future risks for breast cancer survivors.
- Women with a history of DCIS have risk of invasive breast cancer that depends on type of treatment for DCIS a cancer doctor can provide information on this risk.
- Women with a history of LCIS can use the IBIS Breast Cancer Risk Evaluation Tool to estimate the risk of invasive breast cancer or DCIS. A cancer doctor can also provide information on the risk.
Treatment with Radiation to the Chest
- Women who received radiation for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma have higher than average risk of breast cancer. These risks are discussed in the scientific manuscript Travis, L.B et al. .
A Known Mutation in Either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 Gene
- Women with a known mutation in either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene can use the BOADICEA model to estimate their breast cancer risk.
Other Rare Breast Cancer-Causing Syndromes, such as Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
- Women with a known or suspected inherited breast cancer-causing syndrome should consult a specialist in medical genetics.
Benefits Of Mammographic Screening
The ACS systematic review also examined the effect of screening mammography on life expectancy. Although the review concluded that there was high-quality evidence that mammographic screening increases life expectancy by decreasing breast cancer mortality, the authors were not able to estimate the size of the increase 23.
You May Like: Mary Ellen Locher Breast Cancer Center
How To Interpret Your Estimated Breast Cancer Risk
The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool was designed to be used by health care providers. So, if you use the tool on your own, it may be hard to understand the results and use the information to make decisions about your care.
If you have questions about your breast cancer risk based on the results of this tool, talk with your health care provider.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for this meta-analysis included the following: studies validating the performance of the original or modified Gail model in women calibration of the Gail model was prospectively estimated focusing on cohort studies that provided the E/O ratio and its 95% confidence interval or offered sufficient data for calculating the expected and observed number of breast cancer discrimination of the Gail model was estimated focusing on the studies providing the C-statistic or AUC and its 95% CI for the Gail model the diagnostic meta-analysis included publications that provided sufficient data for calculating the true positive , false positive , false negative and true negative values of the Gail model, respectively the threshold of the Gail model was limited to 1.67% the sample size should be higher than 100 and the mean follow-up period for the cohort studies should be longer than 1 year and when multiple publications included the same population, studies with larger sample size or longer follow-up period were incorporated and studies with independent validations in subsequent articles were included.
Don’t Miss: Which Type Of Breast Cancer Has The Best Prognosis