Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
02 August 2021
03 April 2020
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Selvi Radhakrishna, Ramesh B. V. Nimmagadda
28 June 2021
Fabio Puglisi, Lorenzo Gerratana, Lucia Del Mastro
11 July 2022
Rachel Yoder, Bruce F. Kimler, Priyanka Sharma
volume 118, pages 1723
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor is reported in 89% of TNBC and is considered an attractive therapeutic target, particularly in BL2 subtype tumors . The expression of this gene results in primary tumorigenesis and metastasis. The EGFR inhibitor gefitinib lowers the proliferation of cancer cells and increases carboplatin and docetaxel cytotoxicity . Several EGFR inhibitors, such as lapatinib and erlotinib, are currently being tested against TNBC, in addition to cetuximab and panitumumab . The synergistic therapeutic approach of monoclonal antibodies and chemotherapeutics is considered to be more effective. This can be exemplified by the combined use of carboplatin and cetuximab, and cisplatin and cetuximab proved to be more efficacious in patients with advanced TNBC . Additionally, tri-inhibitor therapy, including carboplatin, gefitinib, and docetaxel, enhances TNBC cytotoxicity. Cannabidiol inhibits breast cancer metastasis by interfering with the epidermal growth factor pathway . The epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway is presented along with activator and inhibitor points of action, as shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 3. Inhibition of poly polymerase in BRCA-1/2-associated and sporadic cancers .
Can Tnbc Be Prevented
Researchers dont know all the factors that cause triple negative breast cancer. They have identified the BRAC1 gene mutation as one potential cause for triple negative breast cancer. Unfortunately, you cant prevent BRAC1 because you inherit this gene mutation from your parents.
But there are steps that help prevent breast cancers, including TNBC:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- Know your family medical history.
- Monitor your breast health. Studies show 95% of women whose breast cancer was treated before it could spread were alive four years after diagnosis.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about genetic testing for the BRCA gene if you have a family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic or prostate cancer. If you have the BRCA gene, there are steps you can take to prevent breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Does Alcohol Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer
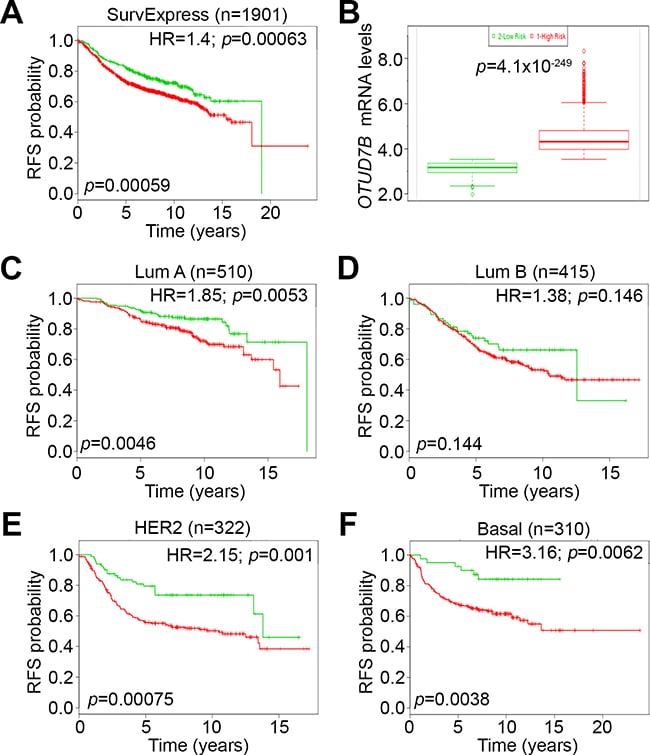
Tumour Size Nodal Status And Tnm Stage
Pathologic T and N status was coded according to AJCC 4th edition for 20052008 and AJCC 6th edition for 20082015 and categorized as pT1 , pT2 , pT3 , pT4, pN0 , pN1 , pN2 , pN3 and pN+ , and combined as pT1pN0, pT2pN0, pT1-2pN+ and pT3-4pN0/+ according to Norwegian treatment guidelines. Patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment were missing pTN status. Pathologic TNM stage was categorized into I, IIA, IIB, IIIA, IIIB or IV . This was combined with a SEER summary stage variable based on clinical data when pTNM missing into a TNM stage variable .
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Don’t Miss: Secondary Cancer After Breast Cancer
Sabcs 202: Adding Capivasertib To Fulvestrant Improves Progression
In patients with hormone receptor -positive, HER2-negative tumours resistant to aromatase inhibitors, addition of the investigational AKT inhibitor capivasertib to fulvestrant doubled the median progression-free survival compared with placebo plus fulvestrant in the phase III CAPItello-291 clinical trial, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, held December 6-10, 2022.
Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer are commonly treated in the first line with an endocrine therapyâsuch as an aromatase inhibitor, which blocks the production of estrogenâalongside a CDK4/6 inhibitor, which stalls the cell cycle.
Eventually, however, most tumours develop resistance to these therapies, and options for further treatment are limited.
âAfter progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors, further endocrine therapies given alone have relatively low efficacy,â said Nicholas Turner, MD, PhD, a professor of molecular oncology at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, who presented the study.
âWe need new treatment options for these patients.â Nicholas Turner
Many HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancers also harbor genetic alterations in AKT pathway genes, such as AKT, PIK3CA, and PTEN, which promote tumour growth and have been implicated in the development of endocrine resistance.
Limitations of this study include immature overall survival data.
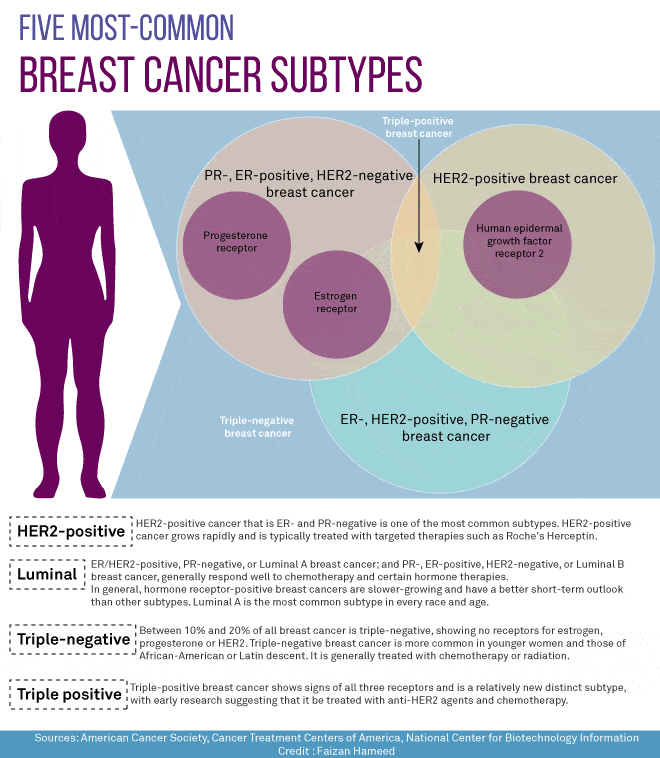
Understanding Her2+ Status And Survival
Doctors use three markers to help define breast cancers and guide treatment. One of those is the HER2 protein. The other two are hormone receptors . When a cancer has none of these, doctors call it triple negative. Until recently, there wasnât much information about how these markers changed survival rates for breast cancer.
A recent study looked at the National Cancer Institute data to see if there were differences in survival for women based on these markers. The study shows there are. Overall, women who have HR+ and HER2- breast cancer do best. But in the later stages, those who have the HER2+ type have better survival rates than those with HER2-. Breast cancers that are triple negative have the lowest survival rates. The 4-year survival rates are as follows:
- HR+/HER2-: 92.5%
- HR-/HER2-: 77.0%
Also Check: Breast Cancer Stages Survival Rates
Emerging New Targets In Er
LoRusso: Samuraciclib with fulvestrant is active in patients who had previously progressed on CDK4/6 inhibitors. In a phase 1/2 trial investigating , patients with TP53 wild-type disease had the best safety outcomes. Samuraciclib is going to be looked at in an upcoming study in combination with oral SERDs, and it has been granted fast-track status by the FDA.
Im also excited about the future of AZD5305 . It is the first of several PARP1 selective agents. Its safety, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic profiles . We did see resistance though many of the patients who responded went on to progress. That may have had to do with prior platinum exposure or prior PARP inhibitor exposure, as platinum resistance lends itself to PARP inhibitor resistance. We need to see whether bringing this drug up earlier in the therapeutic regimen will have a longer-lasting, more durable, sustainable impact. The future for this series of .
History Of Breast Diseases
The initial symptoms of cancer are cancerous lesions in the breast . Regarding the family history of disease, the other risk factors associated with breast cancer are in-situ carcinoma, atypical hyperplasia, proliferative lesions and non-proliferative lesions . Breast cancer risks include a family history of breast cancer and benign lesions .
Also Check: What Causes Hormonal Breast Cancer
Options For Luminal Breast Cancer
with luminal or other types of HR-positive breast cancer receive hormone therapy. Some people call this endocrine therapy.
Triple-negative breast cancer does not respond to hormone therapy because it is HR-negative.
Anti-estrogen therapy
Anti-estrogen therapy works by preventing estrogen from attaching to the estrogen receptors of breast cancer cells.
The four different types of anti-estrogen therapy are:
- selective estrogen-receptor response modulators, such as tamoxifen
- aromatase inhibitors
- estrogen-receptor downregulators, such as fulvestrant
- luteinizing hormone releasing agents, including goserelin and leuprolide , prevent the ovaries from producing estrogen
The type of anti-estrogen therapy a person receives depends on various factors, including:
- the stage of the breast cancer
- whether the person has any other medical conditions
- whether the person has been through menopause
A person usually continues hormone therapy for at least .
Other hormone therapies
In some cases, HR-positive breast cancer may not respond to the above treatments. Consequently, a doctor may recommend one of the following hormone therapies for more advanced cancer:
- progestin medications, such as megestrol
- an anabolic steroid, such as fluoxymesterone
Targeted therapies
Targeted therapies focus on specific genetic mutations that play a role in a cancers growth and spread. These drugs are usually combined with hormone therapy.
Examples of CDK4/6 inhibitors include:
History Of Radiation Therapy
A history of radiotherapy can lead to the development of secondary tumors. This is mainly dependent on the patients state and age . Patients aged < 30 years are considered at higher risk , and radiotherapy treatments, such as multiple-field IMRT and double partial arc techniques can increase the chances of secondary tumors . Radiotherapy in patients with a family history of breast cancer is considered to be at a higher risk .
Recommended Reading: What Do I Do If I Have Breast Cancer
What Makes It Triple
Triple-negative refers to the fact that this type of breast cancer is not fueled by certain substances such as hormones or growth proteins in the body.
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are found in some types of breast cancer. Triple-negative breast cancer doesnt show hormone receptors on the cancer cells and most likely wont respond to breast cancer treatments using hormone blockers to slow the growth of cancer cells like many other types of breast cancer.
Another feature important for classifying breast cancer is the presence of the HER2 protein. Healthy cells have some HER2, but about 20% of breast cancer diagnoses have an excess of this protein, signaling the cells to grow and divide rapidly. Cancers that test positive for an excess of HER2 protein may be effectively treated using targeted therapies that disrupt the function and growth of HER2. Triple-negative cancer patients do not have a significant amount of HER2 protein fueling the cancer.
Data Collection Tool And Quality
The data were collected from patients medical chart with primary breast cancer diagnosis and newly-initiating treatment at the Black Lion Specialized Hospital between January 2012 and January 2018. The data collection tool was developed from previous related literature to assemble necessary information from patients medical files. To maintain the quality of the data, training on data abstraction was given to data collectors and supervisors for 1 day before the actual data collection. Pre-test was done on registrations that were not included in the final study for consistency of understanding the review tools and completeness of data items. The collected data were reviewed and checked for completeness every day and before data entry. All completed data collection forms were examined for completeness and consistency during data management, storage, cleaning, and analysis. Three oncology nurses, who were working on the oncology unit, collected the data. The principal investigator of the study controlled the overall activity.
Recommended Reading: Papillary Thyroid Cancer And Breast Cancer
What Is The Life Expectancy For Each Cancer Stage
Your outlook depends on the stage of your cancer when its discovered. Cancer is staged by number, starting with 0 and going to 4. Stage 0 is the very beginning and stage 4 is the last stage, also called the metastatic stage, because its when cancer has spread to other areas in the body.
Each number reflects different characteristics of your breast cancer. These characteristics include the size of the tumor and whether the cancer has moved into lymph nodes or distant organs, like the lungs, bones, or brain.
Research on survival statistics for people with breast cancer tends to separate participants into categories of women and men.
Survival statistics of women with the major subtypes of breast cancer such as ER-positive, HER2-positive, and triple-negative are grouped together. With treatment, most women with very early stage breast cancers of any subtype can expect a normal life span.
Survival rates are based on how many people are still alive years after they were first diagnosed. Five-year and 10-year survival are commonly reported.
Survival Rates For Her2
Cancer survival statistics are typically reported using a 5-year survival rate. This is the percentage of individuals that are still living 5 years after their diagnosis.
Survival rates can vary based off of the subtype of breast cancer that you have. A publication from the reports 5-year survival rates for HER2-negative breast cancers as:
- 92 percent for HER2-negative, HR-positive breast cancer
- 77 percent for triple-negative breast cancer
Keep in mind that HER2 and HR status arent the only factors that can influence outlook. Other important factors at diagnosis include:
- the stage of the cancer
- the specific type of breast cancer
- your age and overall health
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Spread During Chemo
Relative Survival Rates For Breast Cancer
The National Cancer Institute gives 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer based on how far the disease had spread before a doctor found it.
- Localized : 99%
- Unknown stage: 55%
- All stages: 90%
While these numbers can give you a general idea, they are an average for women with any type of breast cancer. They arenât specific to the HER2+ type. They also come from data that researchers collected from 2010 to 2016, so they donât reflect more recent treatment advances.
Prognosis And Survival For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis . A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Survival is the percentage of people with a disease who are alive at some point in time after their diagnosis. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors.
The doctor will look at certain aspects of the cancer or a characteristic of the person. These are called prognostic factors. The doctor will also look at predictive factors, which influence how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment.
Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a prognosis and a treatment plan just for you. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis and chances of survival.
Doctors use different prognostic and predictive factors for newly diagnosed and recurrent breast cancers. The following are prognostic and predictive factors for both.
Also Check: Is Immunotherapy Used For Breast Cancer
Exposure To Chemicals And Drugs
Females who have been exposed to dreadful carcinogenic chemicals are at higher risk of breast cancer and epigenetic alterations and mutations. Exposure and duration of exposure contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer mutagenesis . Exposure of mammary glands to polychlorinated biphenyl and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane chemicals increases the risk of breast cancer . Furthermore, continuous exposure to organic solvents, insecticides, and oil mist increases the risk of breast cancer . Antibiotics, statins, antidepressants, and antihypertensive drugs can increase the risk of breast cancer. Similarly, NSAIDs that contain aspirin and ibuprofen are considered major risk factors for breast cancer .
Breast Cancer Hormone Receptor Status
Breast cancer cells taken out during a biopsy or surgery will be tested to see if they have certain proteins that are estrogen or progesterone receptors. When the hormones estrogen and progesterone attach to these receptors, they stimulate the cancer to grow. Cancers are called hormone receptor-positive or hormone receptor-negative based on whether or not they have these receptors . Knowing the hormone receptor status is important in deciding treatment options. Ask your doctor about your hormone receptor status and what it means for you.
You May Like: Biopsy For Breast Cancer Results
Predictors Of Breast Cancer Death By Estrogen Receptor Status
In the Cox regression analysis for the incidence of death, estrogen receptor negative women had a higher risk of mortality with an event risk of 95% compared with ER positive in the unadjusted model. And after full adjustments for age, clinical stage, baseline comorbidity, histological grade, surgical margin, node status, type of surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, tumor size, histology type, and place of residence, the mortality event risk was 32% higher among ER negative women .
|
Table 3 Cox Regression Results for Death According to Estrogen Receptor Status |
What Is A Hormone Receptor
Hormones are chemical messengers that circulate in the bloodstream. Hormone receptors are proteins located in and around breast cells. When the corresponding hormone binds to a receptor, it tells the cells how to grow and divide.
In the case of breast cancer, these receptors allow abnormal cells to grow out of control, which results in a tumor.
You May Like: Breast Cancer Hormone Receptor Positive
What Is Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
What Is Triple Negative Early Breast Cancer
Triple negative breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that does not have any of the three receptors commonly found on breast cancer cells the oestrogen, progesterone and HER2 receptors. Around 15% of early breast cancers are triple negative.
Triple negative breast cancer generally responds well to chemotherapy. Five years after diagnosis, people with triple negative breast cancer are no more likely to experience a recurrence of their breast cancer than people with other types of breast cancer. In the longer term , a recurrence is less likely with triple negative breast cancer.
Read Also: How To Support Breast Cancer