How Is Breast Cancer Treated
If the tests find cancer, you and your doctor will develop a treatment plan to eradicate the breast cancer, to reduce the chance of cancer returning in the breast, as well as to reduce the chance of the cancer traveling to a location outside of the breast. Treatment generally follows within a few weeks after the diagnosis.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on the size and location of the tumor in the breast, the results of lab tests done on the cancer cells, and the stage, or extent, of the disease. Your doctor will usually consider your age and general health as well as your feelings about the treatment options.
Breast cancer treatments are local or systemic. Local treatments are used to remove, destroy, or control the cancer cells in a specific area, such as the breast. Surgery and radiation treatment are local treatments. Systemic treatments are used to destroy or control cancer cells all over the body. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are systemic treatments. A patient may have just one form of treatment or a combination, depending on her individual diagnosis.
Over Threefold Higher Risk Of Death Versus Screening
byIan Ingram, Deputy Managing Editor, MedPage Today September 25, 2020
Women diagnosed with interval breast cancers — those detected between routine screenings — had a higher risk for aggressive disease and death, a restrospective study in Canada indicated.
Among women participating in a national screening program, and with a median follow-up of 7 years, breast cancer-specific mortality was more than threefold higher for women diagnosed with interval breast cancers compared to those whose cancers were found on screening, which included a sojourn time of 2 years to account for lead-time bias , reported Saroj Niraula, MD, MSc, of the University of Manitoba in Canada, and colleagues.
The findings highlight the differences in the natural history of these cancers “and highlights inadequacies in current breast cancer screening practice,” the group wrote in JAMA Network Open. “Many of the aggressive and lethal forms of breast cancers either go unnoticed on mammogram or develop in the interval between mammograms.”
Compared to those found on screening, interval cancers were more likely to be high-grade and estrogen-receptor negative , according to the findings.
Adjustments for patients’ age and income did not change the overall findings, nor did sensitivity analyses that extended the sojourn time up to 4 years, though the effect size diminished.
-
Ian Ingram is Managing Editor at MedPage Today and helps cover oncology for the site.
Disclosures
Primary Source
What Is The Chance I Could Die In The Next 5 Years
The average 5-year survival rate for all people with breast cancer is 89%. The 10-year rate is 83%, and the 15-year rate is 78%. If the cancer is located only in the breast , the 5-year survival rate is 99%. More than 70% of breast cancers are diagnosed at an Early Stage.
All survival statistics are primarily based on the stage of breast cancer when diagnosed. Some of the other important factors are also listed below that affect survival.
Stage 0 breast cancer can be also described as a pre-cancer. If you have DCIS you can be quite confident you will do well. DCIS does not spread to other organs. What can be concerning is when an invasive cancer grows back in the area of a prior lumpectomy for DCIS. This type of local recurrence does carry a risk to your life. Luckily, this does not happen frequently. Also, be aware that those who have had DCIS in the past are at a higher risk for developing an entirely new, invasive breast cancer. Take our video lesson on Non-Invasive DCIS to learn more.
Stage I invasive breast cancer has an excellent survival rate. The chance of dying of Stage I breast cancer within five years of diagnosis is 1 to 5% if you pursue recommended treatments.
Stage II breast cancer is also considered an early stage of breast cancer. There is a slightly increased risk to your life versus a Stage I breast cancer. Altogether, the risk of Stage II breast cancer threatening your life in the next 5 years is about 15%.
Read Also: What Are Common Treatments For Breast Cancer
Patient Samples And Geographic Region
These studies follow appropriate ethical standards and are in accordance with and have been approved by IRBs from both the University of Notre Dame and Moi University . The tissue samples were collected with patient consent at Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital , which is the primary academic hospital that serves the entire western Kenya community and is located in the city of Eldoret town , Uasin Gishu district, North of Rift Valley province of Kenya. Uasin Gishu County is home to 894,179 people. Therefore, the the catchment area for MTRH is a fairly large community and represents a large population. Eldoret is surrounded by agricultural regions and is 330 km northwest of Nairobi. The significant distance between Eldoret and Nairobi makes MTRH a highly utilized hospital facility. As a regional hospital, MTRH treats patients not only from western Kenya but also from eastern Uganda and southern Sudan. Accruing patient samples from one hospital is common in related population-focused studies .
What Is Tumor Grading
After surgery to remove the tumor, a doctor will check it and assign a grade to it. The grade depends on how closely the cancer cells resemble normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Low-grade cancer cells are similar to normal breast cells. Higher grade breast cancer cells look more different. They show the cancer is more aggressive.
The doctor will also test for estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors. This test will show whether the female hormones — estrogen and progesterone — influence the cancer cells. If the test is positive, it means hormones cause the cancer cells to grow. In that case, therapies to suppress or block hormones may help treat the cancer.
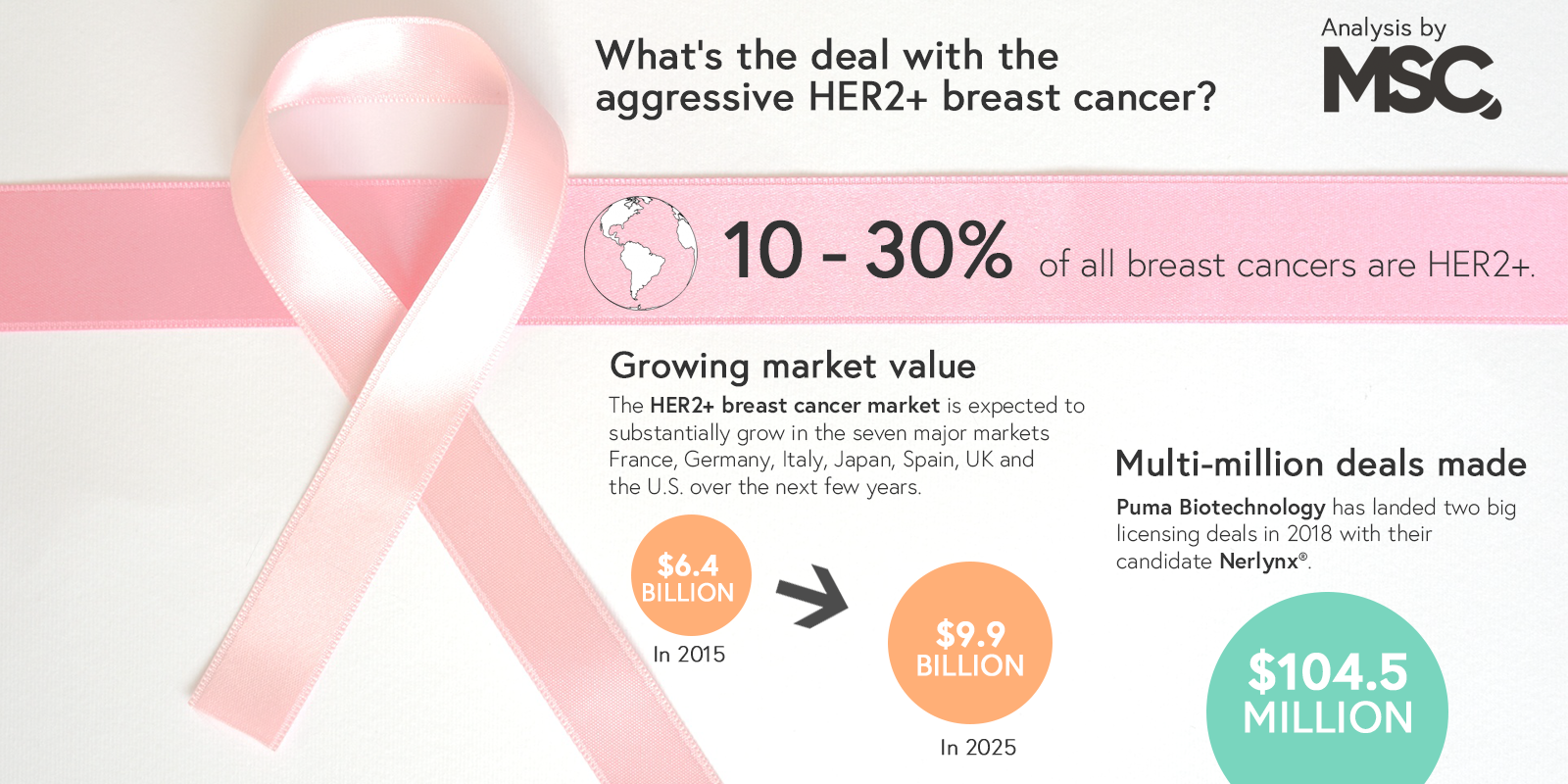
The cancer will also be tested for a gene called HER2. If itâs found, additional drugs like trastuzumab can be used.
Other tests will see if the cancer has spread from the breast to other areas of the body.
Read Also: Estrogen Induced Breast Cancer
What Are The Signs Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may have no signs or symptoms, especially during the early stages. As the cancer grows, you may notice one or more of the following:
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that continues after your monthly menstrual cycle
- A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea
- A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast
- A blood-stained or clear fluid from the nipple
- A change in the feel or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple — dimpled, puckered, scaly, or inflamed
- Redness of the skin on the breast or nipple
- A change in shape or position of the nipple
- An area that is distinctly different from any other area on either breast
- A marble-like hardened area under the skin
You may notice changes when you do a monthly breast self-exam. By doing a regular self-check of your breast, you can become familiar with the normal changes in your breasts.
Risk Factors For Triple
Doctors aren’t sure what makes you more likely to get triple-negative breast cancer. Not many women do — it only affects up to 20% of those who have breast cancer. You’re most at risk for triple-negative breast cancer if you:
- Are African-American or Latina
- Are under 40
- Have what your doctor will call a BRCA mutation , especially the gene BRCA1
Also Check: Breast Cancer Under 40 Prognosis
New Treatment For Aggressive Breast Cancer Announced At Esmo 2020
Scientists say theyve found a practice changing new treatment for a common type of aggressive breast cancer.
The drug Verzenio when added to hormonal therapy can significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in women with a form of early-stage but high-risk breast cancer known as HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, according to data presented September 19 at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual 2020 Congress.
The treatment represents the first new approach in 20 years for this subtype of breast cancer, said the lead author of the study, Stephen Johnston, PhD, a professor with the Royal Marsden Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London.
Hormone receptor positive breast cancer is the most common type of breast cancer. Many patients with early-stage disease are cured using a range of treatments, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hormone treatment.
But about 20 percent of patients have high-risk disease and suffer a recurrence in the same breast or somewhere else in the body within 10 years of the initial treatment, Dr. Johnston said.
Verzenio is a drug known as a CDK4/6 inhibitor. It has shown success in treating metastatic breast cancer in recent years. The new study, a phase 3 trial known as monarchE, tested whether adding the drug to hormone therapy in patients with high-risk early breast cancer lowered the risk of disease recurrence.
Breast Cancer Pathologies Are Predominantly Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
We next examined the pathologies of the breast tissue samples using H& E tissue sections from each tumor. Invasive ductal carcinoma was the predominant pathology seen in the malignant tumors . Additional pathologies represented in the patient population also included mucinous carcinoma, Pagets disease, adenocarcinoma, invasive carcinoma, lobular carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma, papillary carcinoma, invasive cribiform carcinoma, and undifferentiated carcinoma or sarcoma. Some of these tumors had significant inflammatory infiltration or mucinous pathologies associated with the carcinoma .
The pathologies of the non-malignant tissues included normal breast tissue as well as fibroadenoma and adenosis, fibrocystic disease, ductal hyperplasia, atypical ductal hyperplasia, apocrine metaplasia , intraductal papilloma, papillary hyperplasia, tubular adenoma, and lobular hyperplasia . Only one sample had the pathology of ductal carcinoma in situ.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iiia Breast Cancer Prognosis
Certain Breast Cancer Subtypes Have A Better Statistical Prognosis
In general, tubular, mucinous and medullary breast carcinomas have a better prognosis than the other sub-types.
The table below gives a very general approximation of the survival rates that may be associated with the different breast cancer subtypes.
However, please bear in mind that these figures are a rough generalization only and survival will always be determined by the individual characteristics of each breast cancer and each patient.
Nonetheless, the relative aggressiveness of the different breast cancer subtypes can be interpreted from the table.
and is almost always near 100% curable.)
| breast cancer sub-type | |
| Inflammatory breast carcinoma | 65% 35% |
How Much Do Anastrozole And Exemestane Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Studies have shown that both anastrozole and exemestane can lower the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk of the disease.
In one large study, taking anastrozole for five years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 53 percent. In another study, taking exemestane for three years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 65 percent.
The most common side effects seen with anastrazole and exemestane are joint pains, decreased bone density, and symptoms of menopause .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/31/2018.
References
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares women with the same type and stage of breast cancer to women in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of breast cancer is 90%, it means that women who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as women who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Increased Infiltration Of Cd163+ M2 Macrophages Cd25+ T Regulatory Cells And Cd4+ T Helper Cells But Not Cd20+ B Cells Or Cd8+ Cytotoxic T Cells In Kenyan Breast Cancer Tissue
Since the analysis of the pathology of these tumors identified a large number of tumors with inflammatory cell infiltration, we wanted to identify which kinds of inflammatory cells were recruited to the tumor microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Macrophages, B cells, and T cells are among the most common leukocytes found in the stroma of neoplastic breast tissue . We stained the patient breast tissue samples for markers used to distinguish between these inflammatory cell types. We stained and scored patient tissue samples for CD68 , which is a macrophage marker, and CD163 , which stains M2 macrophages. The cancer tissue samples had increased CD68+ cells as well as increased M2 macrophage activation compared to the non-cancerous tissues. These results suggest that the cancer tissues have increased macrophage infiltration, marked by an increase in M2 macrophages.
Fig. 3
To investigate the adaptive immune response in cancer, we stained and quantified the tissue samples for markers of both the cellular and humoral immune responses by immunohistochemistry. We stained tissues for CD4 , CD8 , and CD20 . Cancer tissues had increased recruitment of CD4+ T helper cells . In contrast, CD20 and CD8 positive cells were not differentially recruited to cancer versus non-cancer tissues .
Fig. 4Fig. 5
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Mayo Clinic
A Path To Aggressive Breast Cancer
Baylor College of Medicine
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have followed the progression of breast cancer in an animal model and discovered a path that transforms a slow-growing type of cancer known as estrogen receptor +/HER2+ into a fast-growing ER-/HER2+ type that aggressively spreads or metastasizes to other organs.
The study, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, has implications for breast cancer therapy as it suggests the need to differentiate cancer subtypes according to the path the cells follow. Different paths might be linked to different cancer behavior, which should be taken into consideration to plan treatment appropriately.
“In general, ER-/HER2+ breast cancer is more aggressive than ER+/HER2+ breast cancer, but the ER- type also is heterogenous in its behavior,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Jianming Xu, Baylor’s Gordon Cain Endowed Professor in Cell Biology in the Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology. “In some patients, the ER-/HER2+ cancer responds to therapy and never returns, but in others, the cancer comes back, grows rapidly, aggressively metastasizes to other organs and does not respond to treatment, which causes death. However, what determines the aggressiveness of individual ER-/HER2+ breast cancer is poorly understood.”
Following the path of cancer
Looking into what mediates different behavior in ER-/HER2+ breast cancer
Journal
More Advanced Aggressive Breast Cancers Diagnosed During Covid
Chang SB, et al. Abstract SS2-06. Presented at: San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Dec. 8-11, 2020.
Disclosures: We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
More patients presented with more advanced-stage and aggressive types of breast cancer during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic compared with the same period in 2019 across the Kaiser Permanente Northern California health care system.
The data, presented at the virtual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, also showed that in the 2 months after California instituted its initial stay-at-home order, which reduced screening mammograms and halted elective surgeries, 64% fewer patients were diagnosed than during the year-ago period. Among those who did receive a breast cancer diagnosis, researchers observed reductions in time to surgery and time to chemotherapy.
The results show the ability of a large, integrated system to provide timely care to patients who present with symptomatic disease amid the constraints of the pandemic and highlight the significance of screening in the early detection of breast cancer, according to researchers.
Tang and colleagues sought to evaluate the presentation and treatment patterns of patients with breast cancer included in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system who were diagnosed during the shelter-in-place period.
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Survival Rates For Triple
Triple-negative breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Tissue Fixation And Processing
Harvested specimens were fixed in 10 % neutral buffered formalin, then routinely processed in a Leica TP 1020 tissue processor , and paraffin embedded in Paraplast X-tra . The embedded tissue blocks were transferred from the MTRH hospital to the University of Notre Dame and submitted for further studies following IRB approval from both institutions. The Kenyan tissue samples were subsequently melted down and re-embedded in Surgipath EM_400 paraffin , using a Sakura Tissue TEK5 embedding station. Paraffin sections for all studies were cut at 34 m in thickness on a Leica RM2125-RTS rotary microtome for hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining.
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda