The Role Of Caregivers
Caregivers also play a vital role in helping a person with cancer be as comfortable as possible. To help, a caregiver can:
According to the American Society for Clinical Oncology, in 2018, doctors will diagnose invasive breast cancer in an estimated 268,670 people in the United States.
The ACS state that the 5-year relative survival rate for people with metastatic breast cancer is around 22 percent. This means that people with metastatic breast cancer are 22 percent as likely as people without the condition to live at least 5 years following diagnosis.
However, many factors can affect how long a person with metastatic breast cancer lives for, including:
- the type of breast cancer
- the stage of breast cancer
- where the cancer has spread to
- how well the cancer responds to treatment
- any other health issues that the person has
Everyoneâs outlook is different. It is also important to note that survivals rates are just estimates, and that doctors base these figures on data from at least 5 years ago. Continuing advancements in cancer treatments means that survival rates are improving.
Hormone Therapy For Postmenopausal Women
After menopause, hormone therapy for women with metastatic breast cancer can be an aromatase inhibitor, tamoxifen, fulvestrant or other hormone therapy drug.
If the first hormone therapy stops working and the cancer starts to grow again, a second hormone therapy can be used. If the second drug stops working, another can be tried.
Ovarian suppression isnt helpful for postmenopausal women because their ovaries have already stopped producing large amounts of estrogen.
Breast Cancer Subtypes Hormonal And Her2 Status And Survival Rates
Many research studies over the years have shown that Estrogen-positive breast cancers have better survival rates than all of the Estrogen-negative subtypes.
Progesterone-positive breast cancer also appears to have improved survival rates in comparison to progesterone-negative cases.
A recent research study combines hormone receptivity, HER2 status and stage and found some interesting results:-
For ER+ sub-types survival rates were significantly better than all other subtypes. For example, at stage 1b,
ER+ PR+ HER2- 5-year survival rates were 98.6%ER+ PR- HER2+ 5-year survival rates were 97.3%
The subtype triple negative breast cancer had the worst survival rates over all three stages. At stage I the 5-year survival rate was 92.9% and at stage III 48.9%.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 4 Life Expectancy
Treatment For Physical Symptoms
The American Cancer Society urge that a person should not have to endure pain in the final months and days of life.
Many people find relief with opioid medications, but these can cause side effects such as fatigue and constipation. A person may use opioids in combination with other pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Other drugs, such as antidepressants and antiseizure medications, can also treat certain types of pain.
Doctors can also prescribe medications for nausea and vomiting. Some drugs for treating nausea can make a person drowsy. However, these drugs may help people eat and drink more or simply make it easier for them to function and interact with other people.
Her2 Status And Genetics

Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 is a gene that promotes cancer metastasis. The HER2 gene is a mutation, and it is not inherited. HER2 is a protein that promotes cancer cell growth because acts as a fertilizer, helping the cancer cells to rapidly reproduce. Approximately 20%30% of women with breast cancer have extra copies of this protein.
Having extra HER2 enables a persons breast cancer to be classified as HER2 positive. The primary significance of this is that a specific type of drug can work to block the HER2 receptor in the body. Therefore, knowing the HER2 status can guide therapeutic choices.
You May Like: Does Cancer Hurt In Breast
Can Earlier Detection Of Recurrence Improve Breast Cancer Outcomes
The risk of metastatic relapse weighs heavily on the minds of patients, physicians and caregivers for years, sometimes decades, after treatment of the primary tumour is complete. Nearly 17 million cancer survivors are living in the United States, 3.9 million of whom are breast cancer survivors, and repeated monitoring for cancer recurrence in these individuals presents a significant challenge to healthcare delivery systems. For breast cancer patients, current American Society of Clinical Oncology and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines limit follow-up care to mammography, medical history and physical exam, stating that in the absence of clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of recurrent disease, there is no indication for laboratory or imaging studies for metastases screening.,Despite these guidelines, however, many patients receive high-cost imaging analysis and tumour marker blood tests during routine follow-up exams, exposing them to radiation and increasing healthcare costs.,,, So, what has led to the current precarious balance between the desire to detect recurrence early and clinical guidelines that limit the use of diagnostic tests?
Table 1 Exploiting tumour dormancy as a window of therapeutic opportunity to target MRD.
Functional Stratification: A New Way To Look At Breast Cancer
As mentioned above, current breast cancer staging is heavily dependent upon the evaluation of pathology specimens. However, recent findings suggest that functional classification of breast tumours may become an important addition to risk prediction and prognosis. Results from preclinical animal models suggest that it might be possible to classify breast cancers on a functional basis, as determined by their ability to promote outgrowth of micrometastatic tumour populations at distant sites. Of note, as presented at the recent Nobel Conference on Breast Cancer, we have the ability to use human tumour cell lines and fresh surgical specimens in our xenograft model to test their ability to promote systemic instigation and/or respond to a protumorigenic host systemic environment .
The ability to determine whether or not a given tumour has the potential to promote the dissemination of tumour cells from the primary tumour, support the proliferation of otherwise indolent disseminated cells or activate systemic signalling pathways that recruit bone marrow cells to the developing tumour stroma of a metastatic lesion would have significant implications for treatment strategies . The ability to use tumour tissue in functional assays to predict tumour behaviour may enable more accurate identification of patients with a high likelihood of future relapse, thereby allowing for potentially curative treatment during the therapeutic window in which the disease can be controlled.
You May Like: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Prognosis
Risk Factors For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Any type of breast cancer can metastasize. It is not possible to predict which breast cancers will metastasize. Whether metastasis happens depends on several factors, including:
- The type of breast cancer, such as hormone receptor-positive and/or HER2-positive, or triple-negative breast cancer .
- How the cancer grows. For example, is it a faster growing cancer or a slower growing cancer?
- The stage of the cancer when first diagnosed, including the tumor size and whether cancer was found in nearby lymph nodes.
There is no proven way to completely avoid developing metastatic breast cancer. Research continues to evaluate why metastatic breast cancer occurs and how to prevent, slow, or stop the growth of metastatic cells.
The next section in this guide is Symptoms and Signs. It explains what body changes or medical problems metastatic breast cancer can cause. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Why Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Happen
Most often, metastatic cancer occurs because treatment didnt destroy all the cancer cells. Sometimes, a few cells remain dormant, or are hidden and undetectable. Then, for reasons providers dont fully understand, the cells begin to grow and spread again.
De novo metastatic breast cancer means that at the time of initial diagnosis, the breast cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. In the absence of treatment, the cancer spreads.
There is nothing you can do to keep breast cancer from metastasizing. And metastatic breast cancer doesnt happen because of something you did.
Recommended Reading: Bob Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Treatment For Metastatic Breast Cancer
There are a number of different approaches to treating metastatic breast cancer. Every cancer is unique and treatment can be tailored to your specific circumstances.
Doctors usually treat metastatic breast cancer in any part of the body with systemic medications, which treat cancer throughout the entire body. Chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy are all systemic medications. Local treatments that target a specific part of the body, such as surgery or radiation, are sometimes recommended.
Most treatment decisions depend on where in the body the cancer has spread, the cancers characteristics , and any cancer treatments youve had in the past.
When Can Metastatic Breast Cancer Occur
Most often, metastatic breast cancer arises months or years after a person has completed treatment for early or locally advanced breast cancer. This is sometimes called a distant recurrence.
Some people have metastatic breast cancer when they are first diagnosed . This is called de novo metastatic breast cancer.
Komen Perspectives
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Treatments Stage 3
Agomelatine: 243 Da 2
Agomelatine is a 243 Da pharmaceutical melatonergic agonist at both melatonins receptors, M1 and M2.212 It has many advantages over the use of melatonin itself213,214 In short, these advantages are: 1) agomelatine is Health Canada and EMA approved and marketed as an antidepressant. As such, it is a well-standardized product, as opposed to over-the-counter melatonin preparations which are exempt from the strict standards of approved medicines 2) agomelatine has considerably tighter affinity to both M1 and M2 receptors than does the natural ligand 3) agomelatine has a much longer dwell time in the body than does melatonin, and 4) absorption is more uniform and reliable than is absorption of melatonin.
Although agomelatine is available for import into the USA, it is not FDA approved. Ramelteon is an equally potent melatonergic agonist at M1 and M2 as is agomelatine. Ramelteon is FDA approved and marketed in the USA. It has similar actions and advantages over melatonin as does agomelatine213,215 and can be substituted for agomelatine in the ABC7 regimen.
Elevation of hepatic transaminases is of potential concern when using agomelatine. This requires regular monitoring. Elevation is dose dependent, occurring in ~3% of those receiving 50 mg once at bedtime.216 It is usually reversible.
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer
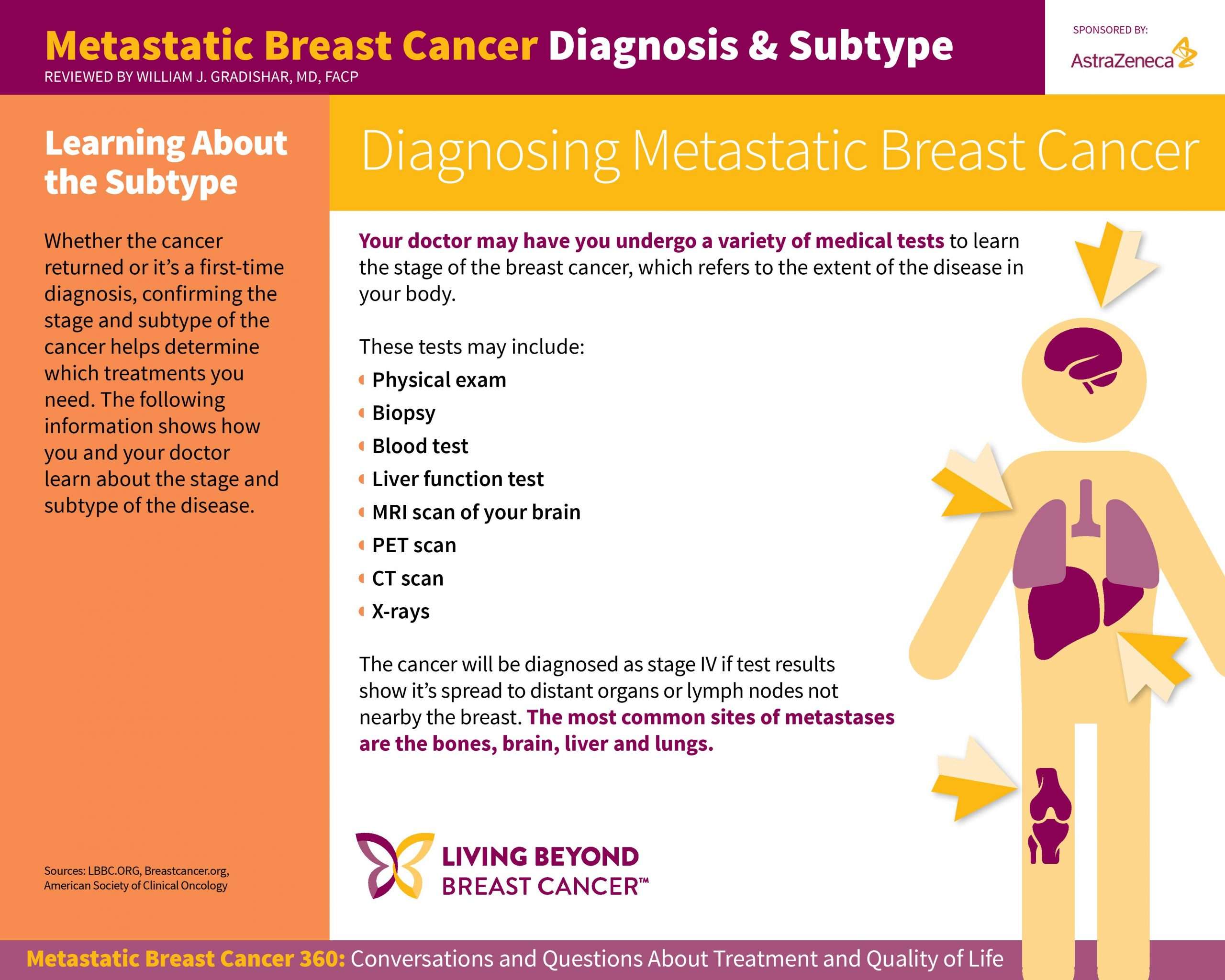
Secondary breast cancer is when cancer cells from a cancer that started in the breast spread to other parts of the body. The cancer that started in the breast is called primary breast cancer.Secondary breast cancer is also called advanced breast cancer or metastatic breast cancer. The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the:
Rarely, breast cancer may spread to other parts of the body, such as the bone marrow, ovaries or lining of the tummy which is called the peritoneum.
Breast cancer can spread to different parts of the body. This does not mean it will go to all these places.
Related Stories & Media
Don’t Miss: Can Weight Gain Be A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
Are New Treatments For Metastatic Cancer Being Developed
Yes. Researchers are now studying new ways to kill or stop the growth of primary cancer cells and metastatic cancer cells. One new area of research includes ways to boost the strength of the immune response against tumors.
Regulatory T-cells and RANKL proteins may play a role in breast cancer metastasisRecent breast cancer research suggests that the bodys regulatory T cells, which are an integral part of the immune response system, may play a key role in metastasis.
It is speculated that the T cells produce a protein which seems to accelerate the spread of breast cancer cells to other areas of the body. The inflammatory protein RANKL seems to influence the T-cells ability to spread cancer cells to distant areas of the body.
It is believed that by interfering with RANKLs ability to interact with the T-cells, the early metastasis of breast cancer cells can be significantly inhibited
Targeted Therapy To Treat Metastatic Breast Cancer
Targeted therapies are treatments that target specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as a protein that allows the cancer cells to grow in a rapid or abnormal way. Targeted therapies are generally less likely than chemotherapy to harm normal, healthy cells. Some targeted therapies are antibodies that work like the antibodies made naturally by our immune systems. Because of this, they are sometimes called immune-targeted therapies.
Learn more about targeted therapies used to treat metastatic breast cancer.
You May Like: Stage 3 Her2 Positive Breast Cancer
Systemic Promotion Of Angiogenesis
The significance of angiogenesis in supporting tumour growth is well established , and the role of the angiogenic switch in facilitating outgrowth of dormant metastases continues to be an active area of investigation . It is noteworthy that the vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor bevacizumab was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of metastatic breast cancer in 2008 . However, approval was revoked in late 2011 after further studies failed to show significant benefit on long-term survival or quality of life . The results of large-scale studies utilizing bevacizumab to treat breast cancer patients were disappointing given the overwhelming laboratory data pointing to a central role for angiogenesis in metastatic growth. Current translational research efforts are now focusing on studies to define more precisely the patient population in which the benefits of anti-angiogenic therapy are likely to outweigh the risks.
How Common Is It
About 155,000 women in the United States live with metastatic breast cancer. Men can have metastatic breast cancer too, but it’s rare.
Only 6% to 10% of women with breast cancer are diagnosed at stage IV. About 20% to 30% of women are diagnosed with an early-stage breast cancer, and then the cancer spreads.
Recommended Reading: Internal Mammary Lymph Nodes Breast Cancer
Does Traditional Classification Of Breast Tumours Apply To Dtcs
Ongoing research continues to demonstrate the underlying genetic and molecular diversity of breast cancer, suggesting that understanding tumourhost interactions may depend upon understanding the unique characteristics of the primary tumour subtype. Traditionally, breast cancer classification relies greatly on the underlying histopathological features of the primary tumour, including expression of the oestrogen and progesterone receptor and amplification of the HER2/neu oncogene product. Under current clinical guidelines, pathology-based review of tumour tissue and determination of tumour staging provide some information about prognosis as well as suggesting treatment options, notably with the use of anti-oestrogen therapies such as tamoxifen or the anti-HER2 agent trastuzumab in appropriate patient populations .
It was recently demonstrated that whole-genome sequencing of circulating cell-free DNA could be used to identify cancer-associated chromosomal markers in a subset of women with breast cancer . Several studies are assessing the utility of evaluating patient blood samples for circulating tumour cells during risk stratification in the diagnosis of early-stage breast cancer and to predict the likely response in patients undergoing pre-operative chemotherapy . There is also some retrospective evidence to suggest that the presence or absence of CTCs in patients with metastatic breast cancer may be of important prognostic significance regardless of molecular subtype .
Trends In Breast Cancer Deaths
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in women. The chance that a woman will die from breast cancer is about 1 in 39 .
Since 2007, breast cancer death rates have been steady in women younger than 50, but have continued to decrease in older women. From 2013 to 2018, the death rate went down by 1% per year.
These decreases are believed to be the result of finding breast cancer earlier through screening and increased awareness, as well as better treatments.
Read Also: 3 Cm Tumor In Breast
Myth #: If An Earlier
Ninety percent of MBC diagnoses occur in people who have already been treated for an earlier-stage breast cancer. Many people are under the impression that remaining cancer-free for five years means that a metastatic recurrence cant happen. However, distant recurrences can occur several years or even decades after initial diagnosis. Factors such as original tumor size and the number of lymph nodes involved can help predict the risk of recurrence.
For example, a 2017 survey of 88 studies involving nearly 63,000 women diagnosed with early-stage, hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer found that the risk of distant recurrence within 20 years ranged from 13% to 41%, depending on tumor size and lymph node involvement.
As KatyK of Idaho comments: that you are cured if you are cancer-free five years after initial diagnosis. I fell for that one myself. When I was diagnosed with MBC 12 years after initial diagnosis I was shocked. I thought I was cured, which to me means all better. Nope! Not even sure medically what cured means.
You May Not Know Im Sick By Looking At Me

I may look perfectly healthy, but Im sick, says Silberman. Treatment is hard. I sleep a lot. I still travel, but its difficult. I just visited a friend in Utah for four days, and it wore me out for two weeks.
Just because someone doesnt look like she has advanced-stage cancer, she can be very sick. It can be an invisible illness, says Silberman. You tell somebody you have cancer, but if you have hair, sometimes they dont believe you.
You May Like: Cancer In Both Breasts Survival Rate
Types Of Recurring Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may recur locally, regionally, or distantly:
Local recurring breast cancer occurs when a new tumor develops in the breast that was originally affected. If the breast has been removed, the tumor may grow in the chest wall or nearby skin.
Regional recurring breast cancer happens in the same region as the original cancer. In the case of breast cancer, this may be the lymph nodes above the collarbone or in the armpit.
Distant recurring breast cancer happens when cancer cells travel to a different part of the body. This new location is far away from the original cancer. When cancer recurs distantly, its considered metastatic cancer.
Not everyone with metastatic breast cancer experiences symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can vary. Symptoms depend on the location of the metastasis and its severity.