How To Tell If Your Cancer Is Back
According to a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, around one in five breast cancer survivors who have had five years of adjuvant therapy have a recurrence within 10 years of treatment.
Areas of recurrenceA recurrence of breast cancer can happen in the same place that the disease originally occurred or in other places if the cancer has metastasized. Breastcancer.org states that the most common areas for a possible recurrence of breast cancer include:
Local recurrence
- The breast or place where the breast was previously
- The chest
- In or on the bones
- On or near the lungs
- The liver
- The brain
Even though the term “breast cancer” makes it seem like this disease can only take place in the breasts, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If you had breast cancer previously and have developed cancer in a different area of your body, it is likely to be another growth of the original cancer, not a different kind.
Signs of recurrenceThe first two years after a patient is treated for breast cancer are the most critical time when it comes to cancer recurrence. Your original cancer diagnosis greatly affects the likelihood that the disease will come back. If you experience any of these signs, go to your doctor immediately:
- A new lump or irregular firmness in the breast
- Nipple discharge
- Redness or inflammation of the skin on a previously cancerous breast
- Nodules on your chest wall
- Thickening of the skin? on or close to a mastectomy scar
Second Opinions For Breast Cancer
Detecting breast cancer can be a complicated process, so health professionals always encourage patients to undergo different tests and get a second opinion prior to beginning any treatment to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Breast tumors and other abnormalities aren’t always cancerous, so breast imaging tests, like mammograms and breast MRI’s, examine deep breast tissue and are necessary to properly diagnose cancer. A second opinion can also help patients determine the best path for treatment, as different specialists can provide different insights for treatment options. Patients should keep records of all visits and diagnoses to maintain evidence for a malpractice lawsuit if a misdiagnosis occurs.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3b Cancer Mean
Are Harmful Variants In Brca1 And Brca2 More Common In Certain Racial/ethnic Populations Than Others
Yes. The likelihood of carrying an inherited mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 varies across specific population groups. While the prevalence in the general population is about 0.2%0.3% , about 2.0% of people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent carry a harmful variant in one of these two genes and the variants are usually one of three specific variants, called founder mutations. Other populations, such as Norwegian, Dutch, and Icelandic peoples, also have founder mutations .
Different racial/ethnic and geographic populations also tend to carry different variants in these genes. For instance, African Americans have BRCA1 variants that are not seen in other racial/ethnic groups in the United States . Most people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent in the United States who carry a BRCA variant have one of three specific variants . In the Icelandic population, a different variant in BRCA1 is common among those who inherit a mutation in BRCA1.
Previous Breast Cancer Or Lump
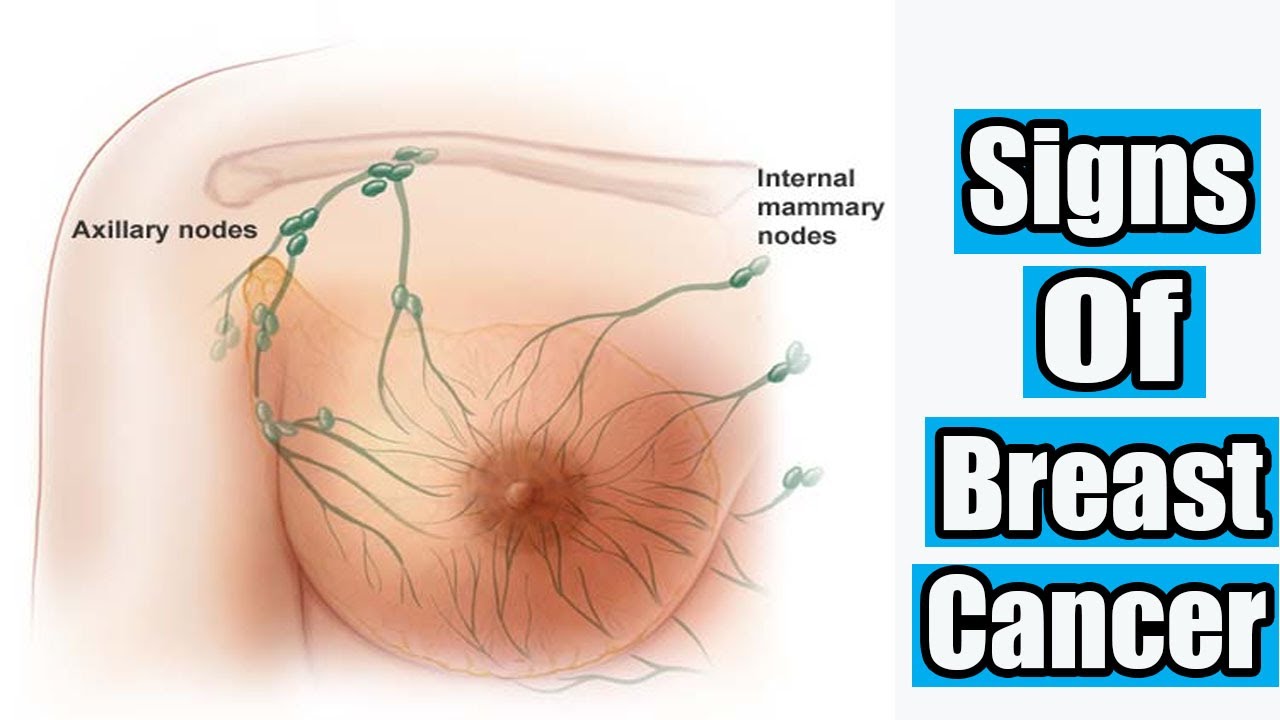
You have a higher risk of developing breast cancer again if you’ve previously had breast cancer. The risk is also higher if you’ve had early non-invasive cancer cell changes in breast ducts. This could have been either in your other breast or in the same breast.
A benign breast lump doesn’t mean you have breast cancer.
Certain changes in your breast tissue, such as cells growing abnormally in ducts , or abnormal cells inside your breast lobules , can make getting breast cancer more likely.
Recommended Reading: Baking Soda And Honey For Cancer
Breast Discomfort And Pain
Women may feel discomfort and pain as the cancer grows and spreads in the breast. Cancer cells do not cause pain but as they grow they cause pressure or damage to surrounding tissue. A large tumor can grow into or invade the skin and cause painful sores or ulcers. It can also spread into the chest muscles and ribs causing obvious pain.
How Were You Informed You Have Cancer
I ask this question as I found out that I had cancer when I opened a letter from the hospital while drinking my morning coffee. The news took some digesting and I was unable to tell anyone ’till my partner got home from work. I am told this is unusual but I have since heard that others have beed told over the phone or called in to see their doctor or asked to come into hospital to discuss the results of their tests. So how did you receive the news that you have cancer?
I saw my GP on the Monday and he faxed a referral through to the breast clinic. I was asked to attend the clinic on the Wednesday and was told by the consultant/surgeon on that day that he was 99% sure I had breast cancer and took a biopsy for confirmation. He phoned me on the Friday with the news that he was now 100% sure. x
Read Also: What Is Stage 3 Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Tests To Determine Specific Types Of Treatment
You’ll also need tests that show whether the cancer will respond to specific types of treatment. The results of these tests can give your doctors a more complete picture of the type of cancer you have and how best to treat it. The types of test you could be offered are discussed below.
In some cases, breast cancer cells can be stimulated to grow by hormones that occur naturally in your body, such as oestrogen and progesterone.
If this is the case, the cancer may be treated by stopping the effects of the hormones, or by lowering the level of these hormones in your body. This is known as “hormone therapy”.
During a hormone receptor test, a sample of cancer cells will be taken from your breast and tested to see if they respond to either oestrogen or progesterone. If the hormone is able to attach to the cancer cells , they’re known as “hormone receptor positive”.
While hormones can encourage the growth of some types of breast cancer, other types are stimulated by a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 .
These types of cancer can be diagnosed using a HER2 test, and treated with medication to block the effects of HER2. This is known as “biological” or “targeted” therapy.
Diet And Lifestyle Changes
Diet
Your GP may suggest some things you can try which might help reduce pain, but theres limited evidence to show these work. These include:
- eating a low-fat diet
- increasing the amount of fibre you eat
- reducing caffeine and alcohol
Well-fitting bra
Wearing a supportive and well-fitting bra during the day, during any physical activity and at night can be helpful.
Relaxation and complementary therapies
Some women have found relaxation therapy useful in reducing their symptoms of cyclical breast pain, such as relaxation CDs or apps, or other complementary therapies such as acupuncture and aromatherapy.
Contraception
If your pain started when you began taking a contraceptive pill, changing to a different pill may help. If the pain continues, you may want to try a non-hormone method of contraception such as condoms, a non-hormonal coil or a cap .
HRT
If your pain started or increased while taking HRT and doesnt settle after a short time, tell your GP.
Evening primrose or starflower oil
Theres evidence that having low levels of an essential fatty acid called GLA can contribute to cyclical breast pain. However, research has shown that taking additional GLA doesnt always help the pain. Despite this, your GP may suggest that you try evening primrose or starflower oil , as some women have found it helps them to feel better generally. Your GP will tell you how much to take and for how long.
Also Check: Hormone Suppression Therapy For Breast Cancer
Breast Lumps Or Lumpiness
Many women find their breasts feel lumpy. Breast tissue naturally has a bumpy texture.
Some women have more lumpiness in their breasts than others. In most cases, this lumpiness is no cause to worry.
If the lumpiness can be felt throughout the breast and feels like your other breast, then its likely normal breast tissue.
Lumps that feel harder or different from the rest of the breast or that feel like a change should be checked. This type of lump may be a sign of breast cancer or a benign breast condition .
See a health care provider if you:
- Find a new lump that feels different from the rest of your breast
- Find a new lump that feels different from your other breast
- Feel something thats different from what you felt before
If youve had a benign lump in the past, dont assume a new lump will also be benign. The new lump may not be breast cancer, but its best to make sure.
How Do I Know If Medical Malpractice Is To Blame For My Misdiagnosis
If you think your breast cancer was misdiagnosed as a result of malpractice, consider scheduling a free consultation with a lawyer who specializes in medical malpractice cases. They should be able to determine if you are qualified and can give you more information about the process based on your individual case.
Don’t Miss: What To Expect During Chemo For Breast Cancer
Being Recalled To The Breast Clinic Following A Routine Screening Mammogram
About four women in a hundred are called back to a breast clinic following routine screening because they need more tests. This happens more often after a womans first mammogram, usually because there are no other mammograms to compare with. Something that may look unusual on your mammogram may be entirely normal for you, and most women who are recalled for assessment will not have breast cancer.
Sometimes you may be recalled because the image taken isnt clear and needs to be repeated. This is called a technical recall and should be made clear in your letter.
If youve been recalled to a breast clinic after a routine mammogram as part of a national breast screening programme, you should receive a letter within two weeks of your mammogram explaining when your breast clinic appointment will be.
Swelling In Or Around Your Breast Collarbone Or Armpit
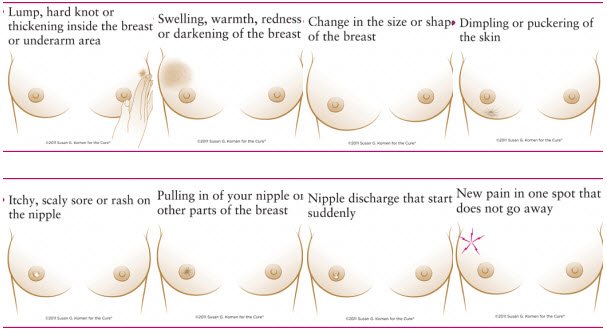
Swelling in these areas can occur for many reasons but may indicate cancer. Breast swelling can be caused by certain types of breast cancer. Swelling or lumps around your collarbone or armpits can be caused by breast cancer that has spread to lymph nodes in those areas. The swelling can occur even before you can feel a lump in your breast. If you have swelling, be sure to let your health care team know as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: What Does Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Mean
How Much Does An Inherited Harmful Variant In Brca1 Or Brca2 Increase A Womans Risk Of Breast And Ovarian Cancer
A womans lifetime risk of developing breast and/or ovarian cancer is markedly increased if she inherits a harmful variant in BRCA1 or BRCA2, but the degree of increase varies depending on the mutation.
Breast cancer: About 13% of women in the general population will develop breast cancer sometime during their lives . By contrast, 55%72% of women who inherit a harmful BRCA1 variant and 45%69% of women who inherit a harmful BRCA2 variant will develop breast cancer by 7080 years of age . The risk for any one woman depends on a number of factors, some of which have not been fully characterized.
Like women with breast cancer in general, those with harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants also have an increased risk of developing cancer in the opposite breast in the years following a breast cancer diagnosis . The risk of contralateral breast cancer increases with the time since a first breast cancer, reaching 20%30% at 10 years of follow-up and 40%50% at 20 years, depending on the gene involved.
Ovarian cancer: About 1.2% of women in the general population will develop ovarian cancer sometime during their lives . By contrast, 39%44% of women who inherit a harmful BRCA1 variant and 11%17% of women who inherit a harmful BRCA2 variant will develop ovarian cancer by 7080 years of age .
Breast Examination After Treatment For Breast Cancer
After surgery
The incision line may be thick, raised, red and possibly tender for several months after surgery. Remember to examine the entire incision line.
If there is redness in areas away from the scar, contact your physician. It is not unusual to experience brief discomforts and sensations in the breast or nipple area .
At first, you may not know how to interpret what you feel, but soon you will become familiar with what is now normal for you.
After breast reconstruction
Following breast reconstruction, breast examination for the reconstructed breast is done exactly the same way as for the natural breast. If an implant was used for the reconstruction, press firmly inward at the edges of the implant to feel the ribs beneath. If your own tissue was used for the reconstruction, understand that you may feel some numbness and tightness in your breast. In time, some feeling in your breasts may return.
After radiation therapy
After radiation therapy, you may notice some changes in the breast tissue. The breast may look red or sunburned and may become irritated or inflamed. Once therapy is stopped, the redness will disappear and the breast will become less inflamed or irritated. At times, the skin can become more inflamed for a few days after treatment and then gradually improve after a few weeks. The pores in the skin over the breast also may become larger than usual.
What to do
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Prognosis
Who Provides Breast Cancer Treatment
A medical team may involve several different health professionals. It may include a GP, a radiologist, an oncologist, a breast care nurse, a surgeon and other allied health professionals such as counsellors and therapists. Having a multi-disciplinary team means a patient can receive the best care possible.
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer is when cancer cells from a cancer that started in the breast spread to other parts of the body. The cancer that started in the breast is called primary breast cancer.Secondary breast cancer is also called advanced breast cancer or metastatic breast cancer. The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the:
Rarely, breast cancer may spread to other parts of the body, such as the bone marrow, ovaries or lining of the tummy which is called the peritoneum.
Breast cancer can spread to different parts of the body. This does not mean it will go to all these places.
Related Stories & Media
Also Check: What Does Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
Further Tests For Breast Cancer
If a diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed, more tests will be needed to determine the stage and grade of the cancer, and to work out the best method of treatment.
If your cancer was detected through the NHS Breast Screening Programme, you’ll have further tests in the screening centre before being referred for treatment.
Living With Secondary Breast Cancer
You will see your cancer doctor or specialist nurse regularly during and after treatment. This means that any symptoms or problems can be managed early on. You may have regular scans to check how the cancer has responded to treatment.
You may need treatment at different times or have ongoing treatment with hormone therapy. There may be long periods when the cancer is controlled and you are getting on with day-to-day life.
We have more about well-being and coping in our information about living with secondary breast cancer.
You may get anxious between appointments. This is natural. It may help to get support from family, friends or a support organisation. Macmillan is also here to support you. If you would like to talk, you can:
You May Like: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
Youll Be Asked To Remove Your Clothing From The Waist Up
Youll stand in front of the mammogram machine.
Your breasts will be placed one at a time on the x-ray machine. The breast will be pressed down firmly on the surface by a clear plate.
At least two pictures of each breast will be taken, one from top to bottom and then a second from side to side to include the part of your breast that extends into your armpit. Youll need to stay in position while the pictures are taken.
Taking the pictures only takes a few seconds.
COVID-19 booster vaccinations
Some people report swelling in the armpit or to the lymph nodes under the arm after a COVID-19 booster vaccination, so you may want to mention to staff at the screening unit if you have recently had a COVID-19 vaccination. Swelling seems to be more common with the Moderna booster vaccination. If you notice any swelling following your booster vaccination, it should disappear within about 10 days, if not, or you have any concerns, contact your GP.
Hormones And Hormone Medicine
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer. However, the risk is a very low one.
Contraceptive pill
Women who use the contraceptive pill have a slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer. The risk starts to decrease once you stop taking the pill. Your risk of breast cancer is back to normal 10 years after stopping.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Ductal Breast Cancer