What Is Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Also called carcinoma in situ, stage 0 is the earliest breast cancer stage. At stage 0, the breast mass is noninvasive, and there is no indication that the tumor cells have spread to other parts of the breast or other parts of the body. Often, stage 0 is considered a precancerous condition that typically requires close observation, but not treatment.
Stage 0 breast cancer is difficult to detect. There may not be a lump that can be felt during a self-examination, and there may be no other symptoms. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis of breast cancer, when the cancer is most treatable. Stage 0 disease is most often found by accident during a breast biopsy for another reason, such as to investigate an unrelated breast lump.
There are two types of stage 0 breast cancer:
Ductal carcinoma in situ occurs when breast cancer cells develop in the breast ducts. Today, stage 0 DCIS is being diagnosed more often because more women are having routine mammogram screenings. DCIS can become invasive, so early treatment can be important.
Menstrual Changes And Fertility Issues
For younger women, changes in menstrual periods are a common side effect of chemo. Premature menopause and infertility may occur and could be permanent. If this happens, there is an increased risk of heart disease, bone loss, and osteoporosis. There are medicines that can treat or help prevent bone loss.
Even if your periods stop while you are on chemo, you may still be able to get pregnant. Getting pregnant while on chemo could lead to birth defects and interfere with treatment. If you have not gone through menopause before treatment and are sexually active, its important to discuss using birth control with your doctor. It is not a good idea for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to take hormonal birth control , so its important to talk with both your oncologist and your gynecologist about what options would be best for you. When women have finished treatment , they can safely go on to have children, but it’s not safe to get pregnant while being treated.
If you think you might want to have children after being treated for breast cancer, talk with your doctor soon after being diagnosed and before you start treatment. For some women, adding medicines, like monthly injections with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analog, along with chemo, can help them have a successful pregnancy after cancer treatment. To learn more, see Female Fertility and Cancer.
Grouping Breast Cancer Stages
There are five stages of breast cancer. These stages are determined based on the tumor size, lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to another part of the body.
Stage 0
Non-invasive or in situ cancer . In Stage 0 there is no evidence of cancer cells breaking out of the part of the breast in which they started. Pagets disease is typically stage 0.
Stage I
Invasive breast cancer with small tumor size and limited nodal involvement.
Stage II
Also Check: Cancer Recurrence After Mastectomy
Where Does Breast Cancer Spread To
Breast cancer cells seem to prefer to settle into:-
- long bones in the arms and legs
- ribs
- skull
With an osteolytic metastasis, the cancer kind of eats away at the bone, creating holes.
With an osteoblastic bone metastasis, the bone mineral density actually increases, but this can cause the bones to fracture more easily. This requires a little more explanation. Breast cancer metastases tend to be lytic when they are untreated, and then they become densely sclerotic as they respond to treatment.
Even if no treatment is given yet, an osteoblastic metastasis from breast cancer generally indicates that the persons own body is trying to fight cancer with some success.
A CT scan may also be used to check for metastasis to the lungs or liver. A CT scan is essentially an X-ray linked to a computer. The breast cancer doctor injects a contrast dye agent into the bloodstream and this makes any cancer cells in the liver and chest easier to see.
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
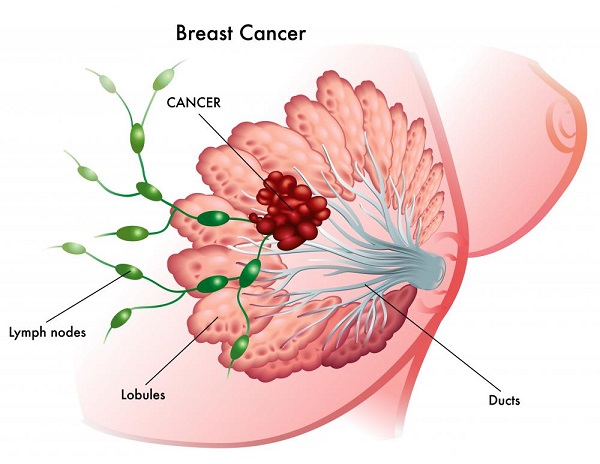
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
You May Like: Hormone Negative Breast Cancer Prognosis
When To Talk With A Doctor
A person should talk with their doctor if they develop any unusual symptoms in or around their breasts. Though it is possible the symptoms are related to another condition, a doctor can help rule out other causes and determine what may be causing the issue.
People assigned female at birth should also follow recommendations for screenings. The recommends the following for screenings:
- 40 to 44: High-risk people in this age group should get screened.
- 45 to 54: Yearly screening.
- Over 55: Screening every 2 years.
How Breast Cancer Spreads And Recurs
Breast cancer is frightening enough without the fear that it could travel to other parts of the body. Metastasis is the term for the spread of cancer. About 250,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer and roughly 40,000 will die from the disease each year. When breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages, many women go on to live cancer-free lives.
Yet for others, the disease is metastatic at the time of diagnosis or later recurs. It’s thought that metastatic disease is responsible for around 66% of the deaths related to breast cancer. How does breast cancer spread or recur?
Recommended Reading: Stage Four Breast Cancer Symptoms
Screening For Breast Cancer
Women aged between 50 and 74 are invited to access free screening mammograms every two years via the BreastScreen Australia Program.
Women aged 40-49 and 75 and over are also eligible to receive free mammograms, however they do not receive an invitation to attend.
It is recommended that women with a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, aged between 40 and 49 or over 75 discuss options with their GP, or contact BreastScreen Australia on 13 20 50.
How Does Staging Relate To Types Of Breast Cancer
In addition to cancer stage, doctors will determine the tumor grade and subtype.
Tumors are graded on a scale of 1 to 3, based on how abnormal the cells appear compared to normal cells. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer, meaning that it tends to be growing quickly.
The subtype is important because treatment and outlook will vary depending on which subtype of breast cancer that you have. Subtypes include:
You May Like: Invasive Breast Cancer Meaning
A Few Tips For Coping
Coping with a new diagnosis is challenging, and you may not know where to begin. One of the best first steps is to ask for help. And when you ask, be willing to receive help. Being diagnosed with breast cancer is not a time to be a hero. Many survivors look back and comment that one of the benefits of being diagnosed is that they learned to accept help, and accepting help can sometimes deepen relationships in a way that’s responding. Being willing to experience the take part of give and take.
Breast Discomfort And Pain
Women may feel discomfort and pain as the cancer grows and spreads in the breast. Cancer cells do not cause pain but as they grow they cause pressure or damage to surrounding tissue. A large tumor can grow into or invade the skin and cause painful sores or ulcers. It can also spread into the chest muscles and ribs causing obvious pain.
Read Also: Breast Duct Cancer Symptoms
Staging And Grading Of Breast Cancer
Knowing the stage and grade of the cancer helps your doctors plan the best treatment for you.
On this page
Your specialist doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes:
- the stage of the cancer
- the grade of the cancer
- whether the cancer has receptors for hormones or a protein called HER2.
This information comes from the results of all the tests you have had, including:
- the biopsy, when the tissue was examined
- other tests that were done on the cells.
Your specialist doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. They will explain how it helps you and your doctor decide on your treatment plan.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. We’re here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
A Note About Depression
A National Academy of Sciences study found that depression is common in breast cancer patients, and it usually develops in the first three months after diagnosis. A 2015 study quantified this, and found that the rates of severe depression was 36%.
Let your healthcare team know that you’re experiencing stress or sadness, so they can suggest counseling and perhaps medication. Depression is more common in people who have previously experienced depression, but is common in people with no history of depression as well.
The alternative therapies mentioned above can be helpful. With support from other survivors, family, friends, and your healthcare providers, you can get through your breast cancer journey more easily.
You May Like: Metastatic Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Progression Of Early Stage Breast Cancer
Left untreated, early stage breast cancer can continue to grow and eventually spread to other areas of the body. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the cancer from progressing, and, in many cases, cure or get rid of it entirely.
Once breast cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, doctors can no longer cure it. Instead, treatment focuses on extending a personâs life, reducing symptoms, and improving quality of life.
Dilemmas Of Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Indeed, there are many serious and personal questions involving stage IV breast cancer. So, overall survival is less likely, and gains from intensive breast cancer treatment are unfortunately rather modest. A serious consideration is, therefore, quality of life during the course of treatment.
These decisions tend to be a dynamic process, based on individual cases, between patients and physicians. Respect needs to be given to the expectations for treatment, the status of the disease and the patient wishes.
Read Also: Can Weight Gain Be A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more:
Breast Cancer Staging Process
Breast cancer staging is determined by how large tumors are, how far theyve spread, and other characteristics like the genetics of the tumor. Your cancer stage can be determined before surgery or after surgery .
Cancers clinical stage is determined through a physical exam, biopsy , and imaging tests. These imaging tests may include X-rays, computed tomography , positron-emission tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , or ultrasound.
After surgery, your breast cancer stage will either be confirmed or updated as a pathologic stage, using the features found and any additional information about how far cancer has spread gathered during surgery.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
What Doesn’t Affect Survival
Just as there are factors associated with a better or worse prognosis, there are some factors that do not appear to make a big difference. These are generally less understood by the general public:
- Aggressiveness of treatment
- Having a positive attitude
The goal of treatment for metastatic breast cancer is often very different than that of early-stage disease, and this can raise anxiety among patients and loved ones of patients. With early-stage breast cancer, the goal is usually to be aggressive in order to reduce the risk that the cancer will come back.
In contrast, with stage 4 disease, the goal is usually to use the minimum amount of treatment possible to control the disease . Studies have found that more aggressive treatment does not improve survival rates but does reduce quality of life.
While having a good attitude may improve your sense of well-being, it has not been shown to affect survival rates. In fact, holding in negative emotions in order to appear positive may be detrimental to your health in general.
Stage Iv Breast Cancers May Be Recurrences Following Initial Treatment
Up to 5% of initial breast cancer diagnoses are of the most advanced or metastatic stage. However, this number has significantly reduced with the implementation of widespread breast cancer screening programs.
Metastatic breast cancer can appear to be a rapid deterioration of a disease that has been present for some time undetected.
But metastatic breast cancer can also be the result of a recurrence of breast cancer after successful initial treatment. Sometimes the terms local and regional recurrence indicate a return of breast cancer to the original tumor site or elsewhere in the breast or contralateral breast.
If the cancer returns in other areas of the body it is a distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
For more detail on Stage IV survival rates, recurrence rates and treatment please see our new post HERE.
Also Check: Stage Zero Breast Cancer Survival Rate
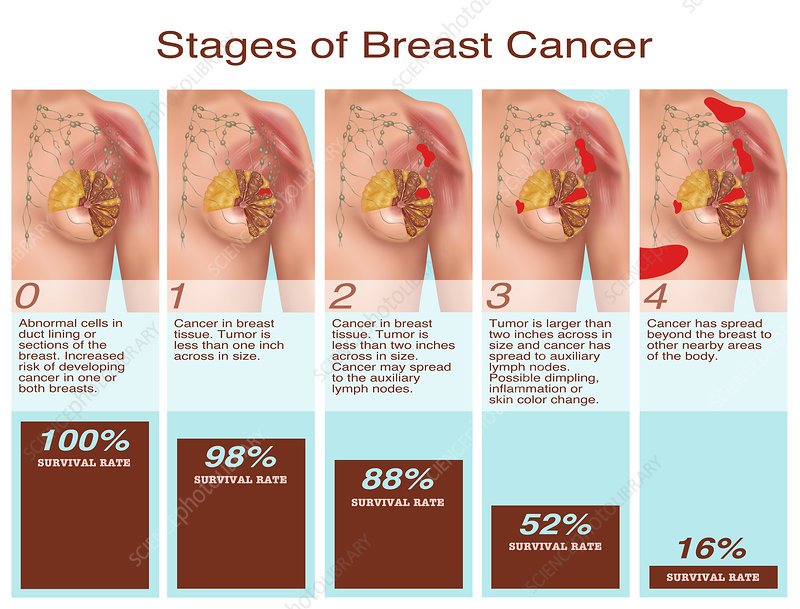
Stages Of Breast Cancer
The stages of breast cancer range from 0 to IV .
The highest stage is any cancer with metastases , no matter the size of the tumor, the lymph node status or other factors. This is known as metastatic breast cancer and is the most advanced stage of breast cancer.
Most often, the higher the stage of the cancer, the poorer the prognosis will be.
The table below lists the TNM classifications for each stage of breast cancer for people who have surgery as their first treatment.
| When TNM is |
| IV |
|
*T1 includes T1mi. **N1 does not include N1mi. T1 N1mi M0 and T0 N1mi M0 cancers are included for prognostic staging with T1 N0 M0 cancers of the same prognostic factor status. ***N1 includes N1mi. T2, T3 and T4 cancers with N1mi are included for prognostic staging with T2 N1, T3 N1 and T4 N1, respectively. |
|
Used with permission of the American College of Surgeons, Chicago, Illinois. The original source for this information is the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, Eighth Edition published by Springer International Publishing. |
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
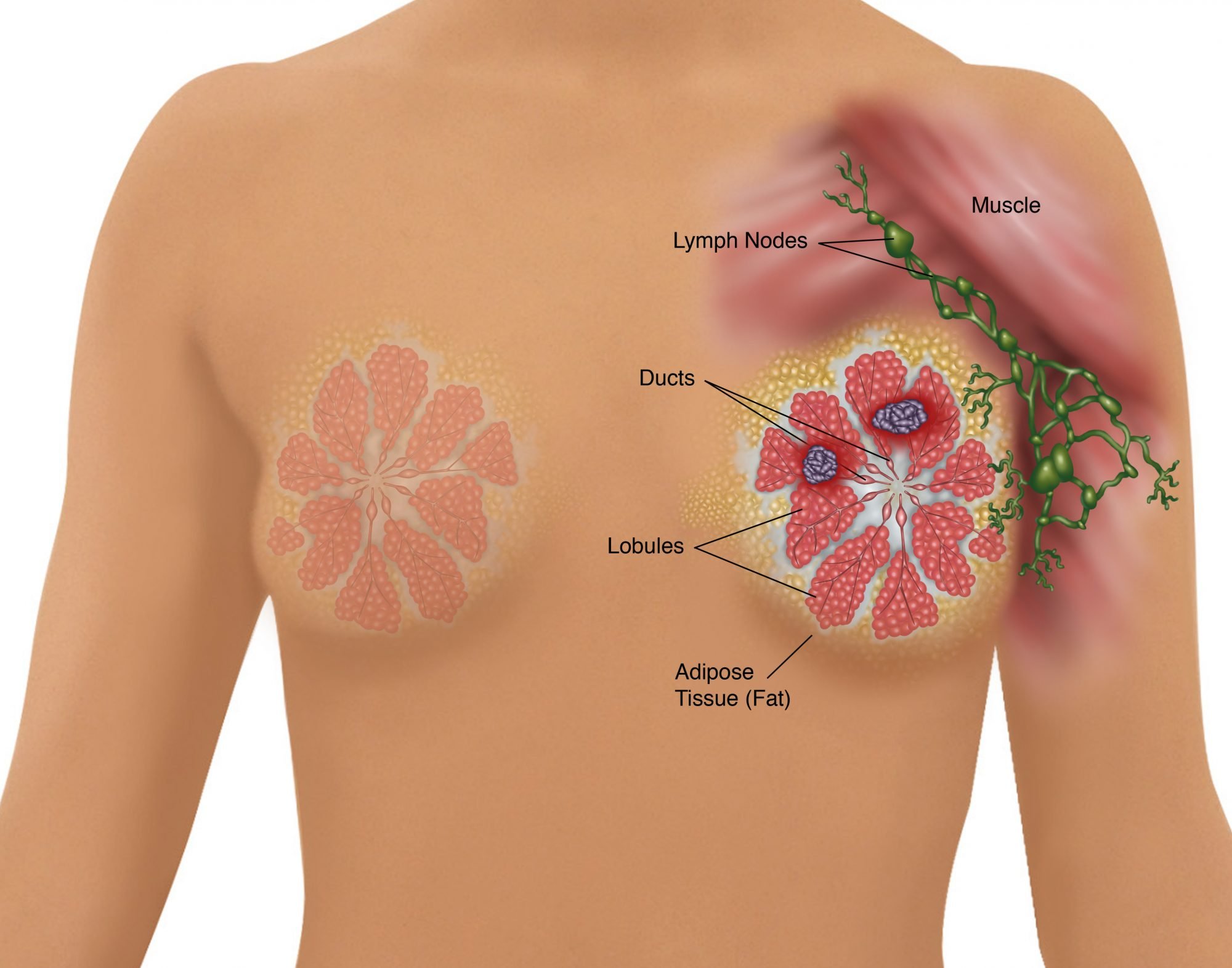
During your regular physical examination, your doctor will take a thorough personal and family medical history. He or she will also perform and/or order one or more of the following:
- Breast examination: During the breast exam, the doctor will carefully feel the lump and the tissue around it. Breast cancer usually feels different than benign lumps.
- Digital mammography: An X-ray test of the breast can give important information about a breast lump. This is an X-ray image of the breast and is digitally recorded into a computer rather than on a film. This is generally the standard of care .
- Ultrasonography: This test uses sound waves to detect the character of a breast lump whether it is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass . This may be performed along with the mammogram.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may or may not request a biopsy to get a sample of the breast mass cells or tissue. Biopsies are performed using surgery or needles.
After the sample is removed, it is sent to a lab for testing. A pathologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing abnormal tissue changes views the sample under a microscope and looks for abnormal cell shapes or growth patterns. When cancer is present, the pathologist can tell what kind of cancer it is and whether it has spread beyond the ducts or lobules .
You May Like: Stage Iii Breast Cancer Prognosis