Drugs That Target Metastasis
Metastatic SuppressorsRecent work has uncovered a group of molecules that act to induce or suppress metastasis without affecting the growth of the primary tumor. Many molecules, termed Metastatic Suppressors, have been identified. These molecules are critical for different stages of metastasis, and may function to inhibit cell death upon loss of cell adhesion, or enhance the ability of cells to migrate through the stroma. Researchers are hopeful that these molecules may prove valuable as anti-cancer/anti-metastasis targets.12
It is important to realize that the majority of current anti-cancer drug studies are conducted using primary or cultured tumor cells, and the efficacy of each drug is measured by its ability to reduce the size of primary tumors or kill cells being grown in laboratories. However, because metastatic suppressors do not affect growth of the primary tumor, it is likely like many potentially useful anti-metastatic drugs have been overlooked. New methods of analyzing the ability of drugs to inhibit metastasis, rather than primary tumor growth, are being developed, and should lead to a useful new class of therapeutic compounds.3
Current research into inhibiting metastasis is focusing on understanding which step of metastasis is the most amenable to therapy. The identification of metastatic suppressor genes has opened up many exciting new potential targets for preventing and inhibiting this deadly event.
Why Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Happen
Most often, metastatic cancer occurs because treatment didnt destroy all the cancer cells. Sometimes, a few cells remain dormant, or are hidden and undetectable. Then, for reasons providers dont fully understand, the cells begin to grow and spread again.
De novo metastatic breast cancer means that at the time of initial diagnosis, the breast cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. In the absence of treatment, the cancer spreads.
There is nothing you can do to keep breast cancer from metastasizing. And metastatic breast cancer doesnt happen because of something you did.
How Breast Cancer Spreads And Recurs
Breast cancer is frightening enough without the fear that it could travel to other parts of the body. Metastasis is the term for the spread of cancer. About 250,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer and roughly 40,000 will die from the disease each year. When breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages, many women go on to live cancer-free lives.
Yet for others, the disease is metastatic at the time of diagnosis or later recurs. It’s thought that metastatic disease is responsible for around 66% of the deaths related to breast cancer. How does breast cancer spread or recur?
Also Check: How I Knew I Had Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Tests To Diagnose Metastatic Breast Cancer
If you have any of the symptoms of metastatic breast cancer, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- blood tests
- whole-body bone scan, with or without X-rays of specific bones
- MRI of the spine or brain
- CT scan of the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and/or brain
- PET scan
- X-ray or ultrasound of the abdomen or chest
- bronchoscopy if you have a constant cough or trouble breathing
- biopsy of any suspicious area
- a “tap,” removal of fluid from the area with symptoms to check for cancer cells a pleural tap removes fluid between the lung and chest wall and a spinal tap removes fluid from around the spinal cord
You can read the following pages for information on symptoms of breast cancer metastasis and diagnosis:
How Are Bone Metastases Treated
Although it is not possible to cure bone metastases, they are not usually life-threatening. Many women enjoy active lives for many years after bone metastases are diagnosed.
Treatments for bone metastases aim to improve your quality of life by reducing symptoms, such as pain or bone fractures. Treatment will depend on:
- which bones are affected
- whether your bones have been weakened and are in danger of breaking
- characteristics of your original breast cancer, such as type of tumour and the type of receptor the tumour had or HER2 receptor)
- other treatments you have had for primary or secondary breast cancer
- systemic cancer treatments which work on the whole body.
Treatments are often very effective in stopping the growth or decreasing the size of cancerous deposits in the bones. Current treatments are not usually able to completely remove all cancer cells from the bones.
There are three types of treatment for bone metastases:
- treatments to control pain
- local treatments for the bones which are directed at a single bone or area
- systemic cancer treatments (such as
- hormone-blocking therapy, HER2-blocking drugs and chemotherapy) which work on the whole body.
Recommended Reading: How Successful Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
How Do Breast Cancers Start
The human body is made of countless cells that reproduce, by splitting, to replace or repair other cells. New cells usually work like their parent cells. Sometimes, however, a new cell has an error. Not all cells with errors are bad some are harmless, or benign. Others, however, reproduce rapidly and harm healthy cells. The offensive cells are said to be malignant because they dont function like healthy parent cells.
Stage Iv Breast Cancers May Be Recurrences Following Initial Treatment
Up to 5% of initial breast cancer diagnoses are of the most advanced or metastatic stage. However, this number has significantly reduced with the implementation of widespread breast cancer screening programs.
Metastatic breast cancer can appear to be a rapid deterioration of a disease that has been present for some time undetected.
But metastatic breast cancer can also be the result of a recurrence of breast cancer after successful initial treatment. Sometimes the terms local and regional recurrence indicate a return of breast cancer to the original tumor site or elsewhere in the breast or contralateral breast.
If the cancer returns in other areas of the body it is a distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
For more detail on Stage IV survival rates, recurrence rates and treatment please see our new post HERE.
Also Check: What Is Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
Genetically Engineered Mice To Study Metastasis
Genetically engineered mice are constructed to model human phenotypes and pathologies. Mutant mice may include transgenes using different delivery methods:
- The use of bacteria-derived tetracycline-inducible system permitting the switching on or off
- Introduction of retro viral mutations
- Introduction of chemically induced mutations
Transgenic mouse models of breast cancer
The mice undergoing the process of transgenesis are known as transgenic mice. A basic transgene has a promoter region, Protein coding sequence, Intron and a stop codon. Mouse mammary tumor virus , is a retro virus that has been a known promoter to cause breast tumors once activated. MMTV is a heritable somatic mutagen whose target range is limited. It harbors a regulatory DNA sequence called the long terminal repeat , which promotes steroid-hormone-inducible transcription. Tumorgenesis that was induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus can also be done by integration of the viral genome. The sites of integration have been known to be critical genes for cellular regulation.Whey acidic protein , is another common promoter used to generate mouse mammary cancer models. For a list of other mammary gland specific promoters and mouse models see.
MMTV-PyMT
MMTV-HER2/neu
Bi-transgenic models
Tri-transgenic models
Treatment Options For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
For women with stage IV breast cancer, systemic therapies are the main treatments. These may include:
- Some combination of these
Surgery and/or radiation therapy may be useful in certain situations .
Treatment can often shrink tumors , improve symptoms, and help women live longer. These cancers are considered incurable.
Read Also: Can I Get Disability For Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Metastasis May Vary Depending On Where The Cancer Has Spread To
Here are some symptoms that vary by locations commonly associated with breast cancer metastasis.
Metastasis in the bone may cause:
- Severe, progressive pain
- Bones that are more easily fractured or broken
Metastasis to the brain may cause:
- Persistent, progressively worsening headache or pressure to the head
- Vision disturbances
- Behavioral changes or personality changes
Metastasis to the liver may cause:
- Jaundice
- Abnormally high enzymes in the liver
- Abdominal pain, appetite loss, nausea, and vomiting
Metastasis to the lungs may cause:
- Chronic cough or inability to get a full breath
- Abnormal chest X-ray
- Chest pain
- Other nonspecific systemic symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can include fatigue, weight loss, and poor appetite, but its important to remember these can also be caused by medication or depression.
If you notice these symptoms, be sure you talk with your physician. They could be important for getting the treatment you need.
Interested in learning more? i3Health is hosting an upcoming webinar Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Applying Treatment Advances to Personalized Care. Learn more here.
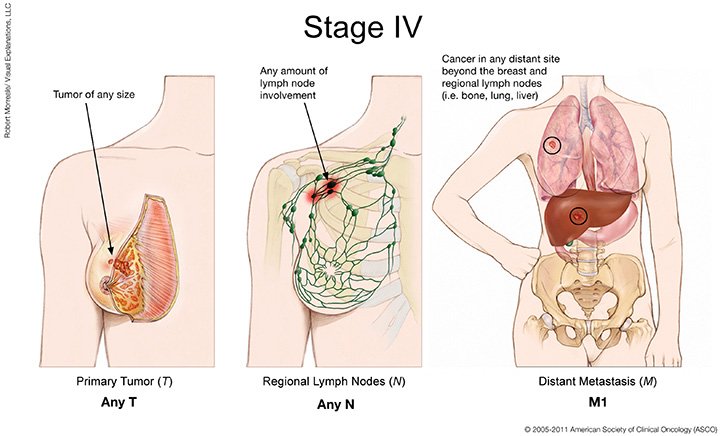
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer and stage 4 metastatic breast cancer are the same thing. Cancer stage refers to how advanced or widespread cancer is in the body. Oncologists, or cancer specialists, use cancer stage to guide important treatment decisions. Your doctor will determine the cancer stage at the time of your initial breast cancer diagnosis. However, breast cancer metastasis can occur years after an original diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Have Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Myth #: People With Metastatic Breast Cancer Look Sick And Lose Their Hair
You dont look sick. You look so well. Why do you still have your hair? Are you sure you have cancer? These are comments that people with MBC report hearing. But there are many treatment options besides chemotherapy, and people often appear well while taking them.
As NancyHB comments: Id much rather be a poster child for how sometimes we can live with, rather than die from, MBC at least for a while. Instead, I find myself defending against people who are increasingly becoming impatient with my lack of cancer-patient appearance. Im grateful for this time of feeling good, and theyre harshing my buzz.
Some people with MBC report that they actually look better than they feel while in treatment. So they sometimes have to let family and friends know that even though they appear fine, they dont feel well.
Shetland Pony notes: If she looks good, she is good. Nope. Many of us suffer from the invisible disability of fatigue. I would venture to say every available treatment causes us some level of fatigue. We struggle to keep up. It may look like we are doing the bare minimum when we are really giving it our all.
JoE777 of Texas adds: The new normals advertised about therapies on TV are deceiving about the side effects. They talk about side effects while women are skipping through life. not looking to show the harsh side effects but think there is something wrong with me that my life is not like that.
How Does Breast Cancer Metastasize
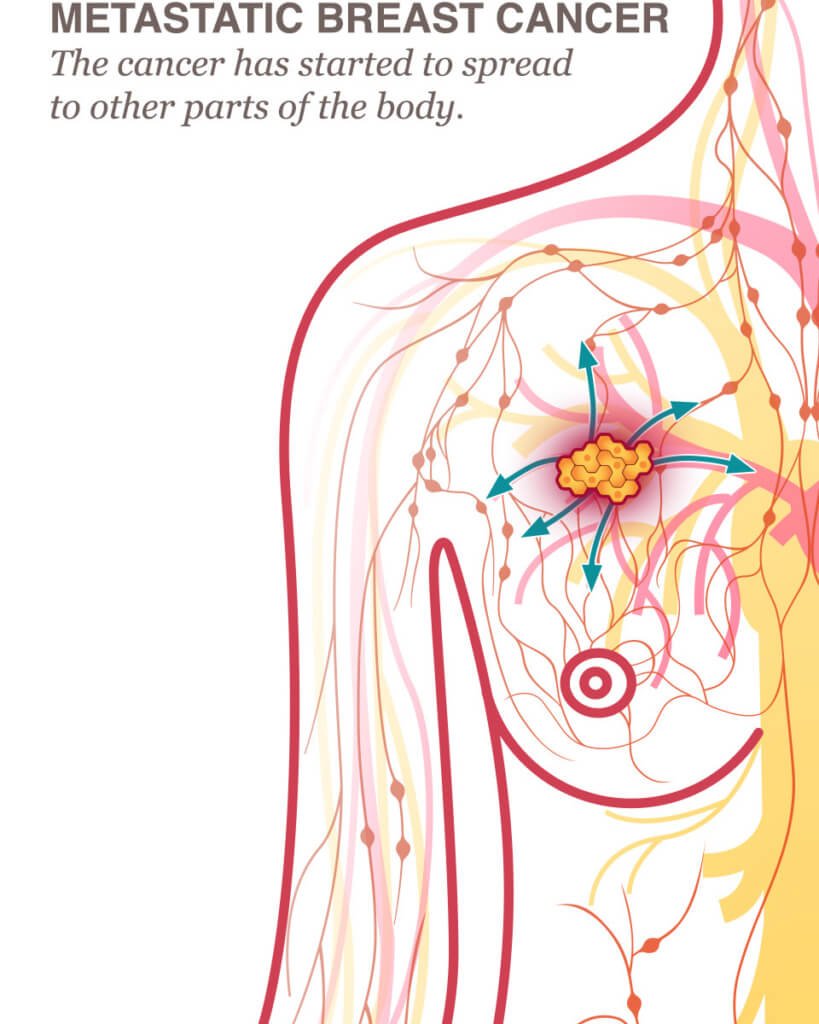
Learn how cancer cells spread from tumors in the breasts to other locations in the body.
Metastasis is the term used to describe the spread of cancer from a primary tumor site to other areas of the body. Any type of cancer can metastasize, including breast cancer. When cancer begins in the breasts and spreads to other areas of the body, this is called metastatic breast cancer, or MBC.
The vast majority of people with MBC are women. The disease is very rare among men, though it does happen.
How does breast cancer metastasize? Cancer spreads when cells break away from the primary tumor and move to other areas of the body. With MBC, this process typically begins with cancer cells from the tumor in the breast moving through the blood vessels or the axillary lymph nodes, which are located in the armpits. Lymph nodes are part of the bodys lymphatic system, a major component of the immune system that produces white blood cells and transports them throughout the body.
Cancer cells can form secondary tumors in the lymph nodes. They can also travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to other locations in the body, where they can continue to reproduce, forming additional secondary tumors. Although breast cancer cells may spread to any part of the body, the most common locations for metastases are the lungs, bones, liver and brain.
Medically reviewed in December 2019. Updated in August 2020.
Don’t Miss: How Does Breast Cancer Look Like
What Are The Subtypes Of Breast Cancer
The three main subtypes of breast cancer are:
Regular Tests Keep Tabs On Your Cancer
Occasionally, you’ll get imaging tests to see inside your body. This is one way that doctors check on how your treatments are working and whether the disease has spread. Common imaging tests include:
- CT scans, where an X-ray machine circles around as you lie on a table
- Bone scans with a shot that helps show areas with cancer. Your doctor may call this scintigraphy.
- PET scans with a special camera and a tracer chemical that goes in your arm by IV
“CT scans examine the chest and abdomen,” says Richard J. Bleicher, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “You can see something on organs like the liver or sometimes the bones.”
Sometimes results are combined for a PET-CT scan. A computer merges the images to find hot spots that may be cancer.
Your doctor will tell you how often you need these tests based on the stage of your disease.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Breast Cancer
What Is Metastatic Cancer
In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed , travel through the blood or lymph system, and form new tumors in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor.
Cancer that spreads from where it started to a distant part of the body is called metastatic cancer. For many types of cancer, it is also called stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When observed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have features like that of the primary cancer and not like the cells in the place where the metastatic cancer is found. This is how doctors can tell that it is cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.
Sometimes when people are diagnosed with metastatic cancer, doctors cannot tell where it started. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown primary origin, or CUP. See the Carcinoma of Unknown Primary page for more information.
Genes Involved In Organ Specific Metastasis
Breast cancer phenotypes periodically express genes in metastasis that are indispensable for the metastatic process. Metastatic diversity is mediated by the activation of genes that act as coupling to organ-specific growth. The growth of lesions at the ectopic site depends on multiple complex interactions between metastatic cells and host homeostatic mechanisms. Lethal protein-protein interactions at the metastatic site aid the survival of adapted cells.
You May Like: How Treatable Is Breast Cancer
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
This is another nuclear scanning technique sometimes used to detect metastases by creating a 3-dimensional picture of your body, with the use of radio waves that show up after an injection. PET scans are not routinely used to look for bone metastases. If your doctor recommends that you have a PET scan you should speak to your doctor about possible costs as it is not usually covered by Medicare.
What Type Of Breast Cancer Is Most Likely To Metastasize
Metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells start in the breast and then multiply, invading the rest of the healthy breast tissue and eventually spreading to lymph nodes under the arms or in other organs.
While all types of breast cancer have the potential to metastasize, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 -positive and triple-negative cancers are more aggressive and more likely to metastasize faster than the other types.
Also Check: What Does Breast Cancer In Men Feel Like
Newly Diagnosed Or Worried About A Symptom
In the days or weeks after a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer, you may feel in turmoil and find it hard to think clearly.
You can read our information for people newly diagnosed with secondary breast cancer, including where to find support.
If you havent been diagnosed but are worried about a symptom, find out more about the signs and symptoms of secondary breast cancer.
How Is Secondary Breast Cancer In The Bone Treated

Treatment for secondary breast cancer in the bone aims to relieve symptoms such as pain, maintain and improve mobility and strengthen the bones, as well as slow down the growth of the cancer.
Treatments can be given alone or in combination.
When making decisions about how the best treatment for you, your specialist team will consider factors such as:
- how extensive the cancer is in the bones
- whether the cancer has spread to other organs
- any symptoms you have
- what treatment youve had in the past
- the features of the cancer
- whether you have been through the menopause
- your general health
Your specialist should discuss any recommendations for treatment with you and take your wishes into account. They will talk with you about your options, explain what the aims of treatment will be and help you weigh up the potential benefits against the possible side effects.
Also Check: Can Cancer Come Back In The Same Breast