How Does Radiation Therapy Work
Radiation therapy uses special high-energy X-rays or particles to damage a cancer cells DNA. When a cancer cells DNA is damaged, it cant divide successfully and it dies.
Radiation therapy damages both healthy cells and cancer cells in the treatment area. Still, radiation affects cancer cells more than normal cells. Cancer cells grow and divide faster than healthy cells and also are less organized. Because of this, it’s harder for cancer cells to repair the damage done by radiation. So cancer cells are more easily destroyed by radiation, while healthy cells are better able to repair themselves and survive the treatment.
The treatment area may include the breast area, the lymph nodes, or another part of the body if the cancer has spread.
Radiation treatments are carefully planned to make sure you receive the greatest benefits and the fewest side effects possible.
There are two main types of radiation therapy used to treat breast cancer:
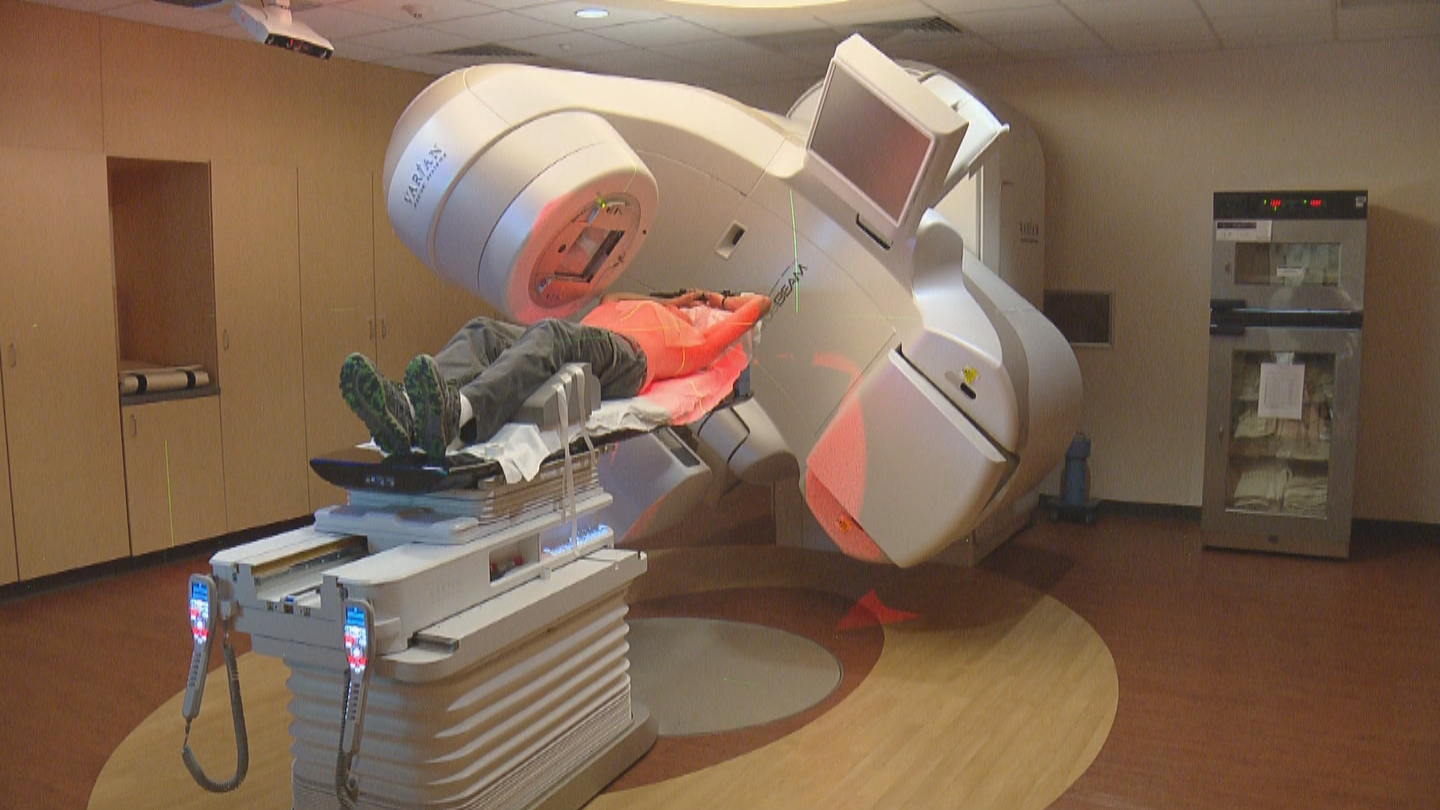
External beam radiation is given by a large machine called a linear accelerator. The machine aims a beam of radiation at the treatment area.
Internal radiation, called brachytherapy by doctors, uses a radioactive substance sealed in seeds or tiny tubes that are placed inside your body directly into the cancer or the place where the cancer was.
Your doctor will look at your pathology report and calculate your risk of breast cancer recurrence based on a number of factors, including:
Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Breast pain and/or swelling
Other long-term side effects of radiation for breast cancer include:
- Changes to the feel or size of the breast
- Difficulty breastfeeding
- Nerve damage that may lead to weakness, numbness or pain
- Damage to the lymph system resulting in lymphedema
- Bone weakness and fractures
Stage Iv Or Recurrent Breast Cancer
Radiation therapy also plays an important role in women with Stage IV or recurrent breast cancer. Chemotherapy and hormonal treatment are the mainstay for women who have Stage IV breast cancer at the time of diagnosis. Local control of breast cancer eradication has less impact on a patients outcome because the major cause of treatment failure is systemic cancer recurrence. Therefore, radiation therapy to the involved breast has not typically been recommended for women receiving systemic chemo-hormonal therapy for metastatic breast cancer.
More recent aggressive chemotherapy treatment of Stage IV breast cancer has been reported to produce long-term survival without cancer recurrence in 15-20% of women. Since these women are not experiencing a systemic cancer recurrence, prevention of cancer recurrence in the breast or lymph nodes is of greater importance. The results of a clinical study in which women with Stage IV breast cancer achieving a complete remission to chemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant and local radiation to the breast was recently reported and raises the question of whether radiation may be beneficial in women with Stage IV breast cancer in complete remission.
Also Check: Cancer Stage 3b
Types Of Radiation Therapy
- External beam radiation is most commonly used to treat breast cancer. A machine outside your body aims a beam of radiation on the area affected by the disease.
- Brachytherapy delivers radiation to the cancer through something implanted in your body.
- Proton therapy sends highly targeted radiation just to your breast tissue and not into your heart or lungs.
Survival Happens Every Day
These rough estimates for how long breast cancer takes to treat can be helpful to plan your life around treatment. More importantly, they provide a light at the end of the tunnel for you to focus on. However, for your daily sanity, it may be better to break down your treatment into smaller parts. Take it from one day to the next. Remember, every day you make it, youre already winning. These factors all affect how long breast cancer takes to treat.
You May Like: Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer Terminal
How Does Radiation Therapy Work / What Is Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy, or radiotherapy, is the use of various forms of radiation to safely and effectively treat cancer and other diseases. Radiation oncologists may use radiation to cure cancer, to control the growth of the cancer or to relieve symptoms, such as pain. Radiation therapy works by damaging cells. Normal cells are able to repair themselves, whereas cancer cells cannot. New techniques also allow doctors to better target the radiation to protect healthy cells.
Sometimes radiation therapy is the only treatment a patient needs. At other times, it is only one part of a patients treatment. For example, prostate and larynx cancer are often treated with radiotherapy alone, while a woman with breast cancer may be treated with surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Radiation may also be used to make your primary treatment more effective. For example, you can be treated with radiation therapy before surgery to help shrink the cancer and allow less extensive surgery than would otherwise be needed or you may be treated with radiation after surgery to destroy small amounts of cancer that may have been left behind. A radiation oncologist may choose to use radiation therapy in a number of different ways. Sometimes the goal is to cure the cancer. In this case, radiation therapy may be used to:
- Shrink tumors that are interfering with your quality of life, such as a lung tumor that is causing shortness of breath.
- Relieve pain by reducing the size of your tumor.
Brachytherapy Via Implantable Device
There are two common types of internal radiation treatment: interstitial brachytherapy and intracavitary brachytherapy.
During interstitial brachytherapy, a doctor will insert several small tubes into your breast where the cancer was removed. The tubes deliver radioactive pellets to that area a few times each day over several days. This procedure is not commonly used today.
Intracavitary brachytherapy is the most common type of internal breast cancer radiation. Your doctor will place a tube-like device into your breast to send radiation to the location of the cancer. The end of the device expands in the breast to keep it in place, while the other end sticks out of the breast. Outpatient treatment sessions happen twice a day for five days.
Side effects of intracavitary brachytherapy may include:
- redness
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer Curable
To Treat Cancer That Has Returned
If a person’s cancer has returned , radiation might be used to treat the cancer or to treat symptoms caused by advanced cancer. Whether radiation will be used after recurrence depends on many factors. For instance, if the cancer has come back in a part of the body that has already been treated with radiation, it might not be possible to give more radiation in the same place. It depends on the amount of radiation that was used before. In other instances, radiation might be used in the same area of the body or a different area. Some tumors do not respond as well to radiation, so radiation might not be used even if they recur.
Internal Breast Cancer Radiation
Internal radiation is a form of partial breast radiation. During the treatment, the physician or surgeon inserts a radioactive liquid using needles, wires, or a catheter in order to target the area where the cancer originally began to grow and tissue closest to the tumor site to kill any possible remaining cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 3 Symptoms
External Radiation Planning And Treatment: What To Expect
Daily external radiation treatments require careful planning to make sure the treatment area is mapped out as accurately as possible and that each day of your treatment goes smoothly.
Heres what you can generally expect from the planning session through your daily treatment routine.
Your first radiation therapy session is called a simulation. It is a planning and practice session, and you receive no radiation.
During the simulation session, your radiation oncology team maps out the area of the breast that needs treatment using imaging such as a CT scan, MRI, or X-ray.
Because it is so important to position the angles of radiation accurately, the simulation session can sometimes last up to an hour.
During the simulation session, your doctor will:
- Advertisement
explain the pros and cons of radiation, the planning and treatment process, and answer any questions or concerns you may have
-
precisely identify the area where you will receive radiation
There are different kinds of immobilization devices. Some look like a cradle others look like a foam box that is shaped to your form. You will not be trapped or closed in. You may be asked to lie down in a custom-shaped mold that just touches your back and sides, or your treatment center may use a “breast board” that places your head, arm, and hand in a fixed position. If you have left-sided breast cancer, you may receive special breathing instructions to help protect your heart during radiation treatment.
Radiation For Metastatic Breast Cancer
For women with breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, radiation can be used to help with symptoms in the affected area. Radiation is particularly useful for cancer that has spread to the bone and is causing pain. Radiation can help relieve pain in approximately 80 percent of women.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Mayo Clinic
How Does Radiotherapy Work
The high-energy radiation that is used during radiotherapy damages the DNA of cancer cells. This stops them from multiplying and spreading, and the body naturally gets rid of them. Healthy cells are also affected by the radiation, but they are able to repair themselves, unlike the cancer cells.Before treatment starts, various body measurements are taken so that the linac machine can pinpoint the radiotherapy in exactly the right place. When I had the treatment, I was given tattoos on my chest, the size of pinheads, for the medical team to line up the machine accurately. Various rulers are also used to ensure that the machine can spare as much healthy tissue as possible by aiming its beams at the cancer only.
Proton Therapy Vs Standard Radiation

Proton therapy and traditional X-ray therapy share many similarities. They both attack and kill cancer cells by damaging the DNA inside the cell. The number of visits needed for proton therapy and X-ray radiation therapy is usually the same.
Traditional X-ray radiation delivers beams of photons that reach both the tumor and the tissues beyond it. When photons damage healthy cells around the tumor, serious side effects can occur.
The protons used in proton therapy have unique properties that healthcare providers can use to deliver the radiation to a specific depth in the body. When proton therapy is administered, all of the energy is released by the time it reaches the tumor site. Because no dosage of radiation goes beyond the tumor, proton therapy has fewer side effects and complications.
Studies show that patients who receive proton therapy are significantly less likely to experience serious side effects than patients who receive X-ray radiation. Patients who undergo proton therapy are also more likely to continue performing their daily activities. The two types of radiation appear to have the same level of efficacy against cancer cells.
It is important to note that proton therapy is more expensive than traditional radiation, and not all insurance policies cover it.
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Feed Cancer
What Happens After Radiation Therapy Treatment Ends
Once treatment ends, you will have follow-up appointments with the radiation oncologist. Itâs important to continue your follow-up care, which includes:
-
Checking on your recovery
-
Watching for treatment side effects, which may not happen right away
As your body heals, you will need fewer follow-up visits. Ask your doctor for a written record of your treatment. This is a helpful resource as you manage your long-term health care.
What To Expect From Your Breast Cancer Radiation Therapy
Many patients with breast cancer will receive radiation therapy at some point in their treatment course. It is often used to decrease the risk of your breast cancer recurring after surgery.
Many patients with breast cancer who are receiving radiation therapy may have had prior therapies for their cancer e.g. a lumpectomy or mastectomy, chemotherapy, or endocrine therapy.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Stage 3 Treatment Options
Easing Worries About Radiation Therapy
Its normal to worry about possible side effects of radiation therapy.
Talk with your health care provider about your concerns.
Your provider may be able to suggest a hospital social worker, patient navigator, psychologist or support group to help ease anxiety related to radiation therapy .
With any standard radiation therapy, you will not be radioactive when you leave the radiation treatment center. You will not pose any radiation risk to your family or your pets.
Learn more about support groups.
Radiotherapy To The Lymph Nodes
Radiotherapy can be given to the lymph nodes under the arm to destroy any cancer cells that may be present there.
It may also be given to the lymph nodes in the lower part of the neck around the collarbone, or in the area near the breastbone .
If radiotherapy to the lymph nodes is recommended, your specialist will explain why.
Also Check: Hormonal Breast Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy
The many side effects of radiotherapy should be explained by your medical team when you are preparing for radiotherapy treatment. The most common side effects of radiation treatment are sore skin, tiredness, localized hair loss, nausea, lack of appetite, sore mouth and difficulty swallowing. Diarrhea is also a common side effect, along with stiff joints and muscles.
There are positive steps you can take to reduce the side effects, such as trying to exercise, which is recommended to limit fatigue exercise will help with mental health too, so it is always worth trying to do some. Make sure you rest as much as possible too, especially if you are feeling extra tired. Sore skin can be treated with regular applications of moisturizer and it only lasts a few weeks after treatment has finished. Your medical team will advise which moisturizer to use, as it varies for each hospital.A healthy diet is important during radiotherapy and you should try and maintain a steady weight as the dose will have been calculated for your body size. You should also try and drink at least two liters of fluid per day.
Anti-sickness tablets can help with nausea and you may receive regular blood tests to check whether you are anemic or have reduced levels of certain cells. You must take care in the sun throughout radiotherapy treatment and for a year afterwards, so ensure you use a high SPF sun cream and stay out of direct sunlight as much as possible.
Does Radiation Therapy Cause Cancer
It has long been known that radiation therapy can slightly raise the risk of getting another cancer. Its one of the possible side effects of treatment that doctors have to think about when they weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment. For the most part, the risk of a second cancer from these treatments is small and is outweighed by the benefit of treating the cancer, but the risk is not zero. This is one of the many reasons each case is different and each person must be part of deciding which kind of treatment is right for them. The risk is different depending on where the radiation treatment will be in the body.
If your cancer care team recommends radiation treatment, its because they believe that the benefits youll get from it will outweigh the possible side effects. Still, this is your decision to make. Knowing as much as you can about the possible benefits and risks can help you be sure that radiation therapy is best for you.
Read Also: Anne Hathaway’s Breasts
Local Recurrence After Mastectomy
Even though the entire breast is removed in a mastectomy, breast cancer can still return to the chest area. If you notice any changes around the mastectomy scar, tell your health care provider.
The more lymph nodes with cancer at the time of the mastectomy, the higher the chances of breast cancer recurrence.
Local recurrence after a mastectomy is usually treated with surgery, and radiation therapy if radiation therapy wasnt part of the initial treatment.
Treatment may also include chemotherapy, hormone therapy and/or HER2-targeted therapy.
You May Like: Hr Positive Her2 Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
Who Gives Radiation Therapy Treatments

During your radiation therapy, a team of highly trained medical professionals will care for you. Your team may include these people:
- Radiation oncologist: This doctor is specially trained to treat cancer with radiation. This person oversees your radiation treatment plan.
- Radiation physicist: This is the person who makes sure the radiation equipment is working as it should and that it gives you the exact dose prescribed by your radiation oncologist.
- Dosimetrist: This person helps the radiation oncologist plan the treatment.
- Radiation therapist or radiation therapy technologist: This person operates the radiation equipment and positions you for each treatment.
- Radiation therapy nurse: This nurse has special training in cancer treatment and can give you information about radiation treatment and managing side effects.
You may also need the services of a dietitian, physical therapist, social worker, dentist or dental oncologist, pharmacist, or other health care providers.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
What Are Some Of The Possible Risks Or Complications
Minor complications include:
- Slight swelling of the breast during radiotherapy. This usually goes away within six to 12 months.
- The skin becomes darker during the course of radiotherapy, similar to tanning from the sun. In most cases, this also fades gradually over six to 12 months.
- Most women will have aches or pains from time to time in the treated breast or the muscles surrounding the breast, even years after treatment. The reason why this happens is not clear however, these pains are harmless, although annoying. They are NOT a sign that the cancer is reappearing.
- Rarely, patients may develop a rib fracture years following treatment. This occurs in less than one percent of patients treated by modern approaches. These heal slowly by themselves.
More serious complications include: