Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections on Cancer.Net:
-
ASCO AnswersFact Sheet:Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to breast cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
ASCO Answers Guide:Get this free 52-page booklet that helps you better understand breast cancer and its treatment options. The booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
Cancer.Net Patient Education Video:View a short video led by an ASCO expert in breast cancer that provides basic information and areas of research.
Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
In its early stages, breast cancer may not cause any symptoms. In many cases, a tumor may be too small to be felt, but an abnormality can still be seen on a mammogram.
If a tumor can be felt, the first sign is usually a new lump in the breast that was not there before. However, not all lumps are cancer.
Each type of breast cancer can cause a variety of symptoms. Many of these symptoms are similar, but some can be different. Symptoms for the most common breast cancers include:
- a breast lump or tissue thickening that feels different than surrounding tissue and has developed recently
- breast pain
- changes to the appearance of the skin on your breasts
- a lump or swelling under your arm
If you have any of these symptoms, it doesnt necessarily mean you have breast cancer. For instance, pain in your breast or a breast lump can be caused by a benign cyst.
Still, if you find a lump in your breast or have other symptoms, you should see your doctor for further examination and testing.
How Is A Breast Cancer Treated
The type of treatment recommended depends on the size and type of the tumor, its growth rate, and the general health of the patient. Treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgery can consist of mastectomy or breast conservation therapy .
- Mastectomy is an operation to remove the entire breast, and usually the entire nipple. Often an axillary sampling is also done which removes the glands under the arm called axillary nodes. The surgeon may evaluate just one or two nodes or may perform a more extensive axillary dissection to check for disease spread. Mastectomy sometimes requires a hospital stay. A drainage tube is sometimes temporarily left in the surgical cavity after a mastectomy to help prevent fluid accumulation. Women who undergo a mastectomy have the option of breast reconstruction.
- BCT surgery removes the breast tumor and a margin of surrounding normal tissues. Radiation therapy usually follows lumpectomy to eliminate any microscopic cancer cells in the remaining breast tissue. The purpose of BCT is to give women the same cure rate they would have if they were treated with a mastectomy but to leave the breast intact, with an appearance and texture as close as possible to what they had before treatment. The surgeon may remove some lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node procedure or axillary dissection at the same time as the lumpectomy procedure or later.
You May Like: 3 Stage Of Cancer
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
Some common risk factors that have been identified to cause breast cancer are as follows.
- Genetic factors: A family history of breast cancer increases the risk of the disease. Breast cancers may occur due to the inheritance of mutated genes. The most affected genes causing breast cancer are BRAC1 and BRAC2. They also increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age. Most women with breast cancer are older than 50 years of age, though a few cases may be seen in younger women.
- Radiation exposure: This could be due to occupational exposure, imaging, or radiotherapy for other conditions to the chest during childhood.
- Early menarche: This is the onset of periods before the age of 12 years.
- Late menopause: Onset of menopause after the age of 55 years.
- Late first pregnancy: Being pregnant after the age of 30 years or never getting pregnant.
- Hormone replacement therapy: Hormonal therapy to reduce the side effects of menopause or for other reasons increases breast cancer risk.
What Are Lymph Nodes

Lymph nodes are small, rounded structures of about 1 mm to 25 mm that are found throughout the body.
The lymph nodes form part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is an important part of the immune system that protects the body from disease and infection. It contains a network of thin tubes called lymph vessels that are found throughout the body. These lymph vessels transport a clear fluid called lymph between the lymph nodes. The lymph nodes filter the lymph to trap or remove substances harmful to the body, such as bacteria or cancer cells. This helps to protect the body from disease or infection. The lymph then passes back to the blood.
The closest lymph nodes to the breast are those in the armpit, which are known as axillary nodes. The axillary nodes drain lymph from nearby tissues, including the breast. There are also lymph nodes under the breastbone and in the neck . The number of lymph nodes varies between different people. There are usually about 15-30 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Because the lymph vessels carry lymph away from the breast, in the case of breast cancer, cancer cells can enter the lymph vessels and begin to grow in the lymph nodes. The axillary nodes are often the first place of cancer spread outside the breast. Usually, surgery is used to remove one or more of the axillary nodes to help check for cancer spread. Cancer found in the lymph nodes affects the staging and treatment of breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Grade 3 Breast Cancer
What Is A Breast Made Of
Both men and women have breasts, but women have more breast tissue than men.
The female breast is made of different components, including:
- lobules, which produce breast milk
- ducts, which carry milk to the nipple
- fatty tissue and connective tissue, which surround the lobules and ducts.
All breasts contain fatty and fibrous tissue. Lobules can also be referred to as glandular tissue. The male breast has ducts but few or no lobes or lobules.
Breast tissue extends from the collarbone to lower ribs, sternum and armpit.
Where Breast Cancer Starts
Breast cancers can start from different parts of the breast. The breast is an organ that sits on top of the upper ribs and chest muscles. There is a left and right breast and each one has mainly glands, ducts, and fatty tissue. In women, the breast makes and delivers milk to feed newborns and infants. The amount of fatty tissue in the breast determines the size of each breast.
The breast has different parts:
- Lobules are the glands that make breast milk. Cancers that start here are called lobular cancers.
- Ducts are small canals that come out from the lobules and carry the milk to the nipple. This is the most common place for breast cancer to start. Cancers that start here are called ductal cancers.
- The nipple is the opening in the skin of the breast where the ducts come together and turn into larger ducts so the milk can leave the breast. The nipple is surrounded by slightly darker thicker skin called the areola. A less common type of breast cancer called Paget disease of the breast can start in the nipple.
- The fat and connective tissue surround the ducts and lobules and help keep them in place. A less common type of breast cancer called phyllodes tumor can start in the stroma.
- Blood vessels and lymph vessels are also found in each breast. Angiosarcoma is a less common type of breast cancer that can start in the lining of these vessels. The lymph system is described below.
To learn more, see Types of Breast Cancer.
You May Like: Stage 2 Breast Cancer
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
There are two different staging systems for breast cancer. One is called anatomic staging while the other is prognostic staging. The anatomic staging is defined by the areas of the body where the breast cancer is found and helps to define appropriate treatment. The prognostic staging helps medical professionals communicate how likely a patient is to be cured of the cancer assuming that all appropriate treatment is given.
The anatomic staging system is as follows:
Stage 0 breast disease is when the disease is localized to the milk ducts .
Stage I breast cancer is smaller than 2 cm across and hasn’t spread anywhere including no involvement in the lymph nodes.
Stage II breast cancer is one of the following:
- The tumor is less than 2 cm across but has spread to the underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 cm .
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm .
Stage III breast cancer is also called “locally advanced breast cancer.” The tumor is any size with cancerous lymph nodes that adhere to one another or to surrounding tissue . Stage IIIB breast cancer is a tumor of any size that has spread to the skin, chest wall, or internal mammary lymph nodes .
Stage IV breast cancer is defined as a tumor, regardless of size, that has spread to areas away from the breast, such as bones, lungs, liver or brain.
What Is A Tumor
When cells divide when new cells are not needed, too much tissue is formed. This mass of extra tissue, called a tumor, can be benign or malignant.
-
Benign tumors:
-
Are rarely a threat to life
-
Do not come back in most cases
-
Do not spread to other parts of the body and the cells do not invade other tissues
Malignant tumors:
May be a threat to life
Can invade and damage nearby tissues and organs
Metastasize – cancer cells can break away from a malignant tumor and enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system to form secondary tumors in other parts of the body
Read Also: Non Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Causes Of Breast Cancer: How Did This Happen
When youre told that you have breast cancer, its natural to wonder what may have caused the disease. But no one knows the exact causes of breast cancer. Doctors seldom know why one woman develops breast cancer and another doesnt, and most women who have breast cancer will never be able to pinpoint an exact cause. What we do know is that breast cancer is always caused by damage to a cells DNA.
Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low . Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells.Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.
Metabolic markers
Don’t Miss: What Is Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Can Tnbc Be Prevented
Researchers dont know all the factors that cause triple negative breast cancer. They have identified the BRAC1 gene mutation as one potential cause for triple negative breast cancer. Unfortunately, you cant prevent BRAC1 because you inherit this gene mutation from your parents.
But there are steps that help prevent breast cancers, including TNBC:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- Know your family medical history.
- Monitor your breast health. Studies show 95% of women whose breast cancer was treated before it could spread were alive four years after diagnosis.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about genetic testing for the BRCA gene if you have a family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic or prostate cancer. If you have the BRCA gene, there are steps you can take to prevent breast cancer.
Cell Changes And Cancer
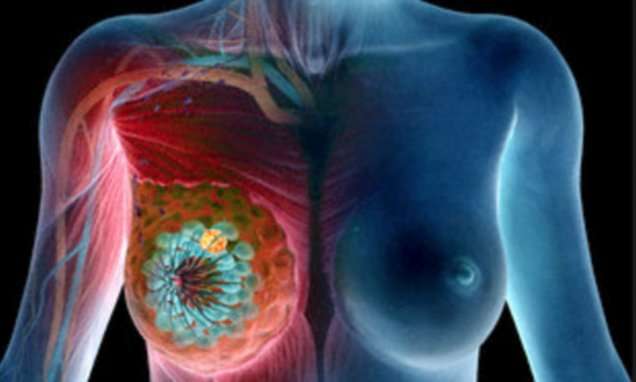
All cancers begin in cells. Our bodies are made up of more than a hundred million million cells. Cancer starts with changes in one cell or a small group of cells.
Usually, we have just the right number of each type of cell. This is because cells produce signals to control how much and how often the cells divide. If any of these signals are faulty or missing, cells might start to grow and multiply too much and form a lump called a tumour.
A primary tumour is where the cancer starts. Some types of cancer, called leukaemia , start from blood cells. They don’t form solid tumours. Instead, the cancer cells build up in the blood and sometimes the bone marrow
For a cancer to start, certain changes take place within the genes of a cell or a group of cells.
You May Like: Is Weight Gain A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
Who Does Breast Cancer Affect
Breast cancer mainly affects older women.
Most breast cancers occur in women over the age of 50. And the older you are, the higher your risk.
Men can also get breast cancer, but this is rare. Most men who get breast cancer are over 60.
Breast cancer is caused by a combination of our genes, environment and lifestyles. Find out more about breast cancer causes.
How Breast Cancer Starts
The breast is a highly complex part of the human body. The female breast goes through many changes over a lifetime from birth, puberty, pregnancy and breastfeeding, right through to menopause.
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, understanding the anatomy of the breast and the role each part has to play can be helpful to understand your diagnosis. It can also help you talk to your doctor about surgery and other treatment options.
In this piece we cover:-Understanding Breast Anatomy-Normal Breast Changes Through Life-How Does Cancer Start in the Breast?-How Does Cancer Spread Beyond the Breast?-Symptoms of Breast Cancer
You May Like: Breast Duct Cancer Symptoms
Previous Breast Cancer Or Lump
If you have previously had breast cancer or early non-invasive cancer cell changes in breast ducts, you have a higher risk of developing it again, either in your other breast or in the same breast.
A benign breast lump does not mean you have breast cancer, but certain types of breast lumps may slightly increase your risk of developing cancer.
Some benign changes in your breast tissue, such as cells growing abnormally in ducts , or abnormal cells inside your breast lobes , can make getting breast cancer more likely.
What Causes Breast Cancer Growth
There is much that we know and much that we have yet to understand. However, we do know that cancer spreads in three important ways:
You May Like: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In Teenagers
Breast Examination After Treatment For Breast Cancer
After surgery
The incision line may be thick, raised, red and possibly tender for several months after surgery. Remember to examine the entire incision line.
If there is redness in areas away from the scar, contact your physician. It is not unusual to experience brief discomforts and sensations in the breast or nipple area .
At first, you may not know how to interpret what you feel, but soon you will become familiar with what is now normal for you.
After breast reconstruction
Following breast reconstruction, breast examination for the reconstructed breast is done exactly the same way as for the natural breast. If an implant was used for the reconstruction, press firmly inward at the edges of the implant to feel the ribs beneath. If your own tissue was used for the reconstruction, understand that you may feel some numbness and tightness in your breast. In time, some feeling in your breasts may return.
After radiation therapy
After radiation therapy, you may notice some changes in the breast tissue. The breast may look red or sunburned and may become irritated or inflamed. Once therapy is stopped, the redness will disappear and the breast will become less inflamed or irritated. At times, the skin can become more inflamed for a few days after treatment and then gradually improve after a few weeks. The pores in the skin over the breast also may become larger than usual.
What to do
Other Types Of Cancer That Occur In The Breast
Most cancers that occur in the breast are breast cancers .
In rare cases:
- Other types of cancer such as lymphomas and sarcomas can occur in the breast
- Cancers from other parts of the body can spread to the breast and mimic breast cancers
Other types of tumors in the breast can be benign or malignant .
Because these cancers are not carcinomas, treatment is different than treatment for breast cancer.
For more information on other cancers that can occur in the breast, such as lymphomas, sarcomas and phyllodes tumors, visit the National Cancer Institute website.
*American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2020. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society, 2020.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Invasive Breast Cancer