How Else Can I Reduce My Risk For Cancer
The following may help reduce the risk of developing cancer:
- Choose a healthy diet to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Eat more vegetables, fruits and whole grains and eat less red and processed meats. These actions may reduce the risk of developing many types of cancer and other diseases.
- Do not smoke. If you currently smoke, quit. Avoid exposure to second hand smoke. For more information on quitting smoking, visit the NYS Smokerâs Quitline at www.nysmokefree.com or call 1-866-NY-QUITS.
- Talk with your health care provider about recommended screenings for other types of cancer.
Who Is Margaret Gates
Margaret Gates, an assistant professor of epidemiology at State University of New York at Albany, was a little surprised by the differences, too. She told Quartz that a number of factors could explain the difference. For instance, treatment regimes in the US may be more aggressive than across the Atlantic.
What Is Cancer Prevalence
Cancer prevalence is defined as the number of living people who have ever been diagnosed with cancer. It includes people diagnosed with cancer in the past as well as those who were recently diagnosed. It does not include the number of people who may develop cancer in their lifetime.
Cancer prevalence is determined by how often a cancer occurs and by how long people normally live after diagnosis . This means prevalence counts are highest for the most common cancers with the longest survival. And, a common cancer with shorter survival may have a lower prevalence count than a less common cancer with longer survival.
For example, although lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in people in the United States, the prevalence count for lung cancer is lower than that for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, a less common cancer. This is because people with non-Hodgkin lymphoma survive longer than those with lung cancer, so there are more people living after a diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma than after a diagnosis of lung cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Your Breasts Removed Without Cancer
Breast Cancer Mortality Rates Worldwide
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality among women in most countries in the world .
Its estimated more than 680,000 breast cancer deaths occurred worldwide in 2020 .
Rates of breast cancer mortality vary around the world
Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer mortality among women in developing countries .
Breast cancer is the second most common cause of cancer mortality among women in developed countries .
List Of People With Breast Cancer
This list of notable people with breast cancer includes people who made significant contributions to their chosen field and who were diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives, as confirmed by public information. Diagnosis dates are listed where the information is known.
According to the United StatesNational Cancer Institute, an estimated 192,370 new cases and 40,170 deaths would occur in the United States in 2009.
Don’t Miss: Encouraging Words For Breast Cancer Patients
What Is The Average American Womans Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer During Her Lifetime
Based on current incidence rates, 12.9% of women born in the United States today will develop breast cancer at some time during their lives . This estimate, from the most recent SEER Cancer Statistics Review , is based on breast cancer statistics for the years 2015 through 2017.
This estimate means that, if the current incidence rate stays the same, a woman born today has about a 1 in 8 chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer at some time during her life. On the other hand, the chance that she will never have breast cancer is 87.1%, or about 7 in 8.
For men born in the United States today, the lifetime risk of breast cancer is 0.13%, based on breast cancer statistics for the years 2015 through 2017. This means that a man born today has about a 1 in 800 chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer at some time during his life.
What About Breast Cancer In Men
Breast cancer in men is rare less than 1 percent of all breast cancer cases but it can still occur, according to the ACS. A mans risk of getting breast cancer during his lifetime is about
The stages of breast cancer relate to how much the cancer has grown and how far its spread. Generally, the earlier breast cancer is diagnosed and treated, the higher the chances for long-term survival.
| Stage 0 | This is a precancerous stage with no invasive cancer cells. |
| Stage 1 | The tumor is small and localized to the breast. There may be a small amount of cancer in nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage 2 | The tumor is still localized to the breast but is larger and may have spread to several nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage 3 | This stage includes cancers that have spread to the skin, chest wall, or multiple lymph nodes in or near the breast. |
| Stage 4 | This is metastatic breast cancer, meaning its spread to one or more distant parts of the body, most commonly to the bones, lungs, or liver. |
The stages of breast cancer are based on the following factors:
- whether the lymph nodes contain cancer cells
- whether the cancer has metastasized, meaning its spread to other, more distant parts of the body
Since 2018, the following factors have also been used to determine breast cancer stage:
- whether the cancer cells have hormone receptors and need estrogen or progesterone to grow
- whether the cancer cells have the HER2 protein that helps them grow
- tumor grade, meaning how aggressive the cells look under the microscope
You May Like: Breast Cancer Society Of America
Metastatic Breast Cancer At Diagnosis
Most often, metastatic breast cancer arises months or years after a person has completed treatment for early or locally advanced breast cancer.
Some people have metastatic breast cancer when they are first diagnosed. This is called de novo metastatic breast cancer. In the U.S., 9 percent of men have metastases when they are first diagnosed with breast cancer .
Learn more about metastatic breast cancer.
Do Some Groups Experience Higher Rates Than Others
Cancer death rates differed by cancer type, sex, racial and ethnic group, and residence in an urban or rural county. Healthy People 2030 objectives include reducing death rates for lung cancerexternal icon to 25.1 deaths per 100,000 population, colorectal cancerexternal icon to 8.9 deaths per 100,000 population, female breast cancerexternal icon to 15.3 deaths per 100,000 female population, and prostate cancerexternal icon to 16.9 deaths per 100,000 male population.
| Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| 19.3 | 18.2 |
NOTES: Deaths were classified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Cancer deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes C00-C97 . Rates were age-adjusted to the 2000 US standard population. Urban/rural status was based on county of residence, classified using the 2013 NCHS Urban-Rural Classification Scheme for Counties.
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
In 2019
- 1,115 children younger than 15 years old died of cancer.
- 9,084 adolescents and young adults between 15 to 39 years old died of cancer.
- 153,928 adults between 40 to 64 years old died of cancer
- 435,462 adults who were 65 years old or older died of cancer.
Note: Age was not recorded for 12 deaths.
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
You May Like: Is Pain Associated With Breast Cancer
What Can I Do To Reduce My Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer
To help reduce the risk of getting breast cancer:
- Be aware of your family history and discuss any concerns with your health care provider.
- Discuss the use of hormone replacement therapy with your health care provider.
- If possible, breastfeed your baby. Studies have shown that breastfeeding for longer periods of time lowers the risk of getting breast cancer.
- Stay at a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Discuss the risks and benefits of medical imaging, such as CT scans, with your health care provider to avoid unnecessary exposure to ionizing radiation.
Regular check-ups and screening tests can find breast cancer at an earlier stage, when treatment works best. The most important action women can take is to have routine breast cancer screenings. For more information on breast cancer screening, call the Cancer Services Program at 1-866-442-CANCER or visit the website at www.health.ny.gov/diseases/cancer/services/.
Giuliana Rancic Tv Personality Underwent A Double Mastectomy
The former E! News host and star of E!’s Giuliana & Bill show revealed she had been diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer in October 2011. The then 36-year-old Giuliana Rancic had gotten a mammogram before receiving another round of IVF treatment for infertility when her doctor discovered the tumor. In December 2011, she underwent a double mastectomy and reconstructive surgery.
Rancic refused to let her diagnosis get in the way of having children. She and her husband had a son via a surrogate in August 2012. She also launched Fab-U-Wish, an initiative that grants fashion, beauty, and celebrity-themed wishes to women undergoing treatment for breast cancer, which she now operates in partnership with the nonprofit organization The Pink Agenda.
Don’t Miss: How Many Stages Of Breast Cancer Are They
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
There are many different signs and symptoms of breast cancer, so regularly checking your breasts for anything different or new is important.
The earlier breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. Getting to know what your breasts look and feel like normally means its easier to spot any unusual changes and check them with your doctor. Common breast cancer signs and symptoms include:
- A lump or swelling in the breast, upper chest or armpit. You might feel the lump, but not see it.
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- A change in skin texture i.e. puckering or dimpling of the skin
- A change in the colour of the breast – the breast may look red or inflamed
- Rash, crusting or changes to the nipple
- Any unusual discharge from either nipple
Over a third of women in the UK do not check their breasts regularly for potential signs of breast cancer.
According to a YouGov survey commissioned by Breast Cancer Now, a third of those who do check their breasts for possible signs and symptoms dont feel confident that they would notice a change.
Asked what stops or prevents them from checking their breasts more regularly, over half forgetting to check, over a third not being in the habit of checking, a fifth not feeling confident in checking their breasts, not knowing how to check , not knowing what to look for and being worried about finding a new or unusual change .
Some factors are outside our control, including:
Who Is Mainly Affected By Breast Cancer

Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women, second only to skin cancer. Its most likely to affect women over the age of 50.
Though rare, men can also develop breast cancer. Approximately 2,600 men develop male breast cancer every year in the United States, making up less than 1% of all cases.
Transgender women are more likely to develop breast cancer compared to cisgender men. Additionally, transgender men are less likely to develop breast cancer compared to cisgender women.
What age does breast cancer occur?
Breast cancer is most often diagnosed in adults over the age of 50, but it can occur at any age.
What race is most affected by breast cancer?
Overall, women who are non-Hispanic white have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race or ethnicity. Women who are non-Hispanic Black are almost as likely as non-Hispanic white women to develop the disease. Statistically, women who are Asian, Hispanic or Native American are the least likely to develop breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Is Intraductal Breast Cancer
Cut From The Same Clot
Died Suddenly can serve as a teachable moment for those of us who study the post-COVID-19 anti-vaccination movement, to help us recognize its traits and see its progression.
We witness motivated reasoning: starting from the conclusion that the vaccines cannot be safe and looking for evidence that matches the conclusion. We see a thick coating of after the fact, therefore because of it, as anybody dying from 2021 onwards is said to be the victim of a vaccine that can kill you instantly, with a delay, or simply worsen a pre-existing condition. The VAERS scare tactic is also briefly adopted, as the database of bad things that happened after getting a vaccine is easily trawled for hits.
Meanwhile, a military whistleblower tells us that deaths are up 40% in the 18-to-64 age group, pointing the finger at the vaccines. Except that its not the vaccines its the COVID-19 pandemic itself. From blood clots to excess mortality, everything caused by the virus is blamed on the vaccines.
Meanwhile, the movie throws everything onto the conspiracy cork board, with Jeffrey Epstein, Anthony Fauci, Justin Trudeau, Greta Thunberg, and Bill Gates flashing before our eyes, next to mentions of MKUltra and a clip from that infamous Sasquatch hoax video.
The anti-vaccination movement no longer sees itself as merely opposing an industry its vociferations are a clarion call for divine salvation.
How Has The Risk Of Being Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Changed In Recent Years
For a woman born in the 1970s in the United States, the lifetime risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer, based on breast cancer statistics from that time, was just under 10% .
The last five annual SEER Cancer Statistics Review reports show the following estimates of lifetime risk of breast cancer, all very close to a lifetime risk of 1 in 8:
- 12.83%, based on statistics for 2014 through 2016
- 12.44%, based on statistics for 2013 through 2015
- 12.41%, based on statistics for 2012 through 2014
- 12.43%, based on statistics for 2011 through 2013
- 12.32%, based on statistics for 2010 through 2012
SEER statisticians expect some variability from year to year. Slight changes may be explained by a variety of factors, including minor changes in risk factor levels in the population, slight changes in breast cancer screening rates, or just random variability inherent in the data.
Selected Reference
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 19752017, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, , based on November 2019 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2020.
Related Resources
- Reviewed:December 16, 2020
Want to use this content on your website or other digital platform? Our syndication services page shows you how.
Read Also: Does Breast Cancer Hurt Before Diagnosis
Breast Cancer Screening And Covid
The COVID-19 pandemic caused many people to miss their mammograms. If you are due for a mammogram, do not wait. Call your health care provider to schedule your appointment as soon as you can. If you are having any symptoms of breast cancer, call your health care provider right away. Getting a mammogram regularly is the best way to find breast cancer early, when it may be easier to treat.
Health care providers are taking steps so that important health visits can happen safely. All staff and patients must wear masks and be screened for COVID-19 symptoms before going in the office. Equipment, exam rooms and dressing rooms are cleaned after each patient. Other safety steps may include socially distanced waiting rooms, on-line check in, and more time added between appointments.
Breast Cancer Rates In Men Over Time
From 2015-2019 , the breast cancer incidence rate in men, as well as in women, increased slightly .
From 2015-2019 , the breast cancer mortality rate in men declined slightly . The breast cancer mortality rate in women has also declined over time. From 2015-2019 the mortality rate in women decreased by about one percent per year .
You May Like: What Do I Need To Know About Breast Cancer
Who Gets Breast Cancer
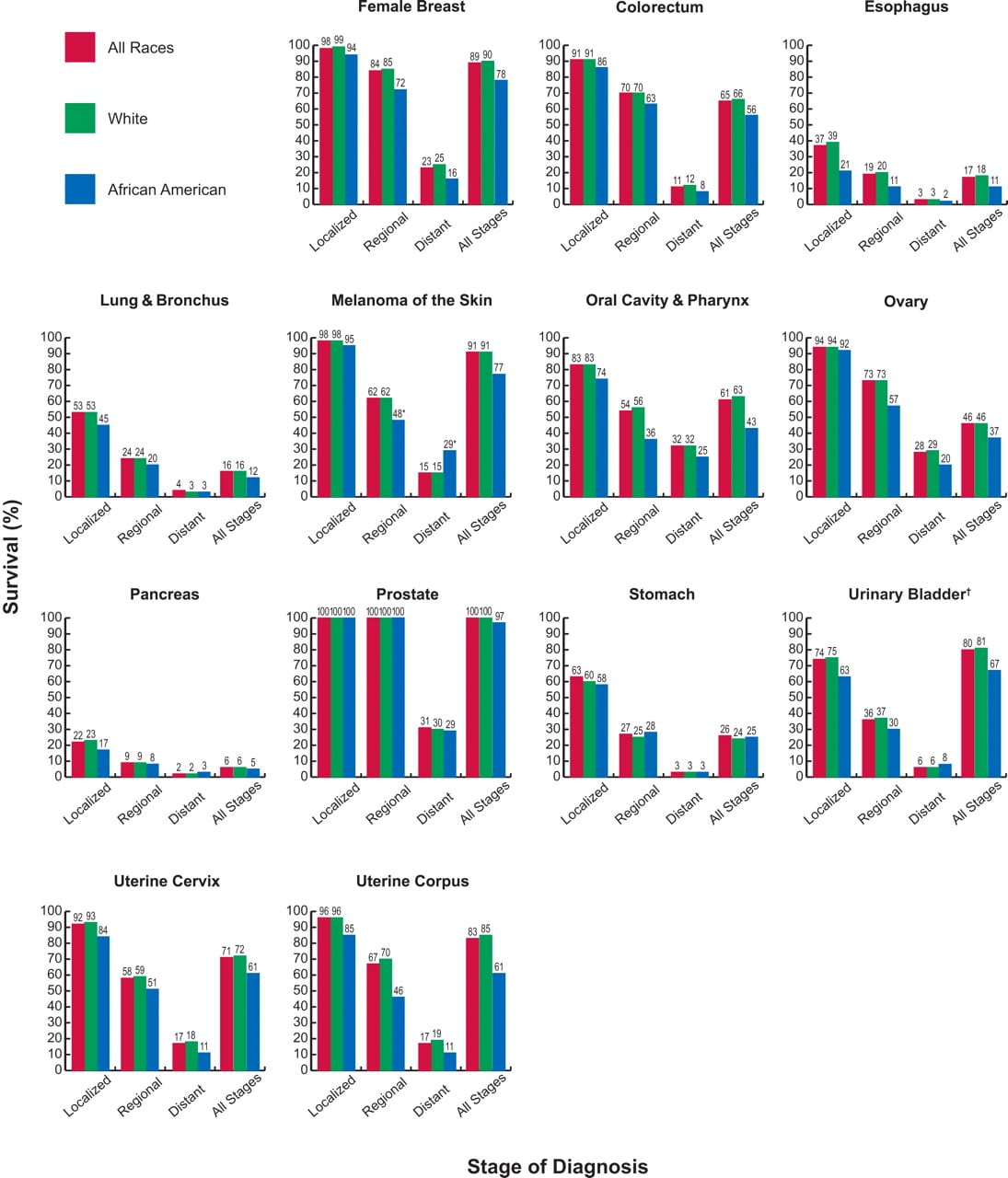
All women can get breast cancer. However, breast cancer is more common among older women. The risk for getting breast cancer increases with age. More than three-quarters of women who get breast cancer are over the age of 50. White women are more likely to get breast cancer than Black women, but, once they have the disease, Black women are more likely to die from it. Asian and Hispanic women are less likely to get breast cancer than White women or Black women. Also, women of higher socioeconomic status are more likely to get breast cancer. Scientists believe this may be related to having their first child at an older age, fewer pregnancies, diet and possible other characteristics shared by women in higher income groups.
How Can I Determine My Risk For Stomach Cancer
Your risk for stomach cancer is influenced by several factors. In addition to genetics, the American Cancer Society reports the following risk factors:
- Age. The risk for stomach cancer increases as people reach their 60s, 70s, and 80s, although stomach cancer occurs in younger people as well.
- Sex. Gastric cancer is more common in men, whose chances of developing it are 1 in 96 . In women, the chance of developing stomach cancer is about 1 in 152.
- Ethnic background. In the U.S., stomach cancer is more common in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, Native Americans, and Asian/Pacific Islanders than in non-Hispanic whites.
- H pylori. This bacteria, which is also associated with peptic ulcer disease, is very commonabout 30 to 40% of people will have H pylori bacteria, and many will never develop stomach cancer. But long-term infection can lead to pre-cancerous changes in the stomachs inner lining. H pylori is also linked to some stomach lymphomas.
- Lifestyle. This includes smoking and drinking alcohol. In addition, such dietary habits as eating few or no fruits, drinking very hot liquids, and consuming large amounts of salted and pickled foods raise the risk of gastric cancer.
- Overweight and obesity. These conditions are related to 13 different kinds of cancer, including upper stomach cancer, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Screening Icd-10