What To Know About Breast Cancer Growth
Breast cancer occurs when normal cells mutate and multiply faster than usual. One cell divides to become two cells, then each of those cells divides to become four cells, and so on. The uncontrolled multiplication of cancer cells creates tumors within the breast tissue.
The speed at which a cancer progresses depends on the growth rate of the cancer cells. It is hard to estimate cancer growth because not all cancer cells multiply and divide at the same speed.
In most cases, breast cancer initially develops in either the milk ducts or the lobules, which are the glands that produce milk, before expanding into the breast tissue.
Breast cancer that develops in ducts or lobules can spread to the connective tissue. From there, it can spread to the surrounding lymph nodes.
Once in the lymph nodes, the cancer cells can enter the lymphatic system or the bloodstream, where they can move to other areas of the body.
One recent
Additional Markers For Breast Cancer Staging
Additional markers specific to breast cancer will further define your stage, which may be helpful in choosing targeted treatments to fight the cancer.
- ER: The cancer has an estrogen receptor. Estrogen is a hormone, and some cancers have receptors that respond to estrogen.
- PR: The cancer has a progesterone receptor. Progesterone is also a hormone.
- HER2: The cancer makes the protein HER2 .
- G: Grade of cancer refers to how different the cells look from normal. Grade 1 indicates that the cells look fairly normal, while grade 2 cells are growing a little faster, and grade 3 cells look markedly different than normal breast tissue.
These markers, along with the TNM measurements, define your stage.
A cancer recurrence refers to cancer that returns in the same breast, and it requires new staging. This new stage is marked by an R at the end to indicate restaging. If it develops in the other breast, its considered a new cancer.
When Does Cancer Spread To The Lymph Nodes
The rate that cancer spreads to a persons lymph nodes may depend on the cancer they have.
Some cancers can spread more quickly to the lymph nodes. Other cancers are slow to develop, and may spread at a slower rate.
Certain cancers may only spread to lymph nodes on rare occasions. Research indicates that osteosarcomas, a form of bone cancer, only spread to the lymph nodes in 411% of cases.
Cancer can affect people in different ways, so it can be hard to predict how it may spread.
When a doctor discusses a persons cancer with them, they may refer to the stage it is at. Different stages of cancer indicate how far it has spread from its original location.
The National Cancer Institute states that the stages of cancer are:
- Stage 0: Stage 0 cancer, also called carcinoma in situ , is when abnormal cells are present, but have not spread.
- Stage 1, 2, and 3: Stages 1 to 3 indicate that there is cancer present. The higher the stage, the larger and more spread out the cancer is.
- Stave 4: Stage 4 cancer is when the cancer has spread to areas that are distant from the original tumor.
Healthcare professionals also break stage 3 into multiple categories, including 3a, b, and c. The stage at which cancer has spread to the lymph nodes varies. According to the United Kingdoms National Health Service, the cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes at stage 3.
| Number beside the N |
- for melanoma
Discovering and treating cancer early can
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Lymph Nodes And What They Do
Lymph vessels send lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes are located in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen , and groin. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas.
What Happens When Cancer Spreads To The Lymph Nodes
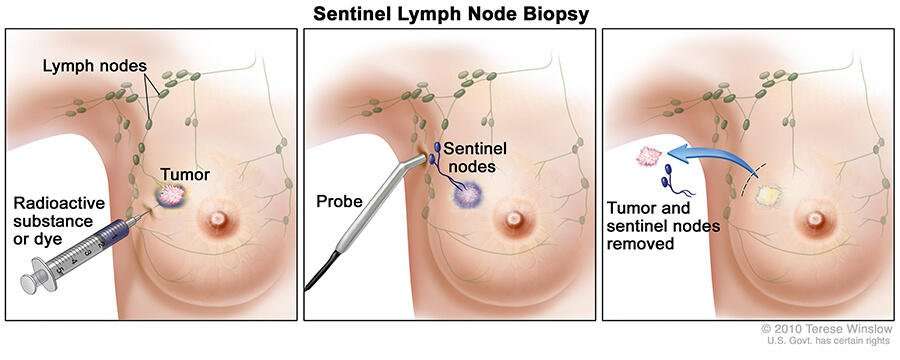
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. BautistaUpdated on: August 26, 2021
Lymph nodes are an important part of the bodys immune system, responsible for attacking germs, bacteria, and viruses. When cancer appears in the lymph nodesits an indicator of cancer spreading from other regions of the body.1 Although, in some cases, it could be the result of cancer originating in the lymph nodes or other parts of the lymphatic system. When cancer originates in the lymph nodes, it is diagnosed as lymphoma.
As cancer cells multiply and overtake healthy functioning cells, they travel at more aggressive rates and grow into new tumors. This progression is referred to as metastasis and is one of the factors that determine a cancer diagnosis, outlook, and treatment.
To further understand what happens when cancer spreads to different lymph nodes, its important to factor in if and how far the cancer cells have metastasized, as well as the tumor size and location. Early symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpit, or in the groin area
- Stomach swelling
- Shortness of breath
- Pain, headaches, and dizziness
Other signs of cancerous cells may be fatigue, extreme weight loss, and adverse effects in regions of the body where there is tumor growth.
Don’t Miss: Breast Pain During Chemo
Understanding Your Cancer And Treatment
Not all breast cancers are alike. Someone elses experience with their treatment may be completely different from yours. Understanding your type and stage can help make sense of your doctors recommendations. This may help you feel better about your treatment choices.
A big part of cancer treatment is the relationship between you and your oncology team. Here are some things youll want to know about early on so youre well informed about your specific type of breast cancer:
Oncologists meet with cancer patients every day and its their job to see you as a whole person. Express your wants and needs. Rest assured that no question is too insignificant to ask.
Breast Cancer Stage: What Do They Mean
Stages are numbers used to describe how far a cancer has advanced and where it has spread in the body. Cancer that has not spread beyond your breast is considered local.
Regional cancer has spread into the breast skin, chest structures, and lymph nodes. When cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is considered distant since it exists far away from just the breasts.
Your prognosis, or your long-term outcome, relies heavily on what stage your cancer is. Cancer stages are often further broken down into subcategories to provide more specific information.
Staging previously relied only on whether it is invasive or noninvasive, the tumors size, which lymph nodes contained cancer, and where and how far the cancer had spread.
Breast cancer stages now also take into account the tumors grade and the cancers estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status.
Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status all have to do with the specific hormones and/or proteins involved in your cancer. The tumor grade describes what the cancer cells look like.
You May Like: What Is Er+ Breast Cancer
The Lymphatic System And Metastasis
The inherent characteristics of the lymphatic physiology serve as the primary route for tumor cell metastasis. The increasing size of the tumor triggers a rise in the intratumoral interstitial fluid pressure, and interstitial fluid is released as the system attempts to achieve homeostasis. Unlike the vascular vessels, the lymphatic vessels are highly permeable the flow rate is approximately 100500x slower, and coupled with lesser shearing stresses due to vasodilation. Therefore, the lymphatic route is superior in facilitating tumor cell dissemination . Distinguishing between lymphatic endothelial and systemic endothelial cells via immunohistochemical staining has allowed studies to confirm tumor cell dispersion via afferent lymphatics and lymphangiogenesis, and implicates the lymphatics as the most significant metastatic route .
Breast Cancer Doubling Time
An important way to think about how fast a breast cancer grows is by looking at what’s called the volume doubling time. Growth rate is a part of tumor doubling time, which is exactly what it sounds like. It is the amount of time it takes for a tumor to double in size.
It would be unethical to leave a cancer untreated to see how rapidly it will grow, so researchers estimate the doubling time. However, when looking at these models, it becomes clear that doubling time estimates vary from study to study.
A 2018 study estimated doubling time by looking at serial ultrasounds in 265 people with invasive breast cancer to see if there were differences among breast cancer subtypes. These images were taken between diagnosis and surgery. The results suggest that growth varied significantly based on the breast cancer subtype and the role of estrogen receptors in those subtypes.
During an average interval of 57 days, 36% of tumors did not change in size, while 64% grew. Of those tumors that increased in size, the average gain in volume was 34.5%. Tumors that were triple negative had greater increases in volume and shorter doubling times than those that were estrogen receptor positive and HER2 negative tumors.
A similar 2016 study looked at growth in 323 people, based on ultrasound images taken between diagnosis and surgery over a 31 day period, On average, the tumors grew from 1.47 centimeters to 1.56 cm in diameter. The daily growth rate based on type was:
Also Check: 3a Breast Cancer
Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
Cancer can appear in the lymph nodes in 2 ways: it can either start there or it can spread there from somewhere else.
Cancer that starts in the lymph nodes is called lymphoma. You can read more about lymphoma in Hodgkin Lymphomaand Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
More often, cancer starts somewhere else and then spreads to lymph nodes. That is the focus of this section.
Surgery As A First Treatment
You may have the whole breast removed . You may be able to have a new breast made . Do speak to your surgeon, they will tell you whether a reconstruction is suitable for you.
You might be able to have breast conserving surgery. This may be possible if you have drug treatment first and the tumour shrinks enough to allow your surgeon to remove just the area of cancer. Before your surgery the lymph nodes in the armpit are checked for cancer cells.
After the surgery you usually have radiotherapy to the breast area.
You might have treatment with chemotherapy for a few months. If your cancer cells have receptors for a protein called HER2 you might have a targeted cancer drug called trastuzumab as well as chemotherapy. You may have this for up to a year.
You usually have hormone therapy for at least 5 years if your cancer cells have hormone receptors.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Prognosis
A Lot To Learn About Alnd In Other Patients
Its important for doctors and patients to understand that these results can only be applied to women whose breast cancer and treatment regimen match those of the participants in the trial, the papers authors cautioned.
The results should not be used to direct the care of women with palpable axillary lymph nodes, women who had breast tumors larger than 5 cm in diameter, women with three or more positive sentinel lymph nodes, women who received chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery, and women who underwent mastectomy instead of breast-conserving surgery with radiation, they wrote.
We still have a lot to learn about ALND in other settings, commented Dr. Giuliano.
One trial, currently underway in Europe, is examining whether ALND can be skipped in some women who have a mastectomy for early-stage breast cancer, but results are not expected for years.
But for now, according to Edward Livingston, M.D., and Hsiao Ching Li, M.D., of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, authors of an accompanying editorial, The ACOSOG Z0011 trial has shattered a century of belief that all cancer containing axillary lymph nodes must be removed in women with breast cancer.
Related Resources
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Also known as locally advanced breast cancer, the tumor in this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter across and the cancer is extensive in the underarm lymph nodes or has spread to other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast. Stage 3 breast cancer is a more advanced form of invasive breast cancer. At this stage, the cancer cells have usually not spread to more distant sites in the body, but they are present in several axillary lymph nodes. The tumor may also be quite large at this stage, possibly extending to the chest wall or the skin of the breast.
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three categories:
Stage 3A: One of the following is true:
- No tumor is found in the breast, but cancer is present in axillary lymph nodes that are attached to either other or other structures, or cancer may be found in the lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm or smaller. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm to 4 cm in size. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that may be attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3C:
Read Also: Cancer Stages 3
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Genetics
One of the leading causes of triple-negative is a womans genetic makeup, specifically the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are genes that are supposed to produce tumor suppressant proteins in the body.
In the case of triple-negative breast cancer, 10% to 15% of Caucasians with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation, while 35% of African Americans with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation.
For a while the BRCA1 gene was the only gene known for increasing the risk of triple-negative breast cancer.
These genes, if defected can increase their risk of getting any type of breast cancer by 20% as well as elevating the chances that their breast cancer diagnosis be triple negative breast cancers .
Why Werent These Escaping Cells Identified The First Time The Cancer Was Treated
Although scans of the body can detect if there is obvious spread to these other organs, for women with early stage breast cancer there rarely is anything that shows up on a scan. There is a limit to what scans can tell us: they wont show extremely tiny spots of cancer, and they definitely cant show us if there are individual cells circulating in the body. Neither will any blood test, or any other test for that matter. So the first time around we perform our surgery and give our treatmentschemotherapy, hormonal therapy, radiationwith the hope that if microscopic spread has already taken place, the treatments will scavenge those cells and kill them before they take up residence someplace in the body.
Unfortunately, these treatments dont work 100 percent of the time. So if cells have spread, and if the treatments we give dont affect them, the cancer cells can persist and take hold someplace, developing into metastases, or spread. This is why and how recurrence happens.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Survival
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Also Check: Where Can Breast Cancer Lumps Be
Breast Cancer Cell Growth
Cancer begins when there are genetic changes, called mutations, in a normal breast cell. These changes happen in genes that control the growth of the cell. These changes may occur over a long period of time, even decades, before a cancer cell forms.
These tumor cells multiply and divide exponentially, meaning that one cell becomes two, two cells become four, and so on. Thats why a tumor size will increase more rapidly, the larger it becomes.
That said, not all cells are dividing at the same time. The cancers growth can change at different stages as a tumor forms. Compared with many types of cancer, breast cancer has a low growth fraction. This means that the proportion of cancer cells that are in an active cell cycle is low.
Some tumors, such as lymphomas and some leukemias, have much higher growth fractions. They may be active for a much shorter period of time before they are detected, even in children.
You May Like: Stage Zero Breast Cancer Survival Rate