Types Of Stage 1 And 2 Breast Cancer
The most common types of invasive breast cancers are named after the area of the breast where they begin. Types of early breast cancers include:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC means that the cancer originated in the milk ducts of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of all breast cancers.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma ILC means that the cancer originated in the milk-producing lobules of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. ILC is the second most common type of breast cancer, and accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
- There are also other less common forms of invasive breast cancer, such as inflammatory breast cancer and Pagets disease of the nipple. For more information on the various types of invasive breast cancer, including the less common forms, please visit Types of Breast Cancer page.
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
What Can I Expect After My First Radiation Treatment
Most people start to feel tired after a few weeks of radiation therapy. This happens because radiation treatments destroy some healthy cells as well as the cancer cells. Fatigue usually gets worse as treatment goes on. Stress from being sick and daily trips for treatment can make fatigue worse.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
What Are Some Of The Cancer Type
Breast and prostate cancers are the most common types of cancer that have their own grading systems.
Breast cancer. Doctors most often use the Nottingham grading system for breast cancer . This system grades breast tumors based on the following features:
- Tubule formation: how much of the tumor tissue has normal breast duct structures
- Nuclear grade: an evaluation of the size and shape of the nucleus in the tumor cells
- Mitotic rate: how many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing
Each of the categories gets a score between 1 and 3 a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for the three categories are then added, yielding a total score of 3 to 9. Three grades are possible:
- Total score = 35: G1
- Total score = 67: G2
- Total score = 89: G3
- Gleason X: Gleason score cannot be determined
- Gleason 26: The tumor tissue is well differentiated
- Gleason 7: The tumor tissue is moderately differentiated
- Gleason 810: The tumor tissue is poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
There Are A Number Of Different Treatments Doctors Recommend
Not only does the stage tell you how serious the disease is, but it can help you and. The earlier the detection of prostate cancer, the better the patient’s chance of survival is. Treatment for bladder cancer depends on your overall health, progression of the c. Your doctor will want to discuss treatment options as well as the prognosis for bladder cancer. Here are 10 more facts about prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. Although it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in american women, breast cancer can impact people of all genders. However, as with other types of cancer,. It may grow slowly and it’s typically treatable. If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early enough stage, it’s treatable. Although the percentage of cases in men is much lower than in women, male breast cancer accounts for a por. But hearing the words can still be scary. Breast cancer is the second most common cancer found in women after skin cancer but that doesn’t mean men aren’t at risk as well.
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on your overall health, progression of the c. One in seven men in the united states will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early enough stage, it’s treatable.
You May Like: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
How Long Does It Take For Stage 1 Breast Cancer To Develop Into Stage 2
It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer. It’s important to know that stage 1 breast cancer could have already been present for a while before being detected, so it may progress quickly.
What Investigations Are Necessary For Staging Breast Cancer
Breast cancer staging almost always involves a bone scan, as breast cancer is highly prone to metastasize to the bones.
During this test, medics inject a small amount of a radioactive substance into the bloodstream, where it eventually collects in the bones. A radiation scanner is then able to detect accumulations of tracer substance in the bones.
If breast cancer spreads beyond the breast, 25% of the time it goes into bones first.
Recommended Reading: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
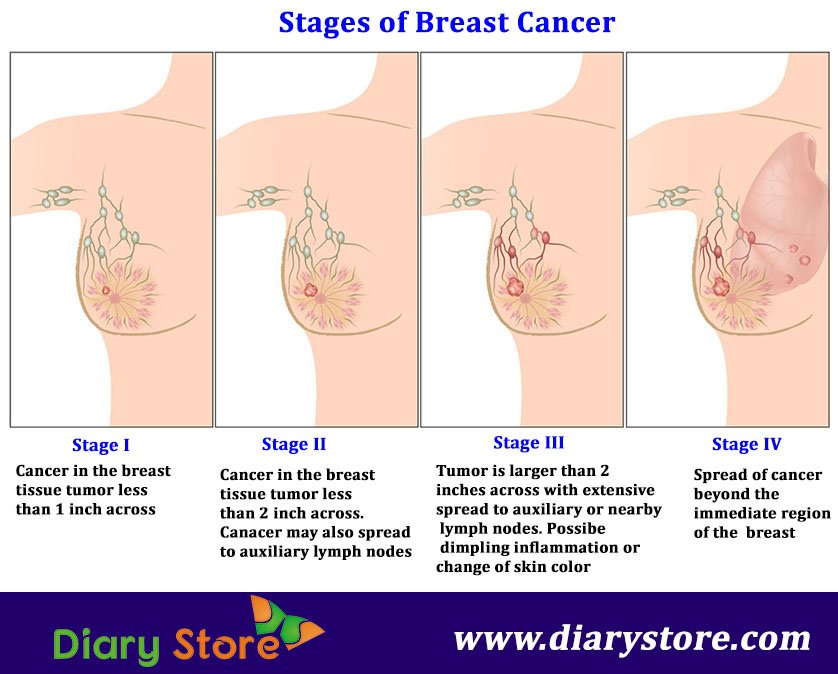
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Also known as locally advanced breast cancer, the tumor in this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter across and the cancer is extensive in the underarm lymph nodes or has spread to other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast. Stage 3 breast cancer is a more advanced form of invasive breast cancer. At this stage, the cancer cells have usually not spread to more distant sites in the body, but they are present in several axillary lymph nodes. The tumor may also be quite large at this stage, possibly extending to the chest wall or the skin of the breast.
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three categories:
Stage 3A: One of the following is true:
- No tumor is found in the breast, but cancer is present in axillary lymph nodes that are attached to either other or other structures, or cancer may be found in the lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm or smaller. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm to 4 cm in size. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that may be attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3C:
Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Breast cancer survival rates vary widely based on many factors.
Two of the most important factors are the type of cancer you have and the stage of the cancer at the time you receive a diagnosis. Other factors that may play a role include your age, gender, and race.
shows theres a higher mortality rate in non-white people diagnosed with breast cancer compared with white people. One reason for this may be healthcare disparities.
The good news is breast cancer survival rates are improving.
According to the ACS , in 1975, the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer in women was 75.2 percent. But for women diagnosed between 2008 and 2014, it was 90.6 percent.
Five-year survival rates for breast cancer differ depending on stage at diagnosis, ranging from 99 percent for localized, early stage cancers to 27 percent for advanced, metastatic cancers.
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 3 Breast Cancer Be Cured
What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer is cancer that is still confined in its primary location. Although its growing, the disease has not yet spread to other body parts. Stage 1 breast cancer occurs in different sub-stages known as 1A and 1B. If identified early, the disease can be treated effectively with excellent prognoses.
When breast tumors are identified as stage 1, they are still small, and if they have spread to lymph nodes at all, the spread is very microscopic. Stage 1A breast cancer means that the tumor is very small and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes. Stage 1B is when the disease is already in the lymph nodes, but still small, the size of a pinprick.
The stages of breast cancer are determined by the TNM system of classification. The system stages the disease by tumor size, if it has spread to any lymph nodes or if the cancer has progressed to other parts of the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer is very treatable since it is in a localized stage. Knowing your stage of tumor can help you get the best treatment option available to eliminate the disease completely.
Although uncommon, early breast cancer can cause signs and symptoms which may not be detected through a mammogram. Here are some of the stage 1 breast cancer symptoms to watch out for:
Swelling in the breast or armpit
Unusual discomfort or pain in the breast
Breast tenderness that is very persistent
Pitted or scaly skin
A retracted nipple
Pain in the nipple or change in its appearance
You Might Also Enjoy…
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patients cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patients outcome, so the best source of information for understanding a breast cancer prognosis is always a physician who is familiar with the patients case.
In general, breast cancer stages are established based on three key variables: the size of a tumor, the extent of lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 to 4 . Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are:
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
What Are The Different Grades Of Breast Cancer
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer:
- Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing
- Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster
- Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing
Sometimes the grade given to a cancer after a biopsy can change after surgery. This is because after surgery theres more tissue for the pathologist to look at, which can give them more detailed information about the cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
How Common Is Breast Cancer Recurrence
Most local recurrences of breast cancer occur within five years of a lumpectomy. You can lower your risk by getting radiation therapy afterward. You have a 3% to 15% chance of breast cancer recurrence within 10 years with this combined treatment. Based on genetic testing, your provider may recommend additional treatments to further reduce your risk.
Recurrence rates for people who havemastectomies vary:
- There is a 6% chance of cancer returning within five years if the healthcare providers didnt find cancer in axillary lymph nodes during the original surgery.
- There is a one in four chance of cancer recurrence if axillary lymph nodes are cancerous. This risk drops to 6% if you get radiation therapy after the mastectomy.
You May Like: What Is The Youngest Age To Have Breast Cancer
Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it’s not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
Also Check: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
breast cancersurvival rates
Over time, invasive lobular carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Although invasive lobular carcinoma can affect women at any age, it is more common as women grow older.
Beside above, what is the treatment for invasive lobular carcinoma? The treatment options for invasive lobular carcinoma include localized approaches such as surgery and radiation therapy that treat the tumor and the surrounding areas, as well as systemic treatments such as chemotherapy and hormonal or targeted therapies that travel throughout the body to destroy cancer cells that may
Also to know, what stage is invasive lobular carcinoma?
Stage 0 means the cancer cells are still within the breast lobule and have not invaded deeper into the surrounding fatty breast tissue. This is called lobular carcinoma in situ , a non-invasive breast cancer. In stage 0 cancer, the cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or distant sites.
Is invasive lobular carcinoma curable?
If treatment cures cancer, this means that it destroys all of the cancer cells, and the cancer will never return. Although this is the goal of treatment, it is not always possible. Often, cancer goes into remission. A person may have few or no clinical symptoms, but cancer cells still exist in the body.
Stage 2 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 2 breast cancer?
Stage 2 breast cancer cells or tumors are larger than Stage 1 cancers, and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are two types of Stage 2 breast cancer:
- Stage 2A Generally speaking, Stage 2A breast cancer can indicate one of the following:
- No tumor can be found in your breast, but cancer larger than 2 millimeters can be found in one to three underarm lymph nodes or near the breastbone.
- The tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller, and has spread the nearby axillary lymph nodes.
- The cancer has not spread to area lymph nodes, however, the tumor measures between 2 and 5 centimeters.
What are the treatment options for Stage 2 breast cancer?
Stage 2 breast cancer treatment timeline
Again, it depends on what treatments or follow-up therapies are needed. Generally, the treatment timeline for Stage 2 breast cancer can last three to six months. Again, certain treatments like hormone therapies designed to stop the cancer from coming back can last for one to 10 years.
Also Check: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer