Other Factors Can Also Affect Prognosis
Its also important to understand that while the stage of the cancer is important, many other factors can also affect a persons outlook. Depending on the cancer type, other important prognostic factors might include:
- A persons age and overall health
- Whether the cancer cells have changes in certain genes, chromosomes, or proteins
- How the cancer responds to treatment
If you have questions about survival rates and how they might be affected by the stage of your cancer or other factors, be sure to talk to your cancer care team.
Stage 3 Breast Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment for stage 3 breast cancers typically involves a combination of surgery along with chemotherapy to shrink the tumor before surgery and radiation after surgery to treat the chest wall and/or lymph nodes. Lymph nodes will also likely be removed during surgery.
Targeted therapies, including hormone therapy, can also be used depending on your cancers specific characteristics.
Why Were New Measures Added To The Staging System
The new measures give information on the biology of the tumor that affects prognosis. Adding these measures improved staging.
For example, with breast cancer, a large tumor may have a better prognosis than a small tumor, based on biological measures. In the same way, a small tumor may have a worse prognosis than a large tumor based on these measures.
You May Like: Type 3 Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
If the tests find cancer, you and your doctor will develop a treatment plan to eradicate the breast cancer, to reduce the chance of cancer returning in the breast, as well as to reduce the chance of the cancer traveling to a location outside of the breast. Treatment generally follows within a few weeks after the diagnosis.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on the size and location of the tumor in the breast, the results of lab tests done on the cancer cells, and the stage, or extent, of the disease. Your doctor will usually consider your age and general health as well as your feelings about the treatment options.
Breast cancer treatments are local or systemic. Local treatments are used to remove, destroy, or control the cancer cells in a specific area, such as the breast. Surgery and radiation treatment are local treatments. Systemic treatments are used to destroy or control cancer cells all over the body. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are systemic treatments. A patient may have just one form of treatment or a combination, depending on her individual diagnosis.
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In Teenagers
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
For a PET scan, a slightly radioactive form of sugar is injected into the blood and collects mainly in cancer cells.
PET/CT scan: Often a PET scan is combined with a CT scan using a special machine that can do both at the same time. This lets the doctor compare areas of higher radioactivity on the PET scan with a more detailed picture on the CT scan.
What Tests Assess Her2
There are two approved tissue testing methods for HER2 status. In 2013, the American Society of Clinical Oncologists and the College of American Pathologists issued an updated joint clinical practice guideline about HER2 testing for breast cancer. The two approved methods currently used in the U.S. to test for HER2 are
- immunohistochemistry and
- in-situ hybridization .
IHC testing uses specially labeled antibodies to show how much of the HER2 protein is present on the cancer cell surface, while ISH testing measures the number of copies of the HER2 gene inside each cell.
There are two main types of ISH tests:
- fluorescence and
- bright-field ISH.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization is referred to as FISH. Both of these tests are performed on the tumor sample that is removed at the time of surgery.
Recommended Reading: What To Expect During Chemo For Breast Cancer
What Is The Triple Test
The triple test includes the following steps:
The earlier breast cancer is detected, the more likely it is that treatment can successfully remove the cancer and prevent it from recurring.
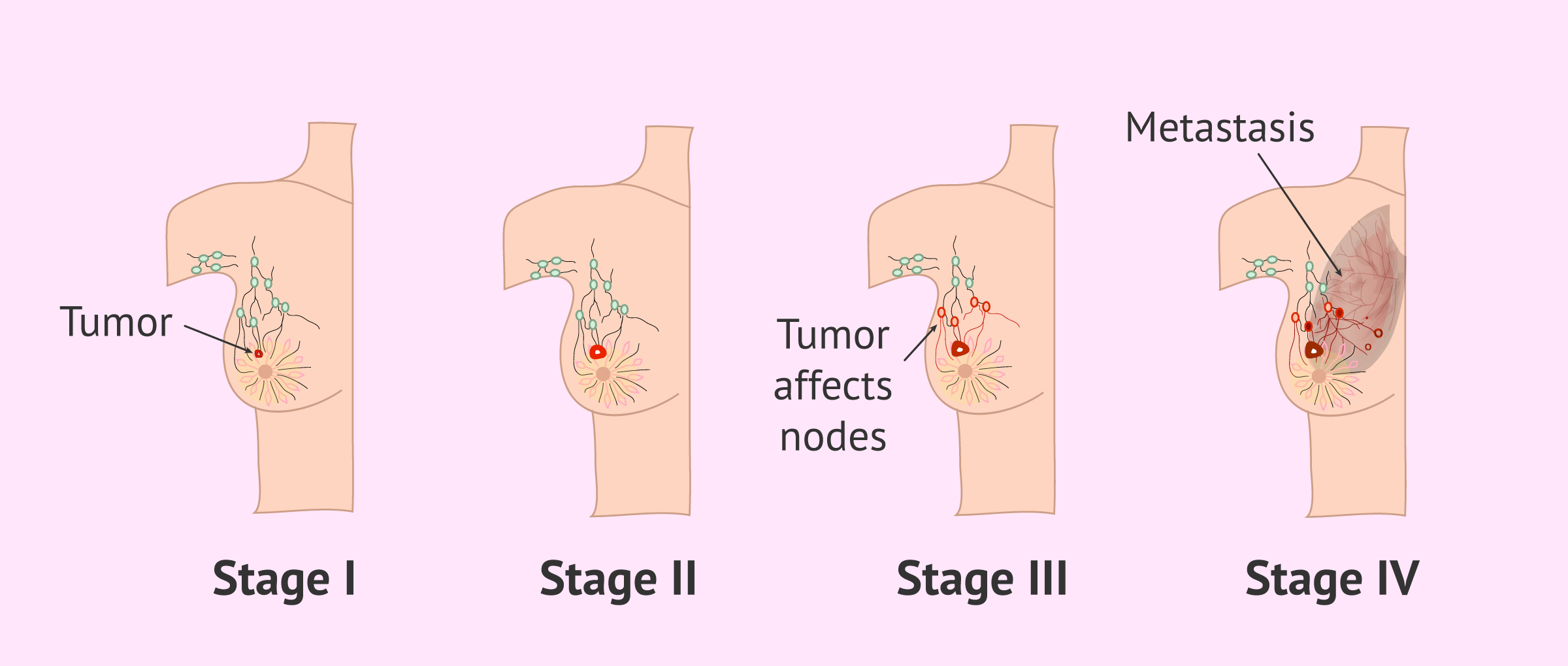
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
Also Check: Stage 3a Cancer
Can Exercise Help Reduce My Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Exercise is a big part of a healthy lifestyle. It can also be a useful way to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in your postmenopausal years. Women often gain weight and body fat during menopause. People with higher amounts of body fat can be at a higher risk of breast cancer. However, by reducing your body fat through exercise, you may be able to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
The general recommendation for regular exercise is about 150 minutes each week. This would mean that you work out for about 30 minutes, five days each week. However, doubling the amount of weekly exercise to 300 minutes can greatly benefit postmenopausal women. The longer duration of exercise allows for you to burn more fat and improve your heart and lung function.
The type of exercise you do can vary the main goal is get your heart rate up as you exercise. Its recommended that your heart rate is raised about 65 to 75% of your maximum heart rate during exercise. You can figure out your maximum heart rate by subtracting your current age from 220. If you are 65, for example, your maximum heart rate is 155.
Aerobic exercise is a great way to improve your heart and lung function, as well as burn fat. Some aerobic exercises you can try include:
- Walking.
- Dancing.
- Hiking.
Remember, there are many benefits to working more exercise into your weekly routine. Some benefits of aerobic exercise can include:
Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two groups:
- Stage 2A
- Stage 2B
Stage 2A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast but cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is 2cm or smaller and cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage 2B can mean:
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm. Cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
You May Like: Triple Positive Breast Cancer Stage 4
How Does Breast Cancer Produce Signs And Symptoms
Breast cancer, which begins when cells grow abnormally and the form tumours in the breast, can cause different types of signs and symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of breast cancer vary depending on the size and location of the tumour as well as the speed at which it is growing.
Diagnostic tests and procedures for breast cancer include physical examination, mammogram, biopsy, ultrasound and breast MRI scan. Blood tests and other scans may be ordered if signs and symptoms suggest the cancer may have spread outside of the breast area.
Does Restaging A Cancer Change The Original Stage
When a cancer is staged again after the initial staging, it is sometimes referred to as restaging. Often the same tests that were done when the cancer was first diagnosed are done again.
With any type of restaging, the new stage classification is added to the original stage, but it doesnt replace it. The stage assigned at diagnosis is still the one that is most important when discussing statistics like survival rates .
You May Like: Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Exams And Tests To Stage Cancer
Different types of exams and tests can be used to figure out a cancers stage.
- Depending on where the cancer is located, a physical exam may give some idea as to how much cancer there is.
- Imaging tests like x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasound, and PET scans may also give information about how much and where cancer is in the body.
- Endoscopy exams are sometimes used to look for cancer. For these exams, an endoscope, which is a thin, lighted tube is put inside the body to look for cancer.
- A biopsy often is needed to confirm a cancer diagnosis. Biopsies might also be needed to find out if a lump felt on an exam or if something seen on an imaging test in another part of the body is really from the spread of cancer. During a biopsy, the doctor removes a tumor or pieces of a tumor to be looked at in the lab. Some biopsies are done during surgery. But biopsies can also be done using a thin, hollow needle or through an endoscope. For more on biopsies, see Testing Biopsy and Cytology Specimens for Cancer.
- Lab tests of cancer cells and blood tests can also be used to help stage some types of cancer.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Read Also: How Do Doctors Treat Breast Cancer
How Is The Stage Determined
The staging system most often used for breast cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The most recent AJCC system, effective January 2018, has both clinical and pathologic staging systems for breast cancer:
- The pathologic stage is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation.
- Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away or at all, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. The clinical stage is used to help plan treatment. Sometimes, though, the cancer has spread further than the clinical stage estimates, and may not predict the patients outlook as accurately as a pathologic stage.
In both staging systems, 7 key pieces of information are used:
- The extent of the tumor : How large is the cancer? Has it grown into nearby areas?
- The spread to nearby lymph nodes : Has the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes? If so, how many?
- The spread to distant sites : Has the cancer spread to distant organs such as the lungs or liver?
- Estrogen Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called an estrogen receptor?
- Progesterone Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called a progesterone receptor?
- HER2 status: Does the cancer make too much of a protein called HER2?
- Grade of the cancer : How much do the cancer cells look like normal cells?
In addition, Oncotype Dx® Recurrence Score results may also be considered in the stage in certain situations.
How Does The Doctor Determine The Stage Of My Breast Cancer
Dr. Victor Vogel answers the question: ‘How does my doctor determine my stage?’
— Question: How does the doctor determine the stage of my breast cancer?
Answer: The stage of the breast cancer is determined by having the pathologist examine the tissue under a microscope and with a ruler, to tell how large the tumor is within the breast.
And by looking under the microscope at the lymph nodes that are removed from under the arm by the surgeon — the axillary lymph nodes — to tell whether or not the lymph nodes are involved.
And finally, the surgeon and the medical oncologist will look at X-ray studies of the chest and the abdomen and the bones to tell whether there’s any evidence of spread of the breast cancer outside the breast.
And then, by putting together all of this information — the size of the tumor in the breast, the involvement or non-involvement of the lymph nodes under the arm, and the results from the imaging studies — all that information together is used to determine the stage of the breast cancer.
Also Check: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Prognosis Without Treatment
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Tnm System For Breast Cancer
Doctors also group cancers by the letters T, N, or M. Each of those letters tells you something about your cancer.
âTâ stands for tumor, or the lump of cancer found in the breast itself. The higher the number assigned after it, the bigger or wider the mass.
âNâ stands for nodes, as in lymph nodes. These small filters are found throughout the body, and they’re especially dense in and around the breast. They’re meant to catch cancer cells before they travel to other parts of the body. Here, too, a number tells you whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many.
âMâ stands for metastasis. The cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Of Breast Cancer
Early Locally Advanced And Secondary Breast Cancer
Early breast cancer means the cancer hasn’t spread beyond the breast or the lymph nodes in the armpit on the same side of the body. So, the cancer hasn’t spread to any other part of the body.
Local recurrence means cancer that has come back in the breast, the armpit, or the chest wall after treatment.
Locally advanced breast cancer means the cancer has spread into the surrounding area, such as the lymph nodes, the skin or chest muscle. But it has not spread to other parts of the body.
Secondary breast cancer is also called metastatic breast cancer, advanced breast cancer, or stage 4 breast cancer. It means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver or bones.