Less Lymph Node Surgery Equivalent Survival
The trial, called ACOSOG Z0011, was designed to compare whether sentinel lymph node biopsy alone provided equivalent survival benefits to ALND after breast-conserving surgery among a subset of women who also received radiation and systemic therapy. The research team enrolled 891 participants into the study from 1999 to 2004.
Women who had stage I or II cancer and metastases in only one or two sentinel nodes were eligible to join the study. All women had undergone SLNB at the time of breast-conserving surgery.
Half of the trial participants received no further surgery, and the other half underwent ALND. Almost 90% of women in both groups had radiation therapy after surgery, and almost all received some type of systemic therapy.
In the initial results from the trial, published in 2010 and 2011, women who had only SLNB did not have worse overall survival than women who underwent full ALND. The two groups also had similar rates of disease-free survival and cancer recurrence in the lymph nodes.
These early results were absolutely practice changing, and at this point the overwhelming majority of surgeons are not doing a full axillary lymph node dissection in patients with one or two positive nodes, said Larissa Korde, M.D., head of Breast Cancer Therapeutics in NCIs Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis.
However, the cancer research community had lingering concerns about the trial, the authors of the new paper explained.
Symptoms Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer may be different than those of early-stage breast cancer, but not always. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all.
You should always speak with your doctor if you experience any new signs or symptoms, but here are some of the most common signs that breast cancer has spread:
- Bone pain or bone fractures due to tumor cells spreading to the bones or spinal cord
- Headaches or dizziness when cancer has spread to the brain
- Shortness of breath or chest pain, caused by lung cancer
- Jaundice or stomach swelling
The symptoms of breast cancer metastasis may also vary depending on where in the body the cancer has spread. For example:
- If the breast or chest wall is affected, symptoms may include pain, nipple discharge, or a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm.
- If the cancer has spread to bones, symptoms may include pain, fractures or decreased alertness due to high calcium levels.
- If the cancer has spread to the lungs, symptoms may include shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, coughing, chest pain or fatigue.
- If the cancer has spread to the liver, symptoms may include nausea, fatigue, swelling of the feet and hands or yellowing skin.
- If cancer has spread to the central nervous system, which includes the brain or spinal cord, symptoms may include pain, memory loss, headache, blurred or double vision, difficulty with and/or movement or seizures.
Is Cancer Of The Lymph Nodes Terminal
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. BautistaUpdated on: August 26, 2021
Lymph nodes are an important part of the bodys immune system. They are located throughout the body and help to attack germs and fight infection. Swollen lymph nodes are a physical sign of a health problem. It could be an infection or cold, injury, or in some cases, cancer. A cancer diagnosis is only confirmed through a biopsy and often leaves people wondering: is cancer of the lymph nodes terminal?
First, to perform a biopsy, doctors remove a fluid sample from one of the infected lymph nodes and look at the tissue up close under a microscope. Second, if cancer is detected, more tests are necessary to determine how far it has spread and where the tumors have originated from. At this point, it can then be determined which stage of cancer is present and whether it is terminal.
Cancerous tumors can develop anywhere in the body and eventually travel to the lymph nodes and other areas of the lymphatic system. When cancer cells escape tumors they may die off before they can begin growth somewhere else, but if they settle, grow, and continue to spread, this is referred to as metastasis.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Metastasis Prognosis
Diagnosing Symptoms Related To Lymph Nodes
When touching an affected area, swollen lymph nodes may feel soft and round, like lumps the size of a pea, peanut or grape. If theyre painful when touched, that may be a sign of inflammation. Since lymph nodes appear in parallelas, for instance, on both sides of the neckyou can feel lymph glands on both sides to see whether they are a normal size on one side and enlarged on the other, which may be a sign of infection.
In determining a diagnosis, its important for doctors to look at other symptoms or factors. Swollen lymph nodes near the ear may indicate an ear infection, for instance. Swollen glands in the neck area near the collarbone, combined with a sore throat and cough, may be a sign of an upper respiratory infection. When multiple regions of lymph nodes are swollen, it may indicate a body-wide disease that needs immediate attention.
Besides reviewing your medical history, doctors may use some of the following methods to diagnose the cause of swollen lymph nodes:
- Physical examination, feeling with fingers the nodes in the affected area to check their size and whether they feel hard, tender or warm
- Lab tests, including blood tests to check for suspected underlying conditions
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
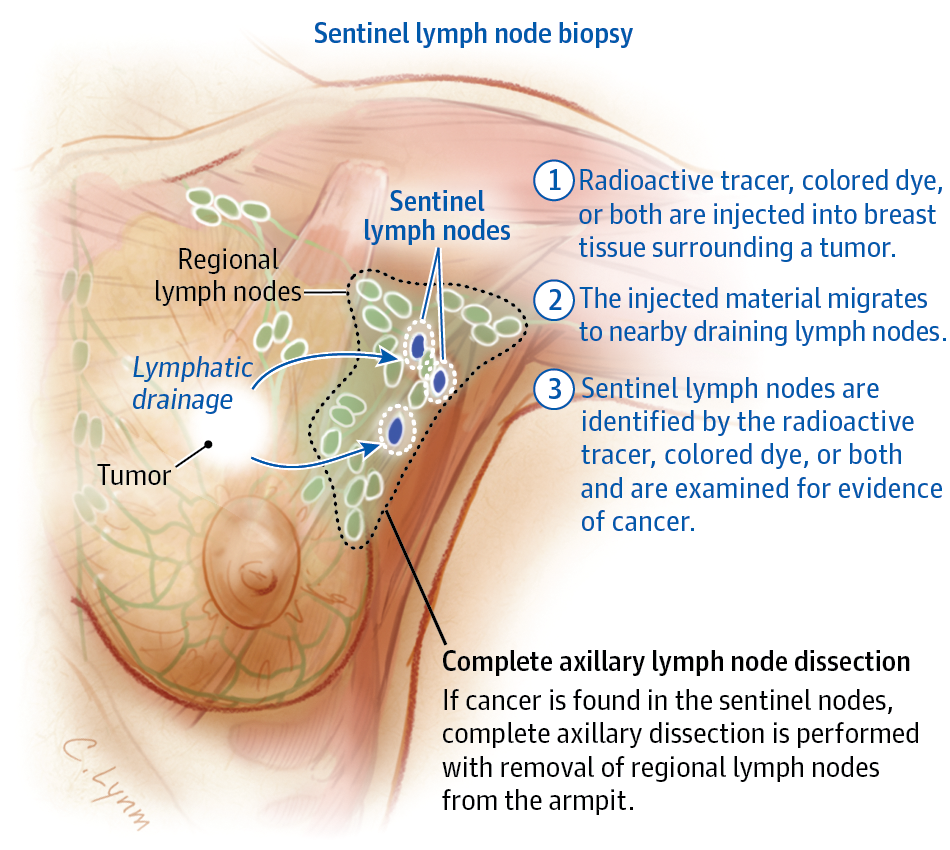
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy , the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which acancer is likely to spread . A radioactive substance and/or a blue dye is injected into the tumor, the area around it, or the area around the nipple. Lymph vessels will carry these substances along the same path that the cancer would likely take. The first lymph node the dye or radioactive substance travels to will be the sentinel node.
After the substance has been injected, the sentinel node can be found either by using a special machine to detect radioactivity in the nodes, or by looking for nodes that have turned blue. Sometimes, both methods are used. The surgeon cuts the skin over the lymph node area and removes the node containing the dye or radioactivity.
The few removed lymph nodes are then checked closely in the lab for cancer cells by a pathologist. Sometimes, this is done during the surgery. Because there is a chance that other lymph nodes in the same area will also have cancer if cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, the surgeon may go ahead with an axillary dissection to remove more lymph nodes while you are still on the operating table. If no cancer cells are seen in the node at the time of the surgery, or if they are not checked by a pathologist at the time of the surgery, they will be examined more closely over the next several days.
Based on the studies that have looked at this, skipping the ALND may be an option for:
Read Also: Breast Tumor Causes
Prognosis For Breast Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Stage III breast cancer in the lymph nodes has a fairly positive prognosis. The five-year survival rate for this stage of breast cancer is 72%. This means that 72% of those diagnosed and treated for breast cancer at this stage will live at least five years. Many women who are diagnosed at this stage are successfully treated and experience remission.
Stages Of Breast Cancer: Stage Iiib
A stage IIIb breast cancer is one in which the tumor may be of any size but it has grown into the chest wall or the skin of the breast. A stage IIIb designation also applies if there is evidence of either
- axillary lymph node metastasis
- internal mammary node metastasis
presenting in such a way as to suggest that total surgical removal is not possible.
There is a unique type of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, that causes the breast to appear red and swollen. This is because the cancer cells block some of the lymphatic vessels. Inflammatory breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis and are generally stage IIIb at least.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
What Is The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels and small, bean-shaped organs called lymph nodes that carry lymph throughout the body. Lymph is a clear, colorless fluid that contains a few blood cells. It starts in many organs and tissues. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system. It helps protect and maintain the fluid balance of your body by filtering and draining lymph and waste products away from each body region. The lymphatic system also helps the body fight infection.
Dormancy In Metastatic Melanoma
The time period between removal of the primary tumor and subsequent recurrence of disease is referred to as metastatic dormancy. In melanomas, a period of dormancy may end with the emergence of recurrent disease at a metastatic site and only rarely at the site of the primary tumor. Melanomas, as well as some other cancers, such as prostate and some types of breast cancer, often have very protracted courses in which metastatic disease does not manifest until years or even decades after removal of the primary tumor. Clinically localized melanoma can recur after disease-free intervals of 10 years or more . In fact, a subset of melanomas will have ultra-long dormancy with recurrence greater than 20 years later . Other tumor types, such as lung and pancreatic adenocarcinomas tend to follow a much swifter clinical course in which discovery of the primary tumor and subsequent metastasis is often a temporally contiguous event . While these differences in metastasis patterns may in part reflect differences in detection amongst different cancer types, it has also been proposed that such observations suggest that certain tumor types might gain full metastatic competency earlier in tumor progression .
You May Like: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Symptom Checker
Will The Treatments Be Any Different To Common Breast Cancer
Breast cancer that has not invaded the lymph nodes will usually be treated with:
- Surgery
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
This is known as “localized breast cancer.” Your surgeon may opt to remove all of the surrounding lymph nodes “axillary lymph node dissection,” to prevent the spread of any cancer cells after surgery and treatment is completed. This will give you more chance for a cure and higher survival rate.
If breast cancer is “regionally advanced” and found in the lymph nodes, the above treatments will be done along with added treatments to stall cancer growth in the lymph nodes and any cancer cells that have spread. These additional treatments may include:
1. Endocrine Therapy
If your breast tumor is “hormone receptor positive” or receptive to estrogen, an estrogen blocking medication will be given. In these types of tumors, estrogen can make the cancer grow faster. Your doctor may also choose to do a hysterectomy and remove the ovaries to prevent further estrogen production in the body. Using these estrogen blocking medications can either stop or slow the growth of breast cancer tumors. Your doctor may also advise you to not use any estrogen containing or estrogen like substances.
2. Targeted Therapy
Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer means that a cancer that began in the breast has spread to another part of the body. Secondary cancer can also be called advanced or metastatic cancer.
It might not mean that you have secondary breast cancer if you have the symptoms described below. They can be caused by other conditions.
You May Like: Stage 3 B Cancer
Lymph Nodes: An Early Warning Sign Of Cancer
Categories:Cancer Screening,Lymphomas
Lymph nodes are part of your immune system, and they let you know when your body is fighting an infection by becoming enlarged or sensitive to the touch. They also function as an early warning system for some types of cancer, including lymphoma, leukemia, and breast cancer.
About The Lymph Nodes

The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. It also drains lymph fluid from the tissues of the body, before returning it to the blood.
The lymphatic system is made up of fine tubes called lymphatic vessels. They connect to groups of lymph nodes throughout the body.
Lymph nodes are small and bean-shaped. They filter bacteria and disease from the lymph fluid. When you have an infection, lymph nodes often swell as they fight the infection.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Cells In Lymph Nodes
Metastasis To Other Sites
Hepatic metastases are detected clinically in 1020% of cutaneous melanoma patients with metastatic disease . Sub-clinical metastases to the liver are much more common, as they are found in 5477% of melanoma patients at the time of autopsy . Liver metastases occur relatively late in disease progression, with an average lifespan of only 24 months in patients with clinically evident liver metastases . Liver metastases are rarely the first site of disease spread in cutaneous melanoma . Work by Song and colleagues has implicated laminin-1 as a mediator of B16 melanoma cells metastasizing specifically to the liver . In these experiments, cells selected for the ability to adhere to laminin-1 were more efficient in forming liver metastases in mice . Vidal-Vanaclocha and colleagues have implicated interleukins, IL-1 and IL-18 in hepatic metastasis . Mice deficient for IL-1 show an 84-95% reduction in experimental liver metastases. IL-18 is thought to increase expression of VCAM-1 in the hepatic sinusoidal epithelium. Blocking IL-18 with a soluble factor can decrease the adhesion of melanoma cells by inhibiting this mechanism . Laminin-1/VCAM-1 can interact with integrins suggesting again that not only adhesive specificity, but also downstream survival signals are important in determining organ specificity of metastasis.
Diagnosing Cancer Of The Lymph Nodes
In addition to a biopsy, the TNM system is commonly used to issue a diagnosis and determine which type of treatment is best. The T refers to the size of the tumor or cancerous growth. The N refers to the number of lymph nodes that contain cancerous cells. And, the M is for metastasis, which refers to cancer thats spread to areas far from the originating tumor.5
This categorization is used in addition to other diagnostic tests and tools to determine the cancer stage such as:
- Imaging tests X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and other types of imaging tests can provide a clearer picture and more information about where the cancer is located and how much is present.
- Endoscopy exams An endoscope is a thin, lighted tube with a video camera attached that looks around on the inside of the body for cancerous areas.
In general, cancers assigned as Stage I are less advanced and have a better prognosis and response to treatment. Whereas, a higher stage indicates that the cancer has spread further and requires a more intense or multiple types of treatment. Other factors that affect treatment are:
Also Check: What Happens To The Cells In Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the breast tissues. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affect women and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women. Men can also develop breast cancer, however, less than 1% of breast cancers are diagnosed in men.
Cancers are a unique group of diseases caused by genetic mutations, which make certain types of cells turn abnormal and grow out of control. Most types of cancers grow into masses of tissue known as tumors. Cancer spreads when tumor cells break off from the primary tumor, migrate to other parts of the body and start growing.
Where Can Breast Cancer Spread
The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the lymph nodes, bone, liver, lungs and brain. The symptoms you may experience will depend on where in the body the cancer has spread to. You might not have all of the symptoms mentioned here.
Remember other conditions can cause these symptoms. They don’t necessarily mean that you have cancer that has spread. But if you have symptoms that you are worried about, discuss them with your GP, cancer specialist, or breast care nurse so that you can be checked.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Curable
The Stages Of Breast Cancer Are As Follows:
Stage 0 is sometimes used to describe abnormal cells that are not invasive cancer. For example, Stage 0 is used for ductal carcinoma in situ . DCIS is diagnosed when abnormal cells are in the lining of a breast duct, but the abnormal cells have not invaded nearby breast tissue or spread outside the duct. Although many doctors dont consider DCIS to be cancer, DCIS sometimes becomes invasive breast cancer if not treated.
Stage I is an early stage of invasive breast cancer. Cancer cells have invaded breast tissue beyond where the cancer started, but the cells have not spread beyond the breast. The tumor is no more than 2 centimeters across.
Stage II is one of the following:
- The tumor is no more than 2 centimeters across. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters . The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters . The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters . The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage III is locally advanced cancer. It is divided into Stage IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.