What Is The Lymph System
The lymph system is a part of your bodys immune system. It includes a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. Lymph vessels are a lot like the veins that collect and carry blood through the body. But instead of carrying blood, these vessels carry the clear watery fluid called lymph. Lymph fluid also contains white blood cells, which help fight infections.
Lymph fluid would build up and cause swelling if it were not drained in some way. Lymph vessels draw up the lymph fluid from around the cells to send it towards the chest. There, lymph fluid collects into a large vessel that drains into a blood vessel near the heart.
When To Contact A Doctor
If a person notices any signs of cancer having spread to their lymph nodes, they should speak with a doctor immediately.
Additionally, if a person with cancer notices any unusual new symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The sooner a person receives treatment for cancer that has spread, the better their chances of survival.
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Neoadjuvant Her2
With neoadjuvant chemotherapy, all the chemotherapy to treat the breast cancer is usually given before surgery . If the tumor doesnt get smaller with the first combination of chemotherapy drugs, other combinations can be tried.
If your tumor is HER2-positive, you may get neoadjuvant trastuzumab and neoadjuvant pertuzumab , but not at the same time as the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin .
If your tumor is estrogen receptor-negative, progesterone receptor-negative and HER2-negative with a high risk of recurrence, you may get neoadjuvant pembrolizumab . Pembrolizumab is an immunotherapy drug.
You May Like: Stage 3 Lymphatic Cancer
Will The Nhs Fund An Unlicensed Medicine
It’s possible for your doctor to prescribe a medicine outside the uses it’s licensed for if they’re willing to take personal responsibility for this ‘off-licence’ use of treatment.
Your local clinical commissioning group may need to be involved, as it would have to decide whether to support your doctor’s decision and pay for the medicine from NHS budgets.
Page last reviewed: 28 October 2019 Next review due: 28 October 2022
Hormonal Therapy For Idc
If the cancer tested positive for hormone receptors, your doctor likely will recommend some form of hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy, also called anti-estrogen therapy or endocrine therapy, works by lowering the amount of estrogen in the body or blocking the estrogen from signaling breast cancer cells to grow. Because hormonal therapy affects your whole body, its sometimes called a systemic treatment.
In some cases of advanced-stage IDC, hormonal therapy can be given before surgery to help shrink the cancer . Still, it’s more common for hormonal therapy to start after other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, unless these treatments arent needed.
Hormone receptors are special proteins found on the surface of certain cells throughout the body, including breast cells. These receptor proteins are the eyes and ears of the cells, receiving messages from the hormones in the bloodstream and then telling the cells what to do. In other words, the receptors act like an on-off switch for a particular activity in the cell. If the right substance comes along that fits into the receptor like a key fitting into a lock the switch is turned on and a particular activity in the cell begins.
You and your doctor will work together to decide which form of hormonal therapy is best in your situation. Two types of hormonal therapy are most frequently used:
Don’t Miss: Breast Duct Cancer Symptoms
How Is Cancer In Lymph Nodes Found
Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when theres infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the bodys surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer.
The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy. Doctors may remove lymph nodes or take samples of one or more nodes using needles. The tissue thats removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist to find out if there are cancer cells in it. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, they may remove one or more of the nearby lymph nodes as well. Removal of one lymph node is considered a biopsy, but when many lymph nodes are removed, its called lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, theres a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo, immunotherapy, targeted therapy or radiation, might be needed after surgery.
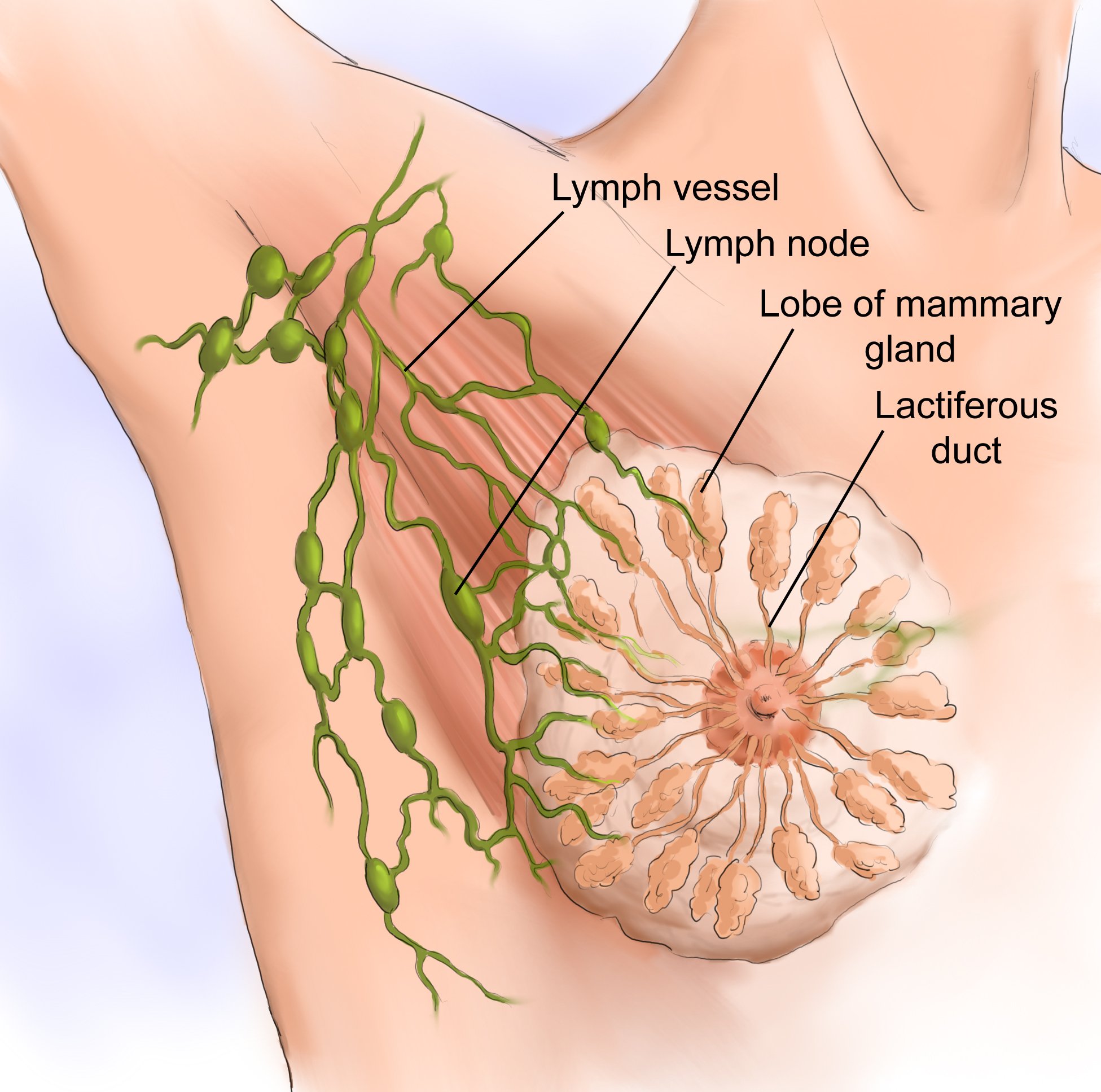
Lymph Nodes And What They Do
Lymph vessels send lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes are located in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen , and groin. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas.
You May Like: How To Remove Breast Cancer Naturally
Removing Lymph Nodes Is Not Without Consequences
Axillary lymph node removal, which typically involves removal of 15 to 25 nodes, can have troubling consequences. Lymph nodes carry fluid, called lymph, through regions of the body to help fight infection and remove toxins. When a large group of the tiny, round nodes is surgically removed, lymph fluid may be unable to flow freely. The buildup of fluid is called lymphedema.
Some women get terrible arm swelling from lymphedema, Giuliano says. You can have shoulder problems, such as a limited range of motion, numbness, and pain that can be chronic and persist long-term. These problems are very difficult to manage.
It may worry some women to leave the lymph nodes intact when cancer is found in one or two sentinel nodes. But, Giuliano points out, most patients with early-stage breast cancer also have radiation therapy, which kills cancer cells in the lymph nodes. Chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy medication prescribed to some women based on the type of breast cancer they have also destroys cancer in lymph nodes.
The study findings only apply to women with early-stage breast cancer who have lumpectomy and additional treatment, such as radiation and chemotherapy. More research is needed on whether other types of breast cancer patients can perhaps avoid axillary lymph node removal.
The Types Of Radiotherapy
The type of radiotherapy you have will depend on the type of breast cancer and the type of surgery you have. Some women may not need to have radiotherapy at all.
Types of radiotherapy include:
- breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, radiation is applied to the whole of the remaining breast tissue
- chest-wall radiotherapy after a mastectomy, radiotherapy is applied to the chest wall
- breast boost some women may be offered a boost of high-dose radiotherapy in the area where the cancer was removed however, this may affect the appearance of your breast, particularly if you have large breasts, and can sometimes have other side effects, including hardening of breast tissue
- radiotherapy to the lymph nodes where radiotherapy is aimed at the armpit and the surrounding area to kill any cancer that may be in the lymph nodes
You May Like: Suspicious Malignancy Breast
Measures Of Treatment Effect
We will carry out statistical analysis using Review Manager 5.1 . We will use fixed-effect meta-analysis for combining data in the absence of heterogeneity. For those outcomes where there are moderate or high levels of heterogeneity, where clinically meaningful, we will use random-effects analysis and these results will be presented as average treatment effects.
For dichotomous data, we will present results as summary risk ratio with 95% confidence intervals. For continuous data, we will use the mean difference if outcomes were measured in the same way between trials. We will use the standardized mean difference to combine trials that measured the same outcome, but using different methods. If there is evidence in the trials of abnormally distributed data, we will report this.
Description Of The Intervention
Axillary node clearance is removal of all axillary nodes in the armpit in patients found to have cancer spread to lymph nodes removed during sentinel node biopsy. This is usually performed at a second operation, which can be difficult due to scarring from the first operation . A drain is left in the armpit for a few days afterwards . The operation lasts one to two hours and requires a stay in hospital of up to five days. It delays the patients return to day-to-day activities and paid work .
Axillary radiotherapy is radiation treatment of the remaining axillary nodes. It is used instead of axillary node clearance for some patients. The prescribed radiation dose is given on a daily basis, five days a week for three to five weeks. Axillary radiotherapy is offered in some specialist centres, and patients may need to travel a considerable distance for treatment.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Prognosis And Survival For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type, stage and characteristics of your cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
Doctors use different prognostic and predictive factors for newly diagnosed and recurrent breast cancers.
Are There Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
You probably wouldnt notice if a few cancer cells reached a lymph node. As the number of cancer cells grows, symptoms can include lumps or swelling in the armpits or around the collarbone.
Its possible to have enlarged lymph nodes even if you havent discovered a lump in your breast. There are also noncancerous conditions that cause enlarged lymph nodes in an area close to the breasts.
If you notice enlarged lymph nodes but no other symptoms or signs, schedule an appointment with a doctor.
- your genetics or inherited genes
Read Also: Is Invasive Breast Cancer Curable
Breast Cancer: Types Of Treatment
Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about the different types of treatments doctors use for people with breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. Standard of care means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are strongly encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option. A clinical trial is a research study that tests a new approach to treatment. Doctors want to learn whether the new treatment is safe, effective, and possibly better than the standard treatment. Clinical trials can test a new drug and how often it should be given, a new combination of standard treatments, or new doses of standard drugs or other treatments. Some clinical trials also test giving less treatment than what is usually done as the standard of care. Clinical trials are an option to consider for treatment and care for all stages of cancer. Your doctor can help you consider all your treatment options. Learn more about clinical trials in the About Clinical Trials and Latest Research sections of this guide.
What Happens When Cancer Spreads To The Lymph Nodes
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. BautistaUpdated on: August 26, 2021
Lymph nodes are an important part of the bodys immune system, responsible for attacking germs, bacteria, and viruses. When cancer appears in the lymph nodesits an indicator of cancer spreading from other regions of the body.1 Although, in some cases, it could be the result of cancer originating in the lymph nodes or other parts of the lymphatic system. When cancer originates in the lymph nodes, it is diagnosed as lymphoma.
As cancer cells multiply and overtake healthy functioning cells, they travel at more aggressive rates and grow into new tumors. This progression is referred to as metastasis and is one of the factors that determine a cancer diagnosis, outlook, and treatment.
To further understand what happens when cancer spreads to different lymph nodes, its important to factor in if and how far the cancer cells have metastasized, as well as the tumor size and location. Early symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpit, or in the groin area
- Stomach swelling
- Shortness of breath
- Pain, headaches, and dizziness
Other signs of cancerous cells may be fatigue, extreme weight loss, and adverse effects in regions of the body where there is tumor growth.
Also Check: 3a Cancer
Are There Any Statistics On Recurrence Rates Or Incidence Of Metastasis
As mentioned, it is very difficult to find statistics on metastatic breast cancer that has recurred after initial diagnosis. However, these cases represent a large proportion of Stage IV breast cancer cases and overall deaths.
Most of the statistical data on Stage IV or metastatic breast cancer is from those women presenting at diagnosis. According to the Metastatic Breast Cancer Network in 2012 new cases of Stage IV breast cancer were between 13,776 to 22,096.
The number of breast cancer recurrences at Stage IV is estimated to be between 20% and 30% of all breast cancer diagnoses.
How The Intervention Might Work
Axillary treatment can eliminate residual disease in the axilla, decrease axillary recurrence and, perhaps, improve overall survival by improving local control. One breast cancer death out of four local recurrences can be prevented over the 15 year period . ANC provides information on the number of positive nodes and this may influence adjuvant systemic therapy and radiotherapy decisions.
Axillary recurrence rates following ANC or ART have been reported to be as low as 1 or 2%, however, both are associated with significant long term problems such as pain, arm swelling , restricted shoulder movement, and sensory changes in the arm and hand .
You May Like: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
What Are Risk Factors For Breast Cancer Recurrence
Anyone with a breast cancer diagnosis can have a recurrence. Your risk of cancer recurrence depends on several factors:
- Age: Women who develop breast cancer before age 35 are more likely to get breast cancer again.
- Cancer stage: Cancer stage at the time of diagnosis correlates with the risk of the cancer being able to recur. Several factors determine cancer stage: tumor size, cancer grade and cancer spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Cancer grade indicates how unusual cancer cells look in comparison to healthy cells.
- Cancer type: Aggressive cancers like inflammatory breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer are harder to treat. Theyre more likely to come back and spread.
What Causes Breast Cancer Recurrence
The goal of cancer treatments is to kill cancer cells. But, cancer cells are tricky. Treatments can reduce tumors so much that tests dont detect their presence. These weakened cells can remain in the body after treatment. Over time, the cells get stronger. They start to grow and multiply again.
Even surgery to remove a cancerous tumor isnt always 100% effective. Cancer cells can move into nearby tissue, lymph nodes or the bloodstream before surgery takes place.
Recommended Reading: Estrogen Induced Breast Cancer
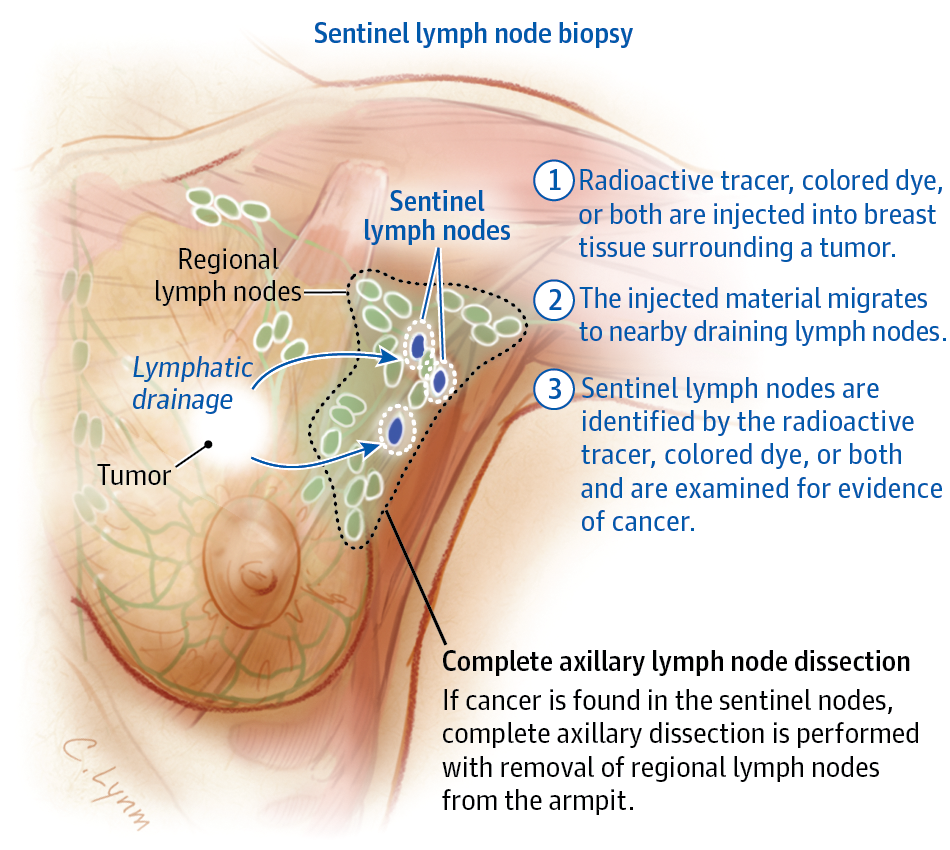
What Is Surgery To The Lymph Nodes
Your surgeon may remove some or all the lymph nodes in your armpit to check for cancer cells. This can:
- remove any lymph nodes that contain cancer cells but you may need more treatment to the armpit if only some lymph nodes were removed
- gives information about the stage of the cancer this helps when making decision about having other treatments.
There are different ways some or all the lymph nodes may be removed:
- a test called a sentinel lymph node biopsy that removes 1 to 3 lymph nodes for testing
- an operation to remove all the lymph nodes under the arm that is called an axillary lymph node dissection.
If you have DCIS you only have a SLNB if you are having a mastectomy. They are done at the same time.
With invasive breast cancer you have an SLNB when the ultrasound of the lymph nodes or fine needle aspiration are normal. If the SLNB shows cancer cells you usually need the remaining lymph nodes in the armpit removed or treated.
Some people have all the lymph nodes from the armpit are removed. This is called an axillary lymph node dissection. You usually have this when tests on the lymph nodes or an SLNB show there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes or there is a high risk of this.