The Role Of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy In Treatment Of Early Stage Tnbc
Programmed cell death ligand-1 is expressed on the surface of tumors and infiltrating immune cells and other cell types. Programmed cell death protein-1 is expressed predominately on T cells. Programmed cell death protein-1 interacts with its ligands . In doing this it directly inhibits apoptosis of tumor cells promotes peripheral T effector cell exhaustion and the conversion of T effector cells to immunosuppressive T regulatory cells.21
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are highly selective monoclonal antibodies that may be specific for PD-L1 e.g atezolizumab or for PD-1 e.g. pembrolizumab. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of many difficult to treat cancers such as lung and melanoma. Before the introduction of ICIs the OS for patients with metastatic melanoma or non-small cell lung cancer was approximately one year, now many patients are experiencing long-term remissions lasting years. As the most immunogenic subtype of breast cancer, the clinical benefit of ICIs has become a reality for patients with TNBC.
A Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitors
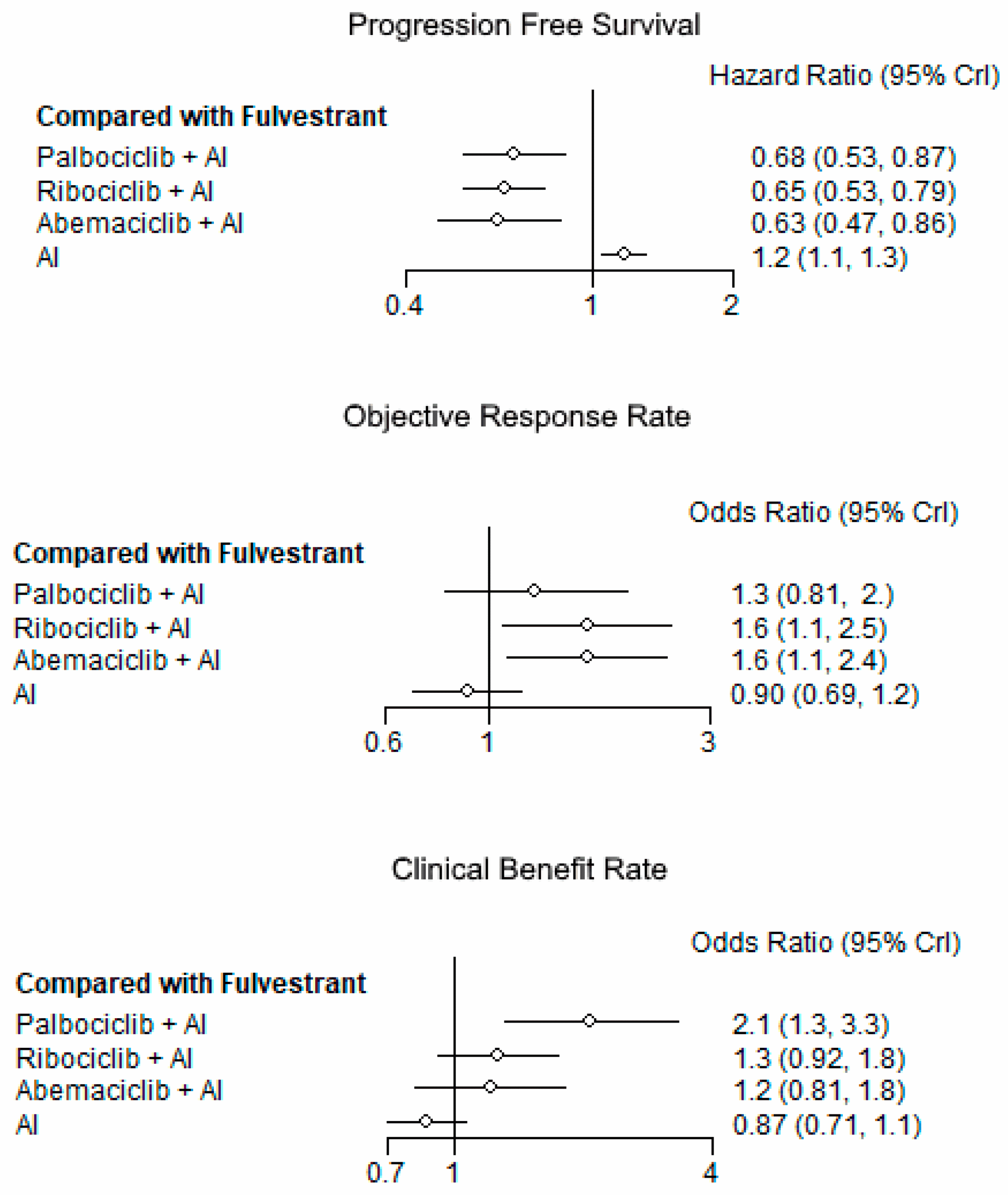
The role of CDK 4/6 inhibitors is well established as first or second line therapy of metastatic HR-positive breast cancer. There are three CDK 4/6 inhibitors approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration in combination with endocrine therapies for the treatment of HR-positive metastatic breast cancer and both ribociclib and abemaciclib have demonstrated OS benefits . Given the PFS and OS benefits seen in advanced disease, these agents are currently being evaluated in the neoadjuvant, adjuvant and residual disease post neoadjuvant settings in an attempt to reduce the rate of recurrence after definitive treatment for early stage HR-positive disease . The PENELOPE-B study is a phase III study of 13 cycles of palbociclib plus standard endocrine therapy for patients with residual disease after taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy . The PALLAS study is a phase III study assessing the addition of 2 years of palbociclib to 5 years of standard endocrine therapy in stage II-III disease . The MonarchE study is a phase III study of abemaciclib plus standard endocrine therapy in patients with high risk, lymph node positive breast cancer and the NATALEE study is a phase III study of ribociclib plus endocrine therapy in the adjuvant setting . Until the results of these studies are reported, the use of adjuvant CDK 4/6 inhibitors, outside of the clinical trial setting, is not recommended.
Options For Luminal Breast Cancer
with luminal or other types of HR-positive breast cancer receive hormone therapy. Some people call this endocrine therapy.
Triple-negative breast cancer does not respond to hormone therapy because it is HR-negative.
Anti-estrogen therapy
Anti-estrogen therapy works by preventing estrogen from attaching to the estrogen receptors of breast cancer cells.
The four different types of anti-estrogen therapy are:
- selective estrogen-receptor response modulators, such as tamoxifen
- aromatase inhibitors
- estrogen-receptor downregulators, such as fulvestrant
- luteinizing hormone releasing agents, including goserelin and leuprolide , prevent the ovaries from producing estrogen
The type of anti-estrogen therapy a person receives depends on various factors, including:
- the stage of the breast cancer
- whether the person has any other medical conditions
- whether the person has been through menopause
A person usually continues hormone therapy for at least .
Other hormone therapies
In some cases, HR-positive breast cancer may not respond to the above treatments. Consequently, a doctor may recommend one of the following hormone therapies for more advanced cancer:
- progestin medications, such as megestrol
- an anabolic steroid, such as fluoxymesterone
Targeted therapies
Targeted therapies focus on specific genetic mutations that play a role in a cancers growth and spread. These drugs are usually combined with hormone therapy.
Examples of CDK4/6 inhibitors include:
Don’t Miss: Is It Possible For Men To Get Breast Cancer
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
Generally, the side effects of hormonal therapies tend to be mild and fairly well tolerated, says Brufsky. The most common side effects are menopausal symptoms , achiness in the joints and bones, and fatigue. AIs can cause some bone loss , but that can typically be well controlled with bone-modifying medications, Brufsky notes. CDK4/6 inhibitors may cause low white blood cell counts as well as some nausea and diarrhea.
Time To Recurrence Or Progression To Advanced Breast Cancer
Time to recurrence or progression to advanced breast cancer was most often defined as the time between date of diagnosis of primary breast cancer, and date of diagnosis of first distant metastasis or recurrence. Disease-free interval , metastasis-free interval , and recurrence-free interval are other terminology used to describe this. In Zhao et al,70 it was defined as the date from surgery to first recurrence. Eight studies did not report the definition.36,45,49,,66,71
The relationship between time to recurrence or progression to advanced breast cancer and OS and PFS was evaluated, with a significant association reported in 78% and 80% of studies, respectively.10,29,36,39,45,48,49,,60,66,70,71,91 In 13 studies, shorter time to recurrence or progression to advanced breast cancer was associated with worse survival relative to longer time, except in Jung et al,48 where the 15 years vs < 1 year MFI was associated with worse OS . The 2-year time interval was the most commonly studied cut-off point. Four studies showed a shorter time to recurrence or progression to advanced breast cancer was associated with worse PFS.29,54,60,70 Consistency in evidence and directionality of association was observed for OS and PFS. The overall effect size of the association between time to recurrence or progression to advanced breast cancer and survival endpoints was moderate.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs Of Breast Cancer In Men
D Extended Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy Recommendations
Recommendations for extended endocrine therapy are summarized in Figure 1 and Figure 2. In patients who are pre- or peri-menopausal at diagnosis and who do not receive OFS as part of their treatment paradigm, current ASCO guidelines recommend treatment with 5 years of adjuvant tamoxifen. After 5 years of tamoxifen, women who remain pre-menopausal are candidates for extended endocrine therapy with an additional 5 years of tamoxifen. Women who become post-menopausal during the first 5 years of tamoxifen in whom extended therapy is planned may either continue tamoxifen for an additional 5 years, or receive 5 years of an AI . NCCN guidelines recommend that women who are pre-menopausal at diagnosis, and who do not undergo treatment with OFS should consider tamoxifen for up to 10 years. Women who are pre-menopausal at diagnosis and who are treated with 5 years of tamoxifen-OFS or AI-OFS may consider an additional 5 years of tamoxifen if they remain pre-menopausal. Women who were pre-menopausal at diagnosis who become post-menopausal, may consider extended endocrine therapy with an AI for a further 5 years following tamoxifen .
What Does It Mean To Be Her2
If your breast cancer is HER2-negative, you do not have an excess of the HER2 gene. Tumors such as these will not respond to therapies that specifically target HER2 receptors.
If your breast cancer is HER2-positive, then you have too much HER2 protein or extra copies of the HER2 gene. These breast cancers tend to be fast-growing. HER2-positive breast cancer treatment typically includes targeted therapy drugs that slow the growth and kill these cancer cells. HER2-positive breast cancers account for about 25% of all breast cancer cases.
Knowing your HER2 status will help your WVCI cancer care team create the best treatment plan for you.
Recommended Reading: Can Breast Cancer Start In The Armpit
Molecular Classification Of Infiltrating Breast Cancer
Infiltrating breast cancer, also called invasive breast cancer, is one that has spread from its original location in the breast to other parts of the body. The most common type is infiltrating ductal carcinoma, which begins in the lining of the milk ducts. Another type is lobular carcinoma, which begins in the milk glands. Invasive ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma may be categorized as any of the four molecular subtypes.
About 85 percent of breast cancers are ductal carcinomas, while 11.4 percent are lobular carcinomas, according to a study published in the Annals of Medicine and Surgery. More than three-quarters of lobular carcinomas fall into the luminal A and triple-negative tumor category.
Astrazeneca And Daiichi Sankyos Enhertu Also Improved Median Overall Survival By More Than 6 Months Vs Chemotherapy In All Patients Evaluated In Destiny
Detailed positive results from the pivotal DESTINY-Breast04 Phase III trial showed that Enhertu demonstrated superior and clinically meaningful progression-free survival and overall survival in previously treated patients with HER2-low 1+ or IHC 2+/in-situ hybridisation -negative) unresectable and/or metastatic breast cancer with hormone receptor positive or HR-negative disease versus standard of care physicians choice of chemotherapy. Results will be presented during the Plenary Session today at the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, and have been simultaneously published in TheNew England Journal of Medicine.
Enhertu is a specifically engineered HER2-directed antibody drug conjugate being jointly developed and commercialised by AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo.
In the primary endpoint analysis for DESTINY-Breast04, Enhertu demonstrated a 49% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death versus physicians choice of chemotherapy in patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancer with HR-positive disease . A median PFS of 10.1 months was seen in patients treated with Enhertu compared to 5.4 months with chemotherapy, as assessed by blinded independent central review .
Results also showed a 36% reduction in the risk of death with Enhertu compared to chemotherapy in patients with HR-positive disease with a median OS of 23.9 months with Enhertu versus 17.5 months with chemotherapy, meeting a key secondary endpoint of the trial.
Notes
References
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Breast Cancer
Her2 Status In Breast Cancer
If your cancer appears to be aggressive and fast-growing, you might have higher levels of a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, or HER2 for short. Some genes, like HER2, and the proteins they make, do more than play a role in the development of breast cancer. They can also influence how your breast cancer behaves as well as how it may respond to specific cancer treatments.
Usually, HER2 receptors help control how a healthy breast cell grows, divides, and repairs itself. However, if the HER2 gene doesnt work correctly and produces too many copies of itself, it leads to the uncontrolled growth of breast cancer cells.
You May Like: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
What Hormone Receptors Do
Hormone receptors, like other cell receptors, are special proteins found in and on the surface of certain cells throughout the body, including breast cells. These receptor proteins are like the eyes and ears of the cells, receiving messages from hormones and other substances in the bloodstream and then telling the cells what to do. The receptors act like an on-off switch for an activity in the cell. If the right substance comes along that fits into the receptor like a key fitting into a lock the switch is turned on and that particular activity in the cell begins.
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Have Breast Cancer
How Common Is Her2
About 4 out of 5 breast cancers donât have extra HER2. Chances are good that your HER2-negative breast cancer is positive for one or both hormone receptors. Almost 70% of breast cancers are HR-positive/HER2-negative. Only about 10% of them are HR-negative/HER2-negative or triple negative.
Cancers can change over time. If your HER2-negative cancer goes away, then comes back or spreads, your doctor may test it again to see if itâs still negative for HER2.
How Metastatic Breast Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, different types of doctors often work together to create a patients overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Breast cancer multidisciplinary care teams typically include medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists. In addition, cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, genetic counselors, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, financial advisors, and other supportive care members. Ask the doctor in charge of your treatment which health care professionals will be part of your treatment team and what they do. This can change over time as your health care needs change.
A treatment plan is a summary of your cancer and the planned cancer treatment. It is meant to give basic information about your medical history to any doctors who will care for you during your lifetime. Before treatment begins, ask your doctor for a copy of your treatment plan. The treatment plan can be updated over time as your treatments change.
The main goals of metastatic breast cancer treatment are to make sure that you have the:
-
Longest survival possible with the disease
-
Fewest possible side effects from the cancer and its treatment
-
Best and longest quality of life possible
Treatment options for metastatic breast cancer vary based on:
You May Like: What Are The 3 Types Of Breast Cancer
Choice Of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy In Post
Suggested Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy Approach for Women who are Post-Menopausal at Diagnosis
AI: Aromatase Inhibitor ET: Endocrine Therapy
*High risk disease defined as tumors with lymph node involvement or aggressive histological features. In lymph node negative disease, high risk defined as large tumor size or poor prognosis identified by genomic assays
^ Extended tamoxifen may be appropriate in post-menopausal patients if toxicities or contraindications to AI
Several adjuvant endocrine therapy options are available for post-menopausal women including AI for 5 years, tamoxifen for 5 years , tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by AI to complete 5 years, tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by 5 years of AI, tamoxifen for 5 years followed by AI for 5 years. While patient factors and patient preferences should be considered, most guidelines recommend the use of an AI, either for 5 years, or for 2-3 years after prior tamoxifen use if possible . Extended AI therapy may be considered for select women and is discussed below.
Grade High Vs Low Or Intermediate
To evaluate racial differences within risk subgroups available in routine clinical practice, we also performed stratified analyses by overall tumor grade in the full study population . Grade is strongly associated with high-risk features and serves as a prognostic and predictive marker in the absence of gene profiling assays . We observed early separation of recurrence curves by race among women with high grade tumors . At 5âyears, Black women with high grade tumors had a recurrence risk of 16.6% , compared with 12.0% among White women. By comparison, Black and White women with low grade tumors had similar 5-year recurrence risk .
Standardized risk of recurrence among hormone receptor-positive/HER2â tumors stratified by race and grade. Pairwise log-rank tests were performed with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Compared with White women with low or intermediate grade, White women with high grade tumors and Black women with high grade tumors were statistically significantly different. Compared with Black women with low or intermediate grade tumors, Black women with high grade tumors were statistically significantly different . No other pairwise comparisons were statistically significant. Risk was standardized for age and stage.
RFD and 95% confidence intervals for treatment history and health insurance status for Black vs White women
| Treatment history and health insurance status . | White, No. nâ=â202 . |
|---|
You May Like: Does Progesterone Cause Breast Cancer
Side Effects Associated With Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy
Although the majority of women will have no or mild symptoms, endocrine therapy can be associated with specific and often bothersome side effects . Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches can help ameliorate these symptoms. As studies have demonstrated an association between side effects and early treatment discontinuation , it is important to educate patients about possible toxicities and encourage them to contact their health care team to discuss possible interventions. Menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and sweats are seen in 40-60% of patients treated with tamoxifen or AIs, and may be more significant with tamoxifen . Vaginal dryness, vaginal discharge and sexual dysfunction are seen with both tamoxifen and AIs . Weight gain, mood disturbances and fatigue are also commonly observed with both tamoxifen and AIs . AI use is associated with an increased risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis, AI-associated musculoskeletal syndrome , a constellation of symptoms that includes arthralgias, myalgias and stiffness, and is also associated with a potential risk of cardiovascular disease . Tamoxifen increases the risk of thromboembolic disease and endometrial cancer, although the incidence of both toxicities remain low, especially in pre-menopausal women .
New Advances In Targeted Therapy Of Her2
- 1Key Laboratory of Drug-Targeting and Drug Delivery System of the Education Ministry and Sichuan Province, Sichuan Engineering Laboratory for Plant-Sourced Drug and Sichuan Research Center for Drug Precision Industrial Technology, West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2State Key Laboratory Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
You May Like: How Often Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
B Bone Modifying Therapies
As estrogen plays an important role in bone homeostasis, systemic therapies that potentially decrease levels of estrogen can also reduce bone mineral density . In breast cancer, the potential risk of BMD loss is affected both by patient age and by therapy received . Patients receiving AIs or GnRH agonists may have increased short and long term osteoporotic fracture risks. In these patients, BMD testing at least every 2 years is recommended, in addition to dietary supplementation of calcium and vitamin D, exercise and lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation .
In addition to the effects on BMD, bisphosphonates have been shown to have anti-cancer therapeutic effects and are associated with improved breast cancer survival in post-menopausal women. An EBCTCG meta-analysis demonstrated that among post-menopausal women, the use of bisphosphonates reduced bone fractures, breast cancer recurrence, breast cancer recurrence in bone, distant metastases and breast cancer related deaths, irrespective of HR status, tumor grade, nodal involvement or chemotherapy use .