Hormone Receptor Status Influences Breast Cancer Survival Rates
The hormone receptor status of a breast tumour is not usually included in formal discussions of prognosis.
Each breast tumour will potentially have a different hormone receptor status. When a breast cancer tumour tests positive for the hormones estrogen and progesterone, it implies two things:-
Therefore, due to improvements in treatments, overall survival rates will be higher for hormone receptor positive breast tumors than for those that are hormone negative.
Comparison Of Overall Survival Between Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma And Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Study Based On Seer Database
- 1Department of Breast Cancer, Cancer Center, Guangdong Provincial Peoples Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, The Eighth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, China
Objective: Invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma account for most breast cancers. However, the overall survival differences between ILC and IDC remain controversial. This study aimed to compare nonmetastatic ILC to IDC in terms of survival and prognostic factors for ILC.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Cancer Database . Women diagnosed with nonmetastatic ILC and IDC between 2006 and 2016 were included. A propensity score matching method was used in our analysis to reduce baseline differences in clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes. Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test were used for survival analysis.
Our results demonstrated that ILC and IDC patients had similar OS after PSM. However, ILC patients with high risk indicators had worse OS compared to IDC patients by subgroup analysis.
Read Also: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
Why Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Going To Be Higher Than The Most Up
It is important to remember that the breast cancer survival rates that are listed on this page are, in reality, going to be higher.
This is because the breast cancer survival rates data is gathered from a large number of people with the disease over a 5 year period. Hence, even the most up-to-date statistics are still going to be a little out of date.
Thus, with the ongoing improvements and advancements in breast cancer screening, research, early detection and advanced tailored treatment, the outcomes at present will be even better than the statistics listed here.
Recommended Reading: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 1 Breast Cancer
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop. The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated.
Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
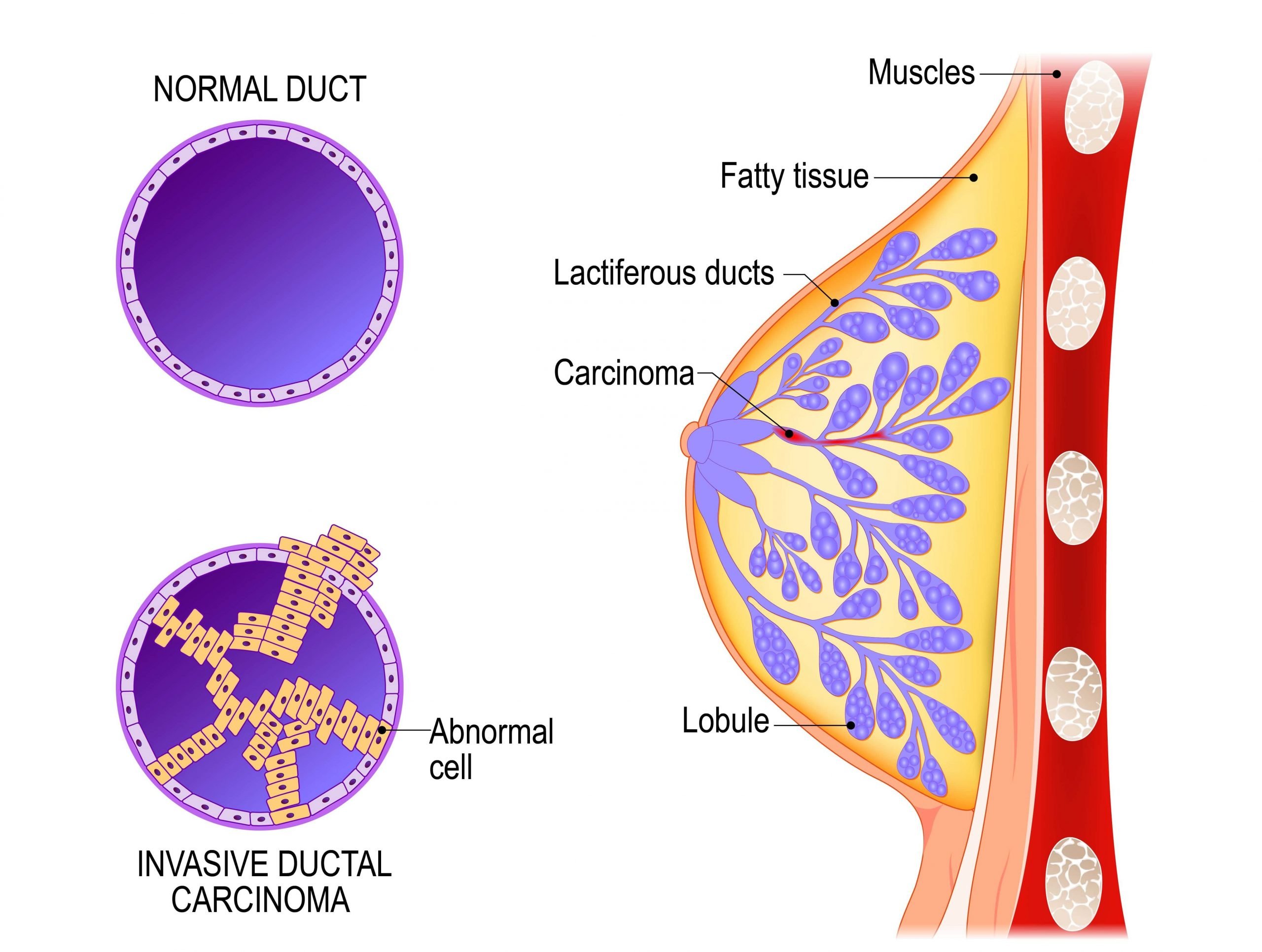
Fully understanding your situation can empower you and help you take control of your health. Here are some questions you might want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What stage of invasive ductal carcinoma do I have?
- How far has my cancer spread?
- What are my treatment options?
- How long will my treatment take?
- Will I be able to work during my treatment?
- What are my chances of survival?
Read Also: Is There Any Cure For Breast Cancer
Stages Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
As with other types of cancer, IDC can be classified by the stage at which it is diagnosed. This allows doctors to categorise how far the cancer has spread beyond the original location of the milk duct and can be useful for diagnosing further treatment. The stage of the cancer depends on the size of the tumour, whether the lymph nodes are involved and how far it has spread beyond the breasts and lymph nodes. Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma are numbered from 1 to 4.
Stage 1 and 2 refer to early breast cancer. This means although the cancer is invasive, it is still contained in the breast. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit or remain confined to the breast . The 5-year survival rate for stage 1 breast cancer is, on average, 100%, and for stage 2, 94.6%.
Stage 3refers to locally advanced breast cancer, including IDC. It is more advanced than stage 2 cancer, having potentially been found in several lymph nodes and tissues near the breast . The 5-year average survival rate for stage 3 breast cancer is 80.2%.
Stage 4is also known as advanced or metastatic breast cancer, meaning it has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast, such as the bones, brain and/or other organs. The 5-year survival rate for stage 4 cancer is 32%.
And Tumor Grade And Necrosis At Diagnosis Of Dcis
There are 3 grades of Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ . If you have been diagnosed with DCIS you will be able to find the Grade on your Pathology Report.
1.Low Grade DCIS 2. Moderate Grade DCIS 3. High Grade DCIS
A Brazilian medical study examined 403 cases of Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ between the years of 2003 to 2008.
This study found that a solid morphology was the most common feature found in 42.2% of the cases. Furthermore, high-grade DCIS was also common and discovered in 72.7% of patients.
A subtype of DCIS, comedo necrosis, associated with necrosis was present in just over half of the cases . In addition, this feature was more common in solid tumors.
Both high-grade DCIS and comedo necrosis were identified more often in younger patients.
In conclusion, this study found high-grade DCIS to be associated with progression to invasive breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Trauma To The Breast Cause Cancer
Diagnosing Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Some women may feel a lump in their breast and seek evaluation, while others may learn they have breast cancer during their mammogram screening or breast X-ray. Other imaging tests and a biopsy may also be ordered to help the doctor assess the patients condition.
During a biopsy, the doctor removes some tissue or fluid from the breast for analysis under a microscope. The sample is sent off to a lab, where a pathologist checks for the presence of cancer cells, and it may take a few days to get the results.
If the diagnosis is breast cancer, the doctor then needs to determine its stage, including whether or not its started to spread inside or outside the breast. The specifics guide any treatment decisions.
Treatment Options For Dcis: Lumpectomy Or Mastectomy
In most cases, the first line of treatment when DCIS is diagnosed is some form of breast surgery.
There are two basic surgical approaches for DCIS treatment:-
Lumpectomy is usually adequate if the area of breast abnormality is very small or only one abnormality is found on a mammogram.
Also, lumpectomy is usually recommended if the DCIS is of a less aggressive type such as non-comedo DCIS.
Lumpectomy is most effective for DCIS patients with small, low-grade DCIS which is easily identifiable on mammogram. In some cases the amount of DCIS is so small that the first exploratory biopsy is enough to remove all of the carcinoma and a subsequent lumpectomy is not required.
You May Like: What Does It Feel Like When You Have Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for female breast cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 85% in women aged 15-39 and peaks at 92% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 70% in 80-99 year-olds for patients diagnosed with breast cancer in England during 2009-2013.
Breast Cancer , Five-Year Net Survival by Age, Women, England, 2009-2013
Dont Miss: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Types Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
These days, people with breast cancer can know more about the tumor than ever before.
In addition to staging, oncologists can now determine a tumors grade and subtype. This information helps the doctor describe the tumor and cancer stage in a more detailed way so that other members of the care team can understand the cancer better.
The tumor grade and subtype of breast cancer can vary between people. Most doctors will test tumors to determine which genes they express, so that treatment options can adapt to the results.
Doctors define different types of stage 3 breast cancer by:
- Tumor grade: This is a measurement of how much the cancer cells differ from healthy cells under a microscope. This also provides a measure of how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow.
- ER status: This describes whether the cancer cells have receptors for the hormone estrogen.
- PR status: This indicates whether the cancer cells have receptors for the hormone progesterone.
- HER2 status: This describes whether the cancer cells are making the HER2 protein.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Breast Cancer Come Back
What Are Cancer Survival Statistics
A key part of making a prognosis is looking at survival rates. These are numbers researchers collect over many years in people with the same type of cancer. These numbers are based on large groups of people. For breast cancer, there are two main measurements:
Breast cancer survivalrates reflect the percentage of women who are alive 5 years or longer after their diagnosis. This means the numbers are based on women who were found to have breast cancer at least 5 years ago. Advances in diagnosing and treating cancer have led to steadily improving survival rates, so the outlook for women diagnosed today is likely better.
Relative survival rates donât take into account the cause of death. Theyâre a measure of the percentage of people with cancer who have lived for a certain time after diagnosis, compared with people who did not have cancer.
How Is Invasive Breast Cancer Treated
![[Full text] Biomarker discovery to improve prediction of breast cancer ... [Full text] Biomarker discovery to improve prediction of breast cancer ...](https://www.breastcancertalk.net/wp-content/uploads/full-text-biomarker-discovery-to-improve-prediction-of-breast-cancer.jpeg)
Different things will determine the type of breast cancer treatment your doctor recommends, including:
- Size of the tumor
- Results of lab tests done on the cancer cells
- Stage of the cancer
- Your age and general health
- If youâve been through menopause
- Your own feelings about the treatment options
- Family history
- Results of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the risk of breast cancer
There are many treatments for invasive breast cancer. They include:
- Surgery. A lumpectomy is a surgical procedure in which a surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. A mastectomy may be performed after chemotherapy. This procedure removes all of your breast.
- Chemotherapy. This drug treatment may be done before surgery to shrink the tumor and make the cancer operable. Itâs also sometimes given after surgery to try to prevent the cancer from coming back.
- Radiation. Often, radiation treatments are given after chemotherapy and surgery to prevent the cancer from coming back.
- Hormone therapy. Certain medications may be given if the cancer cells have hormone receptors.
- Targeted therapy. If the cancer cells have the gene HER2, you may be given drug treatments specifically for that.
The goal of your treatment is to give you the best possible outcome. Your doctor may use one or a combination of them.
Show Sources
Read Also: Can You Get Breast Cancer From Hitting Your Breast
Infiltrating/invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma usually appears as a subtle thickening in the upper-outer breast quadrant.
As the name suggests, these tumours originate mostly in the breast lobules rather than the lining of the breast ducts.
Invasive lobular cancer is a less common type of breast cancer than invasive ductal cancer. This cancer accounts for about 10% of all invasive breast cancer cases.
Prognosis for infiltrating and invasive lobular breast carcinomas will naturally be influenced by tumor size, grade, stage and hormone receptor status..
However, lobular breast cancers, when positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors, tend to respond very well to hormone therapy.
The overall breast cancer survival rates for infiltrating lobular carcinoma, when matched by stage, are a little higher than for ductal carcinoma for the first 5 years.
Survival rates range from about 77% to 93%, but on average, the 5-year survival rate was estimated at about 90%.
90%2010
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the tumor and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
Read Also: Where Can Breast Cancer Spread To
Survival Rates For Triple
Triple-negative breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Survival Outcomes Of Impc And Idc
Only 8 of the 14 studies provided OS data . The ORs and 95% CIs for each study and the summarized OR are shown in Fig. . The individual OR of the 8 articles ranged from 0.51 to 2.33. The overall summarized estimate OR was 0.90 . There was no significant heterogeneity across the studies . Using the random-effects method yielded a similar effect estimate .
Fig. 2
Results of the survival analysis in IMPC compared with IDC. a Forest plot of the odds ratio for overall survival from eligible studies. b Forest plot of the odds ratio for disease-specific survival from eligible studies
Seven studies provided DSS data. The ORs and 95% CIs for each study and the summarized OR are shown in Fig. . The OR from each of the 6 studies ranged from 0.69 to 2.69. The overall summarized estimate OR was 1.16 , with a higher heterogeneity .
Nine articles provided RFS data. The OR and 95% CI for each study and the summarized OR are shown in Fig. . The ORs of the 8 studies ranged from 0.67 to 2.68. The overall summary estimate OR was 2.04 , with no significant evidence of heterogeneity .
Fig. 3
Results of the recurrence analysis in IMPC compared with IDC. a Forest plot of the odds ratio for relapse-free survival from eligible studies. b Forest plot of the odds ratio for local-regional recurrence-free survival from eligible studies. c Forest plot of the odds ratio for distant metastasis-free survival from eligible studies
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
Recommended Reading: Who Is Most Likely To Get Breast Cancer
Survival Rates For Breast Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor, who is familiar with your situation, about how these numbers may apply to you.
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in Australia and the second most common cancer to cause death in women, after lung cancer.
Breast cancer is the abnormal growth of the cells lining the breast lobules or ducts. These cells grow uncontrollably and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Both men and women can develop breast cancer, although it is uncommon in men. Transwomen, non-binary people can also get breast cancer.
Transgender and gender-diverse people can also get breast cancer. A transgender woman taking medication to lower male hormones and boost female hormones may have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
It is estimated that 19,866 women and 164 men in Australia will be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2021.
In Australia, the overall five year survival rate for breast cancer in females is 91%. If the cancer is limited to the breast, 96% of patients will be alive five years after diagnosis this figure excludes those who die from other diseases. If the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, five year relative survival drops to 80%.
Treatment depends on the extent of the cancer.
Also Check: What Is The Best Type Of Breast Cancer To Have