Biological Mechanisms Underlying Metastasis Dormancy
We envision that the dormancy process is comprised conceptually of several components including cell survival mechanisms that constantly sustain the viability of cancer cells, self-renewal mechanisms that maintain tumorigenesis capacity, and activation/suppression mechanisms that restore/prevent aggressive outgrowth. Very importantly, all of these mechanisms are likely to involve crosstalk between dormant cells and their microenvironment. We will focus on bone as the host tissue of dormant cancer cells because it is the most frequent metastatic site of ER+ breast cancer, and is the major reservoir of DTCs.
Bone metastasis progression from a pre-osteolytic stage to the osteolytic vicious cycle
Left, A diagram showing cancer cells and various types of cells in bones before the initiation of the vicious cycle. Conceptual questions that remain to be answered are listed. Right, A simplified diagram showing major cell types and a few molecular players that have been known involved in the osteolytic cycle.
Less Common Types Of Hormone Therapy
Some other types of hormone therapy that were used more often in the past, but are rarely given now include:
- Megestrol acetate , a progesterone-like drug
- Androgens
- High doses of estrogen
These might be options if other forms of hormone therapy are no longer working, but they can often cause side effects.
Swog Researchers Demonstrated That A Blood Serum Test Can Identify Which Patients With Metastatic Hormone Receptor
PORTLAND, OR & dash Researchers with the SWOG Cancer Research Network have found that patients with metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer who have low activity levels of the enzyme sTK1 in their blood serum at the start of anti-estrogen treatment live longer and go longer without their disease progressing than patients with high levels.
The results suggest that patients with low sTK1 activity levels have slow-growing disease that can be controlled initially with single-drug endocrine therapy for a prolonged period. It remains to be determined whether these patients gain further benefit from adding a CDK4/6 inhibitor to their endocrine therapy.
The findings come from an analysis of serum samples from 432 women with breast cancer who took part in the S0226 clinical trial, which was conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a cancer clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute , part of the National Institutes of Health . Results are published today in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
SWOG researchers have demonstrated that a blood serum test can identify which of these patients have slow-growing disease that might be controlled with a simple aromatase inhibitor pill alone, said Dr. Lajos Pusztai, M.D., DPhil, professor of medicine at Yale Cancer Center, who is a co-author on the paper.
Also Check: Does Pain In Your Breast Mean Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
The most common symptom of most breast cancers is a lump in the breast. A painless, hard mass with irregular edges is most likely cancer, but breast cancers can also have a lump that is soft and tender to the touch. Other possible symptoms in the first three stages of breast cancer include:
- Change in the size and shape of the breast
- Asymmetry in the breast compared to the other
- Skin dimpling or other abnormal changes in the breastâs skin
How Does Hormone Therapy Work
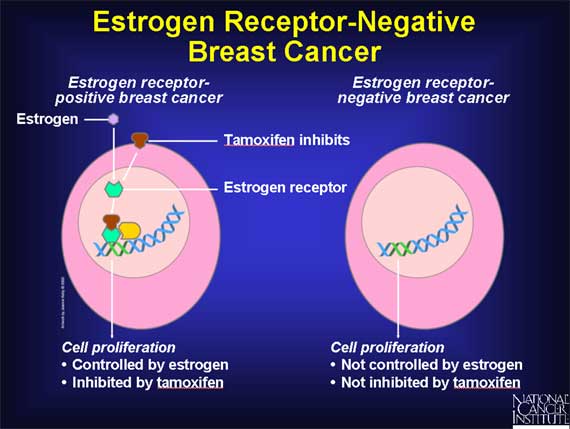
About 2 out of 3 breast cancers are hormone receptor-positive. Their cells have receptors for the hormones estrogen and/or progesterone which help the cancer cells grow and spread.
There are several types of hormone therapy for breast cancer. Most types of hormone therapy either lower estrogen levels or stop estrogen from acting on breast cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: How I Found Out I Had Breast Cancer
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
People may wonder about growth or doubling time when considering how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth is also very important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
The primary treatments for triple negative breast cancers are surgery, radiation and chemotherapy in the first three stages of cancer. In addition, treatment for stage IV cancer include:
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy used to treat triple negative cancer include:
- PARP inhibitors: PARP inhibitors are used to treat triple negative, as well as HR positive and HER2 negative breast cancers which have BRCA mutations. Poly ADP ribose polymerase is an enzyme that helps DNA repair, and PARP inhibitors block the cancer cells from repairing their DNA so they die. PARP inhibitors include:
- Olaparib
- Talazoparib tosylate
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy drugs enhance the ability of immune cells to identify and kill the cancer cells. Immunotherapy is used to treat triple negative cancers that have a protein known as PD-L1 in them.
- PD-1 inhibitors: PD-1 protein in immune cells prevents them from attacking the bodyâs cells, including cancer cells. Blocking PD-1 activity improves T-cellâs ability to kill cancer cells. PD-1 inhibitors used to treat triple negative cancers that have PD-1 in them include:
- Pembrolizumab
You May Like: What Are Some Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Estrogen Receptor Blockers Estrogen Receptor Blocker Drugs Attach Directly To And Block The Estrogen Receptors On Cancer Cells So That The Cancer Cells Cant Use Estrogen They Do Not Affect The Level Of Estrogen In The Body Estrogen Receptor Blockers Are Also Called Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is the most commonly used anti-estrogen drug. It is used in post-menopausal and premenopausal women. Tamoxifen is given by mouth as a pill.
Tamoxifen is the hormonal therapy drug used most often to lower the risk that DCIS or LCIS will lead to an invasive breast cancer.
Tamoxifen very slightly increases the risk for uterine cancer, deep vein thrombosis and stroke. Doctors will carefully weigh these risks against the benefits of giving this drug before they offer it to women who have a personal or a strong family history of these conditions. Usually the benefits of taking tamoxifen outweigh these risks.
Fulvestrant
Fulvestrant is an anti-estrogen drug that reduces the number of estrogen receptors on breast cancer cells. It is given as an injection into the muscles of the buttocks.
Fulvestrant is used in post-menopausal women if the breast cancer has grown after they were treated with tamoxifen. It is also used in postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that have never been treated with hormonal therapy.
Breast Cancer In Postmenopausal Women
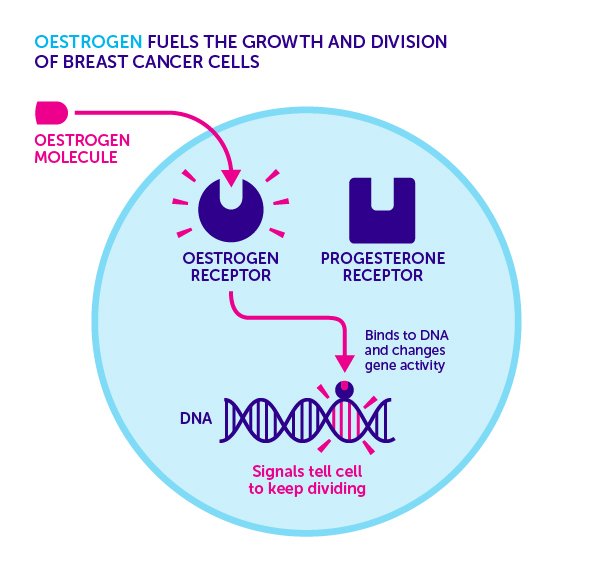
Breast cancer is most common in postmenopausal women, and most breast cancers in postmenopausal women are hormone receptor positive. As women age, the fat cells in their breasts tend to produce greater and greater amounts of an enzyme called aromatase. Aromatase promotes the production of oestrogen. Consequently, with age, the levels of oestrogen present in women’s breasts increases. This locally produced oestrogen plays a role in both the development and growth of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Once established, the tumour acts to increase oestrogen levels to help it grow, with immune cells appearing to boost oestrogen production. Recent studies have also identified a link between obesity and oestrogen production. Data demonstrating that obesity carries a two-fold increased risk of developing breast cancer in older women supports these findings. This makes sense considering that obese women have more of the fat cells responsible for producing oestrogens.
Recommended Reading: What Medications Are Used For Breast Cancer
Factors Associated With More Rapid Spread
Some types of breast cancer, as well as molecular subtypes, are more likely to spread and spread earlier than other types. Ductal carcinoma is more likely to spread than lobular carcinoma, among tumors that are the same size and stage.
While many breast cancers do not spread to lymph nodes until the tumor is at least 2 cm to 3 cm in diameter, some types may spread very early, even when a tumor is less than 1 cm in size.
What Are The Categories Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancers are categorized into the following groups based on the hormone receptor and HER2 status:
- Luminal A: ER and PR positive, and HER2 negative breast cancer
- Luminal B: ER positive, PR negative and HER2 positive breast cancer
- HER2 positive: HR negative and HER2 positive breast cancer
- Triple positive: ER, PR and HER2 positive breast cancer
- Triple negative : HR and HER2 negative breast cancer
Read Also: What Does Breast Cancer Look Like On The Outside
What Does It Mean To Be Her2
If your breast cancer is HER2-negative, you do not have an excess of the HER2 gene. Tumors such as these will not respond to therapies that specifically target HER2 receptors.
If your breast cancer is HER2-positive, then you have too much HER2 protein or extra copies of the HER2 gene. These breast cancers tend to be fast-growing. HER2-positive breast cancer treatment typically includes targeted therapy drugs that slow the growth and kill these cancer cells. HER2-positive breast cancers account for about 25% of all breast cancer cases.
Knowing your HER2 status will help your WVCI cancer care team create the best treatment plan for you.
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass or sheet of cells called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread.When breast cancer is limited to the breast and/or nearby lymph node regions, it is called early stage or locally advanced. Read about these stages in a different guide on Cancer.Net. When breast cancer spreads to an area farther from where it started to another part of the body, doctors say that the cancer has metastasized. They call the area of spread a metastasis, or use the plural of metastases if the cancer has spread to more than 1 area. The disease is called metastatic breast cancer. Another name for metastatic breast cancer is “stage IV breast cancer if it has already spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the original cancer.
Doctors may also call metastatic breast cancer advanced breast cancer. However, this term should not be confused with locally advanced breast cancer, which is breast cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Don’t Miss: What Does Triple Negative Mean For Breast Cancer
Calculating Risk Based On Tumor Size
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center provides a Breast Cancer Nomogram through which you can predict the likelihood that a breast cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes based on tumor size .
To complete this estimate, you are asked to agree to the conditions, and understand that it is only an estimate.
A Hormone Receptor Status Is Either Hormone Receptor Positive Or Hormone Receptor Negative
- Hormone receptor-positive breast cancer cells have either estrogen or progesterone receptors. These breast cancers can be treated with hormone therapy drugs that lower estrogen levels or block estrogen receptors. HR-positive cancers tend to grow more slowly than those that are HR-negative. HR-positive cancers are generally more common in women after menopause.
- Hormone receptor-negative breast cancers do not have estrogen or progesterone receptors. These types of cancers will not benefit from hormone therapy drugs and typically grow faster than HR-positive cancers. HR-negative cancers are more common in women who have not yet gone through menopause.
Read Also: What Are Some Symptoms For Breast Cancer
Biological Models Of Metastasis Dormancy
Before this discussion, it is necessary to define the key parameters of an experimental model for ER+ metastasis dormancy. Such models need to have several key features. 1) Recapitulation of several characteristics of human ER+ tumors including estrogen-dependence, growth inhibition by anti-estrogen strategies, as well as the potential to develop resistance to these treatments. 2) Recapitulation of the natural progression of ER+ tumors, including tumorigenesis, local invasion and intravasation, and the temporal kinetics and anatomical site of metastasis . 3) Opportunities to investigate the roles of major cell types that may be involved in dormancy. In subsequent paragraphs, we will go through the major models/techniques that have been used in breast cancer and point out their strengths and weaknesses for dormancy research. It needs to be noted here that although the abovementioned properties are highly desirable, models lacking these features may still generate useful information. For instance, late recurrences are not exclusively ER+, and the mechanistic insights obtained from ER- models may also be relevant to ER+ diseases.
The roles of Coco and VCAM-1 in metastasis dormancy
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops
You may have heard remarks that cancer has been present for five years before it is diagnosed, and this may sometimes be true.
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown, as estimates based on doubling time assume that this is constant throughout the duration of tumor growth.
If doubling time were constant, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor, and a doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be evident on exam.
In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Since the majority of studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days, it’s likely that most breast cancers that are diagnosed began at least 5 years earlier .
You May Like: Can Men Have Breast Cancer
What Is Hormone Receptor
Breast cancer tumors that are hormone receptor-positive need the hormones estrogen or progesterone to grow. Approximately 75% of breast cancers are hormone-positive in post-menopausal patients. Your healthcare provider will perform a biopsy and laboratory testing to determine the cancer type and most effective treatment.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Each Cancer Stage
Your outlook depends on the stage of your cancer when its discovered. Cancer is staged by number, starting with 0 and going to 4. Stage 0 is the very beginning and stage 4 is the last stage, also called the metastatic stage because its when cancer has spread to other areas in the body.
Each number reflects different characteristics of your breast cancer. These include the size of the tumor and whether cancer has moved into lymph nodes or distant organs, like the lungs, bones, or brain.
The cancer subtype doesnt play a role in staging, only in treatment decisions.
Survival statistics of women with the major subtypes of breast cancer such as ER-positive, HER2-positive, and triple-negative are grouped together. With treatment, most women with very early stage breast cancers of any subtype can expect a normal life span.
Survival rates are based on how many people are still alive years after they were first diagnosed. Five-year and 10-year survival are commonly reported.
According to the American Cancer Society, 5-year survival rates are:
- stage 0 100 percent
- stage 3 72 percent
- stage 4 22 percent
One thing to note is that these statistics also included women with the more aggressive HER2-positive and triple-negative cancers. And it takes five years to get to a five-year statistical survival rate, so newer therapies are not included in these numbers.
Its likely that a woman with ER-positive breast cancer diagnosed today may have a higher chance of survival.
You May Like: Does All Breast Cancer Require Surgery
Three Aromatase Inhibitors Are Approved For Use By The Us Food And Drug Administration : Anastrozole Letrozole And Exemestane
All three aromatase inhibitors have known side effects. The most common is bone and joint pain. Other side effects women report include fatigue, dizziness, hot flashes, and weight gain. All of these side effects can affect your quality of life, and you may be able to tolerate some more than others. If you find the side effects are keeping you from taking the hormone therapy that you were prescribed, you can talk to your doctor about switching to one of the other aromatase inhibitors. You can also discuss switching to tamoxifen.
In June 2014, ASCO updated its hormone treatment guidelines. The new guidelines incorporate new research findings, including a large study that found that 10 years of tamoxifen was more effective than five years of tamoxifen followed by a placebo.
The new treatment guidelines for women with hormone-sensitive breast cancer are:
Hormone Receptor Status And Prognosis

Hormone receptor status is related to the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Hormone receptor-positive tumors have a slightly lower risk of breast cancer recurrence than hormone receptor-negative tumors in the first 5 years after diagnosis .
After 5 years, this difference begins to decrease and over time, goes away .
|
For a summary of research studies on hormone receptor status and survival, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Don’t Miss: Does Sugar Feed Breast Cancer
Estrogen Receptor And Progesterone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Breast tumors are tested to see if they are estrogen receptor and/or progesterone receptor positive or negative. Hormone receptor tests are both prognostic and predictive. In general, tumors that are ER+ and/or PR+ are slightly slower growing and have a slightly better prognosis than tumors that arent. Hormone receptors also provide information about treatment options. If your tumor is ER+ and/or PR+, then your cancer can be treated with a hormone therapy. For this reason, these tumors are also sometimes referred to as hormone sensitive.
Hormone therapies slow or stop cancers growth by changing the hormonal milieu. For early stage cancer, these treatments include tamoxifen and a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors or AIs. Currently three aromatase inhibitors are approved for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration : anastrozole , letrozole , and exemestane . Studies suggest that all three are equally effective. Women with metastatic breast cancer also have other hormone therapy options, including fulvesrant , megestrol acetate , and tormifene .