Sudden Change In Breast Size
IBC can change the appearance of the breasts. This change can occur suddenly. Because this cancer can cause inflammation and swelling, breast enlargement or thickness can occur.
The affected breast may appear noticeably larger than the other breast or feel heavy and hard.
If youve always had symmetrical breasts and you notice a sudden increase or decrease in the size of one breast, speak with your doctor to rule out IBC.
diagnostic criteria for IBC include:
- breast redness, swelling, dimpling, or warmth that comes on quickly, with or without a detectable lump or mass
- redness that includes at least a third of the breast
- symptoms that have lasted for no longer than 6 months
- confirmation of the presence of cancer cells through a biopsy
Now lets explore the diagnostic methods that can be used for IBC in a little more detail.
Challenges Of Diagnosing Ibc
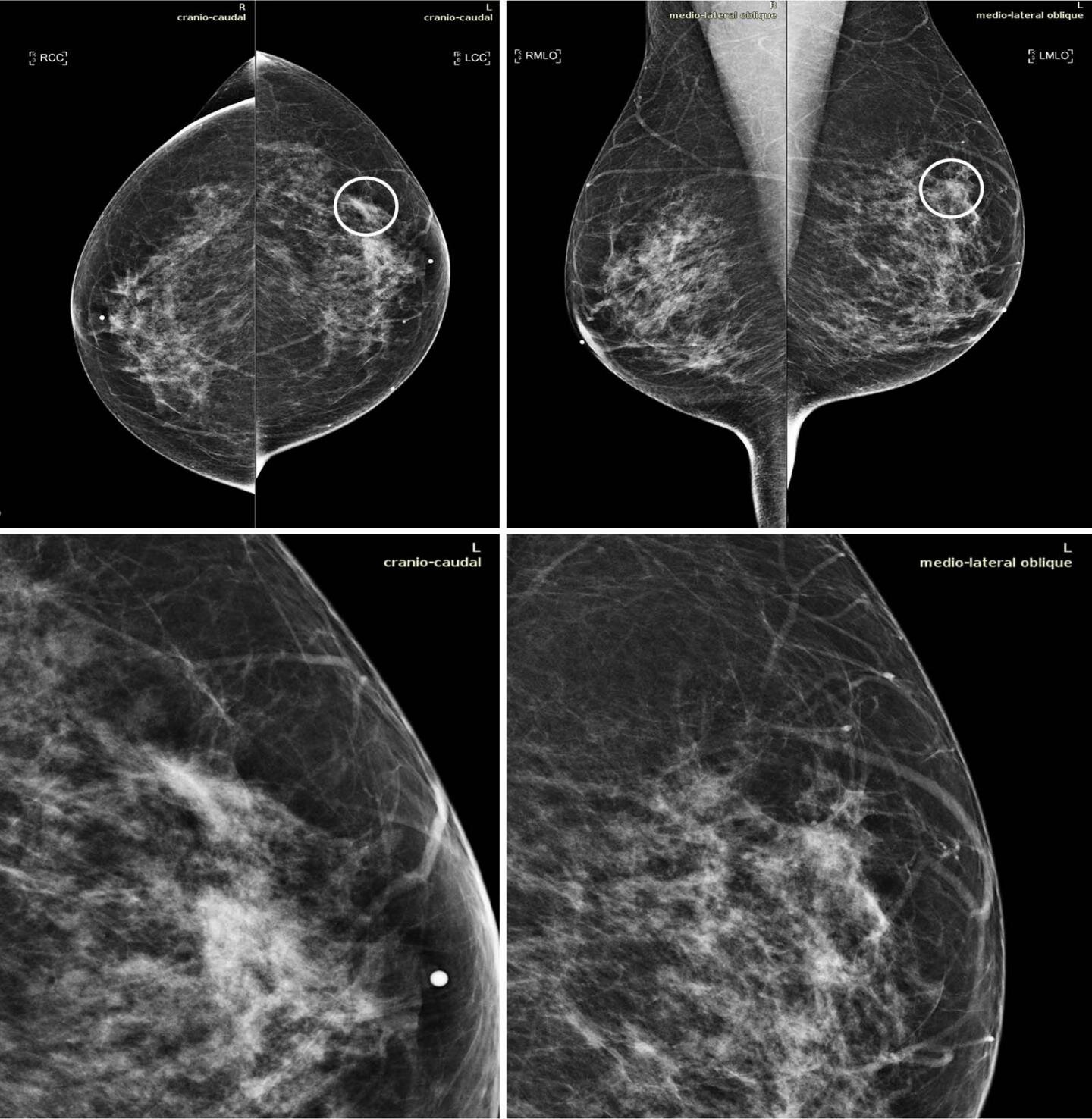
Routine mammography may miss IBC because of its rapid onset, which may happen between scheduled mammograms.
IBC can also be hard to see on a mammogram. IBC often spreads throughout the breast or it may only show up as a sign of inflammation, such as skin thickening .
In some cases, skin changes or a lump may be noted during a clinical breast exam.
IBC may first be mistaken for an infection or mastitis because of symptoms such as redness and swelling, and the frequent lack of a breast lump.
If you have any of the warning signs listed above and they last longer than a week, tell your health care provider. Its always OK to get a second opinion if youre not comfortable with your health care providers recommendation.
Playing An Active Role
You play an active role in making treatment decisions by understanding your breast cancer diagnosis, your treatment options and possible side effects.
Together, you and your health care provider can choose treatments that fit your values and lifestyle.
Learn more about factors that affect treatment options.
|
For a summary of research studies on neoadjuvant chemotherapy and breast cancer treatment, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
|
For a summary of research studies on neoadjuvant hormone therapy and breast cancer treatment, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
|
For a summary of research studies on radiation therapy following mastectomy in women with invasive breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
|
For a summary of research studies on chemotherapy and overall survival in breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
|
For a summary of research studies on survival in women with IBC, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Also Check: What Is Breast Cancer Stage 1a
What Causes Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Most inflammatory breast cancer is considered invasive ductal carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma is cancer that forms from cells lining your milk ducts. An invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer that spreads beyond your milk ducts, invading healthy tissue. Researchers dont know what causes these cells to become malignant .
Inflammatory breast cancer develops when cancer cells block lymph vessels. Lymph vessels are hollow tubes in your lymphatic system that allow lymph fluid to drain out of your breast. The blockage causes your breast to become red, swollen and inflamed. In most cases of IBC, cancer cells spread outward from your lymph vessels. Cancer that has metastasized affects your other organs and is harder to treat.
When To Consider Joining A Clinical Trial
If youre newly diagnosed with IBC, consider joining a clinical trial before starting treatment. For most people, treatment doesnt usually start right after youve been diagnosed. So, theres time to look for a clinical trial.
Once youve begun treatment for IBC, it can be hard to join a clinical trial.
|
Susan G. Komen® Breast Care Helpline |
|
If you or a loved one needs information or resources about clinical trials, call the Komen Breast Care Helpline at 1-877 GO KOMEN or email . The Helpline offers breast cancer clinical trial education and support, such as:
Se habla español. |
BreastCancerTrials.org in collaboration with Susan G. Komen® offers a custom matching service to help find clinical trials that fit your health needs, including trials for people with IBC.
Learn more about clinical trials.
Also Check: Does Mri Detect Breast Cancer
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares women with the same type and stage of breast cancer to women in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of breast cancer is 70%, it means that women who have that cancer are, on average, about 70% as likely as women who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer causes a number of signs and symptoms, most of which develop quickly , including:
- Swelling of the skin of the breast
- Redness involving more than one-third of the breast
- Pitting or thickening of the skin of the breast so that it may look and feel like an orange peel
- A retracted or inverted nipple
- One breast looking larger than the other because of swelling
- One breast feeling warmer and heavier than the other
- A breast that may be tender, painful or itchy
- Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms or near the collarbone
If you have any of these symptoms, it does not mean that you have IBC, but you should see a doctor right away. Tenderness, redness, warmth, and itching are also common symptoms of a breast infection or inflammation, such as mastitis if youre pregnant or breastfeeding. Because these problems are much more common than IBC, your doctor might suspect infection at first as a cause and treat you with antibiotics.
Treatment with antibiotics may be a good first step, but if your symptoms dont get better in 7 to 10 days, more tests need to be done to look for cancer. Let your doctor know if it doesn’t help, especially if the symptoms get worse or the affected area gets larger. The possibility of IBC should be considered more strongly if you have these symptoms and are not pregnant or breastfeeding, or have been through menopause. Ask to see a specialist if youre concerned.
Don’t Miss: What Were Your First Signs Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Subject Ascertainment And Secondary Data Requisition
Patients with IBC and with non-inflammatory breast cancer were ascertained through epidemiologic studies conducted at George Washington University from 2002 to 2012 . All subjects were Caucasian and the same epidemiologic questionnaire asking about reproductive, medical and family history was collected on both groups of patients at the time of recruitment. The family history portion of the questionnaire asked about diagnosis of breast cancer among first-degree relatives of the index case. We subsequently validated the family history questions of this questionnaire by collecting pedigrees on 21 of 67 living IBC patients and by correlating the information from pedigrees and the questionnaires. We found 100 % agreement between the two modes of collecting first-degree breast cancer family history information. We also came across several families with cases of both inflammatory and non-inflammatory breast cancer among the relatives.
Another group of post-menopausal breast cancer cases unselected for family history and healthy controls with no personal history of breast or ovarian cancer was obtained from the Hormone Therapy Trials of the WHI cohort . WHI cases and controls were compared to IBC cases with respect to the prevalence of first-degree breast cancer family history and selected environmental risk factors for breast cancer.
Emt Score Cov Is Higher In Ibc Samples
Finally, after establishing the importance of EMT scores in segregation of IBC and nIBC samples, we compared these scores across IBC and nIBC. There was no significant difference in mean scores of IBC vs. nIBC across the three datasets , with overlapping variance between the two groups. However, the within-group coefficient of variance , a better measure than variance to assess the dispersion around the mean, was consistently higher in 8 out of 9 total cases . This result shows IBC samples are more heterogenous as compared to nIBC in terms of their positioning on EMT spectrum.
Don’t Miss: Does Rash On Breast Mean Cancer
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening mammogram. In addition, most women diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer have dense breast tissue, which makes cancer detection in a screening mammogram more difficult. Also, because inflammatory breast cancer is so aggressive, it can arise between scheduled screening mammograms and progress quickly. The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may be mistaken for those of mastitis, which is an infection of the breast, or another form of locally advanced breast cancer.
To help prevent delays in diagnosis and in choosing the best course of treatment, an international panel of experts published guidelines on how doctors can diagnose and stage inflammatory breast cancer correctly. Their recommendations are summarized below.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- A rapid onset of erythema , edema , and a peau d’orange appearance and/or abnormal breast warmth, with or without a lump that can be felt.
- The above-mentioned symptoms have been present for less than 6 months.
- The erythema covers at least a third of the breast.
- Initial biopsy samples from the affected breast show invasive carcinoma.
Imaging and staging tests include the following:
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treated
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
Don’t Miss: How You Get Breast Cancer
Ssgsea Scores Of Ibc Gene Signatures Helps In Separation Of Ibc And Nibc Samples
As both linear and non-linear combinations of all four gene lists failed to segregate the IBC from nIBC samples in these datasets, we next examined whether as a group, these genes are enriched in IBC samples or not. We used single-sample GSEA , an extension of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis , which calculates separate enrichment scores for each pair of a sample and a gene set. Each ssGSEA enrichment score represents the degree to which the genes in a particular gene set are cumulatively up- or down-regulated within a given sample . We thus tested whether IBC gene signatures are relatively enriched in IBC samples.
We calculated ssGSEA enrichment scores for all four different gene sets and compared these scores between IBC and nIBC samples across three corresponding datasets. This comparison showed some instances of statistically significant differences in ssGSEA scores of IBC and nIBC samples: a) ssGSEA scores of 78 GES for IBC samples was higher than that of nIBC samples in }GSE22597, b) ssGSEA scores of 50 GES and 132 GES was relatively higher for IBC samples in }GSE5847, and c) ssGSEA scores of 132 GES were comparatively higher for IBC samples in }GSE45581 . However, none of the four gene sets showed consistent and statistically significant differences between IBC and nIBC across the three datasets.
Deleterious Brca2 Mutation In A 40
Gloria J. Morris, MD, PhD
Department of Medicine, Mount Sinai Hospital of Queens, Long Island City, New York
Address correspondence to: Gloria J. Morris, MD, PhD, Department of Medicine, Mount Sinai Hospital of Queens, Long Island City, NY 11106 E-mail: dr.gjmorris@gmail.com.
Introduction
Jimenez and associates present and discuss a very intriguing case of a 40-year-old white woman of Irish heritage who presented with an inflammatory, invasive, estrogen receptor -positive, progesterone -negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 -negative right breast cancer, and whose mother had succumbed to the disease at age 35.1 Because of this familial significance, which further included a paternal aunt diagnosed with breast cancer at age 55, the proband met the standard criteria for testing for mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2. Indeed, she was found to harbor a deleterious sequence in BRCA2 of S2670L , reclassified after family studies by the genetic laboratory from a previous characterization of a mere variant of undetermined significance .
Discussion
References
1. Jimenez AM, Growney A, Behrens G, Corbridge C, Chapman DD, Usha L. Hereditary inflammatory breast cancer associated with BRCA2 mutation: a rare disease presentation in mother and daughter. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012 10: 402-404.
3. Rebbeck TR, Lynch HT, Neuhausen SL, et al. Prophylactic oophorectomy in carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2002 346:1616-1622.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Breast Cancer Metastasis
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Ask your healthcare provider about what your cancer diagnosis means for your treatment options and likely outcomes. Questions to ask include:
- What stage is my breast cancer?
- Which specialists will be involved in my care?
- What treatment options would you recommend?
- What outcomes should I expect from treatment?
- What are potential side effects or complications related to treatment?
- Can you connect me with resources ?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of cancerthat spreads quickly. Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider immediately if you notice changes in your breasts, especially a change in one breast but not the other. The changes may be a sign of a less serious condition, like an infection. Still, IBC spreads fast. If your symptoms are a sign of inflammatory breast cancer, youll want to begin treatment as early as possible. Dont delay seeking care that can potentially improve your prognosis.
Correlation Between Ibc Gene Signature Ssgsea Scores And Emt Scores
It has been proposed that IBC cells exhibit a partial EMT behavior, given the retention of E-cadherin levels and the trait of collective cell migration through tumor emboli . Thus, following the assessment of IBC gene signatures, we quantified the EMT-ness of IBC and nIBC samples based on three different EMT scoring metrics KS, 76GS and MLR .
These metrics score EMT on a continuum, based on the transcriptomics of individual samples. While KS and MLR score the samples on a scale of and respectively, the 76GS metric has no pre-defined scale. The higher the MLR or KS score, the more mesenchymal the sample is the higher the 76GS score, the more epithelial the sample is. Thus, KS and MLR scores of samples in a given dataset correlate positively with one another both of them correlate negatively with 76GS scores, as seen across multiple datasets
Correlation between ssGSEA score and EMT scoring methods. A)}GSE5847B)}GSE22597. Pearson’s correlation R and p-values highlighted above each scatter plot.
You May Like: Can Young Women Get Breast Cancer
What Are The Survival Rates For Ibc
IBC is a fast-growing and aggressive cancer. However, many factors may influence your outcome from IBC:
- The location, stage and whether or not the cancer has spread all can affect how you respond to treatment.
- Age and overall health also play a role.
While its true that this type of cancer has a lower survival rate than other forms of breast cancer, its important to remember that your situation is unique, and statistics are generated from previous patients and past treatments.
With localized IBC, meaning it hasnt spread to other organs, the five-year survival rate is about 39 percent. However, statistics on survival depend on several factors, including the cancers stage and the type of treatment you have. For instance, if cancer has spread to other organs in the body, the survival rate is about 18 percent. But if the cancer has spread to only nearby lymph nodes, the survival rate averages about 52 percent.
Expert cancer care
Ngs And Data Analysis
Library preparation included sequence barcodes to discriminate samples and unique molecular indices to identify PCR duplication. Four libraries were pooled together per flow cell and sequenced producing an average of 6,923,890 total reads per sample and 2270 paired-end reads per targeted region . The data was analyzed using Qiagenâs GeneGlobe portal and the variant call format files were generated. Variants were filtered out if no allele fraction was greater than 2% for tumor tissue samples or malignant cells, and greater than 2% for blood cfDNA. AF for a specific variant can be defined as the number of times that variant is observed divided by the total number of reads of that region. In case whole blood or normal tissue was available, germline variants were validated. A total of 82 patient samples were studied by NGS: 33 blood cfDNA samples from 32 patients 29 paired tumor samples from 29 patients and DNA isolated from whole blood or normal tissue from 20 patients to confirm germline variants. Putative germline variants were considered those with an AF around 0.5 or 1.0 in blood cfDNA and tumor tissue .
Recommended Reading: How Early Can You Develop Breast Cancer
Stage 4 Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treatment
Cancer thats spread to more distant areas of the body is typically treated using one or a combination of the systemic therapies mentioned above. These include:
Its unclear exactly what causes IBC. In general, cancer develops due to genetic changes. These can happen due to a variety of factors, such as:
- genetic changes inherited from your parents
- irregularities that naturally occur during cell division
- damage to DNA through environmental exposures
Sometimes gene mutations that are associated with cell growth and division can occur. When this happens, cells can grow and divide out of control.
In IBC, cells in the breast ducts or lobules begin to rapidly grow and divide. As cancer cells build up, they block the lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This leads to the redness, swelling, and dimpling associated with IBC.