Testing For Proteins And Genes
The breast cancer cells will be tested for certain proteins called estrogen and progesterone receptors. If the cancer has these proteins, it’s called a hormone receptor positive breast cancer. The cells are also tested to see if the cancer makes too much of the HER2 protein. If it does, it’s called a HER2-positive cancer. These cancers are sometimes easier to treat. If the cancer doesn’t test positive for any of these proteins, it’s called a triple-negative breast cancer.
The cells might also be tested for certain genes, which can help decide if chemo might be helpful and how likely it is that the cancer will come back. Ask your doctor to explain the tests they plan to do, and what the results might mean.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
After the treatment of breast cancer, long-term follow-up is necessary. There is a risk of local and distant relapse, and hence an interprofessional team approach is necessary. The women need regular mammograms and a pelvic exam. Also, women with risk factors for osteoporosis need a bone density exam and monitoring for tumor markers for metastatic disease. For those who are about to undergo radiation therapy, a baseline echo and cardiac evaluation are necessary. Even though many types of integrative therapies have been developed to help women with breast cancer, evidence for the majority of these treatments is weak or lacking.
Outcomes
Over the past four decades, the survival rates of most breast cancer patients have improved. Of note is that the presence of breast cancer has gradually slowed down over the past decade, which may be due to earlier detection and improved treatments. The prognosis for patients with breast cancer is highly dependent on the status of axillary lymph nodes. The higher the number of positive lymph nodes, the worse the outcome. In general, hormone-responsive tumors tend to have a better outcome. In breast cancer survivors, adverse cardiac events are common this is partly due to the cardiotoxic drugs to treat cancer and the presence of traditional risk factors for heart disease. The onus is on the healthcare provider to reduce the modifiable risk factors and lower the risk of adverse cardiac events. [Level 5)
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
You May Like: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Dogs And Cancer: Get The Facts
A vet answers 10 commonly asked questions about cancer in dogs.
Cancer is the leading cause of death in dogs over the age of 10. But half of all cancers are curable if caught early, experts say. WebMD talked to Dave Ruslander, a veterinary oncologist and past president of the Veterinary Cancer Society, about canine cancers and the latest treatments for dogs diagnosed with the disease.
Q: How common is cancer in dogs, and what are some of the common cancers found in dogs?
A: It has gotten to be pretty common, especially in older dogs. Fifty percent of dogs over the age of 10 develop cancer at some point. We see malignant lymphoma, which is a tumor of the lymph nodes. We see mast cell tumors, which is a form of skin cancer. There are mammary gland tumors, or breast cancer, and soft tissue sarcomas. We also see a fair amount of bone cancer in dogs.
Q: What are some of the symptoms of cancer in dogs?
A: The warning signs of cancer in dogs are very similar to that in people. A lump or a bump, a wound that doesnt heal, any kind of swelling, enlarged lymph nodes, a lameness or swelling in the bone, abnormal bleeding. Those are all classic signs. But sometimes there are little or no signs, at least early on. So any time an animal isnt feeling well, or theres something abnormal or not quite right, the owner needs to bring it to the attention of their veterinarian.
Q: Whats causing these high cancer rates in our dogs?
Continued
Continued
Tailoring Your Treatment Plan
Before a healthcare professional recommends a treatment plan, theyll collect and test a tumor sample to learn what type of breast cancer you have.
Some types of breast cancers are:
- Estrogen receptor-positive. This type of breast cancer grows more quickly in the presence of the hormone estrogen.
- Progesterone receptor-positive. This type of breast cancer grows more quickly in the presence of the hormone progesterone.
- Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 -positive. These cancers produce an overabundance of the HER2 protein, which drives the growth of the cancer cells.
Other types of breast cancers are:
- estrogen receptor-negative
- HER2-negative
These are known as triple-negative breast cancers.
If you have breast cancer thats estrogen receptor-positive, progesterone receptor-positive, or HER2-positive, your doctor may recommend hormone therapy or targeted therapy.
Fewer treatments are available for triple-negative breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Don Harrington Breast Cancer Center
How Is Metastatic Cancer Treated
Most of the time metastatic cancer cannot be cured. The goal of treatment for metastatic cancers is to slow growth, reduce symptoms, and prolong the patients life as long as possible with as much quality as possible.
The treatment for metastatic cancer depends on:
- The original cancer and where it started
- How much the cancer has metastasized and where it is located
- How quickly the cancer is spreading
- The patients age and health
Treatment for metastases may be different from treatment for the original tumor. Treatments for metastatic cancers include one or more of the following:
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares women with the same type and stage of breast cancer to women in the overall population.For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of breast cancer is 90%, it means that women who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as women who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Don’t Miss: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
How Much Do Anastrozole And Exemestane Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Studies have shown that both anastrozole and exemestane can lower the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk of the disease.
In one large study, taking anastrozole for five years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 53 percent. In another study, taking exemestane for three years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 65 percent.
The most common side effects seen with anastrazole and exemestane are joint pains, decreased bone density, and symptoms of menopause .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/31/2018.
References
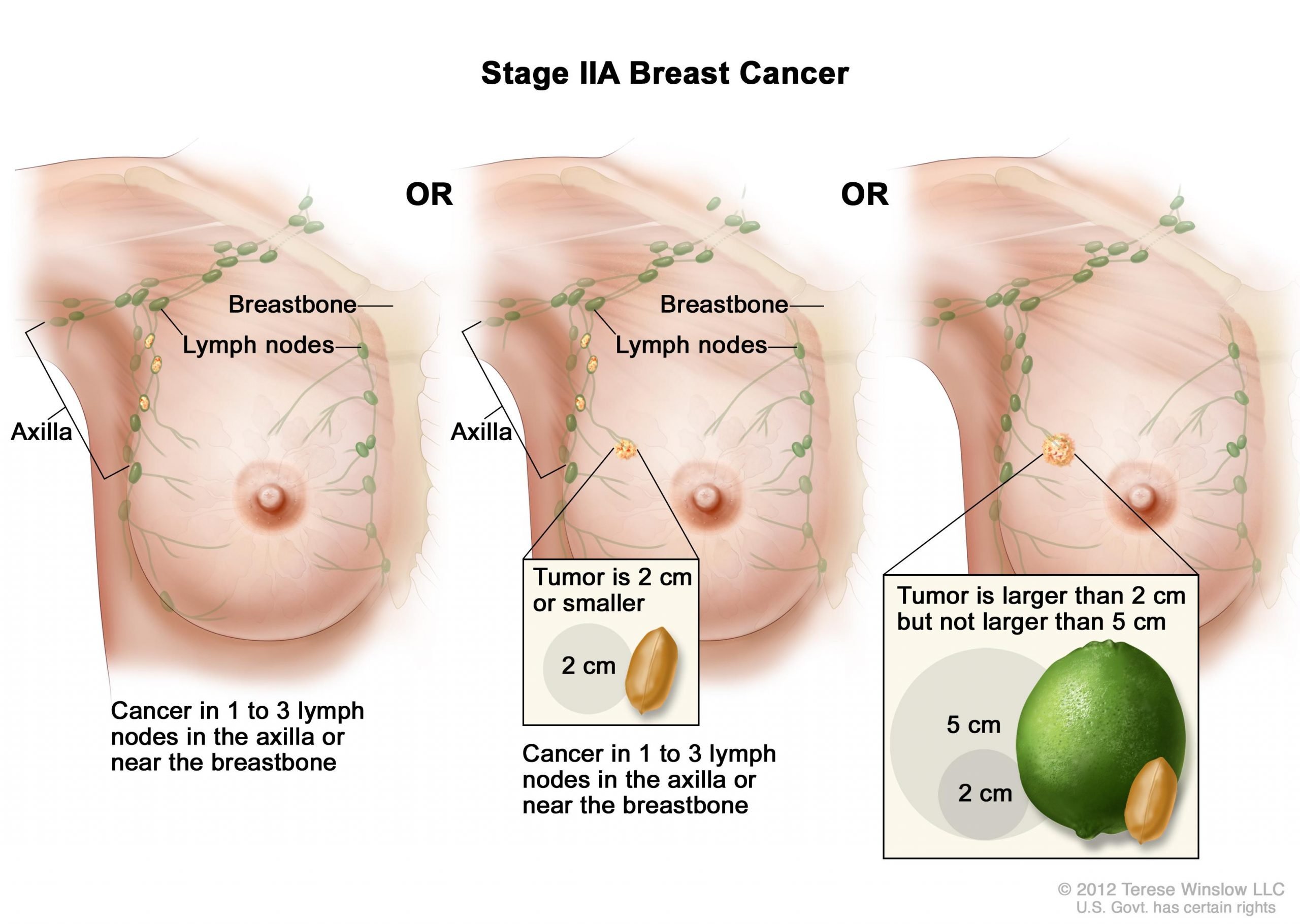
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
A Detailed Introduction About Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
Over the centuries, mankind has been faced with numerous diseases and ailments that have caused immense suffering and even, have proved to be fatal. With medical and technological advancement, humans have been able to diagnose and find a cure to most common diseases and ailments that prevail in the present times. But amidst all these advancements, a disease remains that, though being very common, cannot always be completely cured and even if cured, has serious repercussions on the patient. That ailment is malignant neoplasm, more commonly known as cancer.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive breast cancer. In situ means in place. With DCIS, the abnormal cells are contained in the milk ducts of the breast and have not spread to nearby breast tissue.
Although DCIS is non-invasive, without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive breast cancer over time. So, you may also hear the terms pre-invasive or pre-cancerous to describe DCIS.
Learn about breast anatomy.
Don’t Miss: Does Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
Myth #: When Breast Cancer Travels To The Bone Brain Or Lungs It Then Becomes Bone Cancer Brain Cancer Or Lung Cancer
Not true. Breast cancer is still breast cancer, wherever it travels in the body. However, the characteristics of the cells can change over time. For example, a breast cancer that tested negative for hormone receptors or an abnormal HER2 gene might test positive when it moves to another part of the body, or vice versa . Keep in mind that the cancer cells are trying to survive in the body, so they can change, says Dr. Gupta. We always emphasize rechecking the biology.
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
Also Check: Can Stage 3 Breast Cancer Be Cured
Symptoms Of Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
Unlike other ailments, the symptoms or indicative signs of cancer vary widely depending on a variety of factors like the cancer type, cancer stage, etc. Not only that, the symptoms vary from individual to individual and may also be totally absent until cancer has reached a very advanced stage. However, in case of critical cancers like brain cancer, the symptoms may start exhibiting at the very early stages. Though several symptoms are cancer-type specific, yet an uncontrolled growth of cells leads to certain common problems that may be considered as the typical cancer symptoms which may be indicative of malignant neoplasm. Some symptoms and signs that you need to look out for are:
- Unusual bleeding
- Hoarse voice caused due to continued coughing
- Appetite loss or weight loss
- Continued feelings of vomiting, nausea, and fatigue
- Pain in one or more body parts that occurs intermittently and is usually worse
- Intermittent fevers for no obvious reason
- Recurring infections
- Changes in moles and warts
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Characteristics Of Malignant Neoplasm
A neoplasm or tumor can be either benign or malignant. If the tumor is benign, it doesnt exhibit much activity, but a malignant neoplasm is highly active and has certain important characteristics that may be helpful in its identification. However, it must be remembered that these features of malignant neoplasia arent usually visible from the outside and can be determined only via clinical tests. The important features that a malignant tumor usually exhibits are as follows:
- Malignant tumors undergo a fast increase in their size.
- The cell mass that forms undergoes very little or no differentiation at all, thereby forming a big lump of cells that are totally useless.
- Malignant cells have a tendency to attack nearby cells and either destroy them or make them malignant.
- These cells may also travel to other parts of the body via lymph or blood vessels and affect other normal tissues, thus causing secondary cancer at the other site.
Not only do cancer cells differ in their activities from normal cells, but their cytological differences are also quite prominent which help differentiate them from normal cells. The main cytological features that malignant neoplastic cells possess are as follows:
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer Twice
When To Consider Joining A Clinical Trial
If youre newly diagnosed with early or locally advanced breast cancer, consider joining a clinical trial before starting treatment. For most people, treatment doesnt usually start right after diagnosis. So, theres time to look for a clinical trial that youre eligible for and fits your needs.
Once youve begun standard treatment for early or locally advanced breast cancer, it can be hard to join a clinical trial.
Learn more about clinical trials.
Additional Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma:
There are four types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are less common:
- Medullary Ductal Carcinoma This type of cancer is rare and only three to five percent of breast cancers are diagnosed as medullary ductal carcinoma. The tumor usually shows up on a mammogram and it does not always feel like a lump rather it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
- Mucinous Ductal Carcinoma This occurs when cancer cells within the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma carries a better prognosis than more common types of IDCs.
- Papillary Carcinoma This is a very good prognosis breast cancer that primarily occur in women over the age of 60.
- Tubular Ductal Carcinoma This is a rare diagnosis of IDC, making up only two percent of diagnoses of breast cancer. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Show me more…
You May Like: Baking Soda And Honey For Cancer
Breast Cancer Type’ Is Determined By Cell Shape And Appearance
Breast cancers or carcinomas are mainly of epithelial cell origin.
Epithelial cells are the lining of most of our organs and vessels.
However, there are quite a few very rare types of breast cancers which are comprised of non-epithelial cells . Furthermore, a great many breast cancers are actually not pure, but rather a mixture of different types of cells.
In general, there are six types of standard breast carcinomas, and statistically, some of these tend to show a better prognosis than others.
The six most common types of breast cancer are as follows:-