What Other Additional Laboratory Studies May Be Ordered
Extensive laboratory work-up is not warranted for DCIS and LCIS since they do not have capacity for systemic spread.
No sponsor or advertiser has participated in, approved or paid for the content provided by Decision Support in Medicine LLC. The Licensed Content is the property of and copyrighted by DSM.
How Is The Stage Determined
The staging system most often used for breast cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The most recent AJCC system, effective January 2018, has both clinical and pathologic staging systems for breast cancer:
- The pathologic stage is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation.
- Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away or at all, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. The clinical stage is used to help plan treatment. Sometimes, though, the cancer has spread further than the clinical stage estimates, and may not predict the patients outlook as accurately as a pathologic stage.
In both staging systems, 7 key pieces of information are used:
- The extent of the tumor : How large is the cancer? Has it grown into nearby areas?
- The spread to nearby lymph nodes : Has the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes? If so, how many?
- The spread to distant sites : Has the cancer spread to distant organs such as the lungs or liver?
- Estrogen Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called an estrogen receptor?
- Progesterone Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called a progesterone receptor?
- HER2 status: Does the cancer make too much of a protein called HER2?
- Grade of the cancer : How much do the cancer cells look like normal cells?
In addition, Oncotype Dx® Recurrence Score results may also be considered in the stage in certain situations.
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
Also Check: Estrogen And Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Difficult Decisions For Patients
Toro de Stefani is one of 60,000 U.S. women diagnosed with DCIS each year. Each must decide on a treatment option.
Current guidelines that recommend lumpectomy and radiation are causing concerns that the condition may be overtreated, since most cases never become invasive.
This gives medical professionals enormous uncertainty about how to advise women on an individual basis, says Thompson, professor of Surgery at MD Anderson. And therefore, historically the treatments have ranged from active surveillance on one end of the pectrum all the way to mastectomies on the other.
Thompson says DCIS diagnoses have increased as breast imaging has become more accurate and frequent. The National Institutes of Health estimates that by 2020, more than 1 million women in the U.S. will be living with a DCIS diagnosis, compared to 500,000 in 2005.
Before mammograms became common, many women had the condition for years without being aware of it, because it grows so slowly and causes no symptoms.
Perhaps, surprisingly, given that breast screening has been around for three or four decades, were only now really coming to grips with the fact that we often diagnose some conditions like DCIS as breast cancer even though theyre not conventional, invasive breast cancers, Thompson says.
Hes participating in three DCIS research studies that he hopes will make treatment decisions easier.
Grading For Breast Cancer
Tumour grading describes how active the cells are and how quickly the tumour is likely to grow. To determine tumour grade, a pathologist will study the tumour tissue removed during a biopsy under a microscope.
- Grade 1 Cancer cells look a little different to normal cells. These tumours are usually slow-growing.
- Grade 2 Cancer cells do not look like normal cells. They tend to grow faster than grade 1 cancer cells.
- Grade 3 Cancers cells look very different from normal cells. They tend to grow and spread rapidly.
The breast cancers grade is used to help predict your likely outcome and determine which treatments are likely to be the most effective.
Don’t Miss: Chemotherapy Cycles For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Staging And Prognosis
Breast cancer staging describes how far the cancer has spread within the breast and other parts of the body. It is an important factor in making treatment decisions.
Breast cancer staging is based on tumour size, the extent that cancer has spread to other parts of the body and other clinical factors. Your doctor will assign a stage to your cancer after your physical exam, mammogram, and other diagnostic tests, such as a biopsy .
Breast Cancer Staging Process
Breast cancer staging is determined by how large tumors are, how far theyve spread, and other characteristics like the genetics of the tumor. Your cancer stage can be determined before surgery or after surgery .
Cancers clinical stage is determined through a physical exam, biopsy , and imaging tests. These imaging tests may include X-rays, computed tomography , positron-emission tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , or ultrasound.
After surgery, your breast cancer stage will either be confirmed or updated as a pathologic stage, using the features found and any additional information about how far cancer has spread gathered during surgery.
You May Like: Type 4 Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Lymphatic Cancer
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
Stage 2 breast cancer survival rate
Lifestyle Also Plays A Role
Some risk factors for DCIS are modifiable. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake have all been linked to lower breast cancer rates, says Dr. Meyers, and they are smart habits to develop no matter what type of breast cancer you’re trying to avoid.
For women who have already had DCIS, cutting back on drinking may reduce their risk of a recurrence, according to a 2014 study in the journal Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. “It is possible that alcohol consumption may increase risk of second breast cancer incidence,” the authors wrote in their paper, “but may not substantially increase the likelihood of aggressive second diagnoses that result in death, particularly among DCIS survivors.”
Read Also: Prognosis Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Are There Other Ways Cancer Is Staged
Cancers that dont appear as solid tumors are generally cancers of the blood, and for those, there are other staging systems.
For instance, the Ann Arbor staging classification, a four-stage system, helps doctors figure out prognosis and best treatment options by examining the location, number of involved sites, and any systemic symptoms in Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoid malignancies.
This staging cant be used for other cancers of the blood/bone marrow, however, including most types of leukemia, which dont have a clear staging system. Likewise, as we mentioned earlier, central nervous system tumorsso, brain tumorsdont currently have a single staging system.
Whats most important to remember is that the stage of your cancer is one tool, of many, in your oncologists care tool kit. It helps them better predict what your response to treatment might bebiomarkers can help make that prediction, as can past research showing how patients in your particular stage did on certain treatment regimes.
By giving doctors parameters to compare your situation to other patients in the same stage, you can get a lot of information, from how effective one treatment option is versus anotherto what side effects you might experience, and what meds might help you handle them. All of this adds up to creating the most targeted, effective treatment plan for you.
Read Also: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
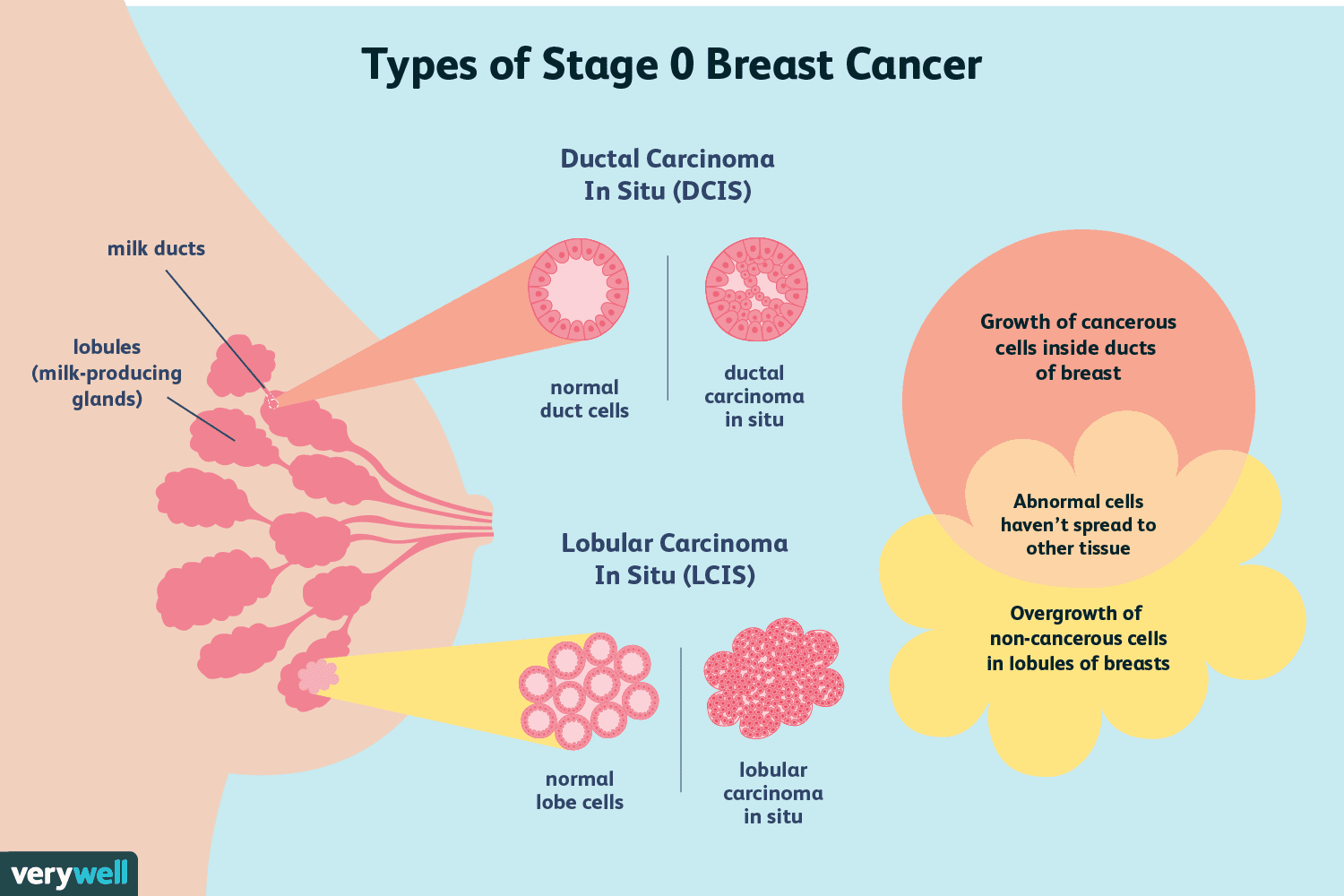
Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Stage 0 breast cancer, or ductal carcinoma in situ , is when there are atypical cells in the lining of your milk ducts. But those cells have not spread beyond the wall of the duct to reach surrounding tissue, your bloodstream, or lymph nodes.
DCIS is noninvasive and is sometimes called precancer. However, DCIS has the potential to become invasive.
Read Also: Tubular Breast Cancer Symptoms
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Cancer Staging And How Dcis Fits In

First, we need to discuss how DCIS fits into the current cancer staging system.
All cancers, no matter what type, are staged and given a number. These numbers range from 0-IV . Stage IV cancers have become metastatic or have spread to other locations in the body. At this stage, cancer can be considered terminal.
Stage IV breast cancer is also called metastatic breast cancer, or MBC. There are treatments available to help slow the progression of MBC and prolong life for patients. Unfortunately, at this time, MBC is not curable.
If you have read in the news or know someone who has died of breast cancer, it is highly likely that person died of metastatic breast cancer.
Read Also: Stage 3 And 4 Cancer
Dcis Can Be Removed Surgically
Treatment for DCIS begins with surgery. Depending on the size of the tumor and how far it has spread within the breast ducts, this can mean either a lumpectomy or mastectomy.
In lumpectomy, which is also known as breast-conserving surgery, partial mastectomy, and wide local excision, only the tumor and a small rim of healthy tissue are removed.
However, if the tumor has spread to many ducts within the breast, your surgeon will most likely decide to perform a mastectomy. In this surgery, the entire breast is removed.
If theres any suspicion your DCIS has become invasive cancer, your surgeon may choose to remove some lymph nodes from under your arm as well. This additional lymph node excision will then be used to help determine the extent of your cancer .
A balanced formulation of leucine-enriched essential amino acids can help accelerate recovery from surgery and protect against muscle loss and inflammation run amok. Read more about healing with the help of amino acids.
Dcis Accounts For 1 In 5 Breast Cancer Diagnoses
Studies have shown that 20% of breast cancer diagnoses are classified as DCIS. With lifespans getting longer and more women getting regular mammograms and access to better technology, DCIS detection rates have increased.
Earlier detection also means more people are getting diagnosed and treated sooner, and theres less chance of the condition turning into invasive breast cancer.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Stage 2 Symptoms
Personalized Treatment Is Key For Stage 0 Breast Cancer
An early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ has stirred controversy in the medical community nationwide.
DCIS, also known as Stage 0 breast cancer, is abnormal cells that are confined to the milk ducts of the breast. The debate is whether all cases of DCIS should be treated immediately with surgery and additional therapy, or if patients should be monitored instead and treated only if the cancer spreads.
A New York Times article from August 2015 has fanned the flames of this controversy. The article features DCIS patients reacting with a mix of gratitude and outrage about their cancer treatment. Some felt their treatment was unnecessary or too severe others were glad they received proactive care.
Both sides of the debate have a viable argument: of course we dont want to perform surgeries that arent needed or expose women to radiation or hormonal therapy unnecessarily, and DCIS in some women will never spread beyond the milk ducts.
But this is our concern: DCIS has a significant chance of turning into invasive cancer. There is currently no way to know which cases will become invasive. Until we have a way to determine that, we cant just sit back and watch women develop breast cancer. We favor a personalized, case-by-case approach to treating Stage 0 breast cancer over watching and waiting.
Ive asked four of our breast cancer experts to explain our position and clear up some misconceptions about the treatment of DCIS.
Cancer Staging Before 2018
Before 2018, cancer staging included less information about the tumor than it does now.
Pre 2018 stagingincluded information about the physical characteristics of the tumor but didnt take into account any additional information about the biology of the cancer.
- T- Tumor Size
- M- Metastases (whether it has spread to other parts of the body
These three pieces of information are combined to determine a cancer stage between 0-IV.
You May Like: Baking Soda And Honey Cancer
Is Surgery The Right Decision For Women With Dcis
Women with ductal carcinoma in situ face the difficult decision of howto treat the condition. Researchers at MD Anderson are studying ways tomake this tough choice easier.
Ligia Toro de Stefani, Ph.D., had just retired from a busy academic medical research career when a mammogram revealed a suspicious mass in her right breast. Her doctors in Brownsville, Texas, referred her to MD Anderson, where she was diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, often called stage 0 breast cancer the very earliest stage.
Toro and her husband, Enrico Stefani, M.D., Ph.D., researched everything they could about the condition before meeting with MD Anderson surgeon Alastair Thompson, M.D., to discuss treatment options.
Investigating came naturally to the scientific couple. Toro is an emeritus professor of anesthesiology and molecular and medical pharmacology at the University of California, Los Angeles. Her husband is a former director of UCLAs anesthesiology division of molecular medicine.
We started reading a lot of papers, not just Googling the disease, but doing a serious literature search, Toro de Stefani says.
DCIS is a cluster of cancer cells inside a milk duct. The cells are held in place by the ducts wall, but they have the ability to break through the wall. Thats when they become invasive.
That wont happen to everyone, Toro de Stefani says, but theres no predicting when cells will break through the duct and spread, and when they wont.
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
You May Like: Tubular Cancer Of The Breast