Associations Between Deliveries And Clinicopathological Characteristics
High parity before an initial breast cancer diagnosis was associated with the presence lymph node metastases in a whole-cohort analysis , but not when the subtypes were assessed separately. Overall, 24.4% of patients with 5 deliveries had a distant recurrence during the follow-up period, in comparison to 9.91% in the group with 4 deliveries . The number of deliveries did not associate with T-class, grade, Ki-67 expression, subtype, HER2, ER or PR expression or the presence of bilateral or multifocal breast cancer. The absolute number of deliveries correlated with the age of breast cancer onset .
What Are My Chances Of Survival If I Am Diagnosed With Luminal B Breast Cancer
Patients with Luminal B breast cancer tend to have good survival rates, however not as high as Luminal A breast cancers. This is because Luminal B breast cancer is more aggressive and may grow and spread faster than a Luminal A breast cancer.
However, your age, stage of disease and tumour type has the greatest impact on your chance of survival. Those diagnosed with stage one breast cancer have an almost 100% chance of surviving five years post diagnosis, however those diagnosed with stage four breast cancer only have a 32% chance of surviving five years post diagnosis.
Overall, the five-year survival rate for women diagnosed with breast cancer is 91.5%, and 86.4% for men.
Advanced Treatments Help You Fight Luminal B Breast Cancer
Doctors put breast cancer into different categories based on how the tumors react to hormones called estrogen and progesterone, as well as if they have the HER2 gene. Estrogen and progesterone can help cancers grow. In addition, the HER2 gene causes cells to have too much HER2 protein, which also makes cancer grow.
Luminal B breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that responds to the hormone estrogen in addition to having the HER2 gene . Due to this combination, luminal B breast cancer can grow very fast and is more likely to spread compared to other types of breast cancers.
Fortunately, new treatments offer women a targeted, effective way to kill cancer cells and keep them from coming back.
To schedule an appointment with a breast cancer specialist at Main Line Health, call or use our .
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 5 Breast Cancer Mean
Targeted Therapies Take Aim At Luminal B Cancers
Along with traditional cancer treatments such as surgery to remove cancer cells, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, your doctor may recommend that you have targeted therapy, sometimes called immunotherapy, biotherapy or monoclonal antibody therapy.
Targeted therapies give you man-made antibodies, which are special immune system cells, to attack HER2 proteins that cause cancer to grow. Without these proteins, cancer cells stop growing and spreading. You can take targeted therapy through an IV or as a pill. Though targeted therapy does have side effects, they are often less severe than chemotherapy side effects.
What Are The Symptoms Of Luminal B Breast Cancer
Some patients diagnosed with Luminal B may not present with any symptoms and are diagnosed on screening mammogram. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- Thickening or hardening in the breast
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering, or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
If the cancer has progressed to the metastatic stage, further symptoms may be present dependent on where the cancer has spread. Learn more about metastatic breast cancer here.
Don’t Miss: How Is Invasive Breast Cancer Treated
Luminal B Breast Cancer
Luminal B is a specific type of breast cancer. Each type is different, so identifying which you have is key to choosing the treatments that are most likely to help.
Read on to learn what it means to have luminal B breast cancer, how its diagnosed, and what you can expect from treatment.
Luminal B breast cancer is one of four main molecular subtypes of breast cancer. These subtypes are based on a molecular analysis of your cancer, including its:
- hormone receptor status
- human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status
- levels of a protein called Ki-67
Luminal B breast cancer is breast cancer that:
- is HR-positive, including estrogen receptor -positive, progesterone receptor -positive, or both
- is either HER2-positive or HER2-negative
- has high levels of Ki-67
The other main breast cancer subtypes are:
- Luminal A. Similar to luminal B, this subtype is ER-positive, PR-positive, or both but luminal A cancer is HER2-negative and has low levels of Ki-67.
Luminal B breast cancer has the same signs and symptoms as other breast cancers. These can include:
- lump in the breast or underarm
- thickening, swelling, or change in size or shape of breast
- red, flaky, or dimpling skin
- nipple inversion or nipple discharge
Breast cancer doesnt always cause symptoms in its early stages. It helps to get familiar with the way your breasts look and feel so youll notice changes sooner rather than later. Routine breast cancer screenings can also help detect cancer.
Is It Better To Be Hr
What is the survival rate for HR positive breast cancers? The survival rate for breast cancers are excellent if the cancer is detected early, and in general HR positive cancers grow slower and have a better prognosis. Overall, breast cancers that are both HR positive and HER2 negative have the best outcomes.
Read Also: What Is Er Pr Positive Breast Cancer
How Is Luminal B Breast Cancer Treated
As Luminal B cancers are hormone receptor positive, patients with early-stage breast cancer who undergo breast surgery may receive hormonal treatments to block hormones from fuelling cancer growth. These can include drugs such as tamoxifen, anastrozole or letrozole which are to be taken daily for at least five years in the case of early-stage breast cancer, after all other breast cancer treatments are completed. Other treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. In the case of metastatic breast cancer, hormonal treatments are also used and continue for as long as they are providing a benefit to the patient.
If the cancer is HER2 positive, treatment will also likely include a HER2 targeted drug such as trastuzumab . The most commonly used HER2 targeted therapy is trastuzumab, sometimes in combination with pertuzumab. This was proven to help reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in the early-stage breast cancer by 46%, in the Breast Cancer Trials HERA Clinical Trial. If the cancer is metastatic, other targeted therapies including pertuzumab , T-DM1 or lapatinib may be used.
Ethics Approval And Patients
This was an observational, retrospective study. Our procedures respected ethical standards in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and were reviewed and approved by a Human Research Ethics Committee at our institution . Patients were treated between 1997 and September 2017 at the Cancer Center Nuestra Señora de La Esperanza in the Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile and the Red de Salud UC CHRISTUS. Only patients with advanced metastatic ER-positive disease were included in the study. They were further categorized as either: being diagnosed with metastatic disease at diagnosis or being diagnosed with early disease but whom later developed a systemic or unresectable disease . Clinical data analyzed included: Age, clinical presentation, recurrence status, calendar year at diagnosis and overall survival , defined as the time period between the diagnosis of ABC and the time of patient death by any cause.
Also Check: What Type Of Breast Cancer Is Aggressive
Identification Of Breast Cancer Subtypes By Gep Studies
Subsequent studies revealed that similar molecular subtypes of breast cancer could be identified in multiple cohorts of breast cancers and that luminal cancers could be subclassified into 2 or 3 groups and different molecular subtypes were shown to have distinct clinical outcomes. Sørlie et al investigated the clinical relevance of gene expression profiles in 78 breast carcinoma patients. Of these patients, 51 were part of a prospective study with locally advanced tumors and had received doxorubicin based chemotherapy before the surgery. The authors showed a highly significant difference in overall survival between the subtypes. Both the basal-like and ErbB2-positive subtypes were associated with the shortest survival times. The authors subclassified the luminal-like breast cancer into three subclasses comprising luminal-A, luminal-B and luminal-C and identified luminal-A subgroup of ER-positive tumors as being associated with the best outcome. Vant Veer et al also investigated node-negative breast cancer patients and found 231 genes significantly associated with disease outcome, as defined by the presence of distant metastasis at the 5th year. These data revealed that each breast tumor has its own unique molecular portrait, providing the basis for an improved molecular taxonomy of the disease.
Molecular Subtypes Of Breast Cancer
Researchers are studying how molecular subtypes of breast cancer may be useful in planning treatment and developing new therapies.
The complex profile of each subtype is determined using molecular and genetic information from tumor cells.
Most studies divide breast cancer into 4 main molecular subtypes:
These subtypes also appear in ductal carcinoma in situ .
There are many other less common molecular subtypes, including claudin-low and molecular apocrine types.
Read Also: Genetic Test For Breast Cancer
Impact Of Tumor Subtype On Os And Bcrs
After a median 18.7 years of follow-up, 140 all-cause death events were recorded. Median OS was 18.5 years .
In the univariate analysis, menopausal status, T, N, stage, and PgR status were associated with OS . Median OS was 21.2 years among luminal A-like, 15.0 years among luminal B-like/HER2-negative, 18.5 years among HER2-positive, and 17.1 years among TN BCs. Overall, we did not observe statistically significant differences in OS by subtype , but luminal A-like tumors showed a trend for better OS than luminal B-like/HER2-negative tumors .
Table 2.
Univariate analysis and multivariate Cox proportional regression models
Fig. 2.
A Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival according to tumor subtype. B Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival comparing nonluminal A-like and luminal A-like tumors. HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 HR, hazard ratio CI, confidence interval. * Adjusted for menopausal status, tumor size, nodal status, and adjuvant treatment.
In the multivariable model, the following factors impacted OS: menopausal status , T , and N . Luminal B-like/HER2-negative and TN tumors had a higher risk of death than luminal A-like tumors , though these associations were not statistically significant .
Comparing luminal A-like versus nonluminal A-like tumors, tumor subtype impacted OS in the univariate analysis , but this effect was attenuated after multivariate analysis .
Table 3.
Competing risks regression analyses
Fig. 3.
Predicting Survival Among Hormone Receptorpositive Breast Cancers With The Surrogate Immunopanel Of Er Pr Her2 And Ki67
When we used HER2 and Ki67 immunohistochemistry to subtype the 2598 hormone receptorpositive tumors in the BCCA series, we classified 1530 as luminal A, 846 as luminal B, and 222 as luminalHER2-positive tumors. In comparison with luminal A, both luminal B and luminalHER2-positive tumors were statistically significantly associated with younger age at diagnosis, higher grade, larger tumor size, positive lymph node involvement, and lymphovascular invasion .
Association of patient and tumor characteristics with relapse-free survival and breast cancerspecific survival among 883 patients with lymph nodenegative, hormone receptorpositive breast cancer with complete data for covariates and who did not receive any adjuvant systemic therapy
Univariate survival by breast cancer subtype among 943 patients with lymph nodenegative, hormone receptorpositive breast cancer who received no adjuvant systemic therapy. A ) Relapse-free survival. B ) Breast cancerspecific survival. CI = confidence interval.
Association of patient and tumor characteristics with relapse-free survival and breast cancerspecific survival among 828 hormone receptorpositive patients with complete data for covariates and who received tamoxifen as their sole adjuvant systemic therapy and among 167 patients with hormone receptorpositive tumors with complete data for all the covariates and who received both tamoxifen and chemotherapy as adjuvant systemic therapies
Recommended Reading: Where To Donate For Breast Cancer Research
Stratification By Molecular Subtype
In Table 4 we show that the luminal A and TN subtypes predict a lower incidence of nodal involvement compared with luminal HER2 and luminal B subtypes . Similarly, the luminal B, luminal HER2, and HER2 subtypes present a greater percentage of high-volume nodal involvement compared with luminal A disease. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression was used to describe the association between node status and 5-year DFS or 5-year BCSS in different constructed molecular subtypes as shown in Table 5. After adjusting for age, tumor size, and histological grade there was no difference in 5-year DFS and 5-year BCSS between the N1 or N2 and N0 groups of patients with luminal A disease. For women with the HER2 subtype, similarly, there was no difference in 5-year DFS and 5-year BCSS between the N1 and N0 groups. However, nodal involvement patients showed a significant difference for 5-year DFS and 5-year BCSS compared to the reference group with the luminal B, luminal HER2, and TN subtypes.
Endpoints And Statistical Analysis
Overall survival was defined as the time from the first diagnosis of primary breast cancer to death from any cause. Disease-free survival was defined as the time from the diagnosis of breast cancer to the development of any local recurrence or metastatic disease. Patients without any evidence of relapse or death were censored at the last date they were known to be alive.
Statistical analysis was carried out with SPSS, version 16.0 . The Chi-square test was used to compare patient and clinical-pathological characteristics between sub-groups, and the nonparametric KruskalWallis rank test was used for ordinal categorical variables. Survival distributions were estimated by the KaplanMeier method, and the comparison between subgroups was done by the log-rank test. Multivariate analysis was carried out using Coxs proportional hazard regression model, and hazard ratios are presented with their 95% confidence intervals. All statistical tests were two sided, and P< 0.05 was considered significant.
Also Check: Breast Cancer That Has Spread To Lymph Nodes
Clinical Trials With Immune Checkpoint Blockade In Hr+ Bc
Several early phase trials have tested the safety and efficacy of immunotherapy alone or in combination with other agents in luminal BC patients . In the neoadjuvant setting, pembrolizumabin combination with chemotherapyincreased the pCR rates, varying from 15 to 30%, depending on the chemotherapy backbone . In the advanced setting, ORR ranges from 12% for pembrolizumab alone to 34% in association with eribulin and 29% when combined with the CDK4/6i, abemaciclib . As maintenance therapy, durvalumab improved OS compared to chemotherapy in HR+ BC .
Table 1 Completed clinical trials with immune checkpoint inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer
Scientists are also trying to use the immunomodulatory and antigenic exposure effect of CT in order to enhance the activity of ICB. Previous findings demonstrated that the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin treatment is dependent on IL-1b, IL-17, and interferon gamma production, and CD8+ cell recruitment. The efficacy of eribulin may be attributed to its biological effects on the immune system, such as the reduction of PD-L1 and FOXP3 expression , shifting the balance from a pro- to an anti-tumor immune response. Furthermore, the immune-modulating effects of taxanes appear to synergize with ICB. In particular, the reduction in Tregs and MDSCs paired with the recruitment of T cells and mature DCs to the tumor could render ICB-induced T cells more effective within the TME .
Bc Subset And Survival Analyses
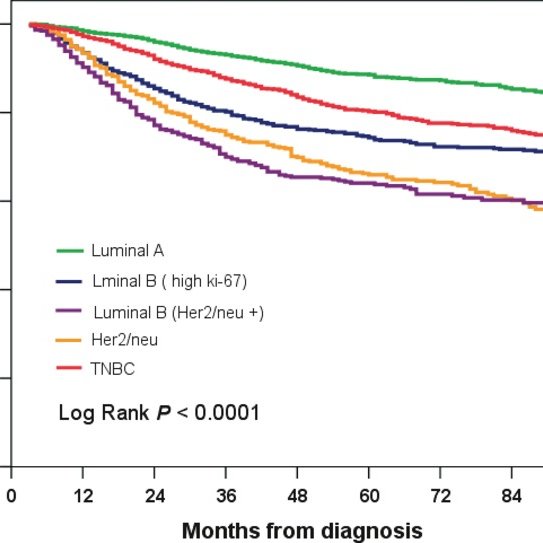
Briefly, tumors were classified as Luminal A when they expressed ER and/or the Progesterone Receptor with a histological grade 1 or 2. Luminal B were ER+ and/or PR+ and HG = 3 or positive for the Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor type 2 8,9 HER2+ was defined as Immunohistochemistry HER2 overexpression equal to 3+ or by HER2 gene amplification measured by Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization in IHQ2+ cases. As explained above, survival rates of patients were also analyzed according to the year of diagnosis, dividing into two groups: 1997-2006 and 2007-2017, in order to assess the impact of novel therapies and management strategies over the last decade. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistics OS were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method and curves were compared using the Log Rank test in the XLSTAT statistic software v. 19.4.
- 8Breast Cancer at Extreme Ages – a Comparative Analysis in ChileAsian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2015
- Predictive value of conventional immuno-histochemical biomarkers in breast cancerRev Med Chile, 20159. Acevedo F, Camus M, Vial C, Panay S, Abarca M, Domínguez F, et al. Predictive value of conventional immuno-histochemical biomarkers in breast cancer. Rev Med Chile 2015 143 : 724-32.
You May Like: Who Should Get Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
The Tumor Microenvironment In Luminal Bc
The tumor microenvironment includes a variety of non-immune and immune cells producing many factors that can drive a chronic inflammatory, differently balanced situation: either a pro- and an anti-tumor or pro-angiogenic tumor environment . Among the non-immune cells, the stromal components of the TME consist of cancer-associated fibroblasts , endothelial cells, and pericytes. Immune cells are particularly abundant in the stroma and less numerous in intra-tumoral areas . They are composed of macrophages , dendritic cells , myeloid-derived suppressor cells , natural killer cells, mast cells , granulocytes, plus the cells of the adaptive immunity, B and T lymphocytes. Naïve T cells represent the minority, while memory T cells are the majority of cells, including cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and different subsets of CD4+ T helper and immunosuppressive regulatory T cells . It is noteworthy that B and T lymphocytes can be organized in tertiary lymphoid structures whose role in BC has not been clearly defined yet . One can speculate that, potentially, all of these cells could have different impacts at different times and/or phases of tumor progression to control the balance of the TME.
Fig. 1
The role of TME components in modulating the response to anti-estrogen therapy in HR+ BC has not been fully clarified. However, pre-clinical data validated several cytokines that drive resistance to HT and Neuregulin 1 ) .