Systemic Treatments For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Treatment often continues until the cancer starts growing again or until side effects become unacceptable. If this happens, other drugs might be tried. The types of drugs used for stage IV breast cancer depend on the hormone receptor status, the HER2 status of the cancer, and sometimes gene mutations that might be found.
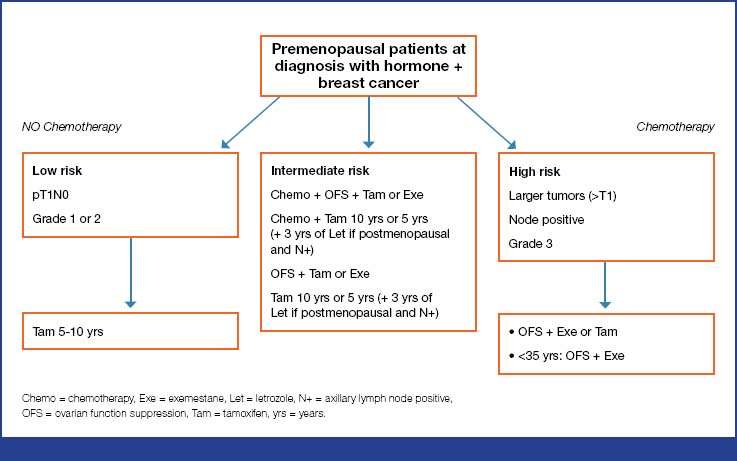
Extended Adjuvant Therapy In Premenopausal Women
Tam can be extended for up to 10 years . Extended adjuvant treatment with 5 years of Tam should also be offered to those patients with ovarian suppression and Tam or AI for their initial treatment . If the patient is confirmed as being postmenopausal within the first 5 years, endocrine therapy can be continued after 5 years of Tam with 2.55 years of letrozole .
Dealing With Visible Side Effects Of Treatment
You may be able to see some of the side effects of breast cancer treatment, and this can take an emotional toll. But thereâs a lot you can do to overcome them, and that can help you feel better.
Breast changes
If you’ve had a mastectomy, you can use an external prosthesis instead of, or before, breast reconstruction surgery. You tuck it into a bra or attach it to your skin with double-sided tape.
If you chose to get one:
- Ask your doctor for a prescription for an external prosthesis. Then, it can usually be covered by insurance.
- Ask your oncologist for referral to a specialized store that sells external prostheses. You may also find them in some lingerie departments.
- Make an appointment with a breast prosthesis consultant and allow yourself about an hour to get fitted.
- Try a variety of them to see which feels and looks the best on you.
Some chemotherapy kills fast-growing cells like hair follicles, whether those cells are cancer or not. Hair loss is different for everyone, and it depends on the type of chemo you’re taking. Radiation and hormonal treatments may also cause this side effect.
If you lose hair from chemo, it’s likely to fall out within 1 to 2 weeks of starting treatment. It may thin or fall out almost all at once. It’s common to lose hair over your whole body, not just on your head. This means you may lose eyelashes and eyebrows as well as arm, leg, and pubic hair.
Here are some other tips that may help:
Arm swelling
Weight gain or loss
You May Like: How Common Is Breast Cancer In 20s
Complementary Therapy And Survivorship
The integration of complementary interventions is still a challenge in the standard treatment of breast cancer. The two main reasons for this are:
-
lacking general definition of complementary medicine, and
-
only a few conventional studies exist providing clear evidence on the efficacy of complementary approaches and benefit-risk ratios.
In 2020, the AGO recommendations for Complementary Therapy and Survivorship did not change substantially compared to 2019. Recently published studies and review articles underline the effects of physical exercise on quality of life, cardio-respiratory fitness, physical performance, sleep, pain, depression, lymphedema, and fatigue . Evidence is growing that mind-body interventions, including cognitive behavioral therapies, relaxation techniques, and meditation, improve quality of life among breast cancer patients, and therefore clinical guidelines have begun to include recommendations. A systemic review and meta-analysis of 19 RCTs revealed evidence that mind-body interventions are efficacious for reducing fear of cancer recurrence, although further investigations are recommended to analyze the optimal integration of mind-body practices .
Central Nervous System Metastases
Systemic therapy in patients with brain metastases in addition to local therapy should be performed as for other metastatic sites. Actual systemic therapy might be continued if the patient has the first diagnosis of brain metastases with stable extracranial disease .
In patients with HER2-positive disease, HER2-directed therapy should be continued if remission of extracranial disease is achieved. Up to now, no newly developed targeted therapy has been able to prove superiority over other cytotoxic agents in the brain. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and new chemotherapeutic options are being investigated in clinical trials.
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Return After Mastectomy
Treatment Option Overview For Early/localized/operable Breast Cancer
Treatment options for early, localized, or operable breast cancer may include the following:
Surgery:
Postoperative radiation therapy:
Postoperative systemic therapy:
Progression During Hormone Therapy
For hormone receptor-positive cancers that were being treated with hormone therapy, switching to another type of hormone therapy sometimes helps. For example, if either letrozole or anastrozole were given, using exemestane, possibly with everolimus , may be an option. Another option might be using fulvestrant or a different aromatase inhibitor, along with a CDK inhibitor. If the cancer has a PIK3CA mutation and has grown while being treated with an aromatase inhibitor, fulvestrant with alpelisib might be considered. If the cancer is no longer responding to any hormone drugs, chemotherapy immunotherapy, or PARP inhibitors might be options depending on specific features of the cancer or any gene changes that might be present.
Don’t Miss: Is Chemotherapy Always Necessary For Breast Cancer
Immunotherapy To Treat Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy medicines work by helping your immune system work harder or more efficiently to fight cancer cells.
Your immune system is made up of a number of organs, tissues, and cells that work together to protect you from foreign invaders that can cause disease. When a disease- or infection-causing agent, such as a bacterium, virus, or fungus, gets into your body, your immune system reacts and works to kill the invaders. This self-defense system works to keep you from getting sick.
Immunotherapy uses substances either made naturally by your body or man-made in a lab to boost the immune system to:
Learn more about immunotherapies used to treat metastatic breast cancer.
Targeted Therapy To Treat Metastatic Breast Cancer
Targeted therapies are treatments that target specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as a protein that allows the cancer cells to grow in a rapid or abnormal way. Targeted therapies are generally less likely than chemotherapy to harm normal, healthy cells. Some targeted therapies are antibodies that work like the antibodies made naturally by our immune systems. Because of this, they are sometimes called immune-targeted therapies.
Learn more about targeted therapies used to treat metastatic breast cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Rate Of Breast Cancer
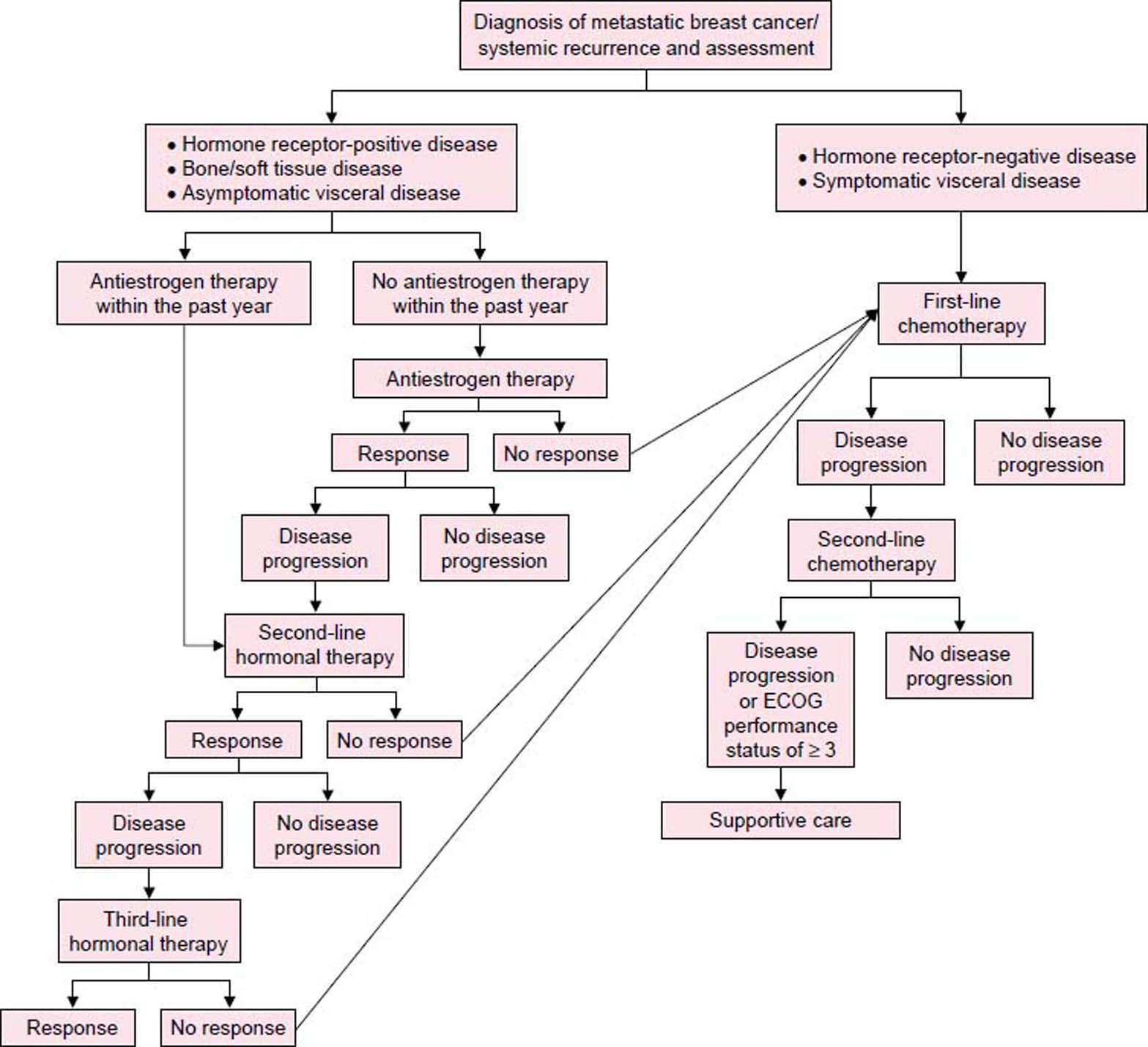
Guideline Stratification For Systemic Therapy For Stage Iv/recurrent Disease
The systemic treatment of breast cancer recurrence or stage IV disease prolongs survival and enhances quality of life but is not curative. Therefore, treatments associated with minimal toxicity are preferred. Thus, the use of the minimally toxic endocrine therapies is preferred to the use of cytotoxic therapy whenever reasonable.12 Guidance for treatment of patients with breast cancer and brain metastases is included the NCCN Guidelines for Central Nervous System Cancers.
Patients with recurrent/stage IV breast cancer at diagnosis are initially stratified according to whether bone metastases are present. These 2 patient subsets are then stratified further by tumor HR and HER2 status.
Breast Cancer Surgery Under Oncological Aspects
Oncoplastic methods led to the transition from radical surgical concepts towards BCS. No ink on tumor is the accepted standard for resection margins for patients who undergo primary BCS or surgery, provided that all suspicious lesions according to preoperative imaging are resected . Therefore, BCS is also an option for patients with multifocal and multicentric disease, when R0 resection is confirmed . SLNE is the standard of care staging procedure in cN0 patients with invasive disease . Suspicious lymph nodes should be assessed by CNB. The significance of axillary surgery for patients with 12 positive sentinel lymph nodes after primary surgery continues to decline. This is mainly due to the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 trial, confirmed by the 10-year follow-up and the AMAROS trial as well as confirming studies with no differences in locoregional control, disease-free survival , and OS.
Following neoadjuvant therapy , SLNE should be available and performed after NACT since it reduces the rate of ALND and axillary remission provides additional prognostic information . SLNE before NACT remains an option if an impact on adjuvant treatment decisions is expected . In patients with a clinically negative axilla before NACT and tumor-infiltrated SLN after NACT , a full ALND should be performed .
Fig. 2.
Management of the axillary lymph nodes in the neoadjuvant chemotherapy concept.
You May Like: What Doctor To See For Breast Cancer
Ajcc Anatomic And Prognostic Stage Groups
There are three stage group tables for invasive cancer:
- Anatomic Stage Group. The Anatomic Stage Group table is used in regions of the world where tumor grading and/or biomarker testing for ER, PR, and HER2 are not routinely available.
- Clinical Prognostic Stage Group. The Clinical Prognostic Stage Group table is used for all patients in the United States. Patients who have neoadjuvant therapy as their initial treatment should have the clinical prognostic stage and the observed degree of response to treatment recorded, but these patients are not assigned a pathological prognostic stage.
- Pathological Prognostic Stage Group. The Pathological Prognostic Stage Group table is used for all patients in the United States who have surgery as initial treatment and have pathological T and N information reported.
In the United States, cancer registries and clinicians must use the Clinical and Pathological Prognostic Stage Group tables for reporting. It is expected that testing is performed for grade, HER2, ER, and PR status and that results are reported for all cases of invasive cancer in the United States.
AJCC Anatomic Stage Groups
AJCC Prognostic Stage Groups
The Clinical Prognostic Stage is used for clinical classification and staging of patients in the United States with invasive breast cancer. It uses TNM information based on the patients history, physical examination, imaging results , and biopsies.
Endocrine And Targeted Therapy In Mbc
In women with hormone receptor-positive MBC , endocrine-based therapy should be considered first choice, irrespective of menopausal status. Premenopausal women rendered postmenopausal by either gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues or other means of ovarian function suppression should then be treated like postmenopausal women.
The majority of patients might be candidates for a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor combination therapy. The evidence concerning palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib has been completed with regard to a variety of patient populations according to therapy line, menopausal status, and endocrine combination partners. Therefore, those combinations therapies are rated with LoE 1b/B/AGO ++ . All 3 drugs have been thoroughly investigated in first and further therapy lines in endocrine-sensitive and -resistant MBC and demonstrated a homogeneous improvement of progression-free survival with HRs between 0.42 and 0.58 . Thus, no subgroup could be identified neither by clinical nor by biomarkers that does not benefit from using a CDK4/6 inhibitor in addition to endocrine therapy . Recently, the first overall survival data were published from the PALOMA-3 trial. Formally, the difference was not statistically significant however, there was a trend towards better overall survival with the CDK4/6 inhibitor . This report on overall survival had no influence on the current recommendations.
Fig. 3.
All other recommendations have not changed and remain valid.
Don’t Miss: Do Fertility Drugs Cause Breast Cancer
Advanced Breast Cancer: Diagnosis And Treatment
Clinical guideline
This guideline covers care and support for people with advanced breast cancer. It aims to help them and their healthcare professionals make shared decisions about tests and treatments to improve outcomes and quality of life.
A table of NHS England interim treatment regimens gives possible alternative treatment options for use during the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce infection risk. This may affect decisions for patients with advanced breast cancer. See the COVID-19 rapid guideline: delivery of systemic anticancer treatments for more details.
In , we reviewed the evidence for assessing oestrogen receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status on disease recurrence and changed the recommendations in section on diagnosis and management.
Local Treatments For Areas Of Distant Metastasis
Local treatments for distant areas of metastasis such as the bones, lungs, brain, or liver are directed to those locations. Although local treatments arent usually the first choice to treat metastatic breast cancer, doctors do recommend them under certain circumstances:
- Advertisement
Local treatments can help alleviate pain or other symptoms caused by metastatic breast cancer that can affect quality of life. The most common example of local treatment is medication to control bone metastasis. Others include surgery to remove the cancer or focused radiation to destroy it.
- Advertisement
Local treatments can be effective when there are just one or two areas of metastasis and doctors believe they can completely remove the cancer, possibly preventing future problems.
Your medical team can work with you to make the best plan that is right for you and your specific situation.
You may be a candidate for local treatment of distant metastasis if:
- Advertisement
metastatic breast cancer is causing pain or other symptoms that are affecting your day-to-day life and function
- Advertisement
you have just one or two areas of metastasis and doctors believe they can completely remove the cancer, possibly preventing future problems
Metastatic breast cancer can affect functioning when:
-
tumors interfere with normal liver function
The goal of local therapies is to improve these symptoms and prevent the cancer from causing further problems.
Learn more about local treatments for:
You May Like: Where Do Breast Cancer Lumps Occur
How Do I Know Which Breast Cancer Treatment To Choose
Your doctor will think about a few things before they recommend a treatment for you:
- The type of breast cancer you have
- The size of your tumor and how far the cancer has spread in your body, called the stage of your disease
- Whether your tumor has things called receptors for HER2 protein, estrogen, and progesterone, or other specific features.
Your age, whether youâve gone through menopause, other health conditions you have, and your personal preferences also play a role in this decision-making process.
The ‘look Good Feel Better’ Program
The American Cancer Society has teamed up with the Personal Care Products Council and the National Cosmetology Association to create “Look Good Feel Better.” This program teaches beauty techniques that can boost your appearance and how you feel about yourself after your cancer treatment.
For more information, call 800-395-LOOK, or go to the website.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: What Makes You High Risk For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Supportive Care And Side Effect Management
Optimal side effect management and supportive care is a major contributor to the overall risk/benefit balance associated with oncological therapies. This chapter of the AGO recommendations details aspects that are particularly relevant for treatment of breast cancer patients and is based on the most recent version of the S3 guidelines and other international guidelines, such as ESMO, wherever available.
Chemotherapy can lead to reactivation of hepatitis B in carriers . Before the start of chemotherapy, screening for hepatitis B should therefore be performed in all patients . If one of the tests is positive, HBV DNA needs to be determined. In case of HBV DNA detection, virustatic therapy needs to be initiated .
For prevention of chemotherapy-induced alopecia, scalp cooling may be used . A meta-analysis reported a relative reduction of alopecia by 43% . Scalp metastases are quite rare and do occur even without scalp cooling .
T-DM1 in the postneoadjuvant setting causes peripheral neuropathy . Thus, in patients pretreated with taxanes, continuing measures for neuropathy prevention, such as compression gloves or tactile stimulation , are very important under subsequent T-DM1.
Detailed and practical management information for new drugs, such as CDK4/6 inhibitors or immunotherapy, can be found in the respective package inserts which are regularly updated.
Prognostic And Predictive Factors
Most of the established prognostic markers, including estrogen and progesterone receptors , are provided by traditional pathology and overlap with parameters used for the prediction of therapeutic response. Commonly, they serve as surrogates for intrinsic subtypes such as luminal A and luminal B. In addition, uPA/PAI-1 provides strong prognostic information and allows prediction of the chemotherapy effect .
In particular, for differentiation of luminal A and B subtype implying the alternative choice between endocrine and chemo-endocrine therapy, there are no generally accepted immunohistochemical algorithms or cut-off values. Several RNA expression assays have been tested to enable a more accurate assignment of individual patients to prognostic groups. The different assays are not interchangeable and the level of concordance is only about 70% . They should only be used in selected patients if all other criteria are inconclusive for therapeutic decision making.
Pathological complete response provides a relevant prognostic parameter after neoadjuvant systemic therapy . Besides clinically determined parameters to predict the prospective success of NAST, such as young age and cT1/cT2 tumors, pathological parameters are predictive. Some histological types such as lobular breast cancer or metaplastic cancers show poor response to NAST.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Chemo For Breast Cancer
Systemic Therapy For Recurrent Or Stage Iv Hr
Women with stage IV or recurrent disease characterized by HR-positive, HER2-positive tumors have the option of receiving HER2-directed therapy as a component of their treatment plan. Options include treatment with a HER2-targeted therapy plus chemotherapy or endocrine therapy alone or in combination with HER2-targeted therapy. Endocrine therapy alone or in combination with HER2-targeted therapy is a less toxic approach compared with HER2-targeted therapy combined with chemotherapy. Premenopausal women treated with HER2-targeted therapy and endocrine therapy should receive ovarian suppression or ablation.
Adding trastuzumab or lapatinib to an AI has demonstrated a PFS advantage compared with AI alone in postmenopausal women with stage IV or recurrent HR-positive, HER2-positive tumors.
In the TAnDEM study, postmenopausal women with metastatic HR-positive and HER2-positive tumors were randomized to receive anastrozole alone or anastrozole plus trastuzumab.105 Compared with single-agent anastrozole, an improvement in PFS was seen with combination therapy . The combination was associated with a higher incidence of toxicities , fatigue , diarrhea , vomiting , and pyrexia serious toxicities were rare in both treatment arms.