What To Know About Breast Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of breast cancer can vary widely and some types of breast cancer may not have any noticeable symptoms.
Sometimes a lump may be too small to be felt or to cause any changes to your breast or surrounding area. In these cases, cancerous cells are often first detected through screening techniques like a mammogram.
When there are symptoms, they can include:
- a lump or thickening of breast tissue that you can feel with your fingers
- breast swelling or changes to your breast size or shape
- changes to the skin on your breast, such as dimpling, redness, or skin irritation
- the nipple turning inward or nipple pain
- a lump in your underarm area
- nipple discharge other than breast milk
Its important to be familiar with how your breasts usually look and feel. This will help you notice any changes and to follow up with your healthcare professional promptly if anything looks or feels different.
Noninvasive breast cancer develops in the cells of a duct or lobule and remains in that location. Its also referred to as in situ which means in the original place.
There are two types of noninvasive breast cancer:
- ductal carcinoma in situ
- lobular carcinoma in situ
Lets take a closer look at each type.
- forms in the cells lining a milk duct
- remains in the duct and does not spread to nearby tissues
- is considered precancer or preinvasive because, if left untreated, it can become invasive and spread into nearby tissue
- accounts for about
There are two types of invasive breast cancer:
How Common Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the United States, except for skin cancers. It is about 30% of all new female cancers each year.
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for breast cancer in the United States for 2022 are:
- About 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women.
- About 51,400 new cases of ductal carcinoma in situ will be diagnosed.
- About 43,250 women will die from breast cancer.
Breast cancer mainly occurs in middle-aged and older women. The median age at the time of breast cancer diagnosis is 62. This means half of the women who developed breast cancer are 62 years of age or younger when they are diagnosed. A very small number of women diagnosed with breast cancer are younger than 45.
Safe Handling In Health Care Settings
As of 2018, there were no set for antineoplastic drugs, i.e., OSHA or the have not set workplace safety guidelines.
Preparation
NIOSH recommends using a that is designed to decrease worker exposure. Additionally, it recommends training of all staff, the use of cabinets, implementing an initial evaluation of the technique of the safety program, and wearing protective gloves and gowns when opening drug packaging, handling vials, or labeling. When wearing , one should inspect gloves for physical defects before use and always wear double gloves and protective gowns. Health care workers are also required to wash their hands with water and soap before and after working with antineoplastic drugs, change gloves every 30 minutes or whenever punctured, and discard them immediately in a chemotherapy waste container.
The gowns used should be disposable gowns made of polyethylene-coated polypropylene. When wearing gowns, individuals should make sure that the gowns are closed and have long sleeves. When preparation is done, the final product should be completely sealed in a plastic bag.
The health care worker should also wipe all waste containers inside the ventilated cabinet before removing them from the cabinet. Finally, workers should remove all protective wear and put them in a bag for their disposal inside the ventilated cabinet.
Administration
Employee training
Housekeeping and waste disposal
Spill control
Read Also: How To Handle Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Types Of Breast Carcinomas
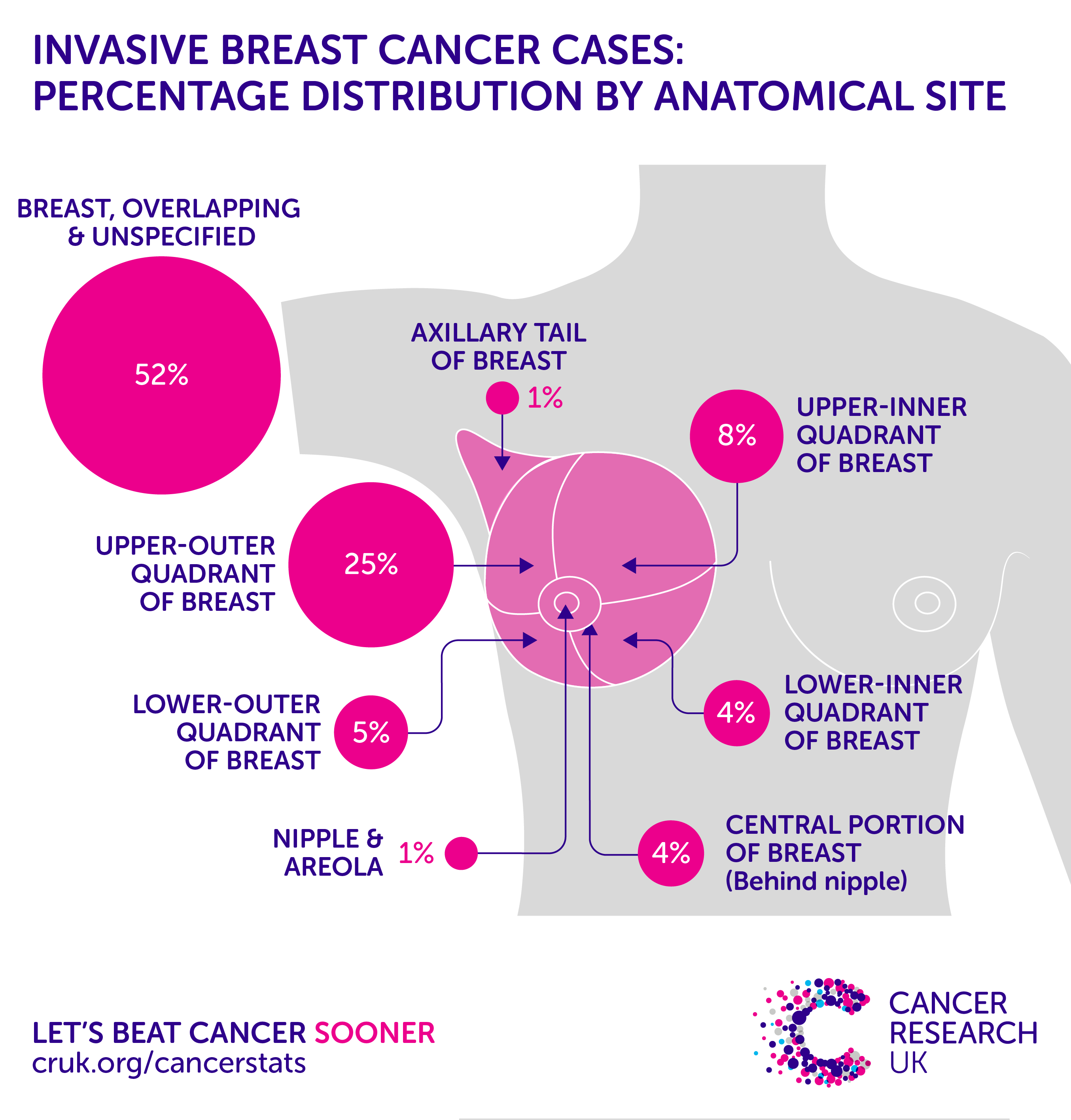
Within the large group of carcinomas, there are many different types of breast cancer. The first major division is between in situ and invasive carcinoma. In situ carcinoma is “pre-invasive” carcinoma that has not yet invaded the breast tissue. These in situ cancer cells grow inside of the pre-exisiting normal lobules or ducts. In situ carcinoma has significant potential to become invasive cancer, and that is why it must be adequately treated to prevent the patient from developing invasive cancer. Invasive cancers have cancer cells that infiltrate outside of the normal breast lobules and ducts to grow into the breast connective tissue. Invasive carcinomas have the potential to spread to other sites of the body, such as lymph nodes or other organs, in the form of metastases.
Approximately 80% of breast carcinomas are invasive ductal carcinoma, followed by invasive lobular carcinomas which account for approximately 10-15% of cases. Invasive ductal carcinomas and invasive lobular carcinomas have distinct pathologic features. Specifically, lobular carcinomas grow as single cells arranged individually, in single file, or in sheets, and they have different molecular and genetic aberrations that distinguish them from ductal carcinomas. Ductal and lobular carcinomas may have different prognoses and treatment options, depending upon all of the other features of the particular cancer.
Benign hyperplasia of the breast epithelial cells lining the ducts and lobules.
A mass.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Breast Cancer Type
What Can I Expect If I Have Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with breast cancer, your healthcare provider will talk with you in detail about your treatment options. Treatment and recovery will be different for everyone, so they can tell you what to expect in your situation.
Is breast cancer fatal?
People with early-stage breast cancer often manage their condition successfully with treatment. In fact, many people whove received a breast cancer diagnosis go on to live long, fulfilling lives. Late-stage breast cancer is more difficult to treat, however, and can be fatal.
What is the survival rate for breast cancer?
The overall five-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90%. This means that 90% of people diagnosed with the disease are still alive five years later. The five-year survival rate for breast cancer that has spread to nearby areas is 86%, while the five-year survival rate for metastatic breast cancer is 28%. Fortunately, the survival rates for breast cancer are improving as we learn more about the disease and develop new and better approaches to management.
Keep in mind that survival rates are only estimates. They cant predict the success of treatment or tell you how long youll live. If you have specific questions about breast cancer survival rates, talk to your healthcare provider.
Breast Exam By Your Doctor
The same guidelines for self-exams provided above are true for breast exams done by your doctor or other healthcare professional. They wont hurt you, and your doctor may do a breast exam during your annual visit.
If youre having symptoms that concern you, its a good idea to have your doctor do a breast exam. During the exam, your doctor will check both of your breasts for abnormal spots or signs of breast cancer.
Your doctor may also check other parts of your body to see if the symptoms youre having could be related to another condition.
Also Check: How To Help Breast Cancer
Occupational Exposure And Safe Handling
In the 1970s, antineoplastic drugs were identified as hazardous, and the has since then introduced the concept of after publishing a recommendation in 1983 regarding handling hazardous drugs. The adaptation of federal regulations came when the U.S. first released its guidelines in 1986 and then updated them in 1996, 1999, and, most recently, 2006.
The has been conducting an assessment in the workplace since then regarding these drugs. Occupational exposure to antineoplastic drugs has been linked to multiple health effects, including infertility and possible carcinogenic effects. A few cases have been reported by the NIOSH alert report, such as one in which a female pharmacist was diagnosed with papillary transitional cell carcinoma. Twelve years before the pharmacist was diagnosed with the condition, she had worked for 20 months in a hospital where she was responsible for preparing multiple antineoplastic drugs. The pharmacist didn’t have any other risk factor for cancer, and therefore, her cancer was attributed to the exposure to the antineoplastic drugs, although a cause-and-effect relationship has not been established in the literature. Another case happened when a malfunction in biosafety cabinetry is believed to have exposed nursing personnel to antineoplastic drugs. Investigations revealed evidence of genotoxic biomarkers two and nine months after that exposure.
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Has Tubular Mucinous Cribriform Or Micropapillary Features
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are “special types” of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, different treatment might be recommended.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Also Check: Does Medicare Cover Breast Reconstruction After Cancer
What If A Carcinoma Is Infiltrating Or Invasive
These words are used to mean that the cancer is not a pre-cancer , but is a true cancer.
The normal breast is made of tiny tubes that end in a group of sacs . Cancer starts in the cells lining the ducts or lobules, when a normal cell becomes a carcinoma cell. As long as the carcinoma cells are still confined to the breast ducts or lobules, without breaking out and growing into surrounding tissue, it is considered in-situ carcinoma .
Once the carcinoma cells have grown and broken out of the ducts or lobules, it is called invasive or infiltrating carcinoma. In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body.
Nonsurgical Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
Radiation. Radiation therapy might be part of your treatment plan if you are undergoing a lumpectomy. Studies show that lumpectomy followed by radiation can be as effective in treating IDC as mastectomy. We dont usually treat patients with radiation after a mastectomy unless theres some cancer in the lymph nodes, Wright says.
Chemotherapy. Deciding on whether to treat invasive ductal breast cancer with chemotherapy, or chemo, depends on features of the tumor cells themselves their genes and proteins. The more the doctor can learn about the characteristics of the cancer cells, the easier it is to determine what type of chemotherapy is likely to be effective.
Hormone therapy. Breast cancers with positive hormone receptors can be treated with estrogen or progesterone. These medications come in pill form, and may be prescribed for several years.
Biologic therapy. This approach uses antibodies or small molecule drugs to activate your bodys immune system to fight the invasive ductal cancer cells.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Breast Cancer
Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Most breast cancers are invasive, meaning the cancer has spread from the original site to other areas, like nearby breast tissue, lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. Invasive breast cancer cells break through normal breast tissue barriers and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph nodes. The two most common types of invasive breast cancer are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
The most common type of breast canceraccounting for roughly 70 to 80 percent of all casesis called invasive ductal carcinoma . IDC is a cancer that starts in a milk duct and grows into other parts of the breast. With time, it may spread further, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type, accounting for roughly 5 to 10 percent of all breast cancers. ILC starts in lobules and then spreads into nearby breast tissue. Like IDC, it may metastasize. However, this cancer is harder to detect on mammograms and other exams than IDC. One in five women with ILC have both breasts affected.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Pagets disease of the breast
Angiosarcoma of the breast
Phyllodes tumors
Other, even more rare, types of invasive breast cancer include adenoid cystic carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma and tubular carcinoma.
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer

To determine if your symptoms are caused by breast cancer or a benign breast condition, your doctor will do a thorough physical exam in addition to a breast exam. They may also request one or more diagnostic tests to help understand whats causing your symptoms.
Tests that can help your doctor diagnose breast cancer include:
- Mammogram. The most common way to see below the surface of your breast is with an imaging test called a mammogram. Many women ages 40 and older get annual mammograms to check for breast cancer. If your doctor suspects you may have a tumor or suspicious spot, they will also request a mammogram. If an atypical area is seen on your mammogram, your doctor may request additional tests.
- Ultrasound. A breast ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the tissues deep in your breast. An ultrasound can help your doctor distinguish between a solid mass, such as a tumor, and a benign cyst.
Your doctor may also suggest tests such as an MRI or a breast biopsy.
If you dont already have a primary care doctor, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
Recommended Reading: Is Back Pain Associated With Breast Cancer
Phyllodes Tumors Of The Breast
A phyllodes tumor is a very rare type of breast cancer that accounts for less than
75 percent of cases, phyllodes tumors arent cancerous, so they usually dont spread beyond the breast. But they can grow quickly and some can be considered borderline, which means they have properties that could make them cancerous at a later stage.
Phyllodes tumors form in the connective tissue of the breast. The most common symptoms include:
- a smooth lump in or around the breast
- a lump that grows quickly and stretches the skin
- breast skin that looks red and feels warm
Other Types Of Breast Cancer
There are some other less common types of invasive breast cancer.
Invasive lobular breast cancer
About 1 in 10 invasive breast cancers start in the lobes of the breast. This type can sometimes be difficult to diagnose on a mammogrambecause of the way it grows. Some women may need an MRI scan.
Inflammatory breast cancer
This is when cancer cells grow along and block the tiny channels in the skin of the breast. The breast then becomes inflamed and swollen. Inflammatory breast cancer is rare.
Pagets disease of the breast
This is a condition that causes a red, scaly rash on the skin of the nipple. Women with Pagets disease of the breast may have DCIS or invasive breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Airport Scanners Detect Breast Cancer
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Your doctor will discuss what you can expect based on the characteristics of the invasive ductal carcinoma and the effectiveness of your treatment.
Specialty centers such as Johns Hopkins Medicines Breast Health Services can offer integrated teams of breast cancer specialists who have skill and experience in surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies.
Medical science is making great strides forward in treating breast cancer, allowing our surgeries to be less invasive and improving surgical outcomes and overall quality of life, Wright says.
Cosmetic Implants And Breast Cancer Survival
The general agreement, based on , is that silicone breast implants do not increase the risk of breast cancer. A 2015 meta-analysis of 17 studies that included participants who had undergone cosmetic breast augmentation discovered no increase in the risk of breast cancer associated with the procedure. In fact, the research showed that the incidence among these participants was lower than expected.
In 2021, another study found that women with cosmetic implants have significantly lower rates of breast cancer than those who do not have them.
Meanwhile, a 2013 meta-analysis found that women who received a diagnosis of breast cancer after getting cosmetic breast implants may have a higher risk of dying from the disease.
However, this research did not factor in other variables that may influence breast cancer mortality, such as body mass index, age at diagnosis, or cancer stage at diagnosis. And at least one of the studies in the analysis looked at overall mortality, instead of breast cancer-specific mortality, thereby potentially skewing the results. As such, a person should consider the finding with caution.
most common type is ductal carcinoma, which begins in a milk duct. Another type is lobular carcinoma, which begins in a lobule, one of the tiny glands that produce milk.
Invasive breast cancer involves cancerous cells spreading to nearby tissue. It is then more likely that the cancer will spread to other parts of the body.
Read Also: How Much Is Breast Cancer Surgery