Nursing Care Plan For Cancer 1
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to a new diagnosis of cancer as evidenced by the patients verbalization of I want to know more about my new diagnosis and care
Desired Outcome: At the end of the health teaching session, the patient will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of cancer and its management.
Cancer Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Cancer NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
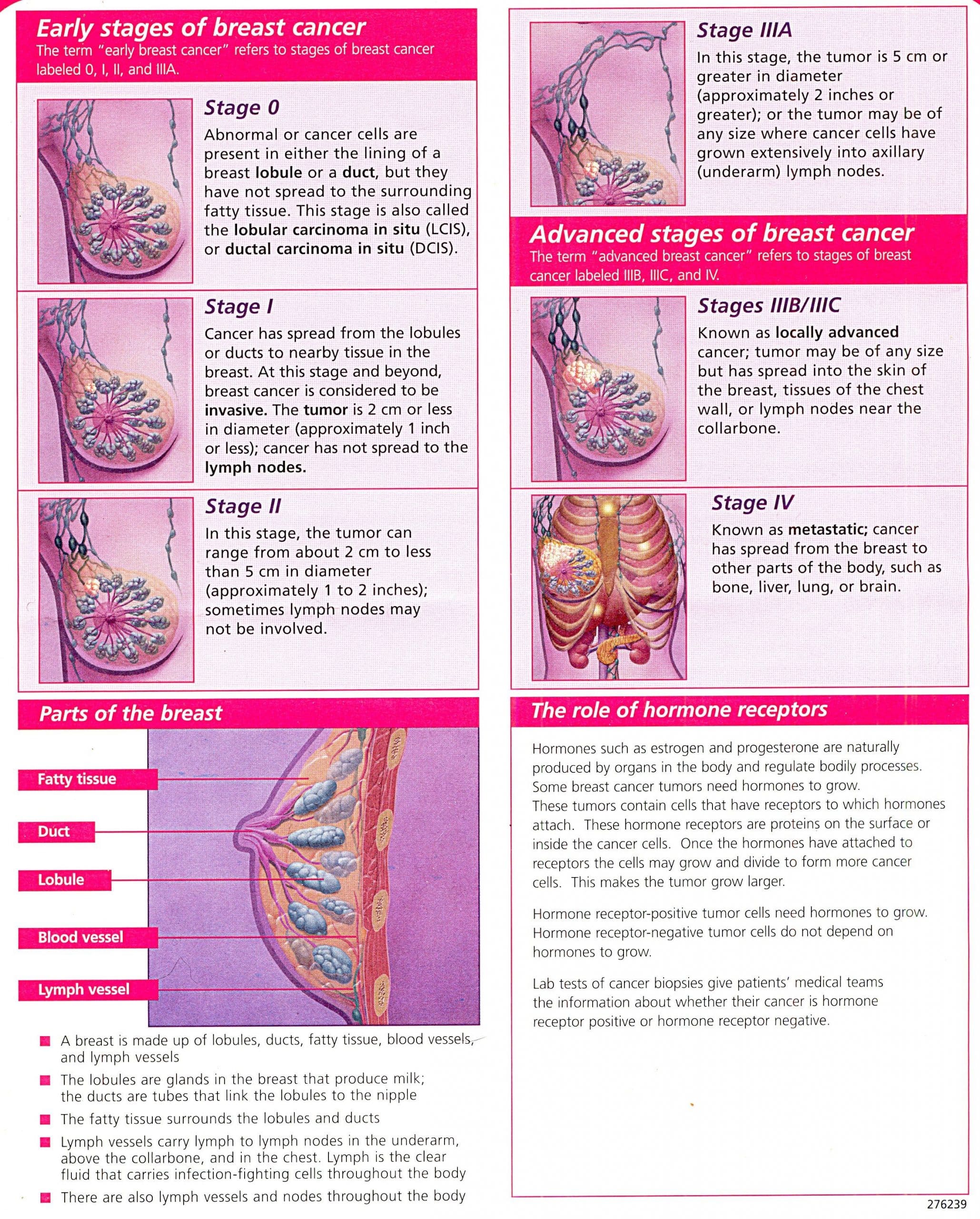
Cancer is an umbrella term for diseases that involve the rapid and uncontrollable division of abnormal cells that are able to cause the destruction of normal body cells and tissues. Cancer is known as a leading cause of death worldwide, second to cardiovascular disease.
However, modern research has tremendously improved treatments for various cancers, resulting in positive leaps in survival rates as well as the quality of life of cancer patients.
Comparison Of Symptom Distress
As shown in Table 3, there were no significant differences regarding the symptom severity score and the symptom distress score before intervention between the two groups . The symptom severity score and the symptom distress score in two groups after intervention were significantly decreased when compared with those before intervention . Compared with the control group, the symptom severity score and the symptom distress score after intervention were significantly lower in the intervention group .
Read Also: How Do They Test For Breast Cancer Gene
Ongoing Screening And Prevention
Specific patient factors, including personal and family history, will help guide screening and preventative care recommendations for breast cancer survivors. In general, patients receiving an aromatase inhibitor should have a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan every two years to assess for bone mineral density loss. Most survivors should adhere to routine gynecologic exams, especially those on endocrine treatment because of the increased risk for uterine cancer.
Survivors should also follow general screening recommendations for other cancers, such as colonoscopy screening beginning at age 45 and an annual skin examination. Encourage healthy lifestyle behaviors, including regular exercise, smoking cessation, limited alcohol consumption, and sun safety. Dietary recommendations include an emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains with an aim to reduce fat, processed foods, and red meat.
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
Patients, family caregivers and professionals were actively involved during this practice improvement process. Patient engagement, i.e. involvement of patients, their families or representatives, in working actively with health professionals to improve health and healthcare services is becoming more and more accepted at various levels across the healthcare system . Since this participation did not imply the collection and reporting of study data, we did not apply the intervention development process to the Institutional Review Board. However, the principles of confidentiality, anonymity, non-binding and well-informed participation were carefully accomplished.
Informed consent did apply for the qualitative study quasi-experimental that were part of steps 1 and 6. These studies took part with the approval Institutional Review Board and are reported elsewhere.
Also Check: Positive Nodes In Breast Cancer
What Every Nurse Needs To Know About Breast Cancer
Youve been a registered nurse for 26 years and cared for dozens of breast cancer patients. Youve listened as they poured out their feelings and fears. Youve consoled them and prepared them for surgery. Youve told them what to expect during chemotherapy and radiation and helped them cope with body-image changes and hair loss.
Suddenly, the tables are turned. You have no family history of breast cancer and no other risk factors, and have had yearly screenings. Yet now, at age 54, you find a lump in your right breast a mammogram and ultrasound confirm an abnormality.
You undergo a breast biopsy. The doctor calls with the results: breast cancer.
You feel like you might faint. You think, This cant be happening to me! Although youve taught many patients about breast cancer and its treatment, your knowledge base seems to have evaporated. Yesterday you could answer all your patients questions. Today, you have nothing but questions of your own.
For you and anyone else newly diagnosed with breast cancerand for everyone who cares for themthis article promotes a better understanding of the disease. It gives a general overview of breast cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment, highlighting information about new diagnostic and therapeutic developments you might not be familiar with.
Comparison Of Vas And Psqi Scores
A visual analogue scale was used for pain assessment. It is widely used clinically in China. The basic method is to use a walking scale about 10cm long. One side is marked with 10 scales, and the two ends are respectively 0 and 10. A score of 0 means no pain. A score of 10 represents the most excruciating pain. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index is suitable for the evaluation of sleep quality in patients with sleep disorders and mental disorders, as well as for the evaluation of sleep quality in the general population. The total score ranges from 0 to 2l, with higher scores indicating poorer sleep quality. As seen in Figure 2, the statistical differences were not found in terms of VAS scores and PSQI scores before intervention between the two groups. In the intervention group, VAS scores and PSQI scores after intervention were significantly lower than those before intervention. Compared with the control group, VAS scores and PSQI scores after intervention in the intervention group were significantly decreased . These experimental results suggest that nursing interventions can improve symptoms in breast cancer patients.
Comparison of VAS and PSQI scores before and after intervention between the two groups. VAS score. PSQI score. Compared with patients in the same group before intervention, P< 0.05. Compared with patients in the control group after intervention, #P< 0.05.
You May Like: What Are Breast Cancer Lumps Like
A Study Testing Nursing Interventions To Combat Fatigue In Breast Cancer Patients
Fatigue is a serious and not uncommon problem in patients with cancer. It is reported by 65%100% of patients. Recent studies suggest that fatigue may be a particular problem in patients undergoing radiation to the breast. The literature suggests that nursing interventions may alleviate some of the problems associated with fatigue. Breast cancer patients were randomized to the study. An experimental group and a control group . Fatigue was measured using the Piper Fatigue Scale, and a fatigue diary was developed. Results indicate that the fatigue experienced by this group of patients was acute in nature. Positive correlations were found between pain, dyspnoea and Tamoxifen related side effects, indicating that symptom control is a major factor in alleviating fatigue. Future studies testing the effectiveness of interventions might prove more useful on a patient population with a high incidence of chronic fatigue, such as that experienced by survivors of Hodgkin’s Disease.
Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
- Breast or underarm lump usually the first symptom of breast cancer does not go away can be seen through a mammogram may be painful or tender
- Swelling may be seen or felt in the breast or in the lymph nodes located in the armpit or collarbone area
- Indentation or flattened area on a breast
- Changes in breast size, texture, color, contour, or temperature
- Unusual nipple discharge can be bloody, clear, or any other color
- Other nipple changes such as inward pulling, dimpling, itchiness, soreness, burning sensation
Also Check: Can I Get Breast Cancer At 17
Benefits Of Breastfeeding For The Mother
- Breastfeeding promotes faster postpartum weight loss by burning 500 additional calories per day to establish and sustain milk production.
- The uterus is stimulated to contract and resume to standard size.
- There is less postnatal hemorrhage.
- Ovarian cancer risk is reduced.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus risk are reduced.
- Reduced cases of endometriosis in lactating mothers.
- With age, there is less osteoporosis.
- Diabetes is less prevalent in breastfeeding mothers.
- Reduced cases of hypertension in breastfeeding mothers
- There is a lesser risk of cardiovascular illness.
Nursing Interventions Benefit Patients With Breast Cancer
Continuous nursing interventions can benefit patients with advanced breast cancer by reducing the incidence of intraoperative pressure ulcers , according to a study published in Gland Surgery.
Researchers searched the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database for relevant data. In total, they analyzed 1431 patients enrolled in 9 studies.
The meta-analysis results demonstrated a marked difference between the nursing intervention group and the control group in the incidence of PUs, as well as better quality of life after nursing intervention.
The investigators concluded that continuous nursing care can attenuate PUs in patients with advanced breast cancer and reduce the severity of wounds associated with PUs. Nursing intervention may also enhance knowledge of PUs in this patient population.
Reference: Ding L, Ding S, He C, Zhang Q, An J. The efficacy of continuing nursing interventions on intraoperative pressure ulcer-related complications in breast cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gland Surg. 2022 11:1078-1085. doi:10.21037/gs-22-258
Read Also: Is The Lump In My Breast Cancer
Signs And Symptoms Of Cancer
Each type of cancer has its own set of warning signs and symptoms, but the following are general signs and symptoms related to cancer:
- Fatigue that is usually unexplained
- Unintentional weight loss or weight gain
- Unexplained bruising and/or bleeding
- Changes in the skin may include erythema or redness, yellowing or darkening of the skin, existing moles that changes in size, shape and/or color, and sores that do not heal
- Bladder or bowel changes
- Indigestion that does not go away
- Unexplained joint and/or muscle pain that may be unrelieved by over-the-counter pain relievers
- Unexplained fevers and/or night sweats
- Persistent indigestion
There are two major causes of cancer and these are:
- Genetics genetic mutations can be inherited by children from their parents.
- Carcinogens chemicals and biologic agents can initiate the malignant transformation of cells. Carcinogenesis or the process of cell transformation due to carcinogens involve:
- Initiation exposure to the carcinogen
- Promotion repeated exposure that causes the alteration of cells
- Progression the abnormal cells show malignant behavior
Breast Cancer Nursing Care Plan 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements related to fatigue, emotional distress, and poorly controlled pain due to chemotherapy secondary to breast cancer, as evidenced by expressions of inadequate food intake, loss of interest in food, inability to ingest food, reduced subcutaneous fat, body weight 20 percent below optimum for height and frame, stomach cramps and constipation.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to demonstrate a stable weight gain toward the goal with normal laboratory values.
- The patient will not show any indicators of malnutrition.
- The patient will be able to participate in specific interventions to gain appetite and increase dietary intake.
Read Also: What Is Her3 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Nursing Care Plan 6
Nursing Interventions: Anticipatory Grieving related to expected decline in physiological health and perceived risk of dying secondary to breast cancer, as evidenced by alterations in eating habits, changes in sleeping patterns, activity levels, and communication patterns, shortness of breath, acute panic, expressions of fear and crying.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to recognize their own emotions and convey them effectively.
- The patient will be able to maintain the normal daily routine while planning for the future and looking ahead one day at a time.
- The patient will be able to express awareness of the dying process.
- The patient will demonstrate ways to identify anxiety to prevent going into a panic state.
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
- Breast Exam. This can be done daily through self-checking. During a breast exam in the clinic, the doctor will observe and feel/palpate the breasts and the lymph nodes in the armpit for any abnormalities such as lumps.
- Mammogram. X-ray of the breast or mammogram is the most common screening test for breast cancer. Women with no history of breast cancer are recommended to have a yearly mammogram once they turn 40 years old.
- Breast Ultrasound. This can determine if a breast lump is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass.
- Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging . This is used to visualize the breast by creating pictures. MRI involves injection of a dye to see the interior of the breast.
- Breast Biopsy. The definitive way to diagnose breast cancer, biopsy involves taking a sample of breast cells to be studied under the microscope.
- Cancer Staging. After diagnosis, the oncologist will assess the extent or stage of breast cancer, from 0 to IV. Cancer staging depends on the blood test results , CT/ PET scan, and other diagnostic results.
Don’t Miss: Risk Factors For Development Of Breast Cancer
Histopathologic Type And Grade
Other factors used to guide treatment and determine prognosis include the tumors histopathologic type and grade. Histopathologic breast cancer types include in situ, ductal, invasive, inflammatory, medullary, mucinous, papillary, lobular, and tubular.
Tumor grade refers to the extent to which the cancer cell resembles a normal cell. Breast cancer cells have three gradeslow, intermediate, and high. In low-grade cancer, cells most resemble a normal cell and prognosis is more favorable. In high-grade cancer, cells look least like a normal cell and the prognosis is less favorable.
Breastfeeding Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Breastfeeding NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Breastfeeding is the practice of providing a child with a mothers breast milk. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, human breast milk is recommended for all newborns.
With few circumstances, this involves premature and ill babies. Breast milk is least likely to provoke allergic responses it is affordable, conveniently available at all times of day or night, newborns readily accept the taste, and antibodies in mothers milk can enable a baby to withstand infections.
Additionally, amino acids, the protein building blocks in breast milk, are well proportioned for the newborn, as well as carbohydrates, mainly lactose, and lipids. The nutrients, enzymes, and minerals in breast milk help the babys digestive tract.
Breastfed infants eat more frequently than bottle-fed babies because breast milk digests and empties the stomach faster.
Furthermore, continuous breastfeeding is an ideal nourishment and adequate to ensure optimum development and growth for the first six months after delivery. Breastfeeding is recommended during the first twelve months of life. Thus, infants withdrawn from breastfeeding before the age of 12 months should not be fed with cows milk but should instead be fed iron-fortified baby formula.
Read Also: What Type Of Radiation Is Used For Breast Cancer
Nursing Care Plan For Breastfeeding 2
Deficient Knowledge / Knowledge Deficit
Nursing Diagnosis: Knowledge Deficit related to poor understanding of necessary information to achieve successful nursing and lack of awareness on proper breast care, different types of holds, and proper storage of milk secondary to breastfeeding, as evidenced by the occurrence of a breast infection, insufficient milk production, and incorrect position of the baby while breastfeeding.
Desired Outcomes:
Selecting Methods And Strategies
In selecting theoretical methods and practical strategies appropriate for the intervention, the panels took into account the evidence on methods and theories linked with the change objectives and determinants recommended by the panel members , methods and strategies used by other nursing interventions aimed at reducing chemotherapy-related symptom burden and methods and strategies suggested by the panel members during previous patient/caregiver and professional meetings. A provisional draft of the intervention was discussed with both panels to further refine the new nursing intervention. An auxiliary nursing panel was organised to query oncology nurses for their opinions on the perceived relevance and feasibility of the intervention.
Recommended Reading: Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Painful
Nursing Care Plan For Breastfeeding 3
Acute Pain
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to inflammation of the breast tissue secondary to breastfeeding-induced mastitis or lactation mastitis as evidenced by tenderness or warmth to the touch in the breast, breast enlargement, breast tissue thickening, or a breast lump, and continuous or intermittent pain or a burning feeling while breastfeeding.
Desired Outcomes:
Nursing Care Plan For Breastfeeding 1
Risk for Ineffective Breastfeeding
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Ineffective Breastfeeding related to a poor infant sucking reflex secondary to breastfeeding as evidenced by the undesirable nursing process, inadequate emptying of each breast during each feeding, and perceived or actual scarcity of milk production.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to communicate her understanding of the cause or contributing circumstances.
- Exhibit strategies for improving or enhancing breastfeeding.
- Accept accountability for practical breastfeeding.
- Achieve a mutually agreeable breastfeeding regimen, with infants satisfied after feedings and sufficient weight gain.
You May Like: How To Lower Your Risk Of Breast Cancer
Surgery And Adjuvant Therapy
Surgery is the definitive treatment for breast cancer. Usually, the patient receives adjuvant therapy in addition to the first therapeutic modality she undergoes. When surgery is the primary treatment, adjuvant therapy may consist of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or antiestrogen therapy given afterward.
In neoadjuvant treatment, chemotherapy is given first to shrink a large tumor before surgery and thus allow a breast conservation technique . It also may be used if surgery isnt feasible at the time of diagnosis.
Breast reconstruction is an option for some women whove had mastectomies. Reconstruction may involve breast expanders, implants, autologous tissue reconstruction, or a combination.
Assessment In A Flash
Hot flashes are a common side effect of breast cancer treatment. Use the Hot Flash Related Daily Interference Scale to assess the effects of hot flashes on patients quality of life.
Patients rank how much hot flashes have interfered with the following aspects of their life during the past week :
- overall quality of life.
Management: Educate patients about diet and behavioral triggers that may precipitate and contribute to the frequency and severity of hot flashes and night sweats. Explain that they should avoid alcohol and caffeine, hot or spicy food, hot baths or showers, and smoking. Healthy lifestyle changes include regular exercise, a balanced nutritious diet, and stress-reduction techniques such as yoga. As with any behavior change, patients may resist, so encourage slow, subtle, and attainable goals on their quest for a healthy lifestyle.
Sexuality and intimacy
Overview: Breast cancer therapy can propel women into menopause, causing a distressing cascade of physical symptoms that result in sexual dysfunction. The psychological effects of a cancer diagnosisanxiety and depression and pre-existing stress and spousal conflict can worsen sexual dysfunction.
Management: Discussing sexuality can be difficult for some patients and requires your sensitivity. The PLISSIT model promotes discussion with open-ended questions, information, specific suggestions, and referrals.
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Be Inherited From Father’s Side