Zoe Winters Explains How To Check For Breast Cancer
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer in the UK, with almost 56,000 new cases a year. And it is the fourth most common cause of cancer mortality, making up seven percent of all cancer deaths. Speaking exclusively with Express.co.uk one expert shared some of the important signals of the disease.
What Causes Skin Dimpling
A condition called fat necrosis is unrelated to breast cancer and can also cause dimpled skin. Sometimes, fatty tissue in the breast can become damaged and die.
This may result in a lump that could be mistaken for a tumor. If the fat necrosis develops near the surface, it may make the skin surface look pitted or dimpled.
Fat necrosis isnt a precursor to cancer, but its symptoms still warrant evaluation. A needle biopsy of the lump can help confirm if its cancerous or not. Fat necrosis doesnt raise the risk of breast cancer.
Dimpled skin is a common sign of inflammatory breast cancer, which draws its name from an inflamed appearance. This form of cancer results in the blockage of lymph vessels in the skin.
These vessels transport lymph, a fluid that helps carry particles and excess fluid, from tissue throughout the body to the bloodstream. The lymph system also supports the bodys immune system.
Inflammatory breast cancer accounts for
If your skin dimpling is caused by inflammatory breast cancer, you may have the following symptoms:
- The affected breast may swell and feel warm.
- The affected breast may be especially tender.
- You may feel pain in the affected breast.
- You may feel a burning sensation in the affected breast.
The affected area often covers about one-third of the breast in inflammatory breast cancer. This can vary depending on the person. If you see dimpled skin on both breasts, its unlikely that the cause is cancer.
Diagnosing Inflammatory Breast Cancer
If you are being treated for swelling or redness of the breast and it doesnt seem to be getting better after taking antibiotics for a week, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests to check for IBC. These tests may include an ultrasound and the following:
- Mammogram This test will be done to check the thickness of the skin and the density of the treated breast in comparison to the healthy breast.
- MRI It takes images of the breast and structures of your body using radio waves and magnets.
- CT This scan provides detailed images of your bodys insides.
- PET This scan, along with a CT, can find cancer in any area of the body, including the lymph nodes.
- Biopsy This test is done by removing a small piece of the skin or tissue of the breast to help diagnose cancer. A biopsy can sometimes be done with a needle or a surgical incision may be needed to remove tissue for testing. The type of biopsy performed with depends on whether a mass is discernible on imaging tests. The test will look for unusual cell growth and check for the presence of proteins found in some cancers.
Stages of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 2b Breast Cancer Curable
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
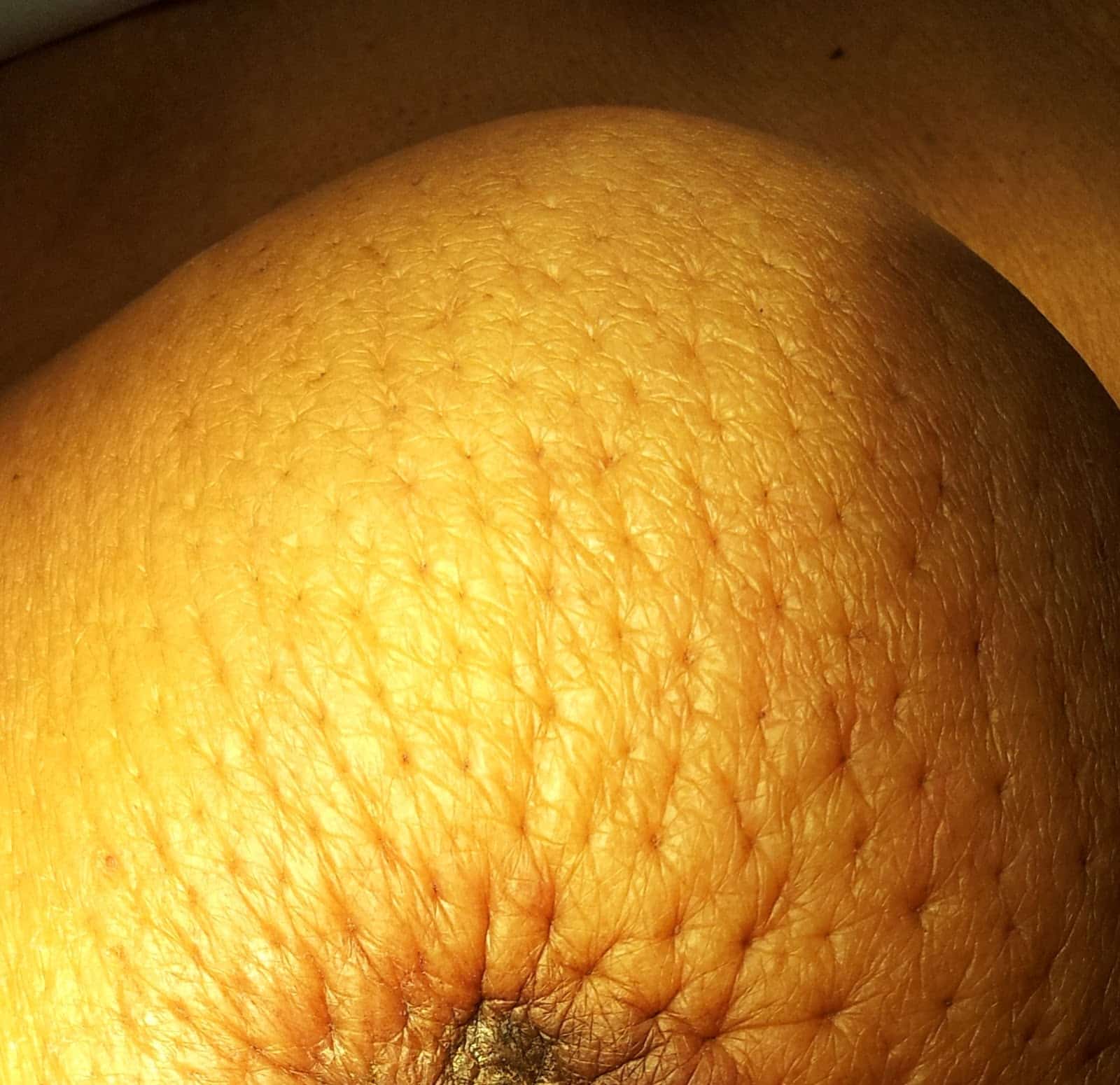
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of cancer that spreads quickly. Unlike most breast cancers, IBC doesnt usually cause lumps in breast tissue. Instead, it appears as a rash, creating skin texture on the affected breast similar to an orange peel. IBC causes pain, redness, swelling and dimpling on the affected breast.
IBC results when cancer cells block lymph vessels the small, hollow tubes that allow lymph fluid to drain out of your breast. The blockage leads to inflammation, causing symptoms that make it easy to mistake IBC for an infection.
IBC grows fast and requires immediate treatment. Healthcare providers usually treat IBC with chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
Signs Of Breast Cancer Everyone Should Know About

The Shape staff is made of up seasoned writers, editors, journalists, and artists who are experts in our field. Some of us even hold fitness or health certifications that allow us to add even more knowledge to the stories you read and the advice you’re given. Whether we’re digging into the latest workout trend to test its validity, speaking to dermatologists about a specific skin concern, or delivering tips about how to strengthen your mental wellbeing, we aim to do that with authority, trust, and approachability.
Roughly 1 in 8 women develop invasive breast cancer in their lifetime, and it’s the second most commonly diagnosed cancer among women in the U.S., according to the American Cancer Society. So it’s vital to be aware when something is awry that is, to know the first signs of breast cancer.
“The key is to know what your healthy breasts look and feel like, and if you notice any changes, go to your doctor for an exam and work-up if needed,” says , medical director of breast oncology at the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Baylor College of Medicine.
Now, these changes definitely don’t mean you 100 percent have breast cancer. And even if they do, it could be signs of a benign tumor, says Roshni Rao, M.D., chief of the breast surgery program at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. “You have to look at the whole picture imaging, exam, and possibly biopsy to make the final call,” she explains.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Only Genetic
S Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Home » Pictures of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
There are images below are graphic medical photos of inflammatory breast cancer.We are sharing these photos for educational purposes.
We hear a great deal about prevention and early detection in cancer. While cancer prevention may never be 100 percent effective, many things can greatly reduce a persons risk for developing cancer, the causes for IBC are unknown and there is not a form of detection prior to a stage three.
This lack of early detection can cause great emotional stress, so it is important that if you are diagnosed with IBC to understand your late stage diagnosis was not your fault. There is not a way to know you have IBC until the outward physical signs are presented.
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening mammogram. In addition, most women diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer have dense breast tissue, which makes cancer detection in a screening mammogram more difficult. Also, because inflammatory breast cancer is so aggressive, it can arise between scheduled screening mammograms and progress quickly. The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may be mistaken for those of mastitis, which is an infection of the breast, or another form of locally advanced breast cancer.
To help prevent delays in diagnosis and in choosing the best course of treatment, an international panel of experts published guidelines on how doctors can diagnose and stage inflammatory breast cancer correctly. Their recommendations are summarized below.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- A rapid onset of erythema , edema , and a peau d’orange appearance and/or abnormal breast warmth, with or without a lump that can be felt.
- The above-mentioned symptoms have been present for less than 6 months.
- The erythema covers at least a third of the breast.
- Initial biopsy samples from the affected breast show invasive carcinoma.
Imaging and staging tests include the following:
Don’t Miss: Can Men Die From Breast Cancer
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Pictures And Symptoms
The symptoms of IBC include a breast that:
- Quickly changes appearance
- Looks larger, thicker or heavier
- Feels very warm
- Has skin that looks dimpled or ridged like an orange
- Is tender, aches or feels painful
- Has larger lymph nodes under the arm or around the collarbone
- Has a flatter nipple or one that is turned inward
Unlike other forms of breast cancer, there is no lump formation with IBC.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Pictures of Different Symptoms
Below are some of the pictures of IBC for reference only, you may not experience them at all. If you find anything abnormal with your breast and are concerned, do not hesitate to visit your doctor.
As these inflammatory breast cancer picture shows, the texture of the breast may change and appear to look dimpled or ridged, like an orange peel. This is referred to as peau dorange, which is French for orange skin and it is caused by cancer cells blocking the lymph vessels beneath the skin, which have formed into ridges or tiny lumps.
One of the first symptoms women experience is the breast appearing to be red, pink or purple. The discoloration may look like bruising that covers one-third or more of the breast. It may also feel warm or be tender.
With IBC, the skin may appear to be splotchy or irritated and there may be bumps present.
Inflammatory breast cancer pictures show the discoloration that can appear.
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Breast Cancer
The most common symptoms of breast cancer include:
- Feeling a lump in the breast area, with or without pain
- Change in breast shape or size
- Dimple or puckering in breast
- A nipple turning inward into the breast
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk, especially if it is bloody
- Scaly, red, darkened or swollen skin in the breast area
- Itchy, scaly sore or rash on the nipple
- Dimple, pitted appearance or feel in the breast area
- Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes around the breast area, including the collarbone and armpits
Although these symptoms can be caused by other conditions, you should check with a doctor preferably a breast health specialist so they can make a definitive diagnosis.
Also Check: Gail Model For Breast Cancer Risk
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed And Staged
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare, with symptoms similar to a more common condition breast infections . Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics and see if it resolves your symptoms to rule out an infection. If they suspect IBC, theyll order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and additional tests to see if the cancers spread beyond your breast.
Diagnosing inflammatory breast cancer
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, imaging studies and a biopsy.
Staging inflammatory breast cancer
Biopsy results can help your healthcare provider stage the cancer, or determine whether its spread outside of your breast tissue. By the time IBC is diagnosed, its either stage III or stage IV. Stage III cancer has only spread to your breast tissue skin. Stage IV cancer has spread to other organs.
Your healthcare provider may order any of the following tests to determine if your cancers spread:
What Are The Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Symptoms of IBC progress quickly, over three to six weeks, and may include:
- Areas of discoloration , a bruise or rash spread over one-third of your breast.
- Dimpling, pitting or thickening of your breast skin that resembles an orange peel.
- Pain, swelling, itchiness, firmness or tenderness in one breast.
- Warmth, burning, heaviness or enlargement of one breast.
- Inverted or retracted nipple .
- Swollen lymph nodes near your collarbone or under your arm.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Breast Cancer From Returning
Signs Of Breast Cancer Women Must Know
Thick mass: A sudden thickening of the breast tissue can be a sign of a serious underlying condition such as lobular or inflammatory breast cancer
Indentation: Some people notice a dip, or dent, in the breast. This can be because the cancer is tethered to the breast tissue and so pulls it inwards
Skin erosion: In rare cases cancer that is growing under the skin can break through and create a wound
Heat or redness: If the breast feels warm to touch or there’s redness one-third of the breast, it can be a sign of inflammatory breast cancer
New fluid: Spontaneous nipple discharge on one side, which may be blood stained, brown or clear, might mean there is something in the breast that is causing irritation
Dimpling: Dimpled skin is a common sign of inflammatory breast cancer
Bump: A localised swelling, bulge or bump on the breast should always be investigated
Growing vein: Changes such as dilated veins can be a sign that cancer is blocking a blood vessel
Retracted nipple: Developing an inverted nipple – i.e. not being born with one – which can’t be drawn out, may suggest a lump behind the nipple is pulling it in.
New shape or size: Any change in shape or size not associated with the menstural cycle should be investigated
Orange peel skin: Skin that has ridges or appears pitted, like the skin of an orange, can be caused by a build up of fluid in the breast
A lump is by no means the only possible symptom of cancer, but it’s crucial to check your breasts regularly
A Lump In The Breast Or Armpit
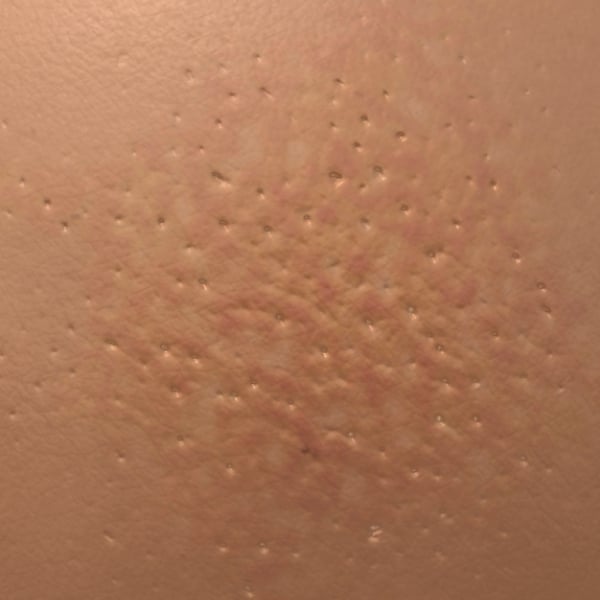
A breast lump or mass is the most obvious and well-known potential indicator of breast cancer. A lump in the breast may be visible to the eye or felt with your hands during a self-breast exam. But lumps or areas of swelling around the breast, under the armpit or near the collar bone may also be signs of cancer.
A breast cancer lump often feels like a pea- or marble-shaped mass just under the skin. In some people, it may resemble a ridge rather than a bump. Often, theyre hard and painless, but some cause discomfort.
Performing regular self-exams once a month may help you identify suspicious lumps. But its a good idea to have a doctor check out any new ones right away. If it does turn out to be cancer, the sooner its diagnosed, the better.
You May Like: Does Having Breast Cancer Make You Tired
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Different From Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Compared to other types of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer has different signs, symptoms, and prognoses.
- Breast lump not likely. Developing a lump in your breast is not typical with IBC.
- Swelling and skin changes. IBC causes swelling, discoloration, and dimpling. The affected breast may feel warmer and heavier than the other. It may develop redness or appear bruised.
- Appears at a younger age. IBC affects people approximately
Peeling Scaling And Flaking
Peeling, scaling, or flaking skin around your nipple may be a sign of breast cancer. The skin may also feel itchy or crusty. You may also notice redness or discoloration of the skin around the nipple.
Changes to the skin on your breasts or around your nipples do not always mean cancer. Peeling and flaking skin around your nipple may be due to nipple eczema.
Nipple eczema often occurs due to irritation from tight clothing, soaps, or other products. People who have experienced eczema on other parts of their body may also be more likely to develop it on their nipples.
Pagets disease of the nipple, a rare form of breast cancer, can also cause peeling and flaking skin that resembles eczema.
You May Like: What Questions To Ask Breast Cancer Surgeon
A Note About Sex And Gender
Sex and gender exist on spectrums. This article will use the terms male, female, or both to refer to sex assigned at birth. .
There are many different types of breast cancer.
Each form of breast cancer develops in a different part of the breast and can affect different tissue types.
Since many breast cancers cause no symptoms, people should attend regular screenings. This can help identify the disease in its early stages.
Below, we outline the types of breast cancer and their symptoms.
Reducing Your Risks For Breast Cancer
Women who breast-feed their children for the recommended length of time can reduce their risk of breast cancer by 25%. You can also reduce your risk by maintaining a low BMI and by getting exercise. You should also cut back on the amount of alcohol you drink. Birth control pills and some forms of hormone therapy after menopause can boost the odds. But the risk seems to go back to normal after you stop these medications. Good lifestyle choices can help survivors, too. Research says physical activity can lower the chances your cancer will return. And it’s a proven mood-booster, too.
Recommended Reading: If My Grandmother Had Breast Cancer Will I Get It
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treated
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
What To Do If You Have Peau Dorange
If you have peau dorange, the first thing to do is visit a healthcare professional. They can help you figure out what is causing your breast dimpling and how to treat it. Your provider will likely perform a thorough breast examination and decide whether you need further tests like a mammogram or biopsy.
Recommended Reading: Can Breastfeeding Cause Breast Cancer
How Does Spreading Happen
There are several ways cancer can spread in the body.
- Direct invasion happens when the tumor has spread to a nearby organ in the body. The cancer cells take root and begin to grow in this new area.
- Lymphangitic spread occurs when cancer travels through the lymphatic system. Breast cancer often involves the nearby lymph nodes, so the cancer can enter the lymph circulatory system and take hold in different parts of the body.
- Hematogenous spread moves in much the same way as lymphangitic spread but through the blood vessels. The cancer cells travel through the body and take root in remote areas and organs.
When cancer starts in the breast tissue, it may often spread to the lymph nodes before affecting other parts of the body. Breast cancer most commonly spreads to the:
The type of test you end up having will depend on your medical history and symptoms. For example, if you or your doctor suspects the cancer may have spread to your abdomen, you may have an ultrasound.
CT and MRI scans can help your doctor visualize various parts of the body all at once. A PET scan can be helpful if your doctor thinks the cancer may have spread but isnt sure where.
All of these tests are relatively noninvasive, and they shouldnt require a hospital stay. You may be given special instructions before your test.
If you have a CT scan, for instance, you may need to drink an oral contrast agent to help outline different features inside your body.