Factors That Put You At Risk
Factors that put you at
If a diagnosis cant be made based on a clinical exam and imaging tests, youll need a breast biopsy. This is the only way to rule out or confirm cancer.
In this procedure, the doctor uses a needle to remove samples of the suspicious tissue. The samples then go to a laboratory, where a pathologist uses a microscope to look for cancer cells.
The pathology report will state whether the sample is benign or malignant . If cancer is found, it will also provide information such as:
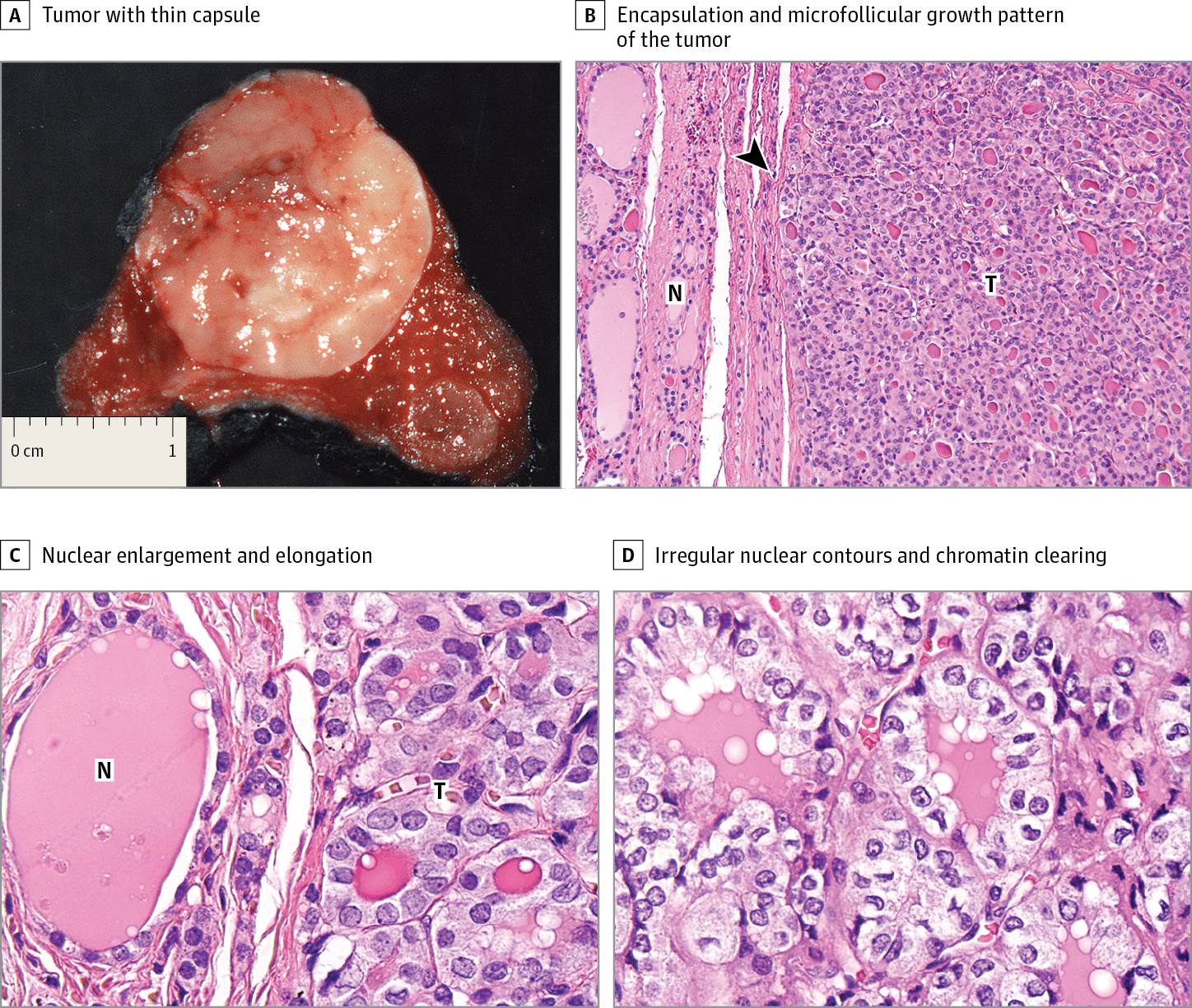
Tumor grade describes how the cells look and behave. Grade 1 means the cells look and behave similar to normal breast cells. Grade 3 means the cells look very different from normal cells and are growing aggressively. Papillary breast cancer is often grade 2.
What Genetic Factors Link The Diseases
In addition, germline mutations in PARP4 were identified in women treated for both cancers . Heightened expression of PARP4 also correlated with longer disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with breast cancer. PARP4 belongs to a family of genes, poly-ADP-ribose polymerases , that encodes enzymes to catalyze synthesis of poly-ADP-ribose . Levels of poly-ADP-ribose increase in response to genetic insults and is a critical component of DNA repair. PARP inhibitors are used clinically to treat ovarian tumors and are in clinical trials for breast cancer . However, existing drugs do not target PARP4. PARP4 is unique in that it can also be found in the cytoplasm, unlike the other members of the PARP family . Unfortunately, PARP4 is not well characterized and more research is needed to determine the biochemical and physiologic processes it regulates.
How Is Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treated
Treatments for papillary thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread .
Surgery is the most common treatment for PTC. Depending on the tumors size and location, your surgeon may remove part of your thyroid gland or all of your gland . If you have cancer present in the lymph nodes of your neck, your surgeon may remove the affected lymph nodes at the time of the initial thyroid surgery or as a second procedure.
If you have a total thyroidectomy, youll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication for the rest of your life.
Additional treatments for PTC include:
- Radioiodine therapy: Thyroid cells and papillary thyroid cancer cells absorb iodine, a mineral found in some food. Because of this, healthcare providers sometimes use a radioactive form of iodine to destroy all remaining normal thyroid tissue and potentially destroy residual cancerous thyroid tissue after a thyroidectomy.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stop cancer growth. Very few people diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
You May Like: What Is The Best Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Fact To Know About Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Most Patients Do Not Need Further Treatment After Surgery
Most often, excellent and thorough thyroid cancer surgery is the only treatment needed for papillary thyroid cancer. Traditional chemotherapy is never used. External or beam radiation therapy is very rarely indicated for further papillary thyroid cancer treatment. Papillary thyroid cancer diagnosis alone is not an indication for further therapy after thyroid surgery.
The most commonly used treatment after thyroid cancer surgery, however, is radioactive iodine . This treatment works better the younger the patient is. Iodine is used by normal thyroid cells to make thyroid hormone. Thyroid cancers can possess the same type of key hole on the surface of their cell called a symporter that allows iodine to be taken into the cell. Although papillary thyroid cancer rarely produces any significant amounts of thyroid hormone itself, it frequently maintains this iodine pump and ability to take up iodine. In the treatment of thyroid cancer, this can be taken advantage of by having the patient swallow an iodine pill that has been radioactively charged.
Learn more about radioactive iodine for papillary thyroid cancer.
Validation Set Of The Study Cohort
For further validation of the eight-genera microbiome signature that could reliably distinguish between different T stages, we recruited another set of patients from Tangdu Hospital in November 2021. All patients were diagnosed with T1 or T2 PTC . Therefore, a ROC analysis was conducted using this set of patients and the patients with T3 or T4 PTC in the old set of samples. In addition, the differential abundance of microbes and their correlations to thyroid hormones and autoimmune thyroid disease-related antibodies were also investigated in this set of samples.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Radiation For Breast Cancer
What Are The Possible Side Effects And Complications Of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Permanent hypothyroidism is an expected side effect of thyroidectomy and radioiodine therapy. Because of this, youll need to take replacement thyroid hormone medication for the rest of your life if you undergo either or both of these treatments.
Possible complications of thyroid surgery include:
- Accidental removal of or damage to your parathyroid glands, which help regulate your blood calcium levels.
- Damage to your recurrent laryngeal nerve, which runs behind your thyroid gland, resulting in hoarseness and a weak voice.
Potential side effects of radioactive iodine therapy include:
- Small risk of leukemia, breast or bladder cancer.
What Causes Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Scientists still dont know the exact cause of papillary thyroid cancer, but they have identified risk factors that increase your risk of developing PTC, including radiation exposure and certain genetic conditions.
Radiation exposure and papillary thyroid cancer
The rates of papillary thyroid cancer are higher in people who have a history of exposure to significant ionizing radiation. This exposure could be due to:
- High-dose external radiation treatments to your neck, especially during childhood, used to treat cancer or some noncancerous conditions.
- Radiation exposure from nuclear plant disasters. The Chernobyl nuclear accident in 1986 led to a 3- to 75-fold increase in PTC cases in fallout regions.
Genetics and papillary thyroid cancer
A few genetic conditions are associated with PTC, including:
Only 5% of all papillary thyroid cases are associated with these genetic conditions.
You May Like: When Is Chemo Used For Breast Cancer
Clinicopathological Characteristics Of Bc In Patients With Tc
The clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC are shown in Table . Patients with BC-TC were less likely to be menopausal and more likely to have a positive family history of malignancy than patients in the control group. In terms of BC features, patients with BC-TC had a smaller invasive tumor size and a lower rate of high Ki67 expression than patients in the BC-alone group. However, no difference was detected in tumor grade, ER status, PR status, HER2 status, or breast cancer subtype.
| Variables |
|---|
Recurrence Of Thyroid Cancer
Although thyroid cancer recurrence is not common, there are many treatment options available if it happens. If a cancer recurrence is detected in the neck lymph nodes, the best course of action is usually an operation to remove the affected node or additional treatment with RAI ablation. In order to determine the best treatment for recurrent thyroid cancer, it is critical to work with an experienced team of thyroid specialists.
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Cause Fluid In The Lungs
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Papillary Breast Cancer
Cancer occurs when there are errors in DNA. As abnormal breast cells grow and divide, they create more cells with errors. Eventually, these cells start to grow out of control and form a tumor. What causes a person to develop papillary breast cancer isnt known.
Papillary breast cancer is most common in postmenopausal people assigned female at birth. However, people assigned male at birth and younger females can get it, too.
Research suggests that papillary breast cancer is typically diagnosed in people ages 63 to 67. Its not always the case, but some may have a preexisting papilloma .
According to the , having one papilloma does not raise the risk of breast cancer unless it has other changes such as atypical hyperplasia. Having several papillomas may slightly increase the risk of breast cancer.
Does Hormonal Disruption Alter Metachronous Cancer Susceptibility
Breast cancer is often hormonally driven through the upregulation of estrogen and progesterone receptors and mimetics of these compounds can be carcinogenic . This relationship has been extensively studied, and although there are still many unanswered questions regarding the mechanistic details, there is little doubt concerning whether estrogenic signaling can promote breast tumorigenesis. Estrogen is also implicated in the development of thyroid cancer, and may explain why women develop the disease at roughly 4 times the rate as men . Numerous studies have linked endocrine disrupting chemicals to obesity, developmental perturbations, and hormone-dependent cancers . Exposure to EDCs at prenatal and early developmental stages are associated with later development of cancers , which could predisposition the same individual to developing both tumor types potentially explaining why the same person develops both diseases in a short time frame and at a younger age. For example, EDCs may stimulate thyroid and breast cancer development through estrogenic signaling. Bisphenol A and flame retardants , mimetics of endogenous estrogen or xenoestrogens, have been implicated in the development of thyroid cancer as well as breast cancers . Bisphenol A binds to TRs and antagonizes thyroid hormone action . As TR is a tumor suppressor in both thyroid and breast cancers, this inhibition may be a common mechanism.
Don’t Miss: How To Support Family Member With Breast Cancer
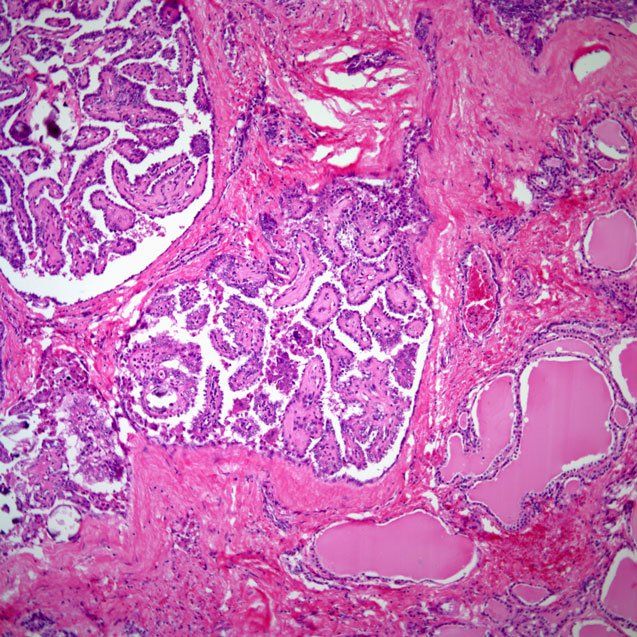
Core Biopsy Versus Surgical Excision
There is some controversy regarding the optimal management of papillary lesions diagnosed by core-needle biopsy, with some authors advocating observation for benign disease and others suggesting surgical excision of all lesions in the same setting. A study conducted at St. Vincentâs Comprehensive Cancer Center examined 71 papillary lesions identified by core needle biopsy that were later surgically excised. Of these lesions, 47 were benign at the time of core biopsy. At the time of surgical excision, however, 4 cases revealed malignancy and 13 cases demonstrated atypical features. Of 13 lesions characterized as atypical at the time of core biopsy, surgical excision revealed malignancy in 7 lesions . Overall, it was noted that 38% of cases were up-graded between assessment at core needle biopsy and at the time of surgical excision. Thus for these lesions, surgical excision should be considered, especially if they are clinically or histologically worrisome.
Trends In Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis By Sex And Cancer Type
As seen in previous studies, the researchers found that diagnoses of thyroid cancer increased sharply beginning in the 1990s. At the peak of this trend, in 2013, about 22 cases of thyroid cancer were diagnosed per 100,000 women, compared with only about 8 per 100,000 men. Papillary thyroid cancer accounted for around 75%80% of cases diagnosed between 1975 and 1989. This increased to 90% between 2010 and 2017.
Correspondingly, between 1983 and 2017, women were more than four times as likely as men to receive a diagnosis of a small, localized papillary thyroid tumor. When larger and more advanced papillary thyroid cancers were included, women were only about 2.5 times as likely as men to receive such a diagnosis.
For more deadly types of thyroid cancer, such as medullary thyroid cancer and anaplastic thyroid cancer, the gap between sexes nearly disappeared, with diagnoses being about equally likely for men and women. And from 1992 to 2017, the overall annual death rate from any thyroid cancer diagnosed during life was approximately the same for women and men.
The researchers also identified eight studiesincluding more than 23,000 people in totalthat reported the prevalence of undiagnosed thyroid cancer on autopsy. Unlike diagnoses made in the living, the prevalence of undiagnosed small papillary thyroid cancer did not differ substantially between women and men.
Also Check: How Does Breast Cancer Form
What Are The Different Types Of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is categorized based on the type of thyroid cells where the cancer begins and how the cancer cells appear under a microscope.
There are two kinds of cells found in the thyroid.
Follicular cells are the most common. They produce thyroid hormone, which is important for growth, mental function and helping the body create energy. Most thyroid cancers develop from follicular cells.
Parafollicular cells, also known as C cells, produce a small amount of the hormone calcitonin, which helps control calcium metabolism. Most parafollicular cells are in the upper third of each lobe. Medullary thyroid cancer is the only thyroid cancer that develops from parafollicular cells.
Thyroid cancers can also be categorized based on the appearance of their cells. Cancer cells that look most like normal, healthy cells are called well differentiated. Patients with well differentiated thyroid cancers are most likely to be disease-free at the end of treatment. Poorly differentiated and undifferentiated cancer cells look less and less like healthy cells. These forms of thyroid cancer are usually harder to treat and the outlook for these patients is worse.
Doctors believe most thyroid cancers start as well differentiated. As the cancer grows, its cells can develop additional mutations, changing it into a less differentiated, harder-to-treat type of thyroid cancer.
What Happens After A Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis
The disparity by sex in the prevalence of small papillary thyroid cancers found during life and after death suggests that many women are receiving treatment for small tumors that might never have caused symptoms, Dr. Davies explained.
The factors that lead more women to get a diagnosis of small papillary thyroid cancer are numerous and complex, she said. Women tend to be more likely than men to seek medical care overall. Theyre more likely to encounter health issues that may have hormonal causes, such as difficulties with pregnancy.
Thyroid ultrasound is widely used to evaluate medical problems that may involve the thyroid. But its not intended to be used to screen people who dont have symptoms for thyroid cancer, Dr. Davies explained. However, she added, it often gets ordered along with other tests to speed the process of diagnosing a potential thyroid issue.
That can lead to finding things that were unrelated to someones symptoms. And that can also distract from discovering the real cause of the problem someone came to the clinic for, said Dr. Davies.
The biggest challenge, said Dr. Haymart, is that its currently impossible to predict which tumors found by chance will pose a threat to health.
How do you determine which cancers might be indolent and just sit there for the rest of the patients life, and which ones might be aggressive and potentially cause harm? she asked. Thats very difficult to tease out.
Also Check: What Is The Average Age For Breast Cancer
Tumor Microbiome Communities Are Significantly Associated With Tumor Invasion In Patients With Resected Ptc
The demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients with PTC are shown in Supplementary Tables and . The tumor microbial diversity was compared among surgically resected patients in different clinical stages. The tumor microbial diversity was measured using different methodologies . The alpha-diversity of the tumor microbiome was significantly lower in patients with T1/T2 PTC than in those with T3/T4 PTC, as shown by the Shannon and Simpson indices . This indicated lower microbiome diversity in patients with T1/T2 PTC. Microbiome richness was measured by the number of observed OTUs , and no significant differences were found among different clinical stages . To gain a better understanding of the role of microbiome diversity, beta-diversity was used to carry out a principal coordinate analysis using BrayCurtis metric distances . Significant differences in -diversity were observed, further suggesting that the tumor microbial communities varied during tumor progression.
Fig. 1: Changes in the intratumor microbiomes of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma at different clinical stages.
What Does The Research Say
Researchers looked at 37 peer-reviewed studies containing data on the relationship between breast and thyroid cancers.
They noted in a 2016 paper that a woman whos had breast cancer is 1.55 times more likely to develop a second cancer of the thyroid than a woman without a history of breast cancer.
A woman with thyroid cancer is 1.18 times more likely to develop breast cancer than a woman without a history of thyroid cancer.
Researchers are unsure about the connection between breast and thyroid cancers. Some research has indicated the risk of developing a second cancer increases after radioactive iodine is used to treat thyroid cancer.
Iodine is generally considered safe, but it could trigger a second cancer in a small number of people. Radiation used to treat certain forms of breast cancer may increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Certain genetic mutations like a germline mutation could link the two forms of cancer. Lifestyle factors like exposure to radiation, poor diet, and lack of exercise, could also increase the risk of both cancers.
Some researchers also noted the possibility of a surveillance bias, which means a person with cancer is more likely to follow up with screening after treatment. This improves detection of a secondary cancer.
They also analyzed the results by dividing the data into groups based on the time between the diagnosis of the first and the second cancer.
Both breast and thyroid cancers have unique screening guidelines.
You May Like: What Is Involved In Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
What Can You Do
After completing treatment for thyroid cancer, you should see your doctor regularly. You may also have tests to look for signs that the cancer has come back or spread. Experts do not recommend any additional testing to look for second cancers in patients without symptoms. Let your doctor know about any new symptoms or problems, because they could be caused by the thyroid cancer coming back or by a new disease or second cancer.
Patients who have completed treatment should keep up with early detection tests for other types of cancer.
All patients should be encouraged to avoid tobacco smoke, as smoking increases the risk of many cancers.
To help maintain good health, survivors should also:
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight
- Keep physically active and limit the time you spend sitting or lying down
- Follow a healthy eating pattern that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limits or avoids red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and highly processed foods
- Not drink alcohol. If you do drink, have no more than 1 drink per day for women or 2 per day for men
These steps may also lower the risk of some other health problems.
See Second Cancers in Adults for more information about causes of second cancers.