What Are The Cosmetic Results Of Breast Conservation Therapy
Eighty percent to 90 percent of women treated with modern surgery and radiotherapy techniques have excellent or good cosmetic results that is, little or no change in the treated breast in size, shape, texture or appearance compared with what it was like before treatment.
Patients with large breasts seem to have greater shrinkage of the breast after radiation therapy than do patients with smaller breasts. However, this problem usually can be overcome with the use of higher x-ray energies or with IMRT. Partial breast radiation using brachytherapy can also be considered if the patient has a small early-stage tumor. This treatment is still undergoing clinical investigation. Certain single institution studies on brachytherapy and intraoperative radiation have shown some promising results. You would need to discuss this with your doctor before or shortly after surgery to determine if you qualify for partial breast radiation.
What Type Of Drug Treatment Might I Get
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include:
- HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab
- Some combination of these
The types of drugs that might work best depend on the tumors hormone receptor status, HER2 status, and other factors.
You May Like: Is Her2 Breast Cancer More Aggressive
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 3 breast cancer?
Stage 3 breast cancer is when tumors are larger than earlier stages or are growing into nearby tissues, and the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are three categories of Stage 3 breast cancer:
- Stage 3A breast cancer In some cases, Stage 3A breast cancer indicates that the cancer spread to four to nine area lymph nodes, and there may or may not be a tumor in the breast. In other cases, it can describe a cancer that has spread less but the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters.
- Stage 3B breast cancer Stage 3B breast cancer can mean that the cancer has spread to the chest wall or to the breasts skin, causing swelling or an ulcer. It may also mean that cancer has spread to up to nine axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breast bone.
- Stage 3C breast cancer Stage 3C breast cancer means the cancer may have spread to the chest wall or breasts skin, or it has spread to 10 or more nearby lymph nodes. It can also mean the cancer has also spread to lymph nodes above or below the collarbone.
What are the options for Stage 3 breast cancer treatment?
What is the Stage 3 breast cancer treatment timeline?
The treatment timeline for Stage 3 breast cancer depends greatly on the severity, extent of spreading, the type of treatment youre undergoing and how youre responding to those treatments. For most Stage 3 cases, treatment can last anywhere from six to 12 months with hormone therapy lasting many years after.
Recommended Reading: How Many People Get Breast Cancer
Radiation Therapy And Mastectomy
Most people who have mastectomy dont need radiation therapy if theres no cancer in the lymph nodes.
In some cases, radiation therapy is used after mastectomy to treat the chest wall, the axillary lymph nodes and/or the lymph nodes around the collarbone.
|
For a summary of research studies on mastectomy versus lumpectomy plus radiation therapy and overall survival in early breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
|
|
For a summary of research studies on radiation therapy following mastectomy for invasive breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
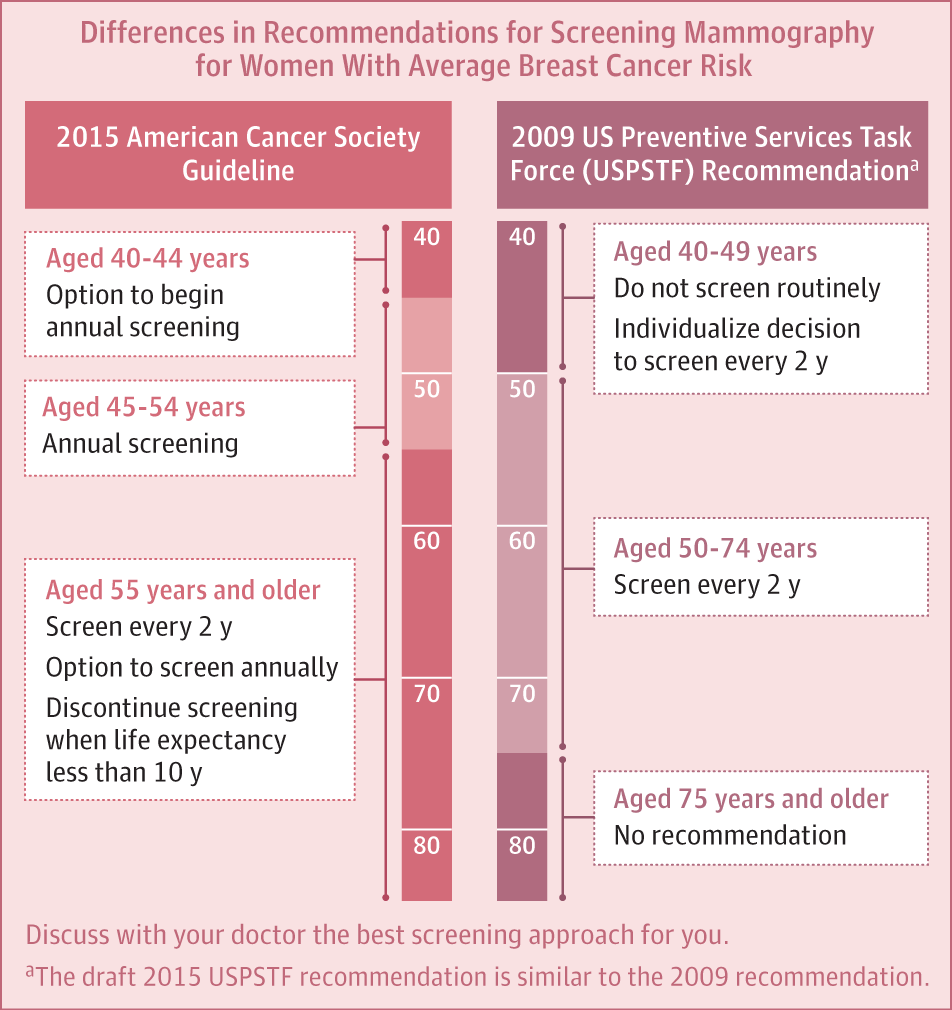
Breast cancer still remains a common malignancy in females, and although there are reports that the incidence is declining in certain countries, prompt diagnosis and treatment are necessary to prevent morbidity and mortality. The management of breast cancer is by an interprofessional team that includes an oncologist, surgeon, radiation oncologist, a pathologist, and an oncologic nurse. With a higher emphasis on breast-conserving surgery followed by radiation, many studies report favorable results. Further, many techniques have been developed to deliver radiation to the breast and studies have shown that the risk of recurrence outside the excised lesion is similar whether the whole or partial breast is treated. The treatment of breast cancer continues to evolve, and there are now studies trying to determine the feasibility of delivering radiation intraoperatively. Because breast cancer is a heterogeneous disorder, the key is proper patient selection to achieve the highest cure rates with the least morbidity.
Recommended Reading: What Fruit Is Good For Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is Lobular Breast Cancer
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy For Luminal Breast Cancer
Neoadjuvant CT is indicated in LABC to reduce the extent of surgery, to treat micrometastases promptly and to monitor the response.
All treatments recommended in the adjuvant setting may also be used in the preoperative setting. If chemotherapy is used, it should be delivered before surgery, without breaks, with the aim to increase the rate of breast-conserving surgery . A sequential regimen of anthracyclines and taxanes is associated with increased probability of pCR and must be recommended . In selected cases of postmenopausal patients with ER+/Her2 disease, neoadjuvant endocrine therapy during at least 16 weeks is a good option. The available data directly comparing neoadjuvant endocrine therapy with neoadjuvant chemotherapy are very limited. Some phase II trials and one meta-analysis showed similar response rates, but a significantly lower toxicity with NET . AIs are better to tamoxifen as NET . The efficacy evaluation of NET has been performed according to surrogate parameters such as the decrease of the Ki67 levels or the preoperative endocrine prognostic index score . Neoadjuvant ET in premenopausal patients is debatable an AI with ovarian suppression or tamoxifen could be considered in selected cases in which chemotherapy is not an option .
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 4 breast cancer?
In Stage 4, the breast cancer has metastasized, which means the disease has spread to distant parts of your body. When breast cancer spreads, it can often invade the lungs, liver and bones, sometimes making its way to the brain or other organs.
What are the options for Stage 4 breast cancer treatment?
- Systemic therapies A combination of systemic therapies are often recommended at specific times during the treatment of Stages 1-3. But in stage four, these therapies are the primary treatment and include:
- Hormone therapy When you have Stage 4 breast cancer, hormone therapy can help slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy This therapy can destroy cancerous cells throughout your body.
- Targeted drug therapies Like chemotherapy, these targeted drugs help reach cancer in distant areas of the body. But depending on your type of cancer, HER2 status and hormone receptor status, different targeted drugs can work alongside chemotherapy or even better than chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy for breast cancer This therapy helps raise your bodys natural immune response to fight of the cancer.
Also Check: How Do You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
How Radiation Is Used With Other Cancer Treatments
For some people, radiation may be the only treatment you need. But, most often, you will have radiation therapy with other cancer treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Radiation therapy may be given before, during, or after these other treatments to improve the chances that treatment will work. The timing of when radiation therapy is given depends on the type of cancer being treated and whether the goal of radiation therapy is to treat the cancer or ease symptoms.
When radiation is combined with surgery, it can be given:
- Before surgery, to shrink the size of the cancer so it can be removed by surgery and be less likely to return.
- During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation. With this technique, doctors can more easily protect nearby normal tissues from radiation.
- After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain.
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer In The Lymph Nodes Curable
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Medically Reviewed on April 15, 2020
What To Know In The Long
Stage 1A breast cancer is a generally favorable and treatable diagnosis, the experts said. But it does still involve long-term care and consideration.
Depending on the type of breast cancer, patients may need to take medication endocrine therapy, also called anti-hormone therapy for five to 10 years. For most stage 1 patients, though, it’s just five years, Mouabbi said.
People who’ve had stage 1 breast cancer also need to stay on top of screening in the future, the experts said.
“The highest risk factor for another breast cancer is a prior history of breast cancer,” Mouabbi said. That’s why it’s so important that, once a cancer patient is in remission, they continue regular breast cancer screening, including mammograms and physical exams.
“The most important thing is catching cancer in this early stage,” Ziedman agreed, adding that some people with a family history or genetic risks for cancer may need to start regular screenings much earlier.
Also Check: What Is Breast Cancer Surgery
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
Some people with breast cancer might be interested in exploring complementary or alternative treatments like vitamins, herbs, acupuncture, and massage.
These treatments are used alongside traditional breast cancer therapies to treat cancer or relieve cancer symptoms and uncomfortable side effects of treatments like chemotherapy. You can explore these treatments at any stage of breast cancer.
Examples of alternative therapy include:
- using massage to relax
- using peppermint tea to reduce nausea
- using cannabis to relieve pain
While some alternative medicine treatments might help you feel more comfortable, its important to keep in mind that many are unproven and could be harmful to your health. To be safe, talk with your doctor about alternative treatments youre interested in pursuing.
Breast cancer that spreads to other parts of the body can cause pain, such as bone pain, muscle pain, headaches, and discomfort around the liver. Talk with your doctor about pain management.
Options for mild to moderate pain include acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as ibuprofen.
For severe pain in a later stage, your doctor may recommend an opioid such as morphine, oxycodone, hydromorphone, or fentanyl. These opioids have the potential for addiction, so they are only recommended in certain cases.
While breast cancer stage has a lot to do with treatment options, other factors can impact your treatment options as well.
You May Like: How Do You Get Tested For The Breast Cancer Gene
Adjuvant Chemotherapy In Hormone Receptor
The use of chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment for ER+Her2-negative disease is recommended for high-risk tumors defined by either clinical or genomic profiling characteristics , considering: T2 to T4 tumors and/or axillary N2-3 involvement extensive LVI, high KI67, low ER expression, younger age or premenopausal status and intermediate to high genomic score. Standard anthracycline and taxane regimens are recommended .
Late Effects Of Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
Radiotherapy to the breast may cause side effects that happen months or years after radiotherapy. They are called late effects.
Newer ways of giving radiotherapy are helping reduce the risk of these late effects happening. If you are worried about late effects, talk to your cancer doctor or specialist nurse.
The most common late effect is a change in how the breast looks and feels.
Radiotherapy can damage small blood vessels in the skin. This can cause red, spidery marks to show.
After radiotherapy, your breast may feel firmer and shrink slightly in size. If your breast is noticeably smaller, you can have surgery to reduce the size of your other breast.
If you had breast reconstruction, using an implant before radiotherapy, you may need to have the implant replaced.
It is rare for radiotherapy to cause heart or lung problems, or problems with the ribs in the treated area. This usually only happens if you had treatment to your left side.
Tell your cancer doctor if you notice any problems with your breathing, or have any pain in the chest area.
Recommended Reading: How Many Stages Of Cancer Are There In Breast Cancer
Treatment For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
for stage 3 breast cancer may include the following, depending on the type of cancer and other factors:
- hormone therapy
- neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery to shrink a tumor
People with stage 3 breast cancer will probably need radiation therapy to kill off any remaining cancer cells. Doctors may also recommend hormone therapy, as well as additional targeted therapies, if necessary.
Internal Beam Radiation Or Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a type of radiation therapy that generates radiation from within the body. In comparison with external beam radiation, which projects particles of radiation from outside the body, brachytherapy can deliver higher doses of radiation in a precise fashion, resulting in fewer side effects and shorter treatment times.
The type of brachytherapy that doctors use depends on the location of the tumor, how much the cancer has spread, and the persons overall health.
Intracavity brachytherapy
The doctor will use a tube or cylinder to deliver a radioactive substance into the body and place it in the tumor.
Interstitial brachytherapy
The doctor will use a needle or catheter to place radioactive material within a cavity either a natural one or one that surgery has created. For breast cancer, they will place it in the breast.
Brachytherapy can also involve either high-dose-rate or low-dose-rate treatments.
High dose rate
This type consists of multiple treatment sessions in which doctors place radioactive material in the body for about 1020 minutes before removing it.
Low dose rate
This type uses substances that release a constant, low dose of radiation over 17 days, during which time a person will likely stay in the hospital. Doctors will remove the radiation source after a designated amount of time.
Also Check: What Age Should You Get Checked For Breast Cancer
You May Like: How Deadly Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Playing An Active Role
You play an active role in making treatment decisions by understanding your breast cancer diagnosis, your treatment options and possible side effects.
Together, you and your health care provider can choose treatments that fit your values and lifestyle.
|
The National Academy of Sciences released the report, Delivering High-Quality Cancer Care: Charting a New Course for a System in Crisis. Susan G. Komen® was one of 13 organizations that sponsored this study. The report identified key ways to improve quality of care:
|
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyBCTeam is the social network for people with breast cancer and their loved ones. On MyBCTeam, members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with breast cancer.
Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with stage 1 breast cancer? Share your experiences in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on MyBCTeam.
Also Check: Breast Cancer In Both Breasts