Mechanisms In The Metastatic Potential Of Breast Cancer Cells
According to the hallmarks of cancer presented by Hanahan and Weinberg, 2000, the capability of a cancer cell to invade and metastasize is an important factor in determining the aggressive features of the disease and is a promising molecular target for drug discovery .
Stages of breast cancer.
Regarding cell to ECM interaction, the key proteins in cancer cell motility and survival are the integrins. Cancer cells attach to the ECM through the function of heterodimeric proteins known as the integrin family of extracellular matrix receptors. Integrins are composed of α and αβ subunits which transduce many signals from the ECM . Previous studies report that in poorly differentiated breast adenocarcinoma cells, expression of integrin α2β1 is reduced . Certain integrins such as integrin α3β1 have been associated with cancer cell invasion, metastasis, and activity of gelatinase β . The MMPs are a family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases which have the ability to degrade ECM component and also mediate proteolysis at the invadopodial front of invasive breast cancer cells .
Recommended Reading: Does Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
How Treatment Can Impact Survival Of Early Stage Breast Cancer
In most cases, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed and treated, the better the chance of survival. Cancer cells often become more difficult to treat and may develop drug resistance once they spread. The aim of treatment for Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer is to remove the breast cancer, and any other cancer cells that remain in the breast, armpit or other parts of the body but cannot be detected. Having treatment at this stage can also reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more:
Er Pr Her2 And Ihc Subtypes
Information on ER, PR and HER2 status was obtained from pathology reports for the whole study period . From 2005 to January 2010, tumours were classified as ER negative if < 10% ER expression, and from February 2010 onwards if < 1% ER expression. PR-negative tumours were defined as < 10% PR expression throughout the study period. HER2 expression was routinely assessed with IHC and verified with in situ hybridization if the IHC results were borderline. We created six IHC subtypes: ER+PR+HER2, ER+PRHER2, ER+PR+HER2+, ER+PRHER2+, ERPRHER2+ and ERPRHER2 . Women with the rarer combinations ERPR+HER2 or ERPR+HER2+ were set to missing in the analysis . In total, n =21,786 women had known IHC subtype, while n =2351 women lacked information on ER, PR or HER2 status .
Table 1 Clinicopathologic characteristics by IHC subtype for women with invasive breast cancer, Norway 20052015 age 2074 years
Read Also: How Can Someone Get Breast Cancer
Getting Support And Information
It can be very difficult to cope with the news that your cancer has come back. At first, you are likely to feel very upset, frightened and confused. Or you may feel that things are out of your control.
It is very important to get the right information about your type of cancer and how it is best treated. People who are well informed about their illness and treatment are more able to make decisions and cope with what happens. Your doctor or breast care nurse can give you information.
It can help to talk to family and friends about how you feel.
You can also contact one of the breast cancer organisations. They have free factsheets and booklets they can send to you. They might also be able to put you in touch with a support group.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
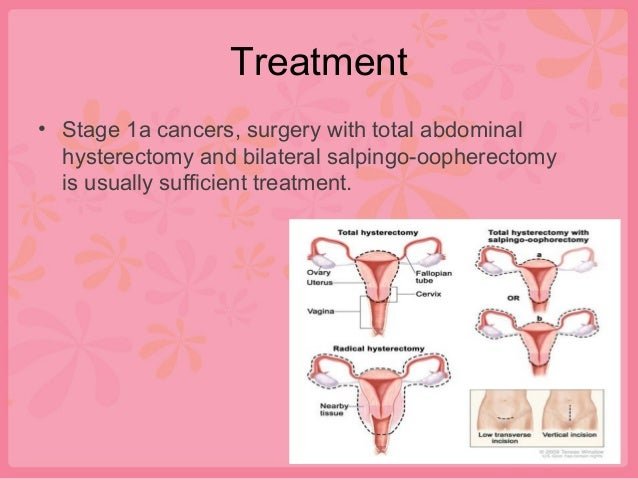
The stage of breast cancer is based on the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether the cancer has spread beyond the part of the breast in which it originated. To determine the stage of breast cancer, healthcare professionals use a scale of stage 0 to stage 4.
Stage 0 breast cancers are isolated in one part of the breast, such as a duct or lobule, and show no sign of spreading into other tissue.
Stage 1 is typically localized, although further local growth or spread may cause the cancer to move into stage 2.
In stage 3, the cancer may be larger and has affected the lymph system. Stage 4 cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes, and into other organs and tissues of the body.
In addition to stages, breast cancers are given grades based on the size, shape, and activity of the cells in the tumor. A higher-grade cancer means a greater percentage of cells look and act abnormal, or they no longer resemble normal, healthy cells.
On a scale of 1 to 3, with 3 being the most serious, TNBC is often labeled grade 3.
American Cancer Society , the symptoms of TNBC can be the same as those for other types of breast cancer. ACS recommends regular screenings such as mammograms to detect breast cancer before symptoms appear, the time when treatment is most effective.
Other signs of breast cancer include:
Any of these signs can be caused by other conditions. But it is always good to have them checked out by your healthcare professional.
Recommended Reading: Is The Lump In My Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 0 Lcis
Lobular carcinoma in situ at Stage 0 generally is not considered cancer. Although it has carcinoma in the name, it really describes a growth of abnormal but non-invasive cells forming in the lobules. Some experts prefer the name lobular neoplasia for this reason because it accurately refers to the abnormal cells without naming them as cancer. LCIS, however, may indicate a woman has an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
If you have been diagnosed with LCIS, your doctor may recommend regular clinical breast exams and mammograms. He or she may also prescribe Tamoxifen, a hormone therapy medication that helps prevent cancer cells from growing.
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Breast Cancer
Treatment For Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Treatment for locally advance breast cancer is likely to include a treatment that affects the whole body .
This might be chemotherapy, hormone therapy or targeted therapy.
Chemotherapy
If you have previously had chemotherapy, you may be offered different chemotherapy drugs this time.
Hormone therapy
If the cancer is oestrogen receptor positive you may be offered hormone therapy.
If you were already taking hormone therapy when your cancer returned, your doctor may consider switching you to a different drug.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapies are a group of drugs that block the growth and spread of cancer.
The most widely used targeted therapies are for HER2 positive breast cancer. However, other targeted therapies are available to treat locally advanced breast cancer that is HER2 negative.
Radiotherapy and surgery
You may be offered radiotherapy if cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes above or below the collarbone, under the breastbone or between the ribs. Its not usually possible to remove the cancer using surgery in this situation.
If the recurrence has affected the muscles on the chest wall, surgery may be offered as well as radiotherapy.
Study Design Setting And Participants
We used the SEER 18 database to conduct a nationwide population-based cohort study. Initially, all patients diagnosed with breast cancer as the primary cancer between 2000 and 2015 were identified . The exclusion criteria were as follows: male aged< 50 years ductal carcinoma in situ American Joint Committee on Cancer cancer staging was not T1-2, N0-1, or M0 diagnosis was made only by autopsy or death certification survival< 1 month incomplete data did not receive RT after BCS and did not receive MAS. Finally, middle-aged, and old women diagnosed with early-stage IDC as the primary cancer between 2000 and 2015 were identified for the analyses. According to the AJCC, the definitions of early-stage IDC are as follows: cancer stage: T1-2, N0-1, or M0 positive lymph nodes3 tumor size< 5 cm. Patients were divided into three treatment groups as follows: BCT , MAS, and MAS+RT.
Figure 1
Flowchart of this study. SEER, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer ER, estrogen receptor PR, progesterone receptor RT, radiotherapy BCS, breast conservative surgery BCT, breast conservative treatment MAS, mastectomy alone.
You May Like: Can You Get Breast Cancer At 27
Overall Breast Cancer Survival Rate For All Stages Of Breast Cancer
The overall 5 year survival rate for women with breast cancer was 89.7%. That is 89.7 out of 100 women were still alive 5 years after diagnosis, regardless of the stage of the cancer. This figure was taken from the SEERS statistics between the years of 2006 and 2012, so could well be even higher now.
How Is Breast Cancer Recurrence Managed Or Treated
Your treatment depends on the type of cancer recurrence, as well as past treatments. If cancer develops in a reconstructed breast, your surgeon may want to remove the breast implant or skin flap.
Treatments for local and regional breast cancer recurrence may include:
- Mastectomy: Your surgeon removes the affected breast and sometimes lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy:Chemotherapy circulates in blood, killing cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy:Tamoxifen and other hormone therapies treat cancers that thrive on estrogen .
- Immunotherapy:Immunotherapy engages your bodys immune system to fight cancer.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy X-ray beams damage and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Treatments target specific cancer cell genes or proteins.
Also Check: What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Systemic Treatments For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Systemic treatments, often termed add-on or adjuvant treatments, treat breast cancer throughout your body and not just at the site of the tumor.
These treatments help destroy cancer cells that have spread beyond your breast but are still too small to be spotted. They include the therapies outlined below.
Chemotherapy
Doctors may recommend chemotherapy, also called chemo, after surgery to help destroy any undetected cancer cells. Chemotherapy may also lower your risk of the cancer coming back at a later stage.
Chemotherapy may be recommended for a smaller tumor if:
- Any cancer cells were found in the lymph nodes.
- You score high on a gene test such as Oncotype DX, which shows whether chemotherapy could help treat your breast cancer and if its likely to come back after surgery.
- The cancer cells are progesterone receptor- and estrogen receptor-negative.
- The breast cancer cells are positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 various therapies can target these receptors.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy can be used to help slow down the growth of cancer cells in people with estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive cancer cells. Hormone therapy works by blocking hormone receptors on the cancer cells or by lowering the amount of estrogen produced in your body.
Its important to ask your doctor about the potential side effects of hormone therapy before you begin this treatment, so can you know what to expect.
Targeted therapy
Stage 1 Or 2 Early Breast Cancer
Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer refers to invasive breast cancer that is contained within the breast, and may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. These stages are also known as early stage breast cancer.
At Stage 1 and 2, some cancer cells may have spread outside the breast and armpit area, but at this stage these cannot be detected.
You May Like: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Come Back
Box 1 How Rapid Autopsy Studies Can Inform On Metastatic Dissemination And Relapse
Definitions
-
Rapid autopsy: rapid post-mortem collection, examination and biobanking of tissuesfresh, snap-frozen and fixedfrom deceased patients shortly after death.
-
Rapid autopsy cancer programme: coordinated effort among oncologists, pathologists and scientists aimed at collecting specimens from cancer patients within a post-mortem interval of 68h before key biological information within the tissues of interest is lost.
Advantages
-
Multiregional biopsies: to conduct extensive, spatial sampling of tissuesprimary and metastatic, cancerous and normalfor in-depth, high-resolution multi-omics analysis.
-
Physiological model: to analyse DTCs in their natural metastatic niche.
-
to generate novel, ex vivo living patient-derived modelsautopsy-derived xenografts and organoids of metastatic tumours from sites that would otherwise be difficult to sample for functional evaluation .
-
Cancer evolution: to study the phylogenetic relationship of each sampled site to each other and infer the complete clonal evolution of a neoplasm.
-
Dormancy: to examine why some DTCs lodged in certain organs of the human body become dormant for years to decades.
-
Drug resistance: to study why DTC spread across different sites responds differently to therapy, with some developing resistance and others remaining sensitive to treatment.
-
Recurrence: to understand why only some DTCs residing in certain sites of the human body give rise to active metastases, ultimately responsible for patients relapse.
Regional Recurrence Within Three Years Carries A Less Favorable Prognosis But Overall Survival Statistics Are Still Good
Generally speaking, if the breast cancer returns regionally lymph nodes) within the first five years following original treatment, the overall likelihood of survival is thought to be somewhat poorer.
Five-year overall survival after an isolated chest wall recurrence is 68% and after intra-breast recurrence it is 81%.
In one 2010 medical research study, the ten year overall survival rate was estimated at 84% for women without recurrence. However, this figure goes down to 49% for women with a locoregional recurrence and 72% for women with a second primary tumour.
A large 2015 study examined the impact of the time of the disease free interval on survival rates. For women with a locoregional recurrence that happened in the first 18 months, the ten year overall survival rate is around 30%. The overall 10 year survival rate for those whose recurrence happened within 3 years goes up to 50%. Furthermore, for those who suffered a recurrence after 3 years the ten year overall survival rate increases to 70%.
This recent study clearly demonstrates that the longer the time span since the primary prognosis and treatment to the recurrence, the better the long-term prognosis.
| 33 | 30 |
The rate of distance breast cancer metastasis and overall survival is most favorable for women in which the recurrence occurred locally and after five years.
However, women with a same-breast recurrence within five years have a distant metastasis rate of about 61%, which are slightly poorer odds.
You May Like: What Type Of Chemo Is Used For Breast Cancer
Understanding Breast Cancer Metastasis
Metastasis is a complex process in which malignantcancer cells from the breast spread into other regions of the body. Once metastasis has occurred, it is much more difficult to effectively treat breast cancer.
If breast cancer has metastasized to other areas of the body, it is termed a Stage IV breast cancer. Sometimes metastasis has occurred at the time the original breast cancer is diagnosed.
However, in other cases, the metastasis of breast cancer is found months or even years after the initial treatment. This would be termed a recurrent breast cancer.
What Causes Breast Cancer Recurrence
The goal of cancer treatments is to kill cancer cells. But, cancer cells are tricky. Treatments can reduce tumors so much that tests dont detect their presence. These weakened cells can remain in the body after treatment. Over time, the cells get stronger. They start to grow and multiply again.
Even surgery to remove a cancerous tumor isnt always 100% effective. Cancer cells can move into nearby tissue, lymph nodes or the bloodstream before surgery takes place.
You May Like: Can Triple Negative Breast Cancer Come Back
What Factors Contribute To The Risk Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
Whilst it is never completely certain that breast cancer has been cured, there are many treatments available that reduce the risk of recurrence. There are a number of risk factors that can contribute to a breast cancer recurrence.
Your age at first diagnosis Younger women, particularly those who had their first diagnosis under the age of 35, have a greater risk of recurrence. This is because those diagnosed at a young age are more likely to have aggressive features in their breast cancer. Additionally women diagnosed with breast cancer before menopause have a greater risk of recurrence.
Tumour size Women who have a larger breast tumour have a greater risk of recurrence.
Lifestyle factors Lifestyle factors can influence the risk of recurrence. Excess weight is associated with a higher risk of postmenopausal breast cancer and is also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer recurrence and death. Smoking has also been shown to increase the risk of recurrence. Women who exercise regularly appear to have a lower rate of breast cancer recurrence.
Lymph node involvement If cancer is found in lymph nodes at the time of the original breast cancer diagnosis, there is an increased risk of breast cancer recurrence. This is the strongest prognostic factor, and the more nodes involved, the higher the risk of recurrence.
Dcis Can Happen At Any Age
âDCIS can happen to anybody, anytime,â says Dr. Meyers, but itâs usually diagnosed in women over 40, the age at which many women begin getting mammograms. According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS rates increase with age, and peak around age 70 to 79.
Women diagnosed with DCIS under age 50 have a higher rate of recurrence or of an invasive cancer, and therefore more aggressive treatment is usually recommended, says Dr. White. Those over 50, on the other hand, can take comfort in knowing that a diagnosis does not raise their risk of early death.
Read Also: What Does Breast Cancer Cause
Also Check: What Is Oligometastatic Breast Cancer