The Role Of Ki67 In Evaluating Neoadjuvant Endocrine Therapy Of Hormone Receptor
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 2Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital and College of Basic Medical Sciences of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Ki67 is a proliferation marker. It has been proposed as a useful clinical marker for breast cancer subtype classification, prognosis, and prediction of therapeutic response. But the questionable analytical validity of Ki67 prevents its widespread adoption of these measures for treatment decisions in breast cancer. Currently, Ki67 has been tested as a predictive marker for chemotherapy using clinical and pathological response as endpoints in neoadjuvant endocrine therapy. Ki67 can be used as a predictor to evaluate the recurrence-free survival rate of patients, or its change can be used to predict the preoperative window of opportunity in neoadjuvant endocrine therapy. In this review, we will elaborate on the role of Ki67 in neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer.
S Of A Pathology Report
Different pathologists may use different words to describe the same findings. Pathology reports from different labs may be organized differently. But most pathology reports include these sections:
This part of a pathology report includes your name, birth date, and the date you had surgery or a blood draw. Make sure all this information is correct. This section also may include a number assigned to you to help keep your identity safe.
This section includes the pathologists and clinicians contact information, as well as the lab where the testing was done.
This part of a pathology report includes details about the tissue sample, which doctors call a specimen. This section includes the date the specimen was removed, the type of biopsy or surgery that was done, and the type of tissue it is. In many cases, tissue will be taken from the breast and/or the lymph nodes. If its suspected that the cancer has spread to parts of the body away from the breast, tissue may come from other areas, such as the liver or bones.
This section includes information about how the cancer was found and may include other information about your medical history.
This part of a pathology report describes what the pathologist can see with their naked eyes before they look at the removed tissue with a microscope. This usually includes:
The final diagnosis usually describes the type of cancer and will likely include information about:
-
anatomic location
Types of invasive carcinoma:
Ki67 In Neoadjuvant Endocrine Therapy
Table 1 Main neoadjuvant endocrine trials.
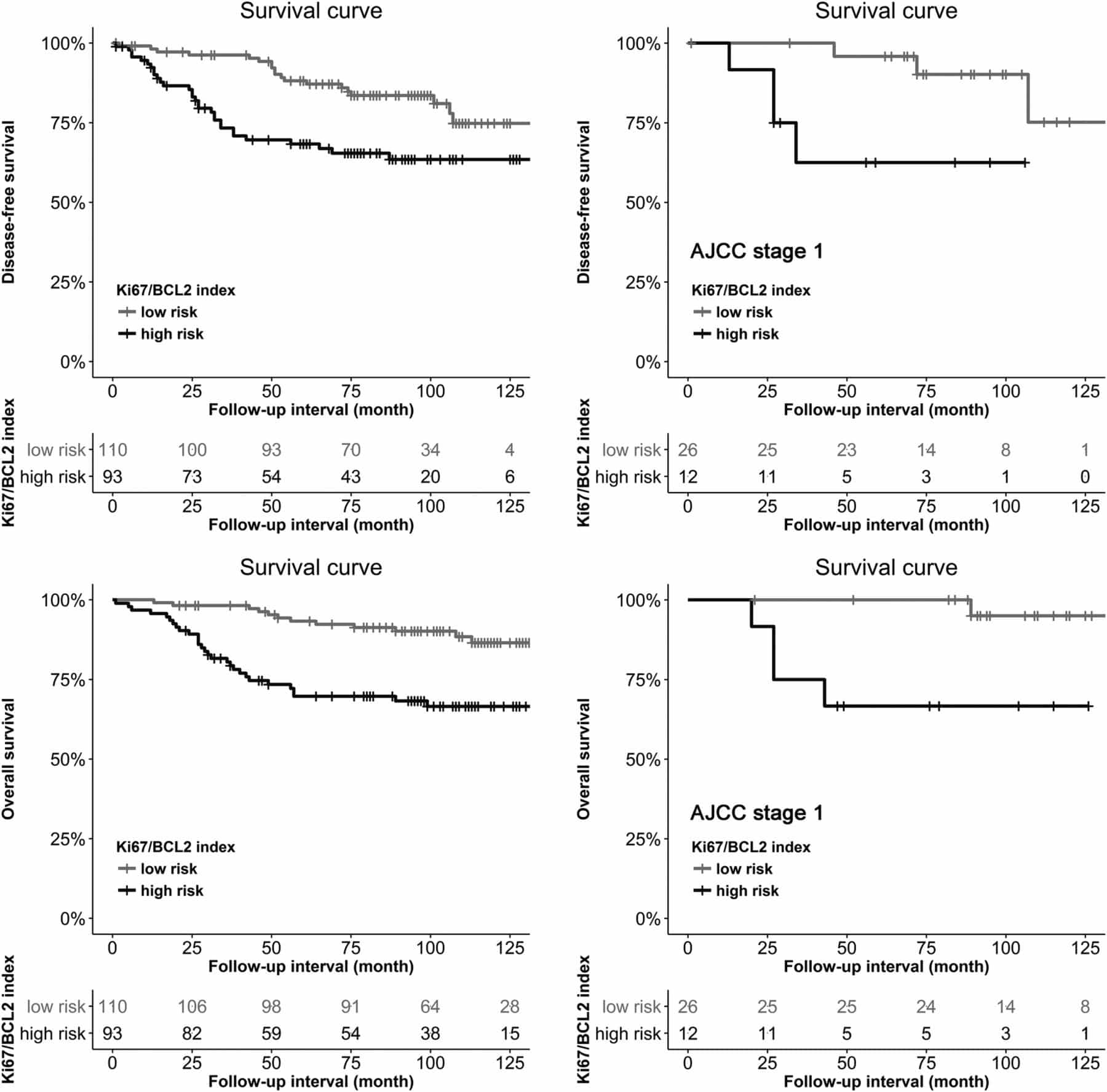
P024 was a randomized, multinational, double-blind study comparing 4 months of letrozole vs. tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with hormone-responsive primary untreated breast cancer . P024 indicated that the percentage of Ki67-positive cells, pathological tumor size, lymph node status, and ER status were independently associated with breast cancer-specific survival and relapse-free survival. Based on these factors, Ellis et al. obtained a clinically valuable prognostic model of preoperative endocrine prognostic index score for the outcome prediction of hormone-positive breast cancer with NET. The Ki67 and PEPI triage approaches can predict the risk of relapse. NET was initially an option for breast cancer patients who were too frail to have surgery or cytotoxic chemotherapy. It is very difficult to evaluate the efficacy of adjuvant endocrine therapy because of its long-term follow-up, and NET offers useful clues. The initial endocrine neoadjuvant therapy clinical trial collected data to evaluate the long-term outcome of adjuvant endocrine therapy indirectly rather than as a neoadjuvant treatment . Future adjuvant endocrine therapy clinical research designs should be based on a biological superiority hypothesis generated by a neoadjuvant endocrine study .
Read Also: Clinical Trial For Breast Cancer
What Is A Normal Ki
The Ki-67 percentage score is defined as the percentage of positively stained tumor cells among the total number of malignant cells assessed . Withal only the positivity is of interest independent of the intensity of coloration. To ensure quality assurance of the staining, positive control tissues are completed.
What If A Carcinoma Is Infiltrating Or Invasive
These words are used to mean that the cancer is not a pre-cancer , but is a true cancer.
The normal breast is made of tiny tubes that end in a group of sacs . Cancer starts in the cells lining the ducts or lobules, when a normal cell becomes a carcinoma cell. As long as the carcinoma cells are still confined to the breast ducts or lobules, without breaking out and growing into surrounding tissue, it is considered in-situ carcinoma .
Once the carcinoma cells have grown and broken out of the ducts or lobules, it is called invasive or infiltrating carcinoma. In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body.
Don’t Miss: What Should Breast Cancer Patients Eat
What Is The Significance Of The Reported Size Of The Tumor
If the entire tumor or area of cancer is removed, the pathologist will say how big the area of cancer is by measuring how long it is across , either by looking at it under the microscope, or by gross examination of the tissue removed during surgery. The size of the tumor in the breast is part of what determines the stage of the cancer, which influences treatment and prognosis.
A needle biopsy only samples a part of the tumor, so measurements of the size of the cancer are often not given. Later, when the tumor is removed , a more accurate measurement is obtained.
Luminal A Vs Luminal B
There are many types of breast cancer. Oncologists recommend treatment based on several different characteristics of the cancer cells. Often, doctors will look at the genes of the cancer cells to better identify and treat the disease. There are several different groupings of cancer types. According to the Mayo Clinic, these are called luminal groups.
Among breast cancers that are hormone-positive, there are two distinct subtypes that have different prognoses and may respond differently to treatment regimens.
Ki-67 has been used as part of the data to separate tumors into these two categories. There are many other tests being studied to help with this classification system. One type, MCM2 appears to be a promising alternative. The two categories are:
- Luminal A tumors : are estrogen receptor-positive , progesterone receptor-positive , HER2-negative and have a Ki-67 index less than 14%.
- Luminal B tumors: Luminal B tumors are estrogen receptor and/or progesterone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, and have a Ki-67 index greater than 14%. Or, they are estrogen receptor and/or progesterone receptor-positive, HER2-positive, and have any Ki-67 index.
Your healthcare team will consider your pathology report, the genetic traits of your cancer, and your overall health, to work with you to make a treatment plan for your breast cancer. Scientists are studying the genetic makeup of cancer hoping better understanding will lead to more effective treatments.
You May Like: Women’s Risk Of Breast Cancer
What Does It Mean If My Doctor Asks For A Special Molecular Test To Be Performed On My Specimen
Molecular tests such as Oncotype DX® and MammaPrint® may help predict the prognosis of certain breast cancers, but not all cases need these tests. If one of these tests is done, the results should be discussed with your treating doctor. The results will not affect your diagnosis, but they might affect your treatment.
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Has Tubular Mucinous Cribriform Or Micropapillary Features
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are “special types” of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, different treatment might be recommended.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Odds Of Surviving Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Analytical Considerations: Visual Interpretation Of Ki67 Index
The major focus of the IKWG has been interpretation of already processed and stained tissue. For immunohistochemical assays , analytical validity requires both robust assay performance with universal standards and reporting . During the first IKWG workshop in 2011, it was clear that there were several different methods of scoring IHC-stained slides to determine Ki67 values . Therefore, the IKWG undertook a series of carefully planned, incremental, multi-institutional studies, and the results are summarized below :
The series of International Ki67 Working Group studies to standardize methods for visual scoring of Ki67 index in breast cancer. Intraclass correlation coefficient through the 3 study phases are shown with error bars representing the lower and upper 95% credible intervals. The numeric values of the various ICCs are shown at the x-axis labels with the 95% credible intervals in parentheses. The horizontal bar lines represent observed ICCs. The extent of the vertical lines indicates 95% credible interval. The dotted grey color line indicates ICC = 0.8. TMA = tissue microarray.
Studies should include a sufficiently large number of participating scorers to represent variability inherent in a broad cross-section of pathology interpretations
Observers doing the scoring in test validation studies need to follow prespecified training methods and score independently and in a fashion blinded to others scores
What Is The Standard Treatment For Breast Cancer
Types of brachytherapy
- Intracavitary brachytherapy. This is the most common type of brachytherapy for women with breast cancer.
- Interstitial brachytherapy. In this approach, several small, hollow tubes called catheters are inserted into the breast around the area where the cancer was removed and are left in place for
- Possible side effects of intracavitary brachytherapy
Also Check: Breast Cancer Swollen Lymph Nodes
How Is The Stage Determined
The staging system most often used for breast cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The most recent AJCC system, effective January 2018, has both clinical and pathologic staging systems for breast cancer:
- The pathologic stage is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation.
- Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away or at all, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. The clinical stage is used to help plan treatment. Sometimes, though, the cancer has spread further than the clinical stage estimates, and may not predict the patients outlook as accurately as a pathologic stage.
In both staging systems, 7 key pieces of information are used:
- The extent of the tumor : How large is the cancer? Has it grown into nearby areas?
- The spread to nearby lymph nodes : Has the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes? If so, how many?
- The spread to distant sites : Has the cancer spread to distant organs such as the lungs or liver?
- Estrogen Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called an estrogen receptor?
- Progesterone Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called a progesterone receptor?
- HER2 status: Does the cancer make too much of a protein called HER2?
- Grade of the cancer : How much do the cancer cells look like normal cells?
In addition, Oncotype Dx® Recurrence Score results may also be considered in the stage in certain situations.
What If My Report Mentions Sentinel Lymph Node
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy, the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which a tumor drains. This lymph node, known as the sentinel node, is the one most likely to contain cancer cells if they have started to spread. This procedure may be done during surgery to remove a breast cancer. It is a way to check for the spread of cancer to underarm lymph nodes without removing as many of them.
The sentinel lymph node is then checked to see if it contains cancer cells. If there is no cancer in the sentinel node, it’s very unlikely that the cancer has spread to other lymph nodes, so no further lymph node surgery is needed.
If a sentinel lymph node does contain cancer, your report will say that cancer was present in the lymph node. It may also say how large the deposit of cancer cells is. In some cases, if cancer is found in a sentinel lymph node, you may then also need additional treatment such as surgery to remove more underarm lymph nodes or radiation therapy to the underarm region. You should discuss this with your doctor.
Recommended Reading: How To Check For Breast Cancer With Implants
Ki 67 Biomarker And Breast Cancer
We are living in a new era-it’s the era of “precision cancer medicine.” There are no longer one size fits all treatment strategies for a growing number of cancer patients. Treatment is tailored to the individual and this “personalized” care is based on the identification of unique biomarkers on the cancer and the identification of individual cancer causing mutations identified with “next generation sequencing” or NGS testing of the actual cancer cell DNA.1-9
Why Is Ki67 Not Used In Clinical Management
Although immunohistochemical detection of the Ki67 antigen has been used for many years to assess cancer proliferation , this marker is still not recommended for routine use in clinical management of breast cancer. The major reason for this situation is a lack of a standardised procedure for Ki67 assessment as well as persistence of several issues of debate with regards to the Ki67 assay interpretation and the markers clinical utility. Nowadays Ki67 assessment is principally used for estimation of prognosis and guiding the decision on adjuvant treatment choice, as well as for prediction of response to neoadjuvant treatment in ER+/HER2- breast cancer. In ER-/HER2+ and ER-/HER2- tumours, high post-neoadjuvant Ki67 index is associated with unfavourable prognosis. We review here the elements impacting analytical validity of the Ki67 immunohistochemical assay, the evidence of its clinical utility and the current recommendations for its use in breast cancer management.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Metastatic Breast Cancer
Stage 1 Breast Cancer With High Ki
Image selection
Two radiologists , who were blinded to the patients pathologic information, retrospectively reviewed the MRI images electronically on the picture archiving and communication system . In the case of disagreements, the two radiologists would reach a final decision by discussion and consensus. The final MRI images selected were exported from the PACS workstation in BMP format for histogram analysis. During export, the window width and window level were adjusted thus, all images had consistent window width and window level, and they were saved on the hard disk.
Histogram analysis
Figure 2Figure 3
Will There Be A Resurgence Of Ki
Don VaughanCURE
An FDA approval put Ki-67 scoring which may predict tumor growth in the spotlight, but what that means long term to patients depends on who you ask.
The speed at which cancer cells grow can be an important factor in determining cancer treatment. Among the best-known biomarkers for the rate of cancer growth is a protein known as Ki-67, which is expressed when tumor cells divide.
A high Ki-67 index indicates aggressive tumor growth.
For example, Kate Laseter of Thornton, Colorado, was diagnosed with stage 2 invasive ductal carcinoma in September 2021 and informed that her Ki-67 score was 65%. Of note, the median Ki-67 score is 15%.
As a histological technician with Theralink Technologies, Laseter immediately knew what that meant.
It was very aggressive and growing rapidly and had invaded everything, she recalls. I looked at my … and I had less than 10% normal tissue in my biopsy.
Because Laseter was just 29 when she noticed a lump in her breast, she was told that it was probably just a fibrous mass and to wait and see. She refused and demanded a biopsy.
Based on her high Ki-67 score, she was placed on treatment immediately and received a chemotherapy regimen that included carboplatin and docetaxel in combination with the targeted therapies Herceptin and Perjeta . She also underwent a bilateral mastectomy.
In March 2022, she was declared in remission and cancer-free.
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer Curable
Clinical Characteristics In Breast Cancer
Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. One hundred and twenty-three FFPE tissue samples were used in this study. Cases were randomly collected according to Korean breast cancer prevalence according to age distribution, followed as 12 cases in 30 s, 38 cases in 40 s, 42 cases in 50 s, 19 cases in 60 s, and 12 cases over 70 s. ER IHC positive cases were 82 . PR IHC positive cases were 70 . HER2 IHC positive cases were 79 .
Read Also: How Do I Get Checked For Breast Cancer
How Do Doctors Use Ki67
Clinicians have made wide use of Ki-67 staining with immunohistochemistry as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer for years.1 The International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group is a panel of breast cancer experts that has confirmed the evidence for Ki-67s clinical value as a prognostic biomarker and clinical studies support Ki-67 measurement to help guide treatment decisions.2-5
Recommended Reading: How To Self Test For Breast Cancer
What If My Report Mentions Micrometastases In A Lymph Node
This means that there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are bigger than isolated tumor cells but smaller than regular cancer deposits. If micrometastases are present, the N category is described as pN1mi. This can affect the stage of your cancer, so it might change what treatments you may need. Talk to your doctor about what this finding may mean to you.