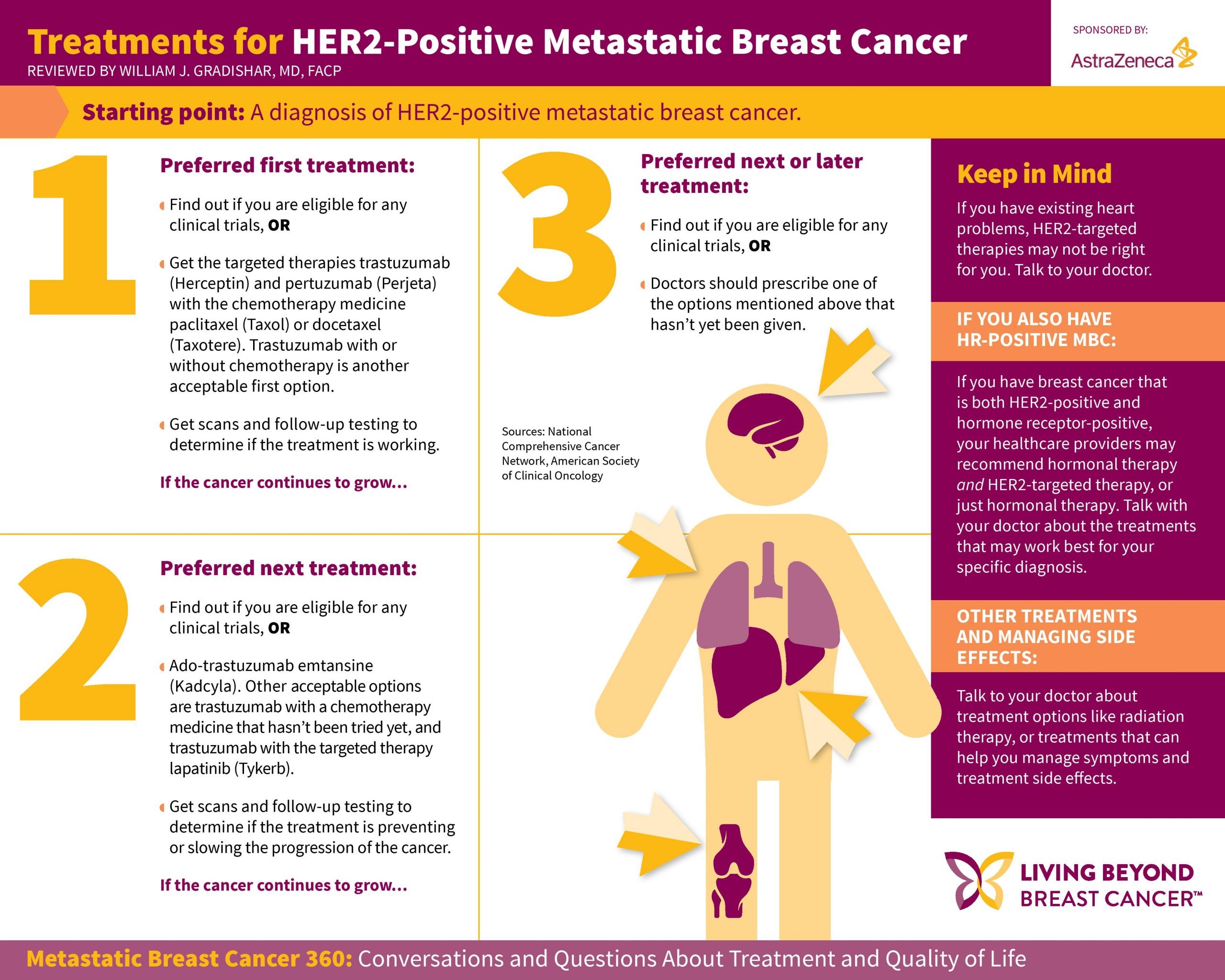
When Is Radiation Usually Used To Treat Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, radiation therapy may be used after lumpectomy to mitigate the risk of cancer cells recurring in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, an oncologist may determine that radiation is necessary if the tumor was larger than 5 cm, if there was lymph node involvement, or if cancer was found outside of surgical margins.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
Your breast cancer stage indicates the severity of the disease upon diagnosis. Your breast cancer stage indicates the severity of the disease upon diagnosis. Your cancer stage will always stay the same, even if the cancer shrinks or spreads during or after treatment. For instance, if youre diagnosed with stage 1 breast cancer, but the tumor later grows and spreads, its not considered stage 3 or 4 breast cancer. To determine whether the cancer has responded to treatment, a new stage may later be assigned an r in front of it to show that its different from the original stage.
Breast cancer staging is classified by:
- The size and location of the tumor
- Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body
- The grade of the tumoror how likely it is to grow and spread
- Whether certain biomarkershormone receptors or other proteinshave been found
All these attributes help your care team determine how to treat your cancer.
To assess the location, size and spread of cancer, your care team will use the TNM Staging System, developed and updated for breast cancer by the American Joint Committee on Cancer .
- TNM stands for Tumor-Node-Metastasis, which are important factors in determining the severity of your cancer.
- All cancers may be evaluated by TNM markers, but breast cancer staging also uses a few extra criteria for a more detailed description.
- Ultimately, your specific combination of TNM and these other markers will determine your cancers stage.
Stage 2b Breast Cancer
With stage 2B breast cancers, the tumor is larger or cancer cells have spread further into the lymph nodes than with stage 2A.
Stage 2B breast cancer meets one of these criteria:
- The breast tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm, and cancer cells have also been found in the armpit lymph nodes.
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm, but it hasnt spread to the lymph nodes.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Check For Breast Cancer
What Is A Hormone Receptor
Hormones are chemical messengers that circulate in the bloodstream. Hormone receptors are proteins located in and around breast cells. When the corresponding hormone binds to a receptor, it tells the cells how to grow and divide.
In the case of breast cancer, these receptors allow abnormal cells to grow out of control, which results in a tumor.
Tumour Reviewtriple Positive Breast Cancer: A Distinct Subtype
HER-2, ER and PgR have a key role in treatment decision making in breast cancer.
-
Triple positive tumours exhibit a unique clinical and biological behavior.
-
TP breast cancer behavior might be also driven by HR status.
-
TP tumors with low disease burden and high HR expression resemble luminal tumours.
-
The identification and characterization of this subset may avoid overtreatment.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Treatment Of Breast Cancer Stages I
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment.
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of systemic drug therapy . In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But your treatment options are affected by your personal preferences and other information about your breast cancer, such as:
- If the cancer cells have hormone receptors. That is, if the cancer is estrogen receptor -positive or progesterone receptor -positive.
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- How fast the cancer is growing
- Your overall health
- If you have gone through menopause or not
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Asco/cap Guidelines For Her2 Testing
In 2013, the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the College of American Pathologists produced and published their updated guidelines on HER2 testing. These guidelines replace the last update from 2007 .
The 2013 ASCO/CAP guidelines are now being implemented to improve the testing for overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in patients with invasive breast cancer.
ASCO and CAP undertook a systematic review of the literature as the basis for their recommendations. The results of this review have implications for diagnostic testing of breast cancer and also for the provision of HER2-directed targeted therapy in certain patients
Also Check: What’s The Youngest You Can Get Breast Cancer
Side Effects Associated With Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy
Although the majority of women will have no or mild symptoms, endocrine therapy can be associated with specific and often bothersome side effects . Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches can help ameliorate these symptoms. As studies have demonstrated an association between side effects and early treatment discontinuation , it is important to educate patients about possible toxicities and encourage them to contact their health care team to discuss possible interventions. Menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and sweats are seen in 40-60% of patients treated with tamoxifen or AIs, and may be more significant with tamoxifen . Vaginal dryness, vaginal discharge and sexual dysfunction are seen with both tamoxifen and AIs . Weight gain, mood disturbances and fatigue are also commonly observed with both tamoxifen and AIs . AI use is associated with an increased risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis, AI-associated musculoskeletal syndrome , a constellation of symptoms that includes arthralgias, myalgias and stiffness, and is also associated with a potential risk of cardiovascular disease . Tamoxifen increases the risk of thromboembolic disease and endometrial cancer, although the incidence of both toxicities remain low, especially in pre-menopausal women .
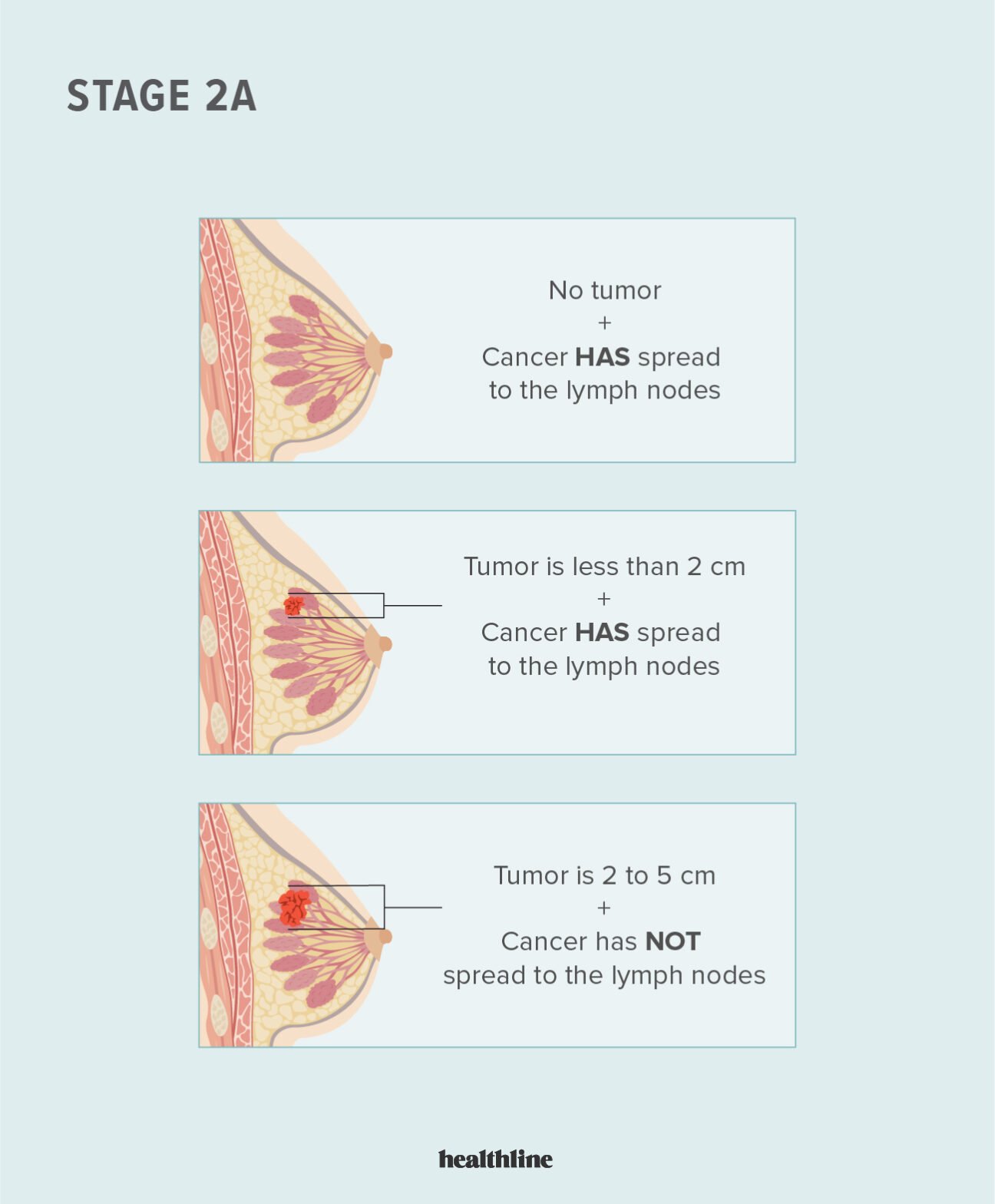
How Big Is My Tumor
Tumor size is another factor that will determine your course of treatment. Your doctor uses the size of your tumor to stage, or further categorize your cancer .
The tumors dimensions are estimated by a physical exam, a mammogram, an ultrasound or an MRI of the breast. The precise size wont be known until a pathologist studies the tumor after surgical removal.
You May Like: Can You Survive Stage 4 Metastatic Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Hormone Receptor Status
Breast cancer cells taken out during a biopsy or surgery will be tested to see if they have certain proteins that are estrogen or progesterone receptors. When the hormones estrogen and progesterone attach to these receptors, they stimulate the cancer to grow. Cancers are called hormone receptor-positive or hormone receptor-negative based on whether or not they have these receptors . Knowing the hormone receptor status is important in deciding treatment options. Ask your doctor about your hormone receptor status and what it means for you.
B Ovarian Function Suppression With Tamoxifen Or An Aromatase Inhibitor
OFS by surgical or pharmacological means should be considered in high-risk pre-menopausal patients. Surgical OFS via bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is irreversible and may be a suitable option for women with increased risk of ovarian cancer, and in those who desire permanent OFS. Pharmacological methods are generally reversible and use gonadtropin-releasing hormone agonists such as goserelin and leuprolide to suppress luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone and subsequently reducing estrogen production from the ovaries . While initial studies of OFS versus no adjuvant therapy and OFS versus adjuvant chemotherapy failed to demonstrate a reduction in recurrence or death overall , data have suggested that OFS benefits may be observed in younger, pre-menopausal women .
Recommended Reading: How Effective Is Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer
Factors To Consider When Discussing Adjuvant Systemic Therapy
Clinical decision-making is a complex process that incorporates patient and tumor characteristics, the expected benefit of systemic therapy, individualized prognostic information and patient preference. Several large groups have provided guidance for the use of adjuvant systemic therapy in early stage HR-positive breast cancer. Cancer Care Ontario and ASCO guidelines recommend consideration of patient demographics such as age, menopausal status and co-morbidities when making adjuvant systemic therapy decisions. In addition, characteristics including tumor size, lymph node status, presence or absence of lymphovascular invasion, histological subtype and genomic testing prognostic information should be considered. Finally, patient preference is a critical consideration in the shared adjuvant systemic therapy decision-making process .
Treatment To The Breast
Your surgeon might remove the cancerous area with a border of normal breast tissue. This is called breast conserving surgery or a wide local excision. After this you usually have radiotherapy to the rest of the breast.
Or you might have the whole breast removed. This is called a mastectomy. You can choose to have a new breast made . You might have radiotherapy to the chest wall after having a mastectomy. You might have treatment with radiotherapy to the lymph nodes under your arm or further surgery to remove the nodes if they contain cancer cells.
You can have a breast reconstruction at the same time as surgery to remove the cancer, or at a later time. Having a reconstruction at the same time should not affect you having radiotherapy after surgery if you need it. The plan to have radiotherapy after a reconstruction might affect the reconstruction options you have.
Your surgeon will discuss all the pros and cons with you.
You usually have other treatments too.
You May Like: What Are Some Causes Of Breast Cancer
What Are The Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy
The side effects of hormone therapy depend largely on the specific drug or the type of treatment . The benefits and harms of taking hormone therapy should be carefully weighed for each person. A common switching strategy used for adjuvant therapy, in which patients take tamoxifen for 2 or 3 years, followed by an aromatase inhibitor for 2 or 3 years, may yield the best balance of benefits and harms of these two types of hormone therapy .
Hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness are common side effects of all hormone therapies. Hormone therapy also may disrupt the menstrual cycle in premenopausal women.
Less common but serious side effects of hormone therapy drugs are listed below.
Tamoxifen
- breathing problems, including painful breathing, shortness of breath, and cough
- loss of appetite
Regional Recurrence Within Three Years Carries A Less Favorable Prognosis But Overall Survival Statistics Are Still Good
Generally speaking, if the breast cancer returns regionally lymph nodes) within the first five years following original treatment, the overall likelihood of survival is thought to be somewhat poorer.
Five-year overall survival after an isolated chest wall recurrence is 68% and after intra-breast recurrence it is 81%.
In one 2010 medical research study, the ten year overall survival rate was estimated at 84% for women without recurrence. However, this figure goes down to 49% for women with a locoregional recurrence and 72% for women with a second primary tumour.
A large 2015 study examined the impact of the time of the disease free interval on survival rates. For women with a locoregional recurrence that happened in the first 18 months, the ten year overall survival rate is around 30%. The overall 10 year survival rate for those whose recurrence happened within 3 years goes up to 50%. Furthermore, for those who suffered a recurrence after 3 years the ten year overall survival rate increases to 70%.
This recent study clearly demonstrates that the longer the time span since the primary prognosis and treatment to the recurrence, the better the long-term prognosis.
| 33 | 30 |
The rate of distance breast cancer metastasis and overall survival is most favorable for women in which the recurrence occurred locally and after five years.
However, women with a same-breast recurrence within five years have a distant metastasis rate of about 61%, which are slightly poorer odds.
Read Also: What Medication Is Taken After Breast Cancer
What Is Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
Evidence Supporting A Limited Role Of Adjuvant Chemotherapy In Hormone
The International Breast Cancer Study Group trial IX randomized 1715 postmenopausal women with lymph node-negative early breast cancer to tamoxifen for 5 years with or without chemotherapy, which consisted of three cycles of classical CMF . Randomization in that study was stratified by ER status, resulting in 23% of patients with ER-negative disease. The overall results of the trial confirmed that three courses of CMF improved disease-free survival significantly. However, analyzing the two subsets based on the status of ER , three cycles of CMF added to tamoxifen had a significant impact on both disease-free and overall survival only in ER-negative patients, with virtually no effect in the ER-positive subset .
| q3 weeks versus q2 weeks doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide and paclitaxel | 7% for q2 weeks versus q3 weeks | 9.1% for q2 weeks versus q3 weeksa | 2.8% for q2 weeks versus q3 weeksa |
HR, hormone receptor DFS, disease-free survival HD, high dose ID, intermediate dose LD, low dose.
aTest of interaction of HR status and efficacy of the experimental regimen were statistically significant.
You May Like: How Do I Self Check For Breast Cancer
What Is My Estrogen Receptor And Progesterone Receptor Status
Your bodys hormones such as estrogen and progesterone may play a role in how your breast cancer progresses.
Normal cells are equipped with receptors that allow them to receive information from circulating hormones, similar to the way your phone picks up satellite signals. Cancer cells may also have hormone receptors, letting them tap into your bodys normal cell growth-regulating system.
Your ER/PR status is determined by testing a sample of breast cancer cells removed during a biopsy. If your breast cancer cells have estrogen and progesterone receptors if theyre ER/PR-positive then theyre capable of detecting estrogens signal and using it to fuel growth. If the cancer cells lack these receptors meaning theyre ER-/PR-negative they cant hear the growth-signaling message.
About 70% of breast cancer patients have positive ER/PR hormone status.
While being ER/PR-positive sounds bad, theres actually a benefit. Doctors can take advantage of the receptors presence. They can use an anti-estrogen drug that blocks the receptors and blocks estrogens growth signal. Or they can use other drugs like aromatase inhibitors that lower your bodys estrogen levels to deprive the cancer cells of fuel.
Choice Of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy In Post
Suggested Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy Approach for Women who are Post-Menopausal at Diagnosis
AI: Aromatase Inhibitor ET: Endocrine Therapy
*High risk disease defined as tumors with lymph node involvement or aggressive histological features. In lymph node negative disease, high risk defined as large tumor size or poor prognosis identified by genomic assays
^ Extended tamoxifen may be appropriate in post-menopausal patients if toxicities or contraindications to AI
Several adjuvant endocrine therapy options are available for post-menopausal women including AI for 5 years, tamoxifen for 5 years , tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by AI to complete 5 years, tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by 5 years of AI, tamoxifen for 5 years followed by AI for 5 years. While patient factors and patient preferences should be considered, most guidelines recommend the use of an AI, either for 5 years, or for 2-3 years after prior tamoxifen use if possible . Extended AI therapy may be considered for select women and is discussed below.
Recommended Reading: How Soon After Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer Is Surgery
The 2013 Asco/cap Her2 Testing Guidelines
- Always test HER2 status on newly diagnosed, invasive breast cancers .
- Ensure that at least one tumor sample is tested for either HER2 protein expression or for HER2 gene amplification.
- Discuss the role of HER2-targeted therapy if the HER2 test result is positive and if there is no apparent histopathologic discordance with HER2 testing.Delay the decision to recommend HER2-targeted therapy if the HER2 test result is equivocal.
- Mandatory re-testing should be done on the same specimen, using the alternative test if the initial HER2 test result is equivocal, or on an alternative specimen.
- Do not administer HER2-targeted therapy if the HER2 test result is negative. If there is apparent histopathologic discordance with the HER2 test result, additional HER2 testing should be considered.
- Report a HER2 test result as indeterminate if technical issues prevent one or both tests from being done in a tumor specimen, or prevent the test from being reported as positive, negative, or equivocal.
- Confirm that the testing laboratory conforms to standards set for accreditation by CAP or an equivalent accreditation authority.
- In rare cases, it may be difficult to know for sure if the result is positive or negative. If additional testing on other tissue specimens is not possible, pathologists and oncologists should consider all available clinical data on the patient prior to recommending HER2-targeted therapy.
Limitations Of Her2 Testing
Before the implementation of the first 2007 ASCO/CAP HER2 testing guidelines, the number of patients with equivocal HER2 test results was rather large.
Since 2007, the quality of HER2 testing has improved the frequency of equivocal and inaccurate results has decreased. These improvements are believed to be due in part to the implementation of the testing guidelines since 2007.
With the increasing number of laboratories performing HER2 testing, uniform standards and quality control are mandatory.
The updated 2013 ASCO/CAP guidelines contain even more detailed recommendations on what physicians should discuss with their patients regarding HER2 status reasons for HER2 testing types of tests used interpretation of test results, and any potential need for re-testing in the case of disease recurrence .
Recommended Reading: How Long Is Breast Cancer Surgery