What Causes Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Most inflammatory breast cancer is considered invasive ductal carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma is cancer that forms from cells lining your milk ducts. An invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer that spreads beyond your milk ducts, invading healthy tissue. Researchers dont know what causes these cells to become malignant .
Inflammatory breast cancer develops when cancer cells block lymph vessels. Lymph vessels are hollow tubes in your lymphatic system that allow lymph fluid to drain out of your breast. The blockage causes your breast to become red, swollen and inflamed. In most cases of IBC, cancer cells spread outward from your lymph vessels. Cancer that has metastasized affects your other organs and is harder to treat.
From Cured To Stage 4
Others, like Teri Pollastro, a 54-year-old stage 4 patient from Seattle, respond surprisingly well.
Diagnosed with early stage ductal carcinoma in situ in 1999, Pollastro underwent a mastectomy but did not receive chemotherapy, radiation or tamoxifen, since her cancer was ER negative.
âThey used the C-word with me, they told me I was cured,â she said. âEvery time I went back to my oncologist, he would roll his eyes at me when I had questions.â
In 2003, Pollastro switched to Seattle Cancer Care Alliance where she saw Dr. Julie Gralow, a breast cancer oncologist and clinical researcher at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. Gralow discovered Pollastroâs cancer had metastasized to her liver.
âMy husband and I were in shock,â said Pollastro of her mets diagnosis. âYou donât go from being cured to stage 4.â
Pollastro went on Herceptin, a type of immunotherapy for women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer, and did six months of chemotherapy.
âI felt better right away with the treatment,â she said. âBut the problem is, it stopped . Thatâs what you can expect with mets. And thereâs always some residual cancer. And that starts percolating.â
And along with mets, she also had to deal with many misconceptions regarding her disease.
The Mercer Island, Washington, mother of two, who often counsels newly diagnosed patients, sometimes even found it difficult to relate to early stage breast cancer survivors.
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 3 breast cancer?
Stage 3 breast cancer is when tumors are larger than earlier stages or are growing into nearby tissues, and the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are three categories of Stage 3 breast cancer:
- Stage 3A breast cancer In some cases, Stage 3A breast cancer indicates that the cancer spread to four to nine area lymph nodes, and there may or may not be a tumor in the breast. In other cases, it can describe a cancer that has spread less but the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters.
- Stage 3B breast cancer Stage 3B breast cancer can mean that the cancer has spread to the chest wall or to the breasts skin, causing swelling or an ulcer. It may also mean that cancer has spread to up to nine axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breast bone.
- Stage 3C breast cancer Stage 3C breast cancer means the cancer may have spread to the chest wall or breasts skin, or it has spread to 10 or more nearby lymph nodes. It can also mean the cancer has also spread to lymph nodes above or below the collarbone.
What are the options for Stage 3 breast cancer treatment?
What is the Stage 3 breast cancer treatment timeline?
The treatment timeline for Stage 3 breast cancer depends greatly on the severity, extent of spreading, the type of treatment youre undergoing and how youre responding to those treatments. For most Stage 3 cases, treatment can last anywhere from six to 12 months with hormone therapy lasting many years after.
Read Also: What Are Five Methods For Detecting Breast Cancer
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs as seen on imaging tests or by physical exam, and/or a biopsy of one of these areas proves cancer has spread and is larger than 0.2mm.
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Stage 4 breast cancer means that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, such as the brain, bones, lung and liver.
Although Stage 4 breast cancer is not curable, it is usually treatable and current advances in research and medical technology mean that more and more women are living longer by managing the disease as a chronic illness with a focus on quality of life as a primary goal. With excellent care and support, as well as personal motivation, Stage 4 breast cancer may respond to a number of treatment options that can extend your life for several years.
You May Like: What Does Grade 2 Mean In Breast Cancer
How You Feel About Yourself And Others
When you have an ulcerating tumour it might affect how you feel about yourself. Also, how you feel about being with other people.
You might feel that you have lost control over your body. This can, in turn, make you feel vulnerable.
Your outward appearance can play a big part in how you feel about social situations. You might be worried and embarrassed about other people noticing your wound. This could stop you wanting to go out or see people and can affect your quality of life.
Applying surgical dressings to your wound might help you to cope better. They can make wearing clothes more comfortable. By covering your wound it might also reduce any smell.
What Are The Symptoms Of Fungating Tumors
The symptoms of ulcerated cancer wounds are unique to each patient, but the telltale signs that your malignant tumor may be breaking through the skin include:
- Presence of necrotic skin
The presence of a fungating tumor is especially prevalent in cancer patients with advanced diseases, so its important to contact your doctor right away if you are experiencing any of these symptoms.
Read Also: Is Ductal Breast Cancer Hereditary
Diagnosing A Stage 4 Bedsore
A doctor determines the by its appearance. In the case of a stage 4 bedsore, the large wound has passed the bodys fatty tissue layer, exposing muscles, ligaments, or even bone.
In some cases, however, health care professionals may not be able to immediately diagnose a late-stage bedsore by examining it.
A stage 4 bedsore may be initially diagnosed as:
- UnstageableWhen a doctor cannot see the bottom of an open sore, they must clean it out to properly stage it.
- Suspected Deep Tissue Injury This diagnosis happens when the surface of a patients skin looks like a stage 1 or 2 sore, but it is actually affecting deeper tissues underneath.
Fungating Wounds From Secondary Tumours
A secondary tumour is a tumour that has spread from a primary site to other parts of the body.
A tumour that spreads to the blood and lymphatic system can travel to the skin. It can develop into an ulcerating tumour, but this is rare.
Always attend follow up appointments after your treatment has finished. This way your doctor can pick up any early signs of problems.
Contact your doctor between follow up appointments if you are worried. You should especially do so if you have any new symptoms, such as unexplained skin lumps or sores.
Read Also: How Is Radiation Administered For Breast Cancer
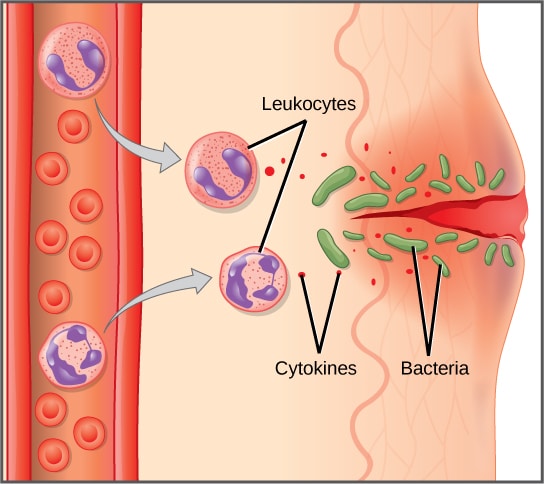
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening mammogram. In addition, most women diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer have dense breast tissue, which makes cancer detection in a screening mammogram more difficult. Also, because inflammatory breast cancer is so aggressive, it can arise between scheduled screening mammograms and progress quickly. The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may be mistaken for those of mastitis, which is an infection of the breast, or another form of locally advanced breast cancer.
To help prevent delays in diagnosis and in choosing the best course of treatment, an international panel of experts published guidelines on how doctors can diagnose and stage inflammatory breast cancer correctly. Their recommendations are summarized below.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- A rapid onset of erythema , edema , and a peau d’orange appearance and/or abnormal breast warmth, with or without a lump that can be felt.
- The above-mentioned symptoms have been present for less than 6 months.
- The erythema covers at least a third of the breast.
- Initial biopsy samples from the affected breast show invasive carcinoma.
Imaging and staging tests include the following:
Symptoms Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
The symptoms of stage 4 breast cancer depend on the location of the cancer and where it has spread in your body.
- If breast cancer has spread to your bones, you may notice a sudden new bone pain. Breast cancer most commonly spreads to your ribs, spine, pelvis, or arm and leg bones.
- If it has spread to your brain, you may experience headaches, vision or speech changes, or memory problems.
- Breast cancer that has spread to your lungs or liver usually causes no symptoms.
The main treatments for stage 4 breast cancer are targeted drug therapies that destroy cancer cells wherever they are in your body.
These treatments may include:
- hormone therapy, which stops or slows the growth of tumors by preventing your body from producing hormones or interfering with the effect of hormones on breast cancer cells
- chemotherapy, where drugs given orally or through an IV travel through your bloodstream to fight cancer cells
- immunotherapy, which uses drugs that stimulate your immune system to destroy cancer cells
- a combination of these therapies
In some cases, surgery or radiation therapy may be used to treat stage 4 breast cancer.
The following are the common treatment options for different types of stage 4 breast cancer.
You May Like: What Type Of Chemo Is Used For Breast Cancer
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Being Your Own Advocate
While there aren’t currently any studies looking at self-advocacy and survival, being your own advocate can’t hurt in maximizing your survival. Oncology is changing rapidly and it’s difficult for any oncologisteven those who specialize in breast cancerto stay aware of all of the latest research and clinical trials taking place.
It can be helpful to research your cancer yourself. Becoming involved via social media such as Twitter is also an excellent way to learn about the latest research, using the hashtag #bcsm, which stands for breast cancer social media.
Getting a second opinion can be helpful as well, especially from one of the larger cancer centers such as a National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center.
There are ways to learn about opportunities, however, that don’t require traveling for opinions. There are now clinical trial matching services in which a nurse navigator can help to match your particular tumor and characteristics with clinical trials in progress all over the world.
Several of the larger cancer centers are now also offering remote second opinions, in which an oncology team can review your medical information and talk to you on the phone about whether there are any opportunities for treatment for you that may not be available elsewhere.
Read Also: What To Give Someone With Breast Cancer
How To Handle Emotions
Coping with the many symptoms that can occur with stage 4 breast cancer can be frustrating and discouraging, and people sometimes wonder if they will have to feel poorly the rest of their lives. Anxiety and depression are also severe for some people with advanced disease.
Fortunately, palliative care team consults are now offered at many cancer centers. While hospice is a form of palliative care, palliative care can be helpful even with early, curable tumors. Working with a palliative care team to address physical and emotional issues frees you up to work with your oncologist on issues that treat your cancer specifically.
While the research is also young, it appears that those people who receive palliative care consults not only have a better quality of life with advanced cancer, but they may actually live longer, too.
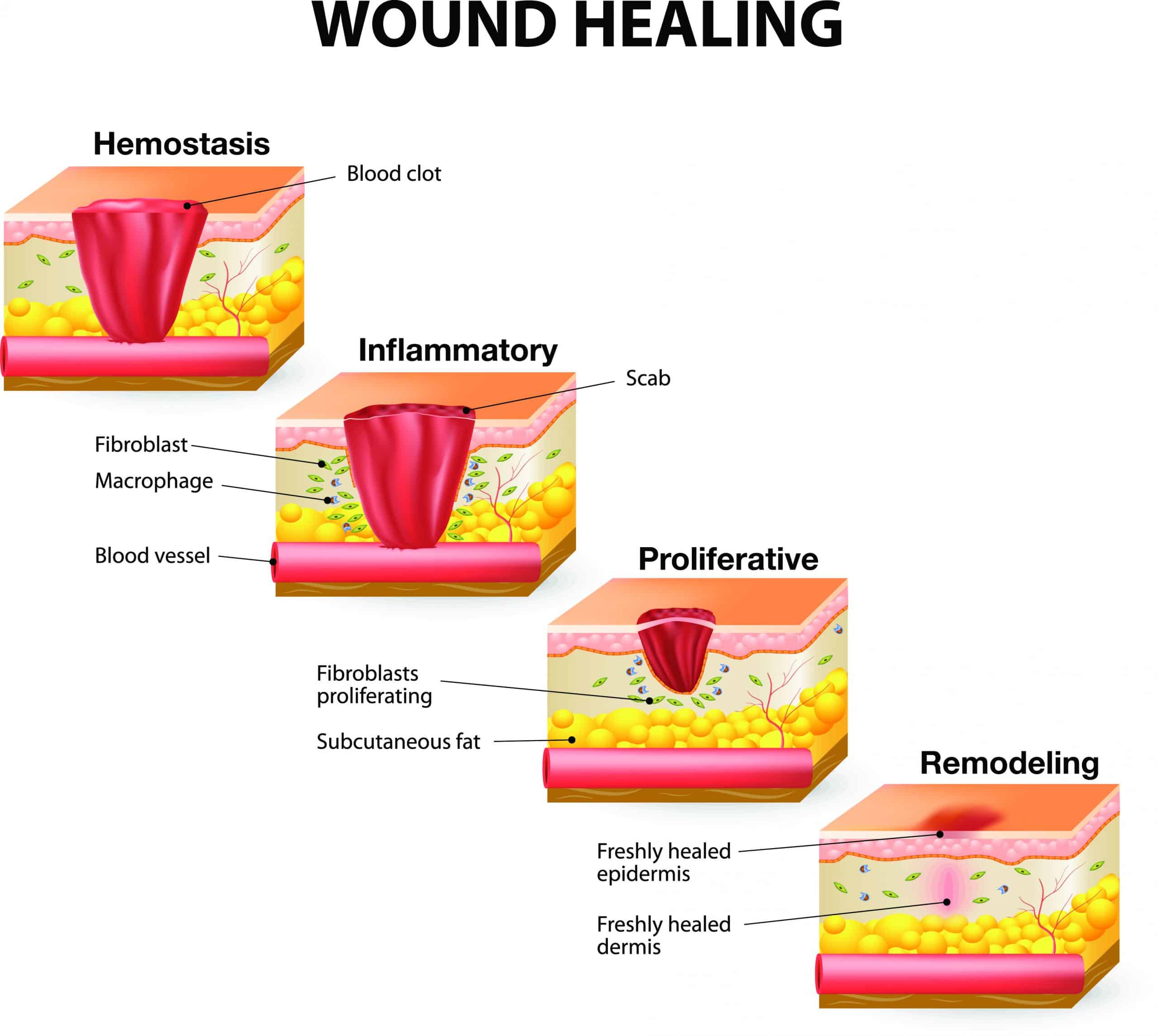
What Are Ulcerating Cancer Wounds
An ulcerating cancer wound is when a cancer that is growing under the skin breaks through the skin and creates a wound. Doctors sometimes call them fungating cancer wounds.
When the cancer grows, it blocks and damages tiny blood vessels. This can reduce the supply of oxygen to the area. This causes the skin and the tissue underneath to die, and the wound may become infected and ulcerated.
Ulcerating wounds are rare. Most people with cancer never develop one. It is more likely to happen in breast cancer, head and neck cancer and melanoma. This is because these cancers develop close to or on the skin.
An ulcerating wound can develop in:
- the area where the cancer started
- a part of the body where the cancer has spread to .
The most common symptoms are:
- leakage or discharge
An ulcerating wound is caused by cancer. Treatments that shrink the cancer may also reduce the wound and improve the symptoms.
The treatment you have will depend on:
- the part of your body that is affected
- the type and size of the cancer and whether it has spread
Commonly used treatments include radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, surgery or a combination of these.
Your doctor will talk with you about which treatment is best for your situation.
Ulcerating cancer wounds are very difficult to heal completely. Cancer treatments may help reduce the size of the wound, but the main aim of treatments is to improve symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Hoda Kotb Breast Cancer Surgery
Tests For Skin Metastases
A member of your treatment team will examine you and look at your skin. Theyll also discuss any other symptoms you have.
To confirm a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer in the skin, you may have a punch biopsy. Youll be given a local anaesthetic before a tiny cutter device is used to take a very small piece of tissue from the area. Its not unusual for the area to bleed a little after the biopsy so a small dressing or plaster will be applied.
The biopsy site may be uncomfortable for a little while, but simple pain relief can be taken to help with this.
You may also have a CT scan to check for any signs of the cancer having spread to other parts of the body.
A CT scan uses x-rays to take a series of detailed pictures of the body. Its painless but during the CT scan you need to lie still for a short period of time. Before the scan you may be given a liquid known as a contrast solution. This is usually injected into a vein, and helps produce clearer images to identify the number, size and location of any areas of cancer.
Drain Leak And Drain Blockage
A blocked or leaking drain is an annoying situation. If the drain leaks simply wash around the drain site, apply a clean pad, and tape it around the drain. If the leak continues, call your doctor or breast care nurse to obtain advice. It may be that the drain is blocked and may need to be removed earlier than planned. This should be checked by your nurse or doctor within 24 hours, alternatively attend the Emergency department.
Read Also: Why Do Women Get Breast Cancer
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Ask your healthcare provider about what your cancer diagnosis means for your treatment options and likely outcomes. Questions to ask include:
- What stage is my breast cancer?
- Which specialists will be involved in my care?
- What treatment options would you recommend?
- What outcomes should I expect from treatment?
- What are potential side effects or complications related to treatment?
- Can you connect me with resources ?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of cancerthat spreads quickly. Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider immediately if you notice changes in your breasts, especially a change in one breast but not the other. The changes may be a sign of a less serious condition, like an infection. Still, IBC spreads fast. If your symptoms are a sign of inflammatory breast cancer, youll want to begin treatment as early as possible. Dont delay seeking care that can potentially improve your prognosis.