Are There Complications Of Breast Cancer
Possible complications from breast cancer treatment include:
- Lymphoedema in some cases, removing your lymph nodes may cause swelling, discomfort and pain in the arm, shoulder and upper body.
- Early menopause certain treatments, especially chemotherapy and hormone therapy, can cause menopause symptoms, such as hot flushes, joint pain, or a change in sex drive, to occur earlier than usual.
- Anxiety and depression research shows that anxiety and depression are common among women with breast cancer. One study found that up to 50 per cent of women with early breast cancer may experience anxiety and/or depression in the year after diagnosis.
What Causes Breast Cancer
While there is no specific cause for breast cancer, some lifestyle factors are associated with a higher risk of developing the condition:
- Drinking alcohol may raise oestrogen levels in the body and is associated with a 30 to 50% increased risk of breast cancer.
- Unhealthy weight Being obese is associated with a 20 to 40% increased risk of breast cancer in post-menopausal women.
- Smoking, particularly if you started as a teenager, increases your breast cancer risk.
Other factors that cant be changed also impact your likelihood of getting breast cancer:
- Your age The older you get, the more likely it is your cells become damaged and progress to cancer. Nearly 4 in 5 new breast cancers are diagnosed in women over 50 years.
- Your family history Women with a first-degree relative with breast cancer are twice as likely to get it themselves than women without one.
- Having BRCA1, BRCA2 or other gene mutations Up to 1 in 10 breast cancers are due to a strong family history of these genetic mutations.
- Dense breasts Women with more dense tissue in their breasts may have a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Previous radiation exposure Women who were exposed to radiation therapy in the chest region may have 5 times the risk of breast cancer as women who were not.
If Cancer Is Found Tests Are Done To Study The Cancer Cells
- how quickly the cancer may grow.
- how likely it is that the cancer will spread through the body.
- how well certain treatments might work.
- how likely the cancer is to recur .
Tests include the following:
Based on these tests, breast cancer is described as one of the following types:
- HER2/neu positive or HER2/neu negative.
- Triple negative .
This information helps the doctor decide which treatments will work best for your cancer.
Don’t Miss: What To Say To Someone Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
How Do Clinical Trials Fit Into The Equation
I think clinical trials in general are very important, because almost every drug we have in practice right now, we learned about through a clinical trial, Henry says.
The Rogel Cancer Center always tries to have clinical trials available for all patients, no matter the stage.
Ask your oncologist about the opportunity to participate in clinical trials, even if it hasnt been mentioned to you, Henry says. Its one way to get access to new exciting drugs, which may be beneficial.
Also Check: Will I Get Breast Cancer
Who Provides Breast Cancer Treatment

A medical team may involve several different health professionals. It may include a GP, a radiologist, an oncologist, a breast care nurse, a surgeon and other allied health professionals such as counsellors and therapists. Having a multi-disciplinary team means a patient can receive the best care possible.
Don’t Miss: Can An 18 Year Old Have Breast Cancer
How Breast Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, doctors specializing in different areas of cancer treatmentsuch as surgery, radiation oncology, and medical oncologywork together with radiologists and pathologists to create a patients overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, nutritionists, and others. For people older than 65, a geriatric oncologist or geriatrician may also be involved in their care. Ask the members of your treatment team who is the primary contact for questions about scheduling and treatment, who is in charge during different parts of treatment, how they communicate across teams, and whether there is 1 contact who can help with communication across specialties, such as a nurse navigator. This can change over time as your health care needs change.
A treatment plan is a summary of your cancer and the planned cancer treatment. It is meant to give basic information about your medical history to any doctors who will care for you during your lifetime. Before treatment begins, ask your doctor for a copy of your treatment plan. You can also provide your doctor with a copy of the ASCO Treatment Plan form to fill out.
Learn more about making treatment decisions.
Treatment For Physical Symptoms
The American Cancer Society urge that a person should not have to endure pain in the final months and days of life.
Many people find relief with opioid medications, but these can cause side effects such as fatigue and constipation. A person may use opioids in combination with other pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Other drugs, such as antidepressants and antiseizure medications, can also treat certain types of pain.
Doctors can also prescribe medications for nausea and vomiting. Some drugs for treating nausea can make a person drowsy. However, these drugs may help people eat and drink more or simply make it easier for them to function and interact with other people.
Read Also: How Can You Feel Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Foods To Avoid
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
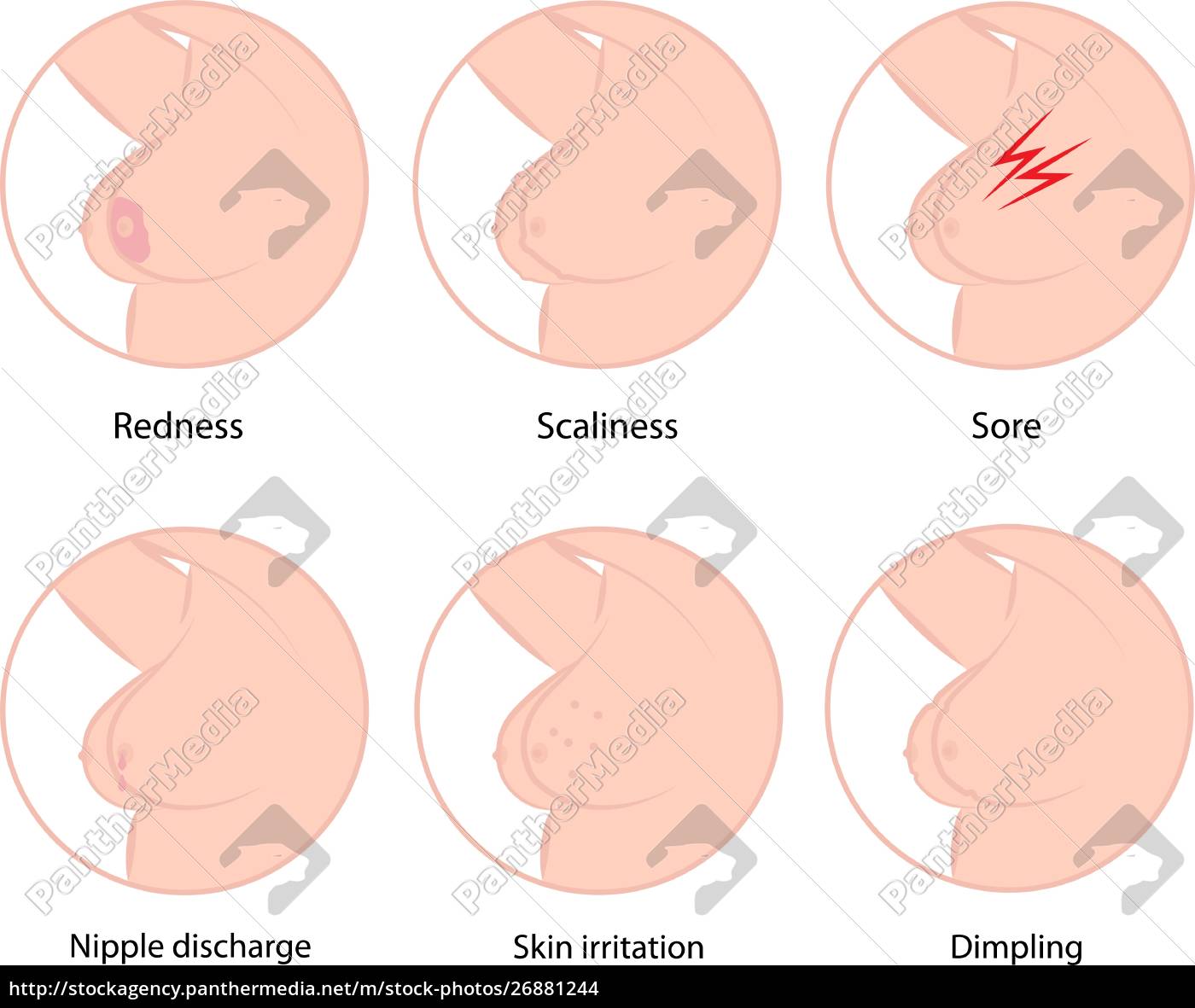
Early Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer
Common symptoms of breast cancer include:
- A lump in your breast or underarm that doesnât go away. This is often the first symptom of breast cancer. Your doctor can usually see a lump on a mammogram long before you can see or feel it.
- Swelling in your armpit or near your collarbone. This could mean breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes in that area. Swelling may start before you feel a lump, so let your doctor know if you notice it.
- Pain and tenderness, although lumps donât usually hurt. Some may cause a prickly feeling.
- A flat or indented area on your breast. This could happen because of a tumor that you canât see or feel.
- Breast changes such as a difference in the size, contour, texture, or temperature of your breast.
- Changes in your nipple, like one that:
Also Check: What Does Breast Cancer Feel Like To Touch
Treatment For Breast Cancer May Cause Side Effects
For information about side effects that begin during treatment for cancer, see our Side Effects page.
Some treatments for breast cancer may cause side effects that continue or appear months or years after treatment has ended. These are called late effects.
Late effects of radiation therapy are not common, but may include:
- Inflammation of the lung after radiation therapy to the breast, especially when chemotherapy is given at the same time.
- Arm lymphedema, especially when radiation therapy is given after lymph node dissection. For more information, see Lymphedema.
- In women younger than 45 years who receive radiation therapy to the chest wall after mastectomy, there may be a higher risk of developing breast cancer in the other breast.
Late effects of chemotherapy depend on the drugs used, but may include:
Late effects of targeted therapy with trastuzumab, lapatinib, or pertuzumab may include:
- Heart problems such as heart failure.
Myth #: Metastatic Breast Cancer Requires More Aggressive Treatment Than Earlier
Related to myth #3 is the notion that because MBC is advanced cancer, doctors have to pull out all the stops to fight it. But thats actually not the case, says Breastcancer.org professional advisory board member Sameer Gupta, MD, a medical oncologist at Bryn Mawr Hospital in Bryn Mawr, Pa., and a clinical assistant professor of medicine at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia. The goal is control rather than cure. Think of it as a marathon vs. a 50-yard dash.
Doctors treat earlier-stage breast cancer more aggressively because the goal is to cure it: destroy all of the cancer cells and leave none behind, reducing the risk of recurrence as much as possible. With MBC, the goal is control so that patients can live well for as long as possible. And chemotherapy isnt necessarily the mainstay of treatment.
DivineMrsM of Ohio shares her experience: eople in general think we should be hooked up to a chemo IV and looking sickly. When I told one woman I took a daily anti-estrogen pill to combat MBC, she looked at me with pity and sadness like I had no clue what I was talking about. Or that I was making up that I had advanced breast cancer, perhaps as a sympathy ploy or for attention. She even asked, Arent you on chemo? And I worked with this woman for a number of years, she was not a stranger!
Don’t Miss: What Happens After Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a disease where cells in the breast grow abnormally and in an uncontrolled way to form a lump, known as a tumour. If left untreated, lumps may spread from breast tissue to other parts of the body, such as the bones, liver or lungs. Breast cancer affects both men and women, although it is less common in men.
Some breast cancers, known as ‘pre-invasive’ or ‘carcinoma in situ’ breast cancers, appear inside the milk ducts or milk-producing lobules of the breast. Other invasive breast cancers grow within normal breast tissue and may spread to elsewhere in the body. There are various types, including Pagets disease, inflammatory breast cancer, ductal carcinoma, lobular carcinoma, hormone receptor positive breast cancer, HER-2 positive breast cancer and triple negative breast cancer .
Breast cancer is the most commonly-diagnosed cancer in women, and its estimated that 8 Australians die from the disease each day. Thankfully, with prompt detection and treatment, 9 in 10 women with breast cancer survive at least 5 years, and many live much longer.
Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Other less common types of breast cancer include invasive lobular breast cancer, which develops in the cells that line the milk-producing lobules, inflammatory breast cancer and Paget’s disease of the breast.
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymph nodes or the bloodstream. If this happens, it’s known as ‘secondary’ or ‘metastatic’ breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Serious Is Breast Cancer
You Notice Changes That Aren’t Related To Your Boobs At All
Back pain, neck pain, and unexplained weight loss were all listed as other breast cancer symptoms that led women to seek medical care and ultimately get diagnosed with breast cancer, according to the study published in Cancer Epidemiology.
That’s because breast cancer can spread before it’s caught, causing symptoms in body parts that have nothing to do with your boobs. It’s not possible to identify every possible sign of breast cancer so when it comes to early detection, you are your own best weapon, says Dr. Denduluri. Overall, any persistent, noticeable change should be checked by a doctor.
Pain As A Side Effect Of Cancer
When the cancer itself causes pain, its often due to a tumor. As a tumor grows, it may put pressure on the surrounding area. Tumors that press on nerves, bones or organs may result in pain.
Two common types of pain caused by cancerous tumors are:
- Spinal cord compression pain. This condition occurs when tumors grow near the spine and constrain spinal cord nerves, leading to pain in the back or neck that is often intense. Other symptoms may include pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or leg. Sudden movements such as coughing or sneezing may aggravate this type of pain. Spinal cord compression is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to shrink the tumoroften using radiation, steroids, surgery, or a combination of these therapies. Without treatment, theres a risk of serious complications, including paralysis.
- Bone pain. When cancer develops in the bones or spreads to them, it weakens them and damages nearby nerves, causing pain. This type of pain may be alleviated with pain medications, treatments to fight the cancer, and drugs or therapies to strengthen the affected bones.
Also Check: Images Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The Grading System Is Used To Describe How Quickly A Breast Tumor Is Likely To Grow And Spread
The grading system describes a tumor based on how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope and how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow and spread. Low-grade cancer cells look more like normal cells and tend to grow and spread more slowly than high-grade cancer cells. To describe how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue are, the pathologist will assess the following three features:
- How much of the tumor tissue has normal breast ducts.
- The size and shape of the nuclei in the tumor cells.
- How many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing.
For each feature, the pathologist assigns a score of 1 to 3 a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for each feature are added together to get a total score between 3 and 9.
Three grades are possible:
- Total score of 3 to 5: G1 .
- Total score of 6 to 7: G2 .
- Total score of 8 to 9: G3 .
Treatment For Brain Metastasis
Metastatic breast cancer in any part of the body is usually treated with systemic medicines, which treat cancer throughout the entire body. For brain metastasis, local treatments that specifically target the brain, such as surgery or radiation, are sometimes recommended.
Still, treating brain metastases can be challenging because of the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is network of blood vessels and tissue that helps keep harmful substances from reaching the brain. The blood-brain barrier lets some things, such as water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and general anesthetics, pass into the brain. But it also keeps out bacteria and other substances, including many medicines used to treat cancer.
While some chemotherapy medicines can help treat brain metastases, many chemotherapy medicines cant cross the blood-brain barrier. Doctors often combine chemotherapy with targeted therapies, which are medicines that target specific characteristics of cancer cells.
Targeted therapies are treatments that target specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as a protein that allows the cancer cells to grow in a rapid or abnormal way. Targeted therapies are generally less likely than chemotherapy to harm normal, healthy cells. Some targeted therapies are antibodies that work like the antibodies made naturally by our immune systems. Because of this, they are sometimes called immune-targeted therapies.
The goals of local treatment depend on your specific situation:
Read Also: Foods That Fight Breast Cancer
Integrative Therapies For Metastatic Breast Cancer
You may find it beneficial to add integrative therapies to your treatment plan. There are many evidence-informed integrative modalities to boost the mind and body. Practices like gentle yoga, meditation, massage and music therapy may feel enjoyable and reduce stress and anxiety levels.
To help our patients maintain quality of life after a metastatic breast cancer diagnosis, our team of breast cancer experts may offer supportive care services to help manage side effects of the disease and its treatments. These may include:
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
When To See A Doctor
Any change in the look or feel in any part of your breasts for which theres no obvious explanation warrants a visit to the doctor, says Dr. Wallace. If you have any of the symptoms described above, see your primary care doctor or gynecologist as soon as you can. And if youre not satisfied with the care you received, see a breast specialist.
In terms of routine screening with mammograms, official recommendations vary about when to start and the frequency to follow. For women ages 40 to 49, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force suggests that women with average breast cancer risk should decide for themselves whether to start screening by getting every-other-year mammograms, while the American Cancer Society recommends women ages 40 to 44 should decide for themselves whether to start breast cancer screening annually, while those ages 45 to 49 should get screened annually.
After age 50 and until age 75, the consensus is that women with normal breast cancer risk should undergo annual or biannual mammograms.
After age 75, recommendations again vary significantly. The ACS states that women in good health with a life expectancy of at least 10 years or more and average breast cancer risk should continue with mammograms, while the American College of Physicians states that they should stop.
Also Check: What Are Some Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer