Thyroid Hormones And Breast Cancer
The most recent piece of research on this topic was published in August 2018 in the journal Breast Cancer Research. Ortega-Olvera et al. analyzed the relationship between thyroid hormones and breast cancer according to menopausal status and BMI. To get their answers, scientists measured serum thyroid hormone and thyroid antibody levels in 682 breast cancer patients and 731 healthy controls.
They tested the link between total T4 and total T3 with breast cancer-bearing in mind factors like a womans weight and her menopause status.
Their findings showed that higher TT4 levels were strongly related to breast cancer in both pre- and postmenopausal women.
On the other hand, lower TT3 concentrations were linked to breast cancer in premenopausal and postmenopausal subjects. Therefore, scientists concluded that there was a strong association between thyroid hormones and breast cancer, but more research is needed to elucidate this topic fully.
Association Between Breast Cancer And Thyroid Cancer: A Descriptive Study
Fang Yu1*, Jinhua Ma2*, Kun Huo3*, Peifeng Li4,5
1 Department of Thyroid and Breast Surgery , General Hospital of Jinan Military Command , 2Department of Pharmacy, 89th Hospital of PLA, Weifang 261021, General Hospital of Jinan Military Command , General Hospital of Jinan Military Command , State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology, Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine , , China
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: K Huo Provision of study materials or patients: F Yu, J Ma Collection and assembly of data: F Yu, J Ma, K Huo Data analysis and interpretation: P Li Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Correspondence to:
Background: This study investigated the prevalence and clinicopathological characteristics of patients with breast cancer and thyroid cancer to explore the possible mechanism underlying co-development of these two cancers.
Methods: A retrospective study was performed in 486 female patients with thyroid cancer, among which 8 patients suffered from breast malignancies. The clinicopathological features, hormone receptor status of the invasive breast cancer, and the expression of human mismatch repair genes were analyzed.
Keywords: Breast carcinoma estrogen receptor human mismatch repair genes thyroid carcinoma
Submitted Oct 28, 2016. Accepted for publication Jan 13, 2017.
doi: 10.21037/tcr.2017.03.44
What Does The Research Say
Researchers looked at 37 peer-reviewed studies containing data on the relationship between breast and thyroid cancers.
They noted in a 2016 paper that a woman whos had breast cancer is 1.55 times more likely to develop a second cancer of the thyroid than a woman without a history of breast cancer.
A woman with thyroid cancer is 1.18 times more likely to develop breast cancer than a woman without a history of thyroid cancer.
Researchers are unsure about the connection between breast and thyroid cancers. Some research has indicated the risk of developing a second cancer increases after radioactive iodine is used to treat thyroid cancer.
Iodine is generally considered safe, but it could trigger a second cancer in a small number of people. Radiation used to treat certain forms of breast cancer may increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Certain genetic mutations like a germline mutation could link the two forms of cancer. Lifestyle factors like exposure to radiation, poor diet, and lack of exercise, could also increase the risk of both cancers.
Some researchers also noted the possibility of a surveillance bias, which means a person with cancer is more likely to follow up with screening after treatment. This improves detection of a secondary cancer.
They also analyzed the results by dividing the data into groups based on the time between the diagnosis of the first and the second cancer.
Both breast and thyroid cancers have unique screening guidelines.
Recommended Reading: Can Smoking Weed Cause Breast Cancer
Breast And Thyroid Cancer At The Same Time
I was diagnosed with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma about 3 weeks ago. Found a couple of small spots either side of the tumor so I have been scheduled for a right mastectomy. No lymph nodes showing up at the moment but they’ll check everything during surgery.
Went for a CT scan last week and a 2cm tumor showed up on my thyroid , and suspicious adrenal enlargement . I had a Fine needle biopsy of my thyroid on Monday and blood and urine tests for adrenals, and am waiting for results next week. I really don’t know what to think now. They don’t think any of it is metastatic, just really bad luck to have 2, possibly 3 cancers diagnosed at the same time.
Anyone in the same boat? Will they do the breast surgery first and then remove the thyroid once I’ve recovered? From what I’ve been researching it seems likely they’ll want to remove the thyroid adenoma even if it is benign.
Was just starting to feel a bit better about everything after getting results of the Breast cancer back and dealing with it, now I’m back waiting for results. Utterly exhausted and really don’t know what to focus on.
Hello AnnInJapan and a warm welcome to our friendly forum!
I hope this helps a little and that you find a lot of support here on this forum from others who may live so many miles away but who are in a similar boat.
Best wishes,
Its All About The Thyroid

The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck that produces thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormone affects almost every cell in the body and has many crucial functions, like controlling metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature.
Some people have hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This can cause weight loss, thinning hair, sweating, anxiety, and a rapid heartbeat. Women are five to 10 times more likely than men to develop an overactive thyroid.
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid develops when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Symptoms of an underactive thyroid include weight gain, fatigue, constipation, depression, dry hair, and a slow heart rate. Like hyperthyroidism, its also more common in women than in men.
In an effort to determine whether having an overactive or underactive thyroid affects a womans risk of breast cancer, researchers looked at a large group of women in Denmark diagnosed with thyroid disease between 1978 and 2013. More than 60,000 of the study participants had an underactive thyroid, and more than 80,000 had an overactive thyroid. They followed the patients for five to seven years and found that those with an overactive thyroid had a slightly increased risk of breast cancer an 11% higher risk, to be specific. However, women with an underactive thyroid had a 6% drop in their breast cancer risk.
You May Like: How Urgent Is Breast Cancer Surgery
Second Cancers After Thyroid Cancer
Survivors of thyroid cancer can be affected by a number of health problems, but often their greatest concern is facing another cancer. Cancer that comes back after treatment it is called a recurrence. But some cancer survivors may develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer.
Unfortunately, being treated for cancer doesnt mean you cant get another. People who have had thyroid cancer can still get the same types of cancers that other people get. In fact, they might be as risk for certain types of cancer.
People who have or had thyroid cancer can get any type of second cancer, but they have an increased risk of developing:
Adrenal cancer risk is especially high in people who had the medullary type of thyroid cancer.
Patients treated with radioactive iodine also have an increased risk of acute lymphocytic leukemia , stomach cancer, and salivary gland cancer.
What Genetic Factors Link The Diseases
In addition, germline mutations in PARP4 were identified in women treated for both cancers . Heightened expression of PARP4 also correlated with longer disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with breast cancer. PARP4 belongs to a family of genes, poly-ADP-ribose polymerases , that encodes enzymes to catalyze synthesis of poly-ADP-ribose . Levels of poly-ADP-ribose increase in response to genetic insults and is a critical component of DNA repair. PARP inhibitors are used clinically to treat ovarian tumors and are in clinical trials for breast cancer . However, existing drugs do not target PARP4. PARP4 is unique in that it can also be found in the cytoplasm, unlike the other members of the PARP family . Unfortunately, PARP4 is not well characterized and more research is needed to determine the biochemical and physiologic processes it regulates.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Spread To Skin Stage Iv
Incidence Of Thyroid Disease In Patients With Bc
We identified a total of 13 978 patients with BC who qualified for analysis, 247 of whom were diagnosed with TC . The mean follow-up time was 64.5 ± 32.3 months. The mean time interval between BC surgery and TC surgery was 1.13 ± 4.97 years. Specifically, 43 patients had TC > 1 year prior to BC , 74 had synchronous BC and TC , and 130 were diagnosed with TC at least 1 year after BC .
Based on the cancer incidence in China in 2013, the incidence of TC in both females and males was 7.37/105 that in females was 11.24/105 in the general population and 19.98/105 in areas of high urbanization. In our cohort of patients with BC, the SIR for second primary TC was 6.92 for both females and males. The SIR for TC was 4.48 for females in the general population and 2.52 compared with the incidence of TC in areas of high urbanization.
Among 247 cases of BC-TC, 203 had specific pathologic information: 200 were thyroid papillary carcinomas, one was a follicular carcinoma, one was a medullary carcinoma, and one was a combination of both papillary and follicular carcinoma. Among 181 cases of known tumor size, 124 were microcarcinomas. Of 202 patients with a known lymph node status, 137 had no lymph node metastasis, 48 had central neck lymph node metastasis, and 17 had lateral neck lymph node metastasis. Of 185 patients with a known number of thyroid cancer lesions, 53 had multifocal lesions.
What Is The Impact Of Cancer Treatment On Future Risk
Radiation, despite being a treatment option for breast cancer, is a well-documented risk factor in the development of cancer and is a major risk factor for thyroid cancer . Multiple recent clinical studies demonstrate alteration of the ability of the thyroid to produce hormones following radiotherapy . Despite this evidence that radiotherapy harms the thyroid, a very large study from Taiwan of over 55,000 patients did not report any association between treating breast cancer with radiation and subsequent thyroid cancer, nonetheless the results did corroborate the previously discussed relationship between thyroid and breast cancers . Another study revealed that although the use of radiotherapy to treat breast cancer was associated with an increased risk of certain tumors, including leukemia and lung cancer, there was not an observed increase in the risk of thyroid cancer .
Although the impact of radiotherapy on thyroid function has been extensively studied, data on chemotherapy is sparse. Studies on patients with breast cancer receiving different chemotherapeutic treatments reveal a reduction in serum T4 levels, but subsequent recovery of thyroid function and thyroid cancer risk was not assessed . Critically, the impact of chemotherapeutic agents on thyroid function and cancer risk needs further study.
Recommended Reading: How Many Chemotherapy Sessions For Breast Cancer
Putting The Study Results Into Perspective
While this study might lead some to conclude that having excess thyroid hormone promotes the development of breast cancer, experts caution that this study does not prove cause and effect. While there may be an association, it is not clear that an overactive thyroid actually causes breast cancer to develop.
Some critics wonder whether women at risk for hyperthyroidism may also be at risk for breast cancer, or whether the treatment for hyperthyroidism may be to blame for increased cancer risk. Another theory is that women with an overactive thyroid see their doctors more often and therefore are more likely to get screened for other problems like breast cancer.
The effect of thyroid hormone on breast cancer risk clearly requires further study. In the meantime, women with an overactive thyroid should stay in close communication with their doctors and follow routine breast cancer screening recommendations.
About the Author
Mallika Marshall, MD, Contributing Editor
Breast Cancer And Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid diseases such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and autoimmune conditions are not the only connections between the function of this gland and breast cancer. Studies show that breast cancer and thyroid cancer are also related.
Nielsen et al. reviewed available evidence on this subject and found that a woman whos had breast cancer is 1.55 times more likely to develop thyroid cancer than a woman without a breast cancer history. At the same time, a woman with thyroid cancer is 1.18 more likely to develop breast cancer compared to a woman who doesnt have a history of thyroid cancer.
Its not quite clear why the two cancers are connected, but radiation and exposure to iodine during treatment could be the reason. In addition, some genetic mutations could also be the link between thyroid cancer and breast cancer. Hormonal risk factors are involved as well.
More precisely, exposure to estrogens and thyroid-stimulating hormones could contribute to the formation of a secondary thyroid or breast cancer. Basically, treatment for first cancer could affect the risk of developing the second. For instance, radiation is a common cancer treatment measure for breast cancer, but it can increase the risk of other types of cancer including that affecting thyroid.
Read Also: How Did You Find Out You Had Breast Cancer
External Beam Radiation To The Breast And The Risk Of Thyroid Cancer
Improvements in adjuvant therapy, combined with better screening and surveillance, has resulted in a higher proportion of early stage breast cancer and an increase in breast cancer survivors. Early-stage breast cancer is typically managed with breast-conserving surgery and postoperative radiation therapy . Following treatment, breast cancer survivors are at a 10â50% greater risk of developing a non-breast second primary cancer as compared to the general population . While some of these second cancers may be sporadic, others may be iatrogenic. Despite improvements in radiation techniques over the past 60 years, minimizing the total radiation exposure to adjacent normal tissues, radiation scatter, and subsequent cancer risk still exists. Thus among cancer survivors, the long-term effects of therapies such as RT is particularly relevant.
Based on these studies, the risk for radiation-induced thyroid cancer following treatment for breast cancer is likely negligible but requires further evaluation. Special surveillance of the thyroid gland is not currently recommended for breast cancer survivors. In addition, management of thyroid nodules in women with a prior history of breast cancer should not be solely influenced by prior radiation treatment for breast cancer .
Radioactive Iodine For Thyroid Cancer And The Risk Of Breast Cancer
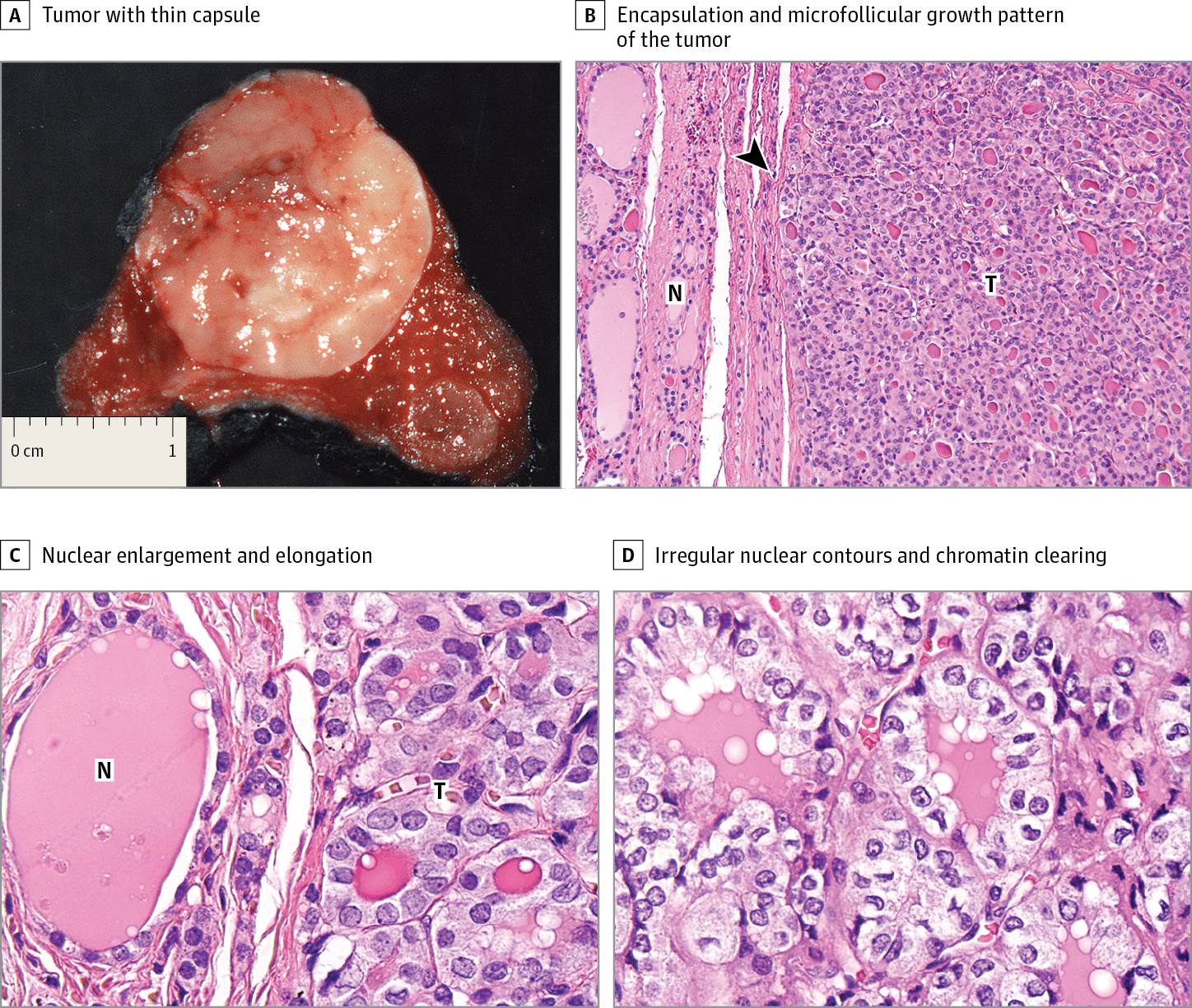
RAI has been used since the 1940âs as an adjuvant treatment of thyroid cancer ablating residual thyroid tissue, involved cervical lymph nodes, and/or distant metastases. Concern about the potential carcinogenic effects of RAI is greatest in organs that concentrate or eliminate iodine or are on the therapeutic route of administration. These organs include the salivary gland, stomach, small intestine, bladder and bone marrow . The mammary gland has the same sodium-iodine symporter as the thyroid gland thus may also be able to concentrate iodine . Lactating breast tissue and breast tissue with atypia or malignancy show an increase in RAI uptake . However 131I whole body scanning does not suggest that quiescent breast tissue concentrates significant levels of iodine. Thus the RAI dose delivered to the breast during thyroid cancer treatment is expected to be low . A role for RAI in breast carcinogenesis cannot, however, be ruled out.
Larger scale studies using SEER data are consistent with the previous findings. The risk of breast cancer following thyroid cancer was significantly elevated in both RAI and non-RAI cohorts, and often higher in the non-RAI cohort . Some studies show a protective effect with higher absorbed doses of RAI for breast cancer risk . Thus there appears to be no significant dose-effect relationship of RAI on breast cancer risk.
Read Also: What Stage Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Iodide Iodine Transport And Breast Cancer
Regulation and expression of the NIS gene in breast cancer. In breast cancer cells, the NIS protein is predominantly expressed in the intracellular space, whereas the protein is located on the basolateral membrane in lactating mammary glands. Mislocalization of the NIS protein may lead to a disparity between the NIS expression level and observed radioiodide uptake
How Common Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in the world, but have you ever wondered how prevalent it is?
According to BreastCancer.org, one in eight women will develop invasive breast cancer sometime in their life. This even more concerning since, the rate of death from breast cancer is the highest for any type of cancer
And besides skin cancer, breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in American women. More than 85% of breast cancers occur in women who have no history of this severe disease in their family.
The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2019 about 268,600 new cases of breast cancer will be diagnosed in women. This year the number of deaths caused by breast cancer is expected to be about 41,760, figures show.
Read Also: Modifiable Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
What Are The Different Types Of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is categorized based on the type of thyroid cells where the cancer begins and how the cancer cells appear under a microscope.
There are two kinds of cells found in the thyroid.
Follicular cells are the most common. They produce thyroid hormone, which is important for growth, mental function and helping the body create energy. Most thyroid cancers develop from follicular cells.
Parafollicular cells, also known as C cells, produce a small amount of the hormone calcitonin, which helps control calcium metabolism. Most parafollicular cells are in the upper third of each lobe. Medullary thyroid cancer is the only thyroid cancer that develops from parafollicular cells.
Thyroid cancers can also be categorized based on the appearance of their cells. Cancer cells that look most like normal, healthy cells are called well differentiated. Patients with well differentiated thyroid cancers are most likely to be disease-free at the end of treatment. Poorly differentiated and undifferentiated cancer cells look less and less like healthy cells. These forms of thyroid cancer are usually harder to treat and the outlook for these patients is worse.
Doctors believe most thyroid cancers start as well differentiated. As the cancer grows, its cells can develop additional mutations, changing it into a less differentiated, harder-to-treat type of thyroid cancer.