Tumor Profiling And Chemotherapy
Some women who have hormone receptor-positive breast cancer should consider getting a tumor profiling test, such as Oncotype DX®, to see if chemotherapy is needed in addition to hormone therapy .
Tumor profiling can be used to help guide chemotherapy for early breast cancers that are all of the following :
- Estrogen receptor-positive
- Tumor size smaller than 5 cm
- HER2-negative
- Lymph node-negative or 1-3 positive lymph nodes
Tumor profiling may also be called genomic testing or molecular profiling.
|
For a summary of studies on trastuzumab and early breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
What Is Stage 0 Dcis
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if its left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
In general, cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Supportive care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive supportive care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Supportive care treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies.
-
Music therapy, meditation, stress management, and yoga for reducing anxiety and stress.
-
Meditation, relaxation, yoga, massage, and music therapy for depression and to improve other mood problems.
-
Meditation and yoga to improve general quality of life.
-
Acupressure and acupuncture to help with nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
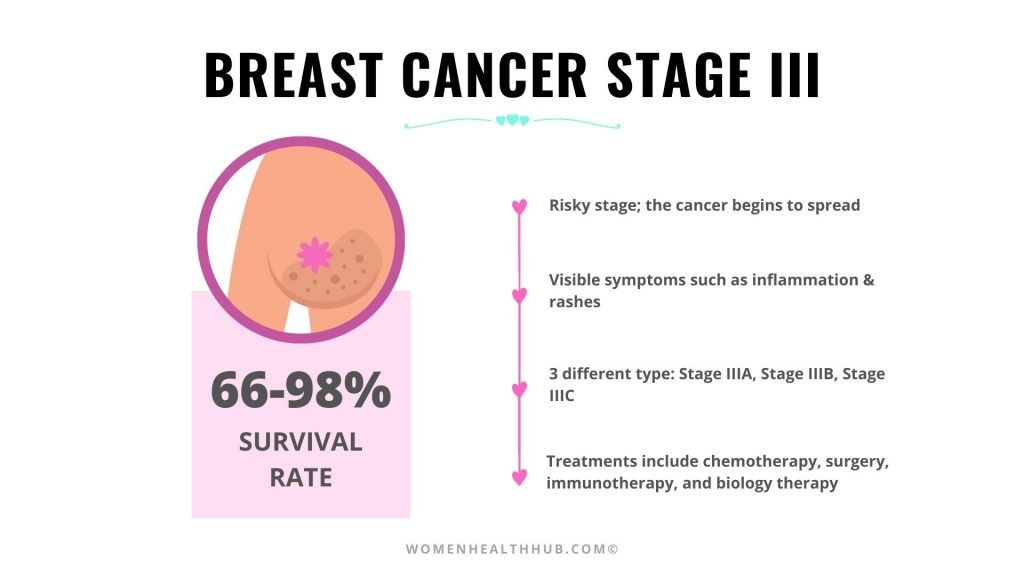
Treating Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large or growing into nearby tissues , or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes. These cancers are treated slightly different from other stage III breast cancers. You can find more details in Treatment of Inflammatory Breast Cancer.
There are two main approaches to treating stage III breast cancer:
What Are The Different Grades Of Breast Cancer
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer:
- Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing
- Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster
- Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing
Sometimes the grade given to a cancer after a biopsy can change after surgery. This is because after surgery theres more tissue for the pathologist to look at, which can give them more detailed information about the cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Feed On
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 1 Breast Cancer
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop. The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated.
Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer.
How Radiation Is Used With Other Cancer Treatments
For some people, radiation may be the only treatment you need. But, most often, you will have radiation therapy with other cancer treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Radiation therapy may be given before, during, or after these other treatments to improve the chances that treatment will work. The timing of when radiation therapy is given depends on the type of cancer being treated and whether the goal of radiation therapy is to treat the cancer or ease symptoms.
When radiation is combined with surgery, it can be given:
- Before surgery, to shrink the size of the cancer so it can be removed by surgery and be less likely to return.
- During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation. With this technique, doctors can more easily protect nearby normal tissues from radiation.
- After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain.
Read Also: What Is The Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
How Is Breast Cancer Treated
There are several breast cancer treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy and targeted drug therapy. Whats right for you depends on many factors, including the location and size of the tumor, the results of your lab tests and whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. Your healthcare provider will tailor your treatment plan according to your unique needs. Its not uncommon to receive a combination of different treatments, too.
Breast cancer surgery
Breast cancer surgery involves removing the cancerous portion of your breast and an area of normal tissue surrounding the tumor. There are different types of surgery depending on your situation, including:
Chemotherapy for breast cancer
Your healthcare provider may recommend chemotherapy for breast cancer before a lumpectomy in an effort to shrink the tumor. Sometimes, its given after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence . If the cancer has spread beyond your breast to other parts of your body, then your healthcare provider may recommend chemotherapy as a primary treatment.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer
Radiation therapy for breast cancer is typically given after a lumpectomy or mastectomy to kill remaining cancer cells. It can also be used to treat individual metastatic tumors that are causing pain or other problems.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer
Immunotherapy for breast cancer
After Breast Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Findout If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Breast Or To Other Parts Of Thebody
The process used to find out whether the has spread within the or to otherparts of the body is called .The information gathered from the staging process determines the of the disease. It isimportant to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of some of the tests used to are also used to stage the disease.
The following tests and procedures also may be used inthe staging process:
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Cause Breast Cancer
Will The Nhs Fund An Unlicensed Medicine
Its possible for your doctor to prescribe a medicine outside the uses its licensed for if theyre willing to take personal responsibility for this off-licence use of treatment.
Your local clinical commissioning group may need to be involved, as it would have to decide whether to support your doctors decision and pay for the medicine from NHS budgets.
Page last reviewed: 28 October 2019 Next review due: 28 October 2022
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 3 breast cancer?
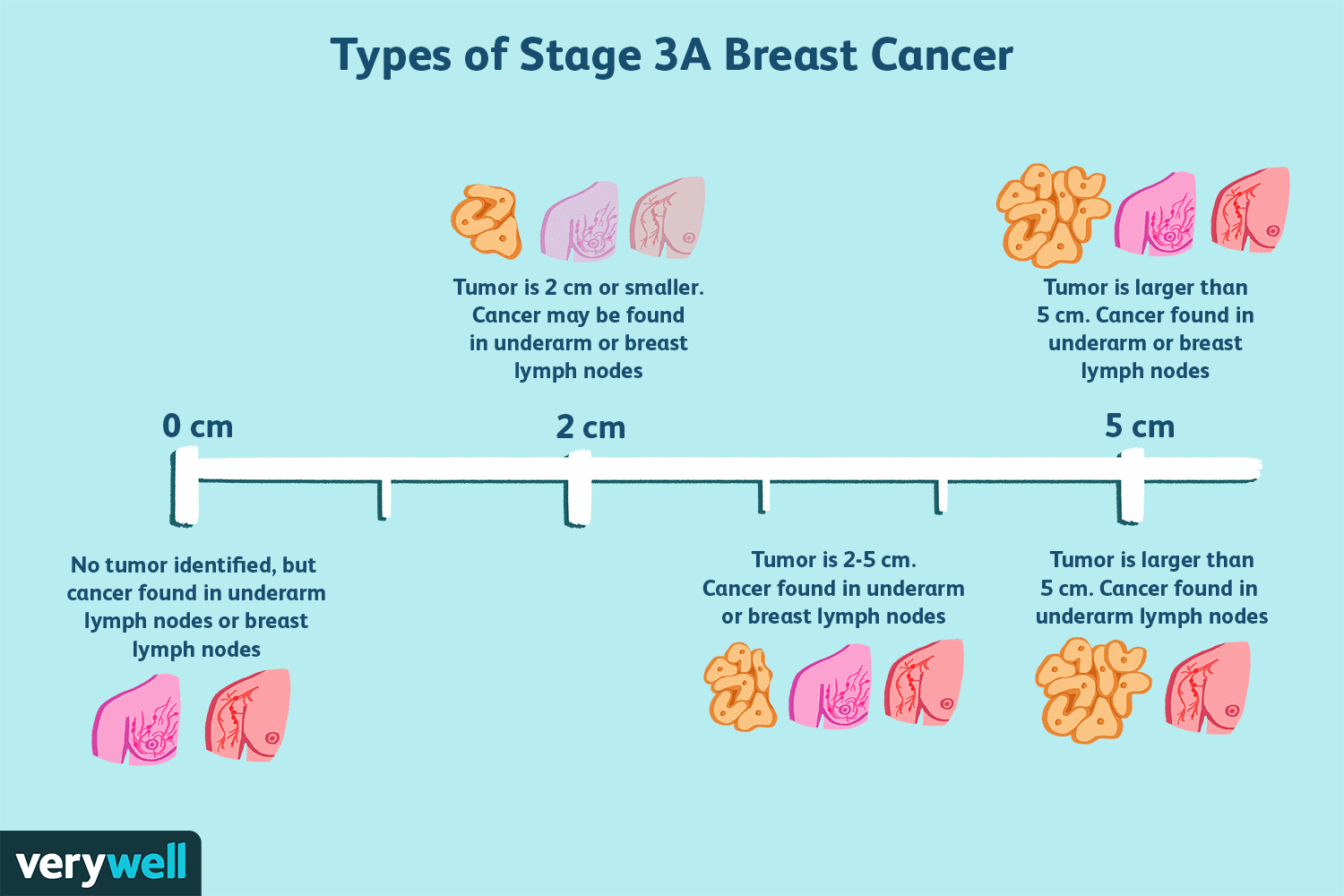
Stage 3 breast cancer is when tumors are larger than earlier stages or are growing into nearby tissues, and the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are three categories of Stage 3 breast cancer:
- Stage 3A breast cancer In some cases, Stage 3A breast cancer indicates that the cancer spread to four to nine area lymph nodes, and there may or may not be a tumor in the breast. In other cases, it can describe a cancer that has spread less but the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters.
- Stage 3B breast cancer Stage 3B breast cancer can mean that the cancer has spread to the chest wall or to the breasts skin, causing swelling or an ulcer. It may also mean that cancer has spread to up to nine axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breast bone.
- Stage 3C breast cancer Stage 3C breast cancer means the cancer may have spread to the chest wall or breasts skin, or it has spread to 10 or more nearby lymph nodes. It can also mean the cancer has also spread to lymph nodes above or below the collarbone.
What are the options for Stage 3 breast cancer treatment?
What is the Stage 3 breast cancer treatment timeline?
The treatment timeline for Stage 3 breast cancer depends greatly on the severity, extent of spreading, the type of treatment youre undergoing and how youre responding to those treatments. For most Stage 3 cases, treatment can last anywhere from six to 12 months with hormone therapy lasting many years after.
Recommended Reading: What Does Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
A Family History Of Breast Cancer And Other Factors Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for breast cancer.
Risk factors for breast cancer include the following:
- A personal history of benign breast disease.
- A family history of breast cancer in a first-degree relative .
- Inherited changes in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes or in other genes that increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Breast tissue that is dense on a mammogram.
- Exposure of breast tissue to estrogen made by the body. This may be caused by:
- Menstruating at an early age.
- Older age at first birth or never having given birth.
- Starting menopause at a later age.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
NCI’sBreast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool uses a woman’s risk factors to estimate her risk for breast cancer during the next five years and up to age 90. This online tool is meant to be used by a health care provider. For more information on breast cancer risk, call 1-800-4-CANCER.
Breast Cancer Is Sometimes Caused By Inherited Gene Mutations
The genes in cells carry the hereditary information that is received from a persons parents. Hereditary breast cancer makes up about 5% to 10% of all breast cancer. Some mutated genes related to breast cancer are more common in certain ethnic groups.
Women who have certain gene mutations, such as a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, have an increased risk of breast cancer. These women also have an increased risk of ovarian cancer, and may have an increased risk of other cancers. Men who have a mutated gene related to breast cancer also have an increased risk of breast cancer. For more information, see the PDQ summary onMale Breast Cancer Treatment.
There are tests that can detect mutated genes. Thesegenetic tests are sometimes done for members of families with a high risk of cancer. See the PDQ summary on Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers for more information.
Recommended Reading: When Is Breast Cancer Month
Signs Of Breast Cancer Include A Lump Or Change In The Breast
These and other signs may be caused by breast cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm area.
- A change in the size or shape of the breast.
- A dimple or puckering in the skin of the breast.
- A nipple turned inward into the breast.
- Fluid, other than breast milk, from the nipple, especially if its bloody.
- Scaly, red, or swollen skin on the breast, nipple, or areola .
- Dimples in the breast that look like the skin of an orange, called peaudorange.
Late Effects Of Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
Radiotherapy to the breast may cause side effects that happen months or years after radiotherapy. They are called late effects.
Newer ways of giving radiotherapy are helping reduce the risk of these late effects happening. If you are worried about late effects, talk to your cancer doctor or specialist nurse.
The most common late effect is a change in how the breast looks and feels.
Radiotherapy can damage small blood vessels in the skin. This can cause red, spidery marks to show.
After radiotherapy, your breast may feel firmer and shrink slightly in size. If your breast is noticeably smaller, you can have surgery to reduce the size of your other breast.
If you had breast reconstruction, using an implant before radiotherapy, you may need to have the implant replaced.
It is rare for radiotherapy to cause heart or lung problems, or problems with the ribs in the treated area. This usually only happens if you had treatment to your left side.
Tell your cancer doctor if you notice any problems with your breathing, or have any pain in the chest area.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Tested For Breast Cancer
The Stages Of Breast Cancer And Your Treatment Options
Compared to most other cancers, staging breast cancer is more complex. And when it comes to treating breast cancer, there isnt a one-size-fits-all approach. Your treatment plan should be created especially for you and be coordinated across specialists and thats where your cancer care team comes in.
At HealthPartners, we believe cancer treatment and care is best managed by a group of doctors and specialists in whats known as multidisciplinary conferences. This is where breast surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, pathologists and other members of your care team gather to discuss the best treatment sequence for you.
Below we dive into the treatment options your care team might recommend at various breast cancer stages.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Returning
What Type Of Drug Treatment Might I Get
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include:
- Chemotherapy
- HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab
- Some combination of these
The types of drugs that might work best depend on the tumors hormone receptor status, HER2 status, and other factors.
You May Like: Is Her2 Breast Cancer More Aggressive
Also Check: Can You Have Breast Cancer In Both Breast
How Do Doctors Determine Different Stages Of Breast Cancer
Cancer doctors or oncologists determine the stage of a breast cancer based on several factors including the following:
Once a patient has been diagnosed with breast cancer, her doctor may request several tests or screenings to determine if cancer cells have spread into other parts of the breast and/or other parts of the body. These may include blood tests, X-rays, mammograms, ultrasounds, magnetic resonance imaging , computerized tomography scans and/or positron emission tomography scans.
Cancer doctors use a staging system called the TNM, , when trying to find out the location and size of the primary tumor and the size and location of lymph nodes where cancer cells are present. It uses numbers from 0-4 to assign a value to the cancer.
Cancer doctors follow a grading system that helps determine how fast a primary tumor can grow and spread within the breast or in other parts of the body.
Cancer doctors also use biomarker testing to determine whether breast cancer cells have specific receptors. The biomarker status is combined with the TNM system and the grading system to diagnose the breast cancer stage.
Stage Zero Breast Cancer: Whats The Optimal Treatment For Dcis
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently.
Often called stage zero breast cancer, DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breasts milk ducts, and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
A new study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons may help women and their physicians narrow down the treatment choices.
DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer, says Apar Gupta, MD, assistant professor of radiation oncology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and lead author of the study.
However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits.
The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the studys findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS. Below are excerpts from the conversation:
Why is DCIS treatment controversial?
How does your study help women make a decision about treatment after lumpectomy?
Is there a role for hormone therapy?
Recommended Reading: How Is Breast Cancer Caused