Exposure To Chemicals And Drugs
Females who have been exposed to dreadful carcinogenic chemicals are at higher risk of breast cancer and epigenetic alterations and mutations. Exposure and duration of exposure contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer mutagenesis . Exposure of mammary glands to polychlorinated biphenyl and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane chemicals increases the risk of breast cancer . Furthermore, continuous exposure to organic solvents, insecticides, and oil mist increases the risk of breast cancer . Antibiotics, statins, antidepressants, and antihypertensive drugs can increase the risk of breast cancer. Similarly, NSAIDs that contain aspirin and ibuprofen are considered major risk factors for breast cancer .
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
You will have lots of questions about your cancer, starting with your diagnosis. Here are some basic questions you might ask:
- What is triple negative breast cancer?
- How do you know my cancer is triple negative breast cancer?
- Why did I get this cancer?
- Do I need genetic testing?
- Has my breast cancer spread, and if so, how far has it spread?
- What is the stage of my cancer?
- What is my prognosis or expected outcome?
- What treatments do you recommend?
- Why do you recommend those treatments?
- What are those treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery? If so, what surgery do you recommend and why?
- Im interested in participating in clinical trials. Are you able to help me find one?
- Do you know if there are any local support groups?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Triple negative breast cancer is one of the more challenging breast cancers to treat. You might be discouraged by what you have read about triple negative breast cancer. But there are a number of very effective treatments for triple negative breast cancer, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation. And every day researchers learn more about this rare cancer. Their knowledge is your power. If youre concerned you arent getting the straight story about your cancer, ask your healthcare provider to walk you through your diagnosis and treatment options.
Baseline Characteristics Of The Study Population
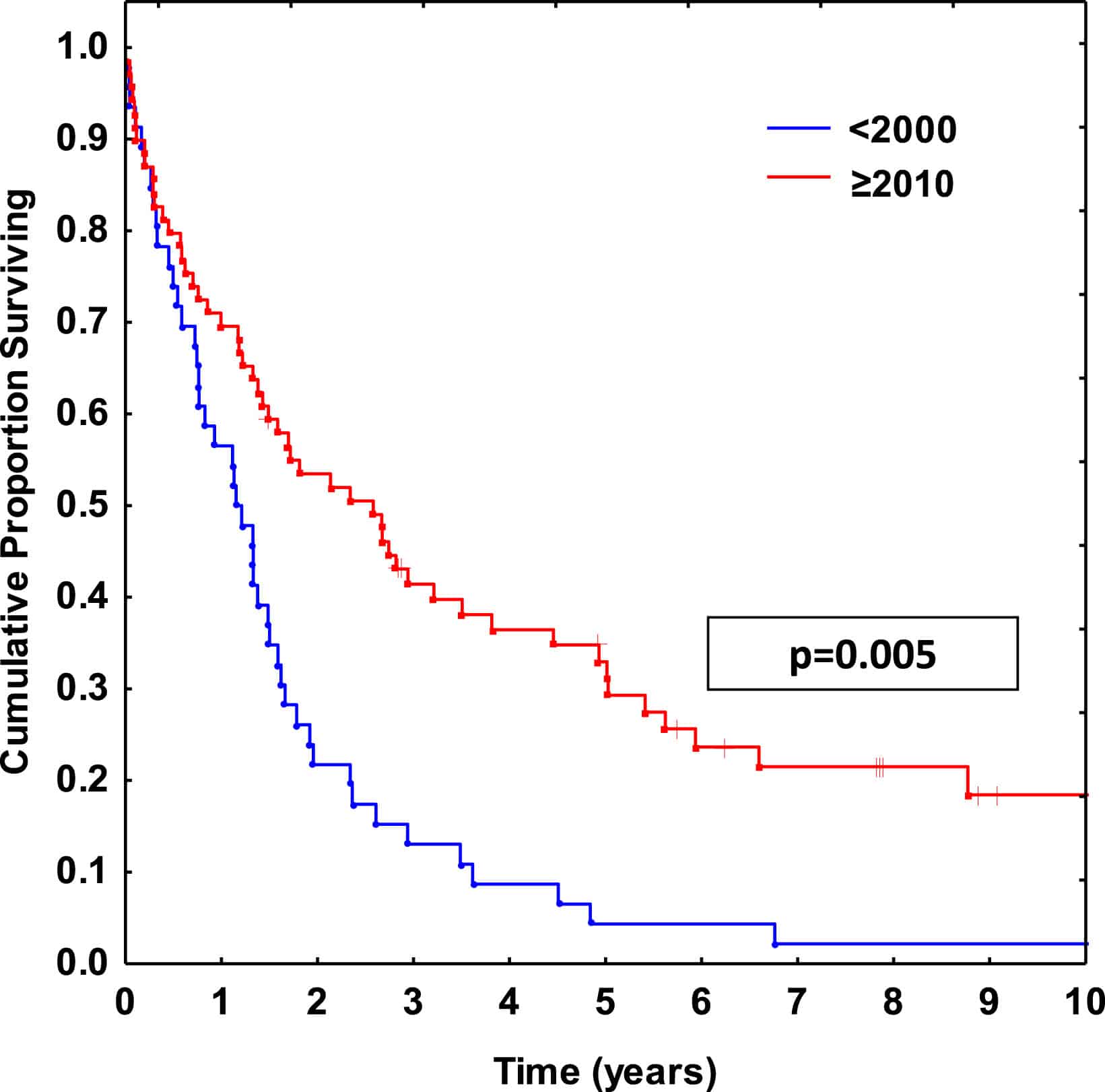
Altogether, there were 1,099 cases that met the criterion of this study . Among them, 278 patients received ACT, and 821 patients never underwent treatment or their ACT treatment was unknown. Median follow-up for these patients was 36 months. Patients with ACT tended to be younger than the group without ACT . The higher the histological grade, the higher the percentage of patients who received ACT . In addition, a higher percentage of patients who received chemotherapy chose mastectomy . No remarkable differences were observed between patients from the two groups in terms of race, marital status, laterality, or radiation therapy . Considering the different distribution of several important prognostic indicators, we conducted a 1:1 matched case-control analysis utilizing a PSM method, and 255 paired patients were finally identified .
Figure 1. The selection and grouping of patients for the study.
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population.
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Metastasis
How Siteman Approaches Triple
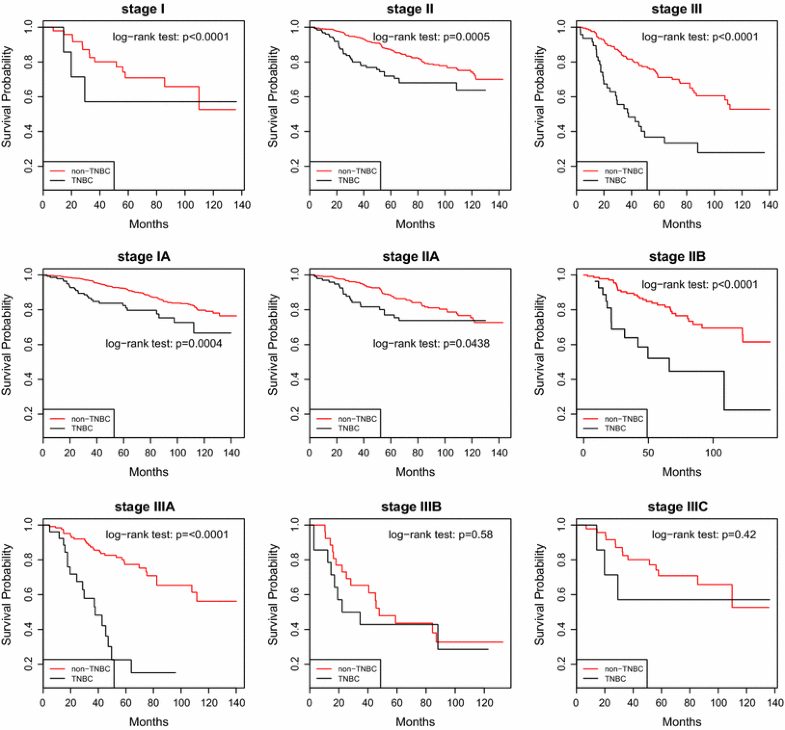
According to the American Cancer Society , triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 10-15 percent of all breast cancers. It develops more quickly, is more likely to spread and is harder to treat than other breast cancers. Because its such an aggressive cancer, TNBC has a poorer prognosis than other invasive breast cancers.
What Makes It Triple
Triple-negative refers to the fact that this type of breast cancer is not fueled by certain substances such as hormones or growth proteins in the body.
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are found in some types of breast cancer. Triple-negative breast cancer doesnt show hormone receptors on the cancer cells and most likely wont respond to breast cancer treatments using hormone blockers to slow the growth of cancer cells like many other types of breast cancer.
Another feature important for classifying breast cancer is the presence of the HER2 protein. Healthy cells have some HER2, but about 20% of breast cancer diagnoses have an excess of this protein, signaling the cells to grow and divide rapidly. Cancers that test positive for an excess of HER2 protein may be effectively treated using targeted therapies that disrupt the function and growth of HER2. Triple-negative cancer patients do not have a significant amount of HER2 protein fueling the cancer.
Don’t Miss: Why Do So Many Women Get Breast Cancer
What Tests And Exams Diagnose Triple
The diagnosis of triple-negative breast cancer requires a sampling of tissue from the breast, known as a breast biopsy.
- Medical professionals may perform the biopsy using imaging techniques, such as mammography or others, for guidance.
- If the biopsy shows cancer, they may perform other tests on the biopsy sample to determine the precise type of cancer.
- In particular, they commonly perform tests for expression of the estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor , and HER2 protein as a first step. If these tests are all negative, they classify cancer as triple-negative breast cancer.
What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers are making significant progress on TNBC treatments. Recent clinical trials are testing new combinations of drugs and new approaches to existing treatments. Some existing treatments are:
- Chemotherapy: Providers might combine chemotherapy and surgery, with chemotherapy being used to shrink your tumor before surgery or after surgery to kill cancer cells throughout your body.
- Surgery: This could be a lumpectomy to remove an individual lump, or a mastectomy to remove an entire breast. Providers then perform a sentinel node biopsy or axillary node surgery to look for signs your breast cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: Post-surgery radiation therapy helps reduce the chances your cancer will return or recur.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates your immune system to produce more cancer-fighting cells or help healthy cells identify and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy can be added to chemotherapy to before surgery to shrink the tumor. You might also receive immunotherapy for about a year after your surgery and post-surgery radiation therapy.
Don’t Miss: How Many Biopsies Are Taken For Breast Cancer
Signs And Symptoms To Know
The signs and symptoms of triple-negative breast cancer are the same as with all breast cancers. It may present as a lump, which is more commonly hard, painless and irregular, but can also be soft, round and painful. Other signs include:
- Breast swelling
- A nipple that turns inward
- Skin changes on the breast or nipple, including redness, dryness, thickening or flaking
Survival Rates And Prognosis
The outlook for breast cancer is often described in terms of relative survival rates.
Relative survival rates are an estimate of the percentage of people who will survive their cancer for a given period of time after diagnosis. Survival among people with cancer is compared to survival among people of the same age and race who have not been diagnosed with cancer.
Five-year relative survival rates tend to be lower for triple-negative breast cancer than for other forms of breast cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, the overall 5-year relative survival rate for TNBC is . However, an individuals outlook depends on many factors, including the stage of the cancer and the grade of the tumor.
Your healthcare professional will be able to give you a more precise outlook based on:
- the stage of your TNBC
Also Check: How Do You Check If You Have Breast Cancer
What About Breast Cancer In Men
Breast cancer in men is rare less than 1 percent of all breast cancer cases but it can still occur, according to the ACS. A mans risk of getting breast cancer during his lifetime is about
The stages of breast cancer relate to how much the cancer has grown and how far its spread. Generally, the earlier breast cancer is diagnosed and treated, the higher the chances for long-term survival.
| Stage 0 | This is a precancerous stage with no invasive cancer cells. |
| Stage 1 | The tumor is small and localized to the breast. There may be a small amount of cancer in nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage 2 | The tumor is still localized to the breast but is larger and may have spread to several nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage 3 | This stage includes cancers that have spread to the skin, chest wall, or multiple lymph nodes in or near the breast. |
| Stage 4 | This is metastatic breast cancer, meaning its spread to one or more distant parts of the body, most commonly to the bones, lungs, or liver. |
The stages of breast cancer are based on the following factors:
- whether the lymph nodes contain cancer cells
- whether the cancer has metastasized, meaning its spread to other, more distant parts of the body
Since 2018, the following factors have also been used to determine breast cancer stage:
- whether the cancer cells have hormone receptors and need estrogen or progesterone to grow
- whether the cancer cells have the HER2 protein that helps them grow
- tumor grade, meaning how aggressive the cells look under the microscope
How Common Is Triple
About 10 to 20% of breast cancers are found to be triple-negative. However, triple-negative cancer cells are found more often in people under the age of 50. This is about 10 years younger than the average age of 60 or older for other types of breast cancer diagnoses. Triple-negative breast cancer is also found in higher percentages of Black and Hispanic patients and less often in Asian and non-Hispanic patients.
Another population that is more likely to be diagnosed with this type of breast cancer has an inherited mutation of the BRCA gene. About 70% of those with triple-negative breast cancer also test positive for having the BRCA mutation. You may qualify for genetic testing based on your family history. Learn more about genetic testing for breast cancer.
Also Check: What Are Signs That You Have Breast Cancer
Prognosis And Survival Rates
Treatment may make triple-negative breast cancer go away. It depends on the size of your tumor, how quickly your cancer grows, and whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of your body. The treatments may cause side effects like nausea, vomiting, pain, fatigue, or mental fuzziness .
Itâs hard to say exactly what the odds are because cancer affects everyone differently. Plus, how well you do depends on how early you catch the cancer and how well you responded to treatment.
In general, about 91% of all women with triple-negative breast cancer are still alive 5 years after diagnosis. If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes near the breast the 5 year relative survival rate is about 65%. If the cancer has spread to distant places, the 5 year relative survival rate is 12%.
Importance Of Regular Screenings For Breast Cancer
Regular screening can also help improve survival rates by ensuring that breast cancer is detected and treated early.
A 2021 study reported that Black and Hispanic women actually met U.S Preventative Services Task Force breast cancer screening guidelines at a higher rate than white women.
However, the study also highlighted that not meeting the guidelines was associated with socioeconomic factors like lower income and lack of access to health insurance. Overall, public health agencies are trying to ensure that all women are able to receive timely screening and treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Is Breast Cancer Caused By
Intake Of Processed Food/diet
According to the WHO, processed foods, such as meat, are confirmed group-1 carcinogen for gastrointestinal cancer and breast malignancy . The excessive use of saturated fats is also considered a carcinogen. The obesity-causing ultra-processed diet plans that are enriched in elements such as sugar, sodium, and fats are thought to be carcinogenic and increase the risk by 11% . Diets that are rich in green vegetables, fresh fruits, protein-enriched grains, and legumes are anti-carcinogenic and therefore reduce the risk of breast cancer . Similarly, diets rich in phyto-estrogen, folate elements, saturated fibers, n-3 PUFA, and vitamin D are regarded as anti-cancer agents . Hence, a low dose consumption of saturated fat and n-6 PUFA has been proposed . The antioxidants found in green tea have also shown anti-carcinogenic properties . Curcuminoids and sulforaphane derived from turmeric are thought to be anti-carcinogens .
When Should I Go To The Emergency Room
You might also have unusually strong side effects from your cancer treatment. While your healthcare provider likely gave you medication to help control your side effects, you should go to the emergency room if your side effects continue despite medication.
Many cancer treatments affect your immune system, increasing the chance you will develop infections. Symptoms that might require an emergency room visit during treatment are:
- Fever of 100.5 and above.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting.
Read Also: How Does Breast Cancer Affect You
Determining Risk Of Recurrence In Triple
A personalized prognosis for patients diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer was the goal of a new study by Katherine Varley, PhD, researcher at Huntsman Cancer Institute and assistant professor of oncological sciences at the University of Utah.
Twenty percent of women diagnosed with breast cancer in the United States will learn they have triple-negative breast cancer. That diagnosis means the three most common proteins known to fuel breast cancer growthestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2are not present in the tumor. Those patients will not respond to any of the targeted therapies developed to treat breast cancer with those characteristics. After surgery, their only treatment option is chemotherapy. Targeted therapy allows healthy cells to survive, but chemotherapy can kill normal cells when eliminating the cancer cells.
Varley worked closely on the study with Rachel Stewart, DO, PhD, assistant professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at the University of Kentucky. They used specimens from patients treated at HCI. The tumor samples were taken more than five years ago, so the researchers could determine how each patient fared in the long term. The next step was developing a way to test for biomarkers of the immune response. The biomarker test was developed using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. This is important because it means this test can be run on tumor biopsy specimens that are routinely collected for breast cancer diagnosis.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Breast Cancer Screening Important
How Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Diagnosed
The first step might be a mammogram to evaluate a suspicious mass or lump in your breast. Based on what they learn, healthcare providers might perform a biopsy to remove breast tissue. Then they examine the tissues cells to determine the cancer subtype. Identifying the cancer subtype is part of the staging process, which is when providers decide how to treat your cancer.
Sometimes providers use the following tests before treatment to check on your tumors size and whether it has spread, or after treatment to monitor response to treatment:
Prognostic Factors Of Dfs Survival
We performed the univariate and multivariate Cox mixture cure model to analyze the prognostic factors for short-term and long-term DFS of breast cancer patients, as shown in Table .
Table 3 Prognostic factors of breast cancer DFS using cox mixture cure model
The effect of factors on survival time and cure probability of patients were indicated by HR and OR, respectively. If the HR is more/less than one, it means that the variable is a risk/protective factor for survival. Whereas the OR more/less than one means that the variable is a protective/risk factor for odds of cure. The greater distance from one, the greater effect.
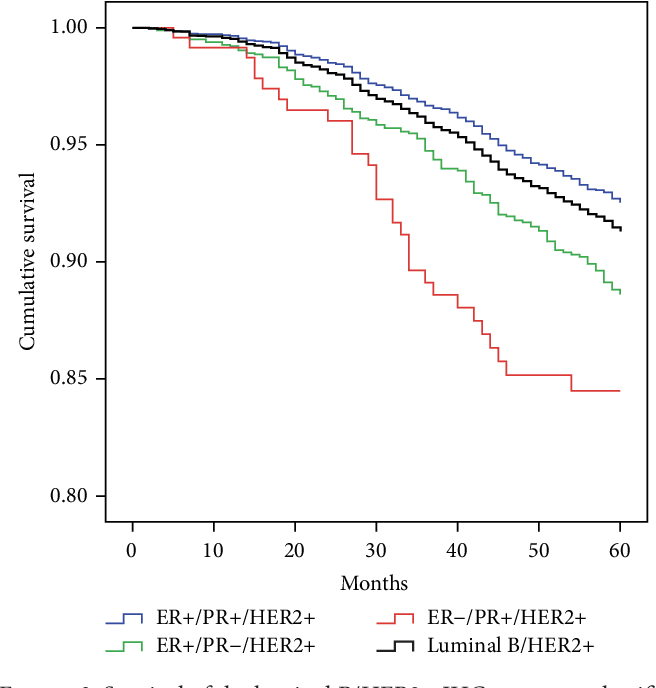
In univariate analysis, the hazard ratio of DFS in the TNBC, HR+/HER2+, and HR/HER2+ were 1.78, 1.53 and 1.38 compared to HR+/HER2 as the reference subtype. However, only the HR/Her2+ subtype was associated significantly with the cure probability . On the other hand, after adjusting for demographic and clinical factors, the risk of mortality, metastasis, and recurrence was not significantly associated with molecular subtype in the short-term. Still, the cure probability of HR/Her2+ patients was significantly lower than HR+/HER2 patients .
Other associated factors with worse short-term DFS included larger tumor size and positive lymph nodes . Furthermore, high-level of education , BCS surgery , and adjuvant chemotherapy had a protective effect on DFS.
Read Also: Is Lobular Breast Cancer Hereditary
Taking Care Of Yourself
After your treatment is over, your doctor will want to see you often to make sure the cancer doesn’t return. For the first 3 years, you’ll likely see them every 3 to 6 months. For 2 years after that, you’ll probably visit every 6 to 12 months. Once you’ve been cancer-free for 6 years, you’ll probably go back only once a year. Tell the doctor right away if you get any new symptoms or if you have pain or other problems that relate to your breasts.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
The stage of breast cancer is based on the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether the cancer has spread beyond the part of the breast in which it originated. To determine the stage of breast cancer, healthcare professionals use a scale of stage 0 to stage 4.
Stage 0 breast cancers are isolated in one part of the breast, such as a duct or lobule, and show no sign of spreading into other tissue.
Stage 1 is typically localized, although further local growth or spread may cause the cancer to move into stage 2.
In stage 3, the cancer may be larger and has affected the lymph system. Stage 4 cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes, and into other organs and tissues of the body.
In addition to stages, breast cancers are given grades based on the size, shape, and activity of the cells in the tumor. A higher-grade cancer means a greater percentage of cells look and act abnormal, or they no longer resemble normal, healthy cells.
On a scale of 1 to 3, with 3 being the most serious, TNBC is often labeled grade 3.
American Cancer Society , the symptoms of TNBC can be the same as those for other types of breast cancer. ACS recommends regular screenings such as mammograms to detect breast cancer before symptoms appear, the time when treatment is most effective.
Other signs of breast cancer include:
Any of these signs can be caused by other conditions. But it is always good to have them checked out by your healthcare professional.
Read Also: What Does It Feel Like If You Have Breast Cancer